Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2)
闲来无事一套CF啊,我觉得这几个题还是有套路的,但是很明显,这个题并不难
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Ted has a pineapple. This pineapple is able to bark like a bulldog! At time t (in seconds) it barks for the first time. Then every s seconds after it, it barks twice with 1 second interval. Thus it barks at times t, t + s, t + s + 1, t + 2s, t + 2s + 1, etc.

Barney woke up in the morning and wants to eat the pineapple, but he can't eat it when it's barking. Barney plans to eat it at time x (in seconds), so he asked you to tell him if it's gonna bark at that time.
The first and only line of input contains three integers t, s and x (0 ≤ t, x ≤ 109, 2 ≤ s ≤ 109) — the time the pineapple barks for the first time, the pineapple barking interval, and the time Barney wants to eat the pineapple respectively.
Print a single "YES" (without quotes) if the pineapple will bark at time x or a single "NO" (without quotes) otherwise in the only line of output.
3 10 4
NO
3 10 3
YES
3 8 51
YES
3 8 52
YES
In the first and the second sample cases pineapple will bark at moments 3, 13, 14, ..., so it won't bark at the moment 4 and will bark at the moment 3.
In the third and fourth sample cases pineapple will bark at moments 3, 11, 12, 19, 20, 27, 28, 35, 36, 43, 44, 51, 52, 59, ..., so it will bark at both moments 51 and 52.
就是检查下x在不在这个数列,数列眉两项之间增加s,有的相邻两项差值是1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t,s,x;
cin>>t>>s>>x;
if(x<t+s){puts(x==t?"YES":"NO");return ;}
int k=(x-t)/s;
if(t+k*s==x||t+k*s+==x)puts("YES");else puts("NO");
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Barney is standing in a bar and starring at a pretty girl. He wants to shoot her with his heart arrow but he needs to know the distance between him and the girl to make his shot accurate.

Barney asked the bar tender Carl about this distance value, but Carl was so busy talking to the customers so he wrote the distance value (it's a real number) on a napkin. The problem is that he wrote it in scientific notation. The scientific notation of some real number x is the notation of form AeB, where A is a real number and B is an integer and x = A × 10B is true. In our case A is between 0 and 9 and B is non-negative.
Barney doesn't know anything about scientific notation (as well as anything scientific at all). So he asked you to tell him the distance value in usual decimal representation with minimal number of digits after the decimal point (and no decimal point if it is an integer). See the output format for better understanding.
The first and only line of input contains a single string of form a.deb where a, d and b are integers and e is usual character 'e' (0 ≤ a ≤ 9, 0 ≤ d < 10100, 0 ≤ b ≤ 100) — the scientific notation of the desired distance value.
a and b contain no leading zeros and d contains no trailing zeros (but may be equal to 0). Also, b can not be non-zero if a is zero.
Print the only real number x (the desired distance value) in the only line in its decimal notation.
Thus if x is an integer, print it's integer value without decimal part and decimal point and without leading zeroes.
Otherwise print x in a form of p.q such that p is an integer that have no leading zeroes (but may be equal to zero), and q is an integer that have no trailing zeroes (and may not be equal to zero).
8.549e2
854.9
8.549e3
8549
0.33e0
0.33
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
char a[];
int main() {
int ex=;
scanf("%c.%[0-9]e%d",&a[],a+,&ex);
int f=;
for(int i=; a[i]; i++) {
if(a[i]!='') {
f=;
}
}
if(!f&&!ex)
printf("%c",a[]);
else {
for(int i=; i<ex+||a[i]; i++) {
if(i==ex+) printf(".");
printf("%c",!a[i]?'':a[i]);
}
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Barney lives in NYC. NYC has infinite number of intersections numbered with positive integers starting from 1. There exists a bidirectional road between intersections i and 2i and another road between i and 2i + 1 for every positive integer i. You can clearly see that there exists a unique shortest path between any two intersections.

