一个Work Stealing Pool线程池的实现
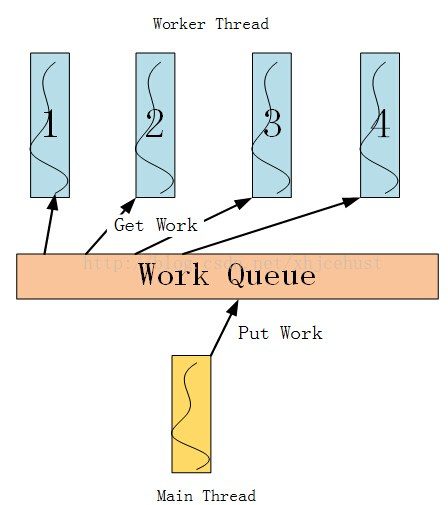
如上图所示,工作队列由主线程和工作者线程共享,主线程将任务放进工作队列,工作者线程从工作队列中取出任务执行。共享工作队列的操作需在互斥量的保护下安全进行,主线程将任务放进工作队列时若检测到当前待执行的工作数目小于工作者线程总数,则需使用条件变量唤醒可能处于等待状态的工作者线程。当然,还有其他地方可能也会使用到互斥量和条件变量,不再赘述。
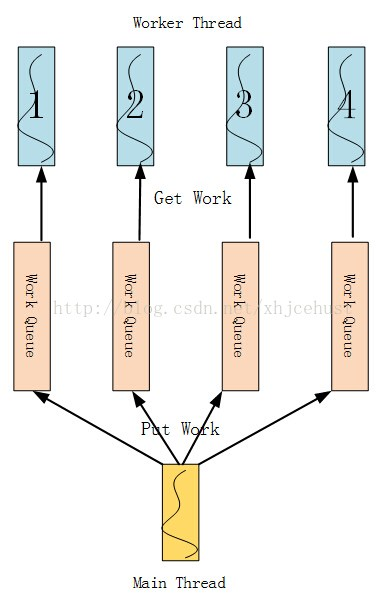
三、无锁化线程池模型
struct thread_pool;
struct future; /* Create a new thread pool with no more than n threads. */
struct thread_pool * thread_pool_new(int nthreads); void thread_pool_shutdown_and_destroy(struct thread_pool *); typedef void * (* fork_join_task_t) (struct thread_pool *pool, void * data); struct future * thread_pool_submit(
struct thread_pool *pool,
fork_join_task_t task,
void * data); void * future_get(struct future *); void future_free(struct future *);
threadpool.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <fcntl.h> #include "threadpool.h" struct future
{
fork_join_task_t task;
void *arg; //parameter
void *result;
sem_t *sem;
int status; //0: not to do, 1: doing, 2: done
int local; //1: internal task, 0: external task
struct future *prev;
struct future *next;
}; struct thread_t
{
pthread_t id;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
int idle; //1: idle, 0: busy
int index; //record the current thread index in pool
int current_task_num; //total task number in current thread
struct thread_pool *pool; //point to the pool area
struct future *head;
struct future *tail;
}; struct thread_pool
{
int max_threads;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
int shutdown; //1: shutdown, 0: normal
struct thread_t *threads;
struct future *head;
struct future *tail;
}; static void *thread_route(void *arg)
{
assert(arg != NULL);
struct thread_t *thread = (struct thread_t *)arg;
assert(thread != NULL);
struct thread_pool *pool = thread->pool;
assert(pool != NULL);
struct future *future = NULL; while()
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex);
if(future != NULL)
{
thread->idle = ;
future->status = ; //doing
future->result = future->task(pool, future->arg);
future->status = ;
sem_post(future->sem);
} while(thread->current_task_num == && pool->shutdown == )
{
//wait for task assigment
pthread_cond_wait(&thread->cond, &thread->mutex);
} if(pool->shutdown == )
{
//pool is shutdown, destroy the local task list
struct future *temp = NULL;
while(thread->head != NULL)
{
temp = thread->head;
thread->head = thread->head->next;
free(temp);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
} //Fist, get task from local task list to do
while(thread->head != NULL)
{
thread->idle = ;
future = thread->head;
thread->head = thread->head->next;
if(thread->tail == future)
thread->tail = NULL;
else
thread->head->prev = NULL; //call the callback to do work
thread->current_task_num--;
future->status = ; //doing
#if 0
if(pool->max_threads == && future->local == )
{
/*
* TBD: in case there is only a thread in pool
* and the task is local task
* we can create a thread to do the task?
*/
}
else
#else
{
future->result = future->task(pool, future->arg);
}
#endif
future->status = ;
sem_post(future->sem); //Let future_get know, the result is ok
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex); thread->idle = ; /*
* The local task work are done, go to global task list to get task
* or go to other work thread to get task.
