hdu 4587(枚举+割顶)
TWO NODES
Time Limit: 24000/12000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2354 Accepted Submission(s): 780
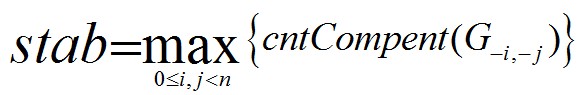
Among the expression,G-i, -j is the remainder after removing node i, node j and all edges that are directly relevant to the previous two nodes. cntCompent is the number of connected components of X independently.
Thus, given a certain undirected graph G, you are supposed to calculating the value of stab.
input will contain the description of several graphs. For each graph,
the description consist of an integer N for the number of nodes, an
integer M for the number of edges, and M pairs of integers for edges
(3<=N,M<=5000).
Please note that the endpoints of edge is marked in the range of [0,N-1], and input cases ends with EOF.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long LL;
using namespace std;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const double eps=0.0000000001;
const int INF=1e9;
const int N=+;
int head[N];
int t,tot;
struct node{
int to,next;
}edge[N<<];
int low[N];
int dfn[N];
int iscut[N];
void init(){
memset(low,,sizeof(low));
memset(dfn,,sizeof(dfn));
t=;
}
void add(int u,int v){
edge[tot].to=v;
edge[tot].next=head[u];
head[u]=tot++;
}
int DFS(int u,int fa,int flag){
low[u]=dfn[u]=++t;
int child=;
for(int i=head[u];i!=-;i=edge[i].next){
int v=edge[i].to;
if(v==flag)continue;
if(dfn[v]==){
child++;
int lowv=DFS(v,u,flag);
low[u]=min(low[u],lowv);
if(lowv>=dfn[u]){
iscut[u]++;
}
}
else if(dfn[v]<dfn[u]&&v!=fa){
low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
}
if(fa<&&child==)low[u]=;
return low[u];
}
int main(){
int n,m;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF){
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
tot=;
for(int i=;i<=m;i++){
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
add(u,v);
add(v,u);
}
int ans=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
int sum=;
init();
for(int j=;j<n;j++){
iscut[j]=;
}
iscut[i]=;
for(int j=;j<n;j++){
if(i==j)continue;
if(dfn[j])continue;
iscut[j]=;
sum++;
DFS(j,-,i); }
for(int j=;j<n;j++){
ans=max(ans,iscut[j]+sum-);
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
hdu 4587(枚举+割顶)的更多相关文章
- P3388 【模板】割点(割顶) 题解 (Tarjan)
题目链接 P3388 [模板]割点(割顶) 解题思路 最近学的东西太杂了,多写点博客免得自己糊里糊涂的过去了. 这个题求割点,感觉这篇文章写得挺好. 割点是啥?如果去掉这个点之后连通图变成多个不连通图 ...
- poj 1144 Network 图的割顶判断模板
Network Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 8797 Accepted: 4116 Descripti ...
- POJ1144 Network 无向图的割顶
现在打算重新学习图论的一些基础算法,包括像桥,割顶,双连通分量,强连通分量这些基础算法我都打算重敲一次,因为这些量都是可以用tarjan的算法求得的,这次的割顶算是对tarjan的那一类算法的理解的再 ...
- 图论(无向图的割顶):POJ 1144 Network
Network Description A Telephone Line Company (TLC) is establishing a new telephone cable network. ...
- uoj#67. 新年的毒瘤(割顶)
#67. 新年的毒瘤 辞旧迎新之际,喜羊羊正在打理羊村的绿化带,然后他发现了一棵长着毒瘤的树. 这个长着毒瘤的树可以用n个结点m 条无向边的无向图表示.这个图中有一些结点被称作是毒瘤结点,即删掉这个结 ...
- 图论算法-Tarjan模板 【缩点;割顶;双连通分量】
图论算法-Tarjan模板 [缩点:割顶:双连通分量] 为小伙伴们总结的Tarjan三大算法 Tarjan缩点(求强连通分量) int n; int low[100010],dfn[100010]; ...
- Tarjan求割点(割顶) 割边(桥)
割点的定义: 感性理解,所谓割点就是在无向连通图中去掉这个点和所有和这个点有关的边之后,原先连通的块就会相互分离变成至少两个分离的连通块的点. 举个例子: 图中的4号点就是割点,因为去掉4号点和有关边 ...
- Tarjan求割点 || Luogu P3388 【模板】割点(割顶)
题面:P3388 [模板]割点(割顶) 题解:无 代码: #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<cstring> ...
- Doves and bombs UVA - 10765(统计割顶所连接的连通块的数量)
题意:给定一个n个点的连通的无向图,一个点的“鸽子值”定义为将它从图中删去后连通块的个数. 求对应的点 和 每个点的“鸽子值” 用一个数组在判断割顶的那个地方 累加标记一下所连接的连通块的数量即可 初 ...
随机推荐
- Python学习之LeetCode刷题之路——简单题【1、7、9】
1.两数之和 给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标. 你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案.但是,你不能重复利用这个 ...
- adb 命令实用
1.adb安装:adbinstall.bat:原理:将apk文件拖进此bat,install命令会强制(覆盖)安装apk安装包.代码如下: @echo on adb install -r % paus ...
- Executors工厂类
newCachedThreadPool 重用之前的线程 适合执行许多短期异步任务的程序. 调用 execute() 将重用以前构造的线程 如果没有可用的线程,则创建一个新线程并添加到池中 默认为60s ...
- c/c++编程排坑(1)-- 数据类型的“安静”转换
这里主要介绍ANSI C的特性:当执行算术运算时,操作数的类型如果不同,就会发生转换.数据类型一般朝着精度更高.长度更长的方向转换,整型数如果转换为signed不会丢失信息,就转换为signed,否则 ...
- SQL学习笔记:一些高级语句
现在以MySQL为模板.学习的方法和别的数据库写法上会有不同,但是思路基本一致. 用到的数据库表的格式: +----+--------------+-------------------------- ...
- BZOJ 5106 [CodePlus2017]汀博尔
[题解] 二分答案.r要设好,不能随便设置为max(s,len),不然check的时候会爆long long #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm& ...
- 【Codeforces 375B】Maximum Submatrix 2
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 如果任意行之间可以重新排序. 问你最大的全是1的子矩阵中1的个数 [题解] 设cnt[i][j] 表示(i,j)这个点往右连续的1的个数 我们枚举列j 然后对 ...
- kafka+spark-streaming实时推荐系统性能优化笔记
1) --conf spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled=false 如果正在使用的是CDH的Spark,修改这个配置为false:开源的Spark版本则默认是false. ...
- springMvc把client传过来一个String类型,转换为日期类型为例
springMvc--接受日期类型参数处理 目录 步骤 2.自定义类型转换规则 3.注册自定义的类型转换类 4.地址栏访问 这个问题,也即是springMvc如何进行参数类型的转换 , 以把cli ...
- 大家好 这个事我的BLOG 站点 欢迎大家 訪问和公布文章技术的 和评论 交流技术使用
地址 http://microlmj.gotoip3.com/blog/article!showAllArticleForPageTest.action ssh+mysql+java+tomcat+b ...
