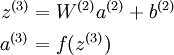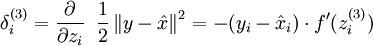Linear Decoders
Sparse Autoencoder Recap
In the sparse autoencoder, we had 3 layers of neurons: an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer. In our previous description of autoencoders (and of neural networks), every neuron in the neural network used the same activation function. In these notes, we describe a modified version of the autoencoder in which some of the neurons use a different activation function. This will result in a model that is sometimes simpler to apply, and can also be more robust to variations in the parameters.
Recall that each neuron (in the output layer) computed the following:
where a(3) is the output. In the autoencoder, a(3) is our approximate reconstruction of the input x = a(1).
Because we used a sigmoid activation function for f(z(3)), we needed to constrain or scale the inputs to be in the range[0,1], since the sigmoid function outputs numbers in the range [0,1].
引入 —— 相同的activation function ,非线性映射会导致输入和输出不等
Linear Decoder
One easy fix for this problem is to set a(3) = z(3). Formally, this is achieved by having the output nodes use an activation function that's the identity function f(z) = z, so that a(3) = f(z(3)) = z(3). 输出结点不适用sigmoid 函数
This particular activation function
is called the linear activation function。Note however that in the hidden layer of the network, we still use a sigmoid (or tanh) activation function, so that the hidden unit activations are given by (say)
, where
is the sigmoid function, x is the input, and W(1) andb(1) are the weight and bias terms for the hidden units. It is only in the output layer that we use the linear activation function.
An autoencoder in this configuration--with a sigmoid (or tanh) hidden layer and a linear output layer--is called a linear decoder.
In this model, we have
. Because the output
is a now linear function of the hidden unit activations, by varying W(2), each output unit a(3) can be made to produce values greater than 1 or less than 0 as well. This allows us to train the sparse autoencoder real-valued inputs without needing to pre-scale every example to a specific range.
Since we have changed the activation function of the output units, the gradients of the output units also change. Recall that for each output unit, we had set set the error terms as follows:
where y = x is the desired output,
is the output of our autoencoder, and
is our activation function. Because in the output layer we now have f(z) = z, that implies f'(z) = 1 and thus the above now simplifies to:
output结点
Of course, when using backpropagation to compute the error terms for the hidden layer:
hidden结点
Because the hidden layer is using a sigmoid (or tanh) activation f, in the equation above
should still be the derivative of the sigmoid (or tanh) function.
Linear Decoders的更多相关文章
- (六)6.16 Neurons Networks linear decoders and its implements
Sparse AutoEncoder是一个三层结构的网络,分别为输入输出与隐层,前边自编码器的描述可知,神经网络中的神经元都采用相同的激励函数,Linear Decoders 修改了自编码器的定义,对 ...
- CS229 6.16 Neurons Networks linear decoders and its implements
Sparse AutoEncoder是一个三层结构的网络,分别为输入输出与隐层,前边自编码器的描述可知,神经网络中的神经元都采用相同的激励函数,Linear Decoders 修改了自编码器的定义,对 ...
- Unsupervised Feature Learning and Deep Learning(UFLDL) Exercise 总结
7.27 暑假开始后,稍有时间,“搞完”金融项目,便开始跑跑 Deep Learning的程序 Hinton 在Nature上文章的代码 跑了3天 也没跑完 后来Debug 把batch 从200改到 ...
- Deep learning:三十八(Stacked CNN简单介绍)
http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2013/05/05/3061457.html 前言: 本节主要是来简单介绍下stacked CNN(深度卷积网络 ...
- [UFLDL] Basic Concept
博客内容取材于:http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2012/06/24/2560261.html 参考资料: UFLDL wiki UFLDL St ...
- [UFLDL] Dimensionality Reduction
博客内容取材于:http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2012/06/24/2560261.html Deep learning:三十五(用NN实现数据 ...
- Deep Learning 教程翻译
Deep Learning 教程翻译 非常激动地宣告,Stanford 教授 Andrew Ng 的 Deep Learning 教程,于今日,2013年4月8日,全部翻译成中文.这是中国屌丝军团,从 ...
- ICLR 2013 International Conference on Learning Representations深度学习论文papers
ICLR 2013 International Conference on Learning Representations May 02 - 04, 2013, Scottsdale, Arizon ...
- Deep Learning基础--线性解码器、卷积、池化
本文主要是学习下Linear Decoder已经在大图片中经常采用的技术convolution和pooling,分别参考网页http://deeplearning.stanford.edu/wiki/ ...
随机推荐
- PostgreSQL Replication之第六章 监控您的设置(1)
在本书的前几章,您已经学习了各种复制以及如何配额制各种类型的场景.现在是时候通过增加监控来让您的设置更加可靠了. 在本章中,您将学习监控什么以及如恶化实施合理的监控车辆.您将学习: • 检查您的 XL ...
- 链表python
无序链表.有序链表 有序列表排序通常是升序或降序,并且我们假设列表项具有已经定义的有意义的比较运算. 许多有序列表操作与无序列表的操作相同. 必须明确链表的第一项位置,一旦知道第一项. 链表实现的基本 ...
- ELK安装笔记
1.jdk安装 2.logstash安装使用 #命令方式[root@ELK ELK]# tar xf logstash-5.3.2.tar.gz [root@ELK logstash-5.3.2]# ...
- NodeJS学习笔记 (26)命令行设计-repl
https://github.com/chyingp/nodejs-learning-guide
- JS触发按钮事件
前台代码: <asp:Button ID="btnSaveBattery" runat="server" Text="保存" OnCl ...
- Python对象引用的所有权
目录 引用所有权 传递引用的所有权--返回值 出借引用的所有权--返回值 占据引用的所有权--参数 出借引用的所有权--参数 引用所有权 谁持有对象引用的所有权,谁就要对对象负责. 引用的所有权对函数 ...
- Test-我喜欢LInux
测试发帖流程 哈哈 习惯一下先.
- [codewars_python]Best travel
Instructions John and Mary want to travel between a few towns A, B, C ... Mary has on a sheet of pap ...
- 关于Github Pages
迁移Github Pages 我稍微有一点强迫症,实在是忍受不了整洁的界面有一些推广的广告.正所谓博客平台不重要,重要的是要有干货,CSDN首页满屏的广告也就忍受了,但是自己的文章的页面有广告看着实在 ...
- 找出BST里面与Target最接近的n个数
http://www.cnblogs.com/jcliBlogger/p/4771342.html 这里给了两种解法,一种是利用C++的priority_queue,然后逐个node输入. 另一种是先 ...