*/ //Step1: Go to globacl task list to get task(From Head)
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
future = NULL;
while(pool->head != NULL && pool->head->status == )
{
//printf("Worker %d get task from global task, current_task %d\n", thread->index, thread->current_task_num);
future = pool->head;
pool->head = pool->head->next;
if(pool->tail == future)
pool->tail = NULL;
else
pool->head->prev = NULL; //Get the future, then put into the local task list?
#if 0
pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex);
if(thread->head != NULL)
{
future->next = thread->head;
thread->head->prev = future;
}
else
{
thread->tail = future;
}
thread->head = future; thread->current_task_num++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex);
if(thread->current_task_num == )
{
//Get 10 tasks, ok, get out, give some changes to other work threads
break;
}
#else
//printf("Worked %d get one task from globack task list.\n", thread->index);
break; //get one task, break
#endif
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex); //Step2: Go to other work thread task list to get task(From Tail)
if(future == NULL && thread->current_task_num == )
{
//printf("Worker %d can not get task from global task, then try other work threads, current_task %d\n", thread->index, thread->current_task_num);
future = pool->head;
int i = ;
struct thread_t *other_thread = NULL;
for(i=; i<pool->max_threads; i++)
{
if(i == thread->index)
continue; //myself if(pool->threads[i].current_task_num == )
continue; //it has no task //lock it?
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->threads[i].mutex);
other_thread = (struct thread_t *)&pool->threads[i];
while(other_thread->tail != NULL && other_thread->tail->status == )
{
future = other_thread->tail;
other_thread->tail = other_thread->tail->prev;
if(future == other_thread->head)
other_thread->head = NULL;
else
other_thread->tail->next = NULL; //Get the future, then put into our local task list?
#if 0
pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex);
if(thread->head != NULL)
{
future->next = thread->head;
thread->head->prev = future;
}
else
{
thread->tail = future;
}
thread->head = future; thread->current_task_num++;
printf("Worker %d get task from other thread task, current_task %d\n", thread->current_task_num);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex);
if(thread->current_task_num == )
{
//Get 4 tasks, ok, get out, give some changes to other work threads
break;
}
#else
//printf("Worked %d get one task from other worker %d.\n", thread->index, i);
break; //get one task, break
#endif
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->threads[i].mutex);
}
}
}
} struct thread_pool * thread_pool_new(int nthreads)
{
struct thread_pool *pool = (struct thread_pool *)malloc(sizeof(struct thread_pool));
assert(pool != NULL); pool->max_threads = nthreads;
pool->head = pool->tail = NULL; pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutex, NULL); pool->threads = (struct thread_t *)malloc(nthreads * sizeof(struct thread_t));
assert(pool->threads != NULL); int i = ;
for(i=; i<pool->max_threads; i++)
{
pthread_mutex_init(&pool->threads[i].mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&pool->threads[i].cond, NULL);
pool->threads[i].idle = ; //idle
pool->threads[i].index = i;
pool->threads[i].pool = pool; //point to the pool area
pool->threads[i].current_task_num = ;
pthread_create(&pool->threads[i].id, NULL, thread_route,(void *)(&pool->threads[i]));
} return pool;
} struct future * thread_pool_submit(
struct thread_pool *pool,
fork_join_task_t task,
void * data)
{
assert(pool != NULL);
struct future *future = (struct future *)malloc(sizeof(struct future));
assert(future); future->task = task;
future->arg = data;
future->prev = future->next = NULL;
future->result = NULL;
future->status = ;
future->local = ; //default is external task int i = ;
unsigned long myself_pid = pthread_self();
for(i=; i<pool->max_threads; i++)
{
if(pool->threads[i].id == myself_pid)
{
future->local = ; //it is internal task
break;
}
} future->sem = (sem_t *)malloc(sizeof(sem_t));
assert(future->sem != NULL);
sem_init(future->sem, , ); //find a idle work thread to put the task
struct thread_t * thread = NULL;
for(i = ; i< pool->max_threads; i++)
{
thread = &pool->threads[i];
pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex);
if(thread->idle == )
{
//find it, insert the task from head
if(thread->head != NULL)
{
future->next = thread->head;
thread->head->prev = future;
}
else
{
thread->tail = future;
}
thread->head = future; thread->current_task_num++; //Just let work thread know, it has work to do
if(thread->current_task_num == )
{
//printf("%s(): Let worker %d to start to work\n", __FUNCTION__, thread->index);
pthread_cond_signal(&thread->cond);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex); return future;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex);
} //can not find idle work thread, just put it into global task list
//printf("%s(): no find idle work thread, just put into global task list\n", __FUNCTION__);
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
if(pool->head != NULL)
{
future->next = pool->head;
pool->head->prev = future;
}
else
{
pool->tail = future;
}
pool->head = future;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex); return future;
} void * future_get(struct future *future)
{
assert(future);
sem_wait(future->sem); //wait for the result ready
return (void *)future->result; }
完整的代码,请看我的GitHub:
一个Work Stealing Pool线程池的实现的更多相关文章
- 分享一个自制的 .net线程池
扯淡 由于项目需求,需要开发一些程序去爬取一些网站的信息,算是小爬虫程序吧.爬网页这东西是要经过网络传输,如果程序运行起来串行执行请求爬取,会很慢,我想没人会这样做.为了提高爬取效率,必须使用多线程并 ...
