D - Nearest Common Ancestors
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
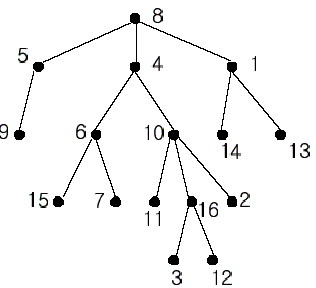
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N , the number of nodes in a tree, 2<=N<=10,000. The nodes are labeled with integers 1, 2,..., N. Each of the next N -1 lines contains a pair of integers that represent an edge --the first integer is the parent node of the second integer. Note that a tree with N nodes has exactly N - 1 edges. The last line of each test case contains two distinct integers whose nearest common ancestor is to be computed.
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Sample Input
2
16
1 14
8 5
10 16
5 9
4 6
8 4
4 10
1 13
6 15
10 11
6 7
10 2
16 3
8 1
16 12
16 7
5
2 3
3 4
3 1
1 5
3 5
Sample Output
4
3
LCA模板套上去就好了
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<float.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#define sf scanf
#define scf(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define pf printf
#define prf(x) printf("%d\n",x)
#define mm(x,b) memset((x),(b),sizeof(x))
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#define rep(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i<n;i++)
#define per(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i>=n;i--)
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod=1e9+100;
const double eps=1e-8;
using namespace std;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int inf=0xfffffff;
const int N = 1010;
int rmq[2*N];//rmq数组,就是欧拉序列对应的深度序列
struct ST
{
int mm[2*N];
int dp[2*N][20];//最小值对应的下标
void init(int n)
{
mm[0] = -1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
mm[i] = ((i&(i-1)) == 0)?mm[i-1]+1:mm[i-1];
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for(int j = 1; j <= mm[n];j++)
for(int i = 1; i + (1<<j) - 1 <= n; i++)
dp[i][j] = rmq[dp[i][j-1]] < rmq[dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]]?dp[i][j-1]:dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1];
}
int query(int a,int b)//查询[a,b]之间最小值的下标
{
if(a > b) swap(a,b);
int k = mm[b-a+1];
return rmq[dp[a][k]] <= rmq[dp[b-(1<<k)+1][k]]?dp[a][k]:dp[b-(1<<k)+1][k];
}
};
//边的结构体定义
struct Edge
{
int to,next;
};
Edge edge[N*2];
int tot,head[N];
int F[N*2];//欧拉序列,就是dfs遍历的顺序,长度为2*n-1,下标从1开始
int P[N];//P[i]表示点i在F中第一次出现的位置
int cnt;
ST st;
void init()
{
tot = 0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
}
void addedge(int u,int v)//加边,无向边需要加两次
{
edge[tot].to = v;
edge[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
}
void dfs(int u,int pre,int dep)
{
F[++cnt] = u;
rmq[cnt] = dep;
P[u] = cnt;
for(int i = head[u];i != -1;i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if(v == pre)continue;
dfs(v,u,dep+1);
F[++cnt] = u;
rmq[cnt] = dep;
}
}
void LCA_init(int root,int node_num)//查询LCA前的初始化
{
cnt = 0;
dfs(root,root,0);
st.init(2*node_num-1);
}
int query_lca(int u,int v)//查询u,v的lca编号
{
return F[st.query(P[u],P[v])];
}
bool root[N];
int main()
{
int n,m,num,v,u;
while(~scff(n,m))//n个点,m个查询点
{
init();
mm(sum,0);
mm(root,true);
rep(i,1,n)
{
sf("%d %d",&u,&v);
addedge(u,v);
addedge(v,u);
root[v]=false;
}
int temp;
rep(i,1,n+1)
{
if(root[i])
{
temp=i;break;
}
}
LCA_init(temp,n);
while(m--)
{
while(getchar()!='(') ;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
while(getchar()!=')') ;
sum[query_lca(u,v)]++;
}
rep(i,1,n+1)
{
if(sum[i])
pf("%d:%d\n",i,sum[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
D - Nearest Common Ancestors的更多相关文章
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors(Targin求LCA)
传送门 Nearest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 26612 Ac ...
- [最近公共祖先] POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors
Nearest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 27316 Accept ...
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors
Nearest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 14698 Accept ...
- POJ1330 Nearest Common Ancestors
Nearest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 24587 Acce ...
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors(Tree)
题目:Nearest Common Ancestors 根据输入建立树,然后求2个结点的最近共同祖先. 注意几点: (1)记录每个结点的父亲,比较层级时要用: (2)记录层级: (3)记录每个结点的孩 ...
- 【POJ】1330 Nearest Common Ancestors ——最近公共祖先(LCA)
Nearest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 18136 Accept ...
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors LCA题解
Nearest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 19728 Accept ...
- POJ - 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors(基础LCA)
POJ - 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000KB 64bit IO Format: %l ...
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors / UVALive 2525 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA)
POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors / UVALive 2525 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA) Description A ...
- pku 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors LCA离线
pku 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors 题目链接: http://poj.org/problem?id=1330 题目大意: 给定一棵树的边关系,注意是有向边,因为这个WA ...
随机推荐
- android应用程序中获取view的位置
我们重点在获取view的y坐标,你懂的... 依次介绍以下四个方法: 1.getLocationInWindow int[] position = new int[2]; textview.getLo ...
- Java8 stream 中利用 groupingBy 进行多字段分组求和
Java8的groupingBy实现集合的分组,类似Mysql的group by分组功能,注意得到的是一个map 对集合按照单个属性分组 case1: List<String> items ...
- space.php
天云信息技术有限公司 | 苏ICP备16033617号 1 0.275 ms SELECT * FROM uchome_session WHERE uid='1' Explain id select_ ...
- Tomcat 9.0 安装配置
本文转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_15126e2170102w5o8.html 一.JDK的安装与配置 1.从官网下载jdk,注意是jdk不是jre.最好从官网下 ...
- 一步步教你轻松学奇异值分解SVD降维算法
一步步教你轻松学奇异值分解SVD降维算法 (白宁超 2018年10月24日09:04:56 ) 摘要:奇异值分解(singular value decomposition)是线性代数中一种重要的矩阵分 ...
- 【PMP】关键路径法与关键链法
通俗理解 关键路径法:把项目上的资源都事先全部分到每个活动上. 关键链法:每个活动不打富余,项目经理自己掌握资源,哪个成员执行过程中遇到困难,再给他单独分配资源. PMBOK定义 关键路径法:关键路径 ...
- 1154:LETTERS
题目链接http://bailian.openjudge.cn/practice/1154/ 总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB 描述 A single-player game i ...
- 免费ss账号网站
下面网址按排序顺序优先使用,数字越小优先级越高 1,https://io.freess.today/ 2,https://free-ss.site/ 3,https://ss.freess.org/ ...
- LaTeX中的各种距离设置总结
LaTeX中的各种距离设置总结 1. 页面设置 A4 会给你一个较小的页面,为了使用更多的控制,可用 geometry宏包 和 命令 \layout . 2. 改变长度 在latex里改变长度 ...
- 记录php中一种骚操作
$options = array( 'config' => array( 'aaa' => 111, 'bbb' => 222, ), 'headers' => array( ...