Initially anyone can pass any road for free. But since SlapsGiving is ahead of us, there will q consecutive events happen soon. There are two types of events:
1. Government makes a new rule. A rule can be denoted by integers v, u and w. As the result of this action, the passing fee of all roads on the shortest path from u to v increases by w dollars.
2. Barney starts moving from some intersection v and goes to intersection u where there's a girl he wants to cuddle (using his fake name Lorenzo Von Matterhorn). He always uses the shortest path (visiting minimum number of intersections or roads) between two intersections.
Government needs your calculations. For each time Barney goes to cuddle a girl, you need to tell the government how much money he should pay (sum of passing fee of all roads he passes).
The first line of input contains a single integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 1 000).
The next q lines contain the information about the events in chronological order. Each event is described in form 1 v u w if it's an event when government makes a new rule about increasing the passing fee of all roads on the shortest path from u to v by w dollars, or in form 2v u if it's an event when Barnie goes to cuddle from the intersection v to the intersection u.
1 ≤ v, u ≤ 1018, v ≠ u, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109 states for every description line.
For each event of second type print the sum of passing fee of all roads Barney passes in this event, in one line. Print the answers in chronological order of corresponding events.
7
1 3 4 30
1 4 1 2
1 3 6 8
2 4 3
1 6 1 40
2 3 7
2 2 4
94
0
32
In the example testcase:
Here are the intersections used:
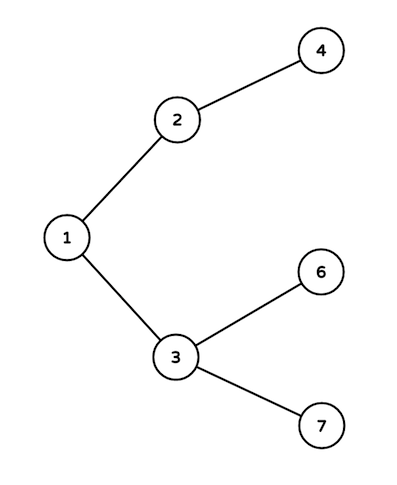
- Intersections on the path are 3, 1, 2 and 4.
- Intersections on the path are 4, 2 and 1.
- Intersections on the path are only 3 and 6.
- Intersections on the path are 4, 2, 1 and 3. Passing fee of roads on the path are 32, 32 and 30 in order. So answer equals to 32 + 32 + 30 = 94.
- Intersections on the path are 6, 3 and 1.
- Intersections on the path are 3 and 7. Passing fee of the road between them is 0.
- Intersections on the path are 2 and 4. Passing fee of the road between them is 32 (increased by 30 in the first event and by 2 in the second).
Do what problem wants from you. The only thing is to find the path between the two vertices (or LCA) in the tree. You can do this in 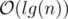 since the height of the tree is
since the height of the tree is 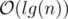 . You can keep edge weights in a map and get/set the value whenever you want. Here's a code for LCA:
. You can keep edge weights in a map and get/set the value whenever you want. Here's a code for LCA:
LCA(v, u):
while v != u:
if depth[v] < depth[u]:
swap(v, u)
v = v/2 // v/2 is parent of vertex v
Time Complexity: 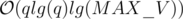
这个C就是有个树,让你统计下这个树的LCA的边值
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
map<ll,ll>road;
int main() {
ll q,rule,u,v,w,ans;
cin>>q;
while(q--) {
cin>>rule;
if(rule==) {
cin>>u>>v>>w;
while(u!=v) {
if(u<v)
swap(u,v);
road[u]+= w;
u /= ;
}
} else {
cin>>u>>v;
ans = ;
while(u!=v) {
if(u<v)
swap(u,v);
ans += road[u];
u /= ;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) C. Lorenzo Von Matterhorn (类似LCA)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/697/D 给你一个有规则的二叉树,大概有1e18个点. 有两种操作:1操作是将u到v上的路径加上w,2操作 ...
- #map+LCA# Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2)-C. Lorenzo Von Matterhorn
2018-03-16 http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/697/C C. Lorenzo Von Matterhorn time limit per t ...
- 【转载】【树形DP】【数学期望】Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) D.Puzzles
期望计算的套路: 1.定义:算出所有测试值的和,除以测试次数. 2.定义:算出所有值出现的概率与其乘积之和. 3.用前一步的期望,加上两者的期望距离,递推出来. 题意: 一个树,dfs遍历子树的顺序是 ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) A.B.C
A. Pineapple Incident time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2)->B. Barnicle
B. Barnicle time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ou ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2)->A. Pineapple Incident
A. Pineapple Incident time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) B 模拟
B. Barnicle time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ou ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) A 水也挂
A. Pineapple Incident time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) D. Puzzles
D. Puzzles time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
随机推荐
- 11.JAVA-Object类之finalize(),clone(),toString()等方法覆写
1.Object介绍 Object类是一个特殊的类,是所有类(包括数组,接口 )的父类,如果一个类没有用extends明确指出继承于某个类,那么它默认继承Object类,所以可以通过向上转型的方法使用 ...
- springMVC 与 struts+hibernate+spring优缺点
springMVC: Spring 框架是高度可配置的,而且包含多种视图技术,例如 JavaServer Pages(JSP)技术.Velocity.Tiles.iText 和POI.Spring M ...
- 基于Myeclipse的三大框架(SSH)整合
文中主要基于Myeclipse进行配置,配置流程为:Hibernate --> Spring --> 整合 --> struts2 -->整合.注意:在此文中,主要讲述基于注解 ...
- IOS中Llabel整理
·UILable是iPhone界面最基本的控件,主要用来显示文本信息.·常用属性和方法有:1.创建CGRect rect = CGRectMake(100, 200, 50, 50);UILabel ...
- Django之CSRF问题
1.csrf全称:cross site request forgery(跨站请求伪造),举例来讲,一个安全的网站A,一个恶意网站B,当你在A网站进行了登录后,这时候浏览器会保存你的cookie和ses ...
- 异步 BeginInvoke
委托的异步调用异步多线程的三大特点:1.同步方法卡界面,原因是主线程被占用:异步方法不卡界面,原因是计算交给了别的线程,主线程空闲2.同步方法慢,原因是只有一个线程计算:异步方法快,原因是多个线程同事 ...
- 校内选拔I题题解 构造题 Codeforces Round #318 [RussianCodeCup Thanks-Round] (Div. 2) ——D
http://codeforces.com/contest/574/problem/D Bear and Blocks time limit per test 1 second memory limi ...
- spring (由Rod Johnson创建的一个开源框架)
你可能正在想“Spring不过是另外一个的framework”.当已经有许多开放源代码(和专有)J2EEframework时,我们为什么还需要Spring Framework? Spring是独特的, ...
- Django ORM 一对一,一对多,多对多, 添加,批量插入和查询
模型类 class Book(models.Model): nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) title = models.CharField(max_ ...
- 树形DP 统计树中长度为K的路径数量——Distance in Tree
一.问题描述 给出一棵n个节点的树,统计树中长度为k的路径的条数(1<=n<=50000 , 1<=k<=500). 二.解题思路 设d[i][k]表示以i为根节点长度为k的路 ...