- 一个Linux下C线程池的实现
什么时候需要创建线程池呢?简单的说,如果一个应用需要频繁的创建和销毁线程,而任务执行的时间又非常短,这样线程创建和销毁的带来的开销就不容忽视,这时也是线程池该出场的机会了.如果线程创建和销毁时间相比任 ...
- 一个boost底下的线程池
Boost的thread库中目前并没有提供线程池,我在sorceforge上找了一个用boost编写的线程池.该线程池和boost结合的比较好,并且提供了多种任务执行策略,使用也非常简单. 下载地址: ...
- 一个简单的python线程池框架
初学python,实现了一个简单的线程池框架,线程池中除Wokers(工作线程)外,还单独创建了一个日志线程,用于日志的输出.线程间采用Queue方式进行通信. 代码如下:(不足之处,还请高手指正) ...
- 一个简单的linux线程池(转-wangchenxicool)
线程池:简单地说,线程池 就是预先创建好一批线程,方便.快速地处理收到的业务.比起传统的到来一个任务,即时创建一个线程来处理,节省了线程的创建和回收的开销,响应更快,效率更高. 在linux中,使用的 ...
- 一个Windows C++的线程池的实现
此线程池所依赖的线程类,请参看<一个Windows C++的线程类实现>: http://blog.csdn.net/huyiyang2010/archive/2010/08/10/580 ...
- Windows下一个比较完美的线程池实现(使用线程池实现的Http上传下载实现)
http://blog.csdn.net/fishjam/article/details/8632049 http://download.csdn.net/user/fishjam
- Spring Thread Pool 线程池的应用
Spring and Java Thread example 扫扫关注"茶爸爸"微信公众号 坚持最初的执着,从不曾有半点懈怠,为优秀而努力,为证明自己而活. Download it ...
- ExecutorService 建立一个多线程的线程池的步骤
ExecutorService 建立一个多线程的线程池的步骤: 线程池的作用: 线程池功能是限制在系统中运行的线程数. 依据系统的环境情况,能够自己主动或手动设置线程数量.达到执行的最佳效果:少了浪费 ...
随机推荐
- jquery解析xml,获取xml标签名
先给一个简单的XML,结构如下 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="uft-8" ?> <msg> <ro ...
- python之删除指定目录指定日期下的日志文件
#=======================================================================================20190521以下脚本 ...
- Jmeter监控内存及CPU等
在进行性能测试时需要查看内存和CPU等信息来判断系统瓶颈,关于CPU和内存的监控,goole开发了一款专门的jmeter插件,弥补了Jmeter这方面的不足,下面来介绍这款插件-JmeterPlugi ...
- 检查EXE、DLL、SYS等文件是32位还是64位的
非.NET文件用:dumpbin.exe /headers file.exe(C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio 12.0\VC\bin) . ...
- python基础教程总结9——模块,包,标准库
1. 模块 在python中一个文件可以被看成一个独立模块,而包对应着文件夹,模块把python代码分成一些有组织的代码段,通过导入的方式实现代码重用. 1.1 模块搜索路径 导入模块时,是按照sys ...
- 用python Image读图
https://www.cnblogs.com/kongzhagen/p/6295925.html import os name = [] with open('/media/hdc/xing/Dee ...
- iOS 骰子战争 Dice Wars
占坑 这个游戏之前在网页端玩过,App Store 上没有搜到特别好的,想自己做个类似的iOS APP 游戏 目测实现难度适中,可玩性较高
- 如何将字符串@“ abc123.xyz789”倒置
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { ...
- Falsy Bouncer-freecodecamp算法题目
Falsy Bouncer(过滤数组假值) 要求 删除数组中的所有假值.(在JavaScript中,假值有false.null.0."".undefined 和 NaN.) 思路 ...
- 数据结构算法与应用c++语言描述 原书第二版 答案(更新中
目录 第一章 C++回顾 函数与参数 1.交换两个整数的不正确代码. 异常 10.抛出并捕捉整型异常. 第一章 C++回顾 函数与参数 1.交换两个整数的不正确代码. //test_1 void sw ...
