DESeq2包
1)简介:
DESeq2-package: for differential analysis of count data(对count data 做差异分析)
2)安装
if("DESeq2" %in% rownames(installed.packages()) == FALSE) {source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R");biocLite("DESeq2")}
suppressMessages(library(DESeq2))
ls('package:DESeq2')
3)对象的使用说明
3.1)coef(Extract a matrix of model coefficients/standard errors,高级用户检验模型系数)
语法:coef(object, SE = FALSE, ...)
参数解释:
object:a DESeqDataSet returned by DESeq, nbinomWaldTest, or nbinomLRT.
例子:
dds <- makeExampleDESeqDataSet(m=4)
dds <- DESeq(dds)
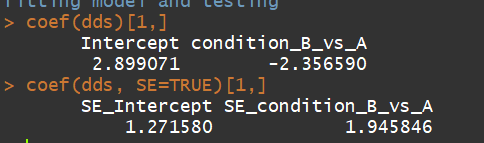
coef(dds)[1,]
coef(dds, SE=TRUE)[1,]
3.2) collapseReplicates:Collapse technical replicates in a RangedSummarizedExperiment or DESeqDataSet(用于消除技术重复)
用法:collapseReplicates(object, groupby, run, renameCols = TRUE)
参数:
object:A RangedSummarizedExperiment or DESeqDataSet
groupby:a grouping factor, as long as the columns of object,分组因子
run:optional, the names of each unique column in object. if provided, a new column runsCollapsed will be added to the colData which pastes together the names of run (测序run)
renameCols:whether to rename the columns of the returned object using the levels of the grouping factor
例子:
dds <- makeExampleDESeqDataSet(m=12)
str(dds)
dds$sample <- factor(sample(paste0("sample",rep(1:9, c(2,1,1,2,1,1,2,1,1))))) (#共9个样品:其中 3个样品有2个技术重重)
dds$run <- paste0("run",1:12) #12个run道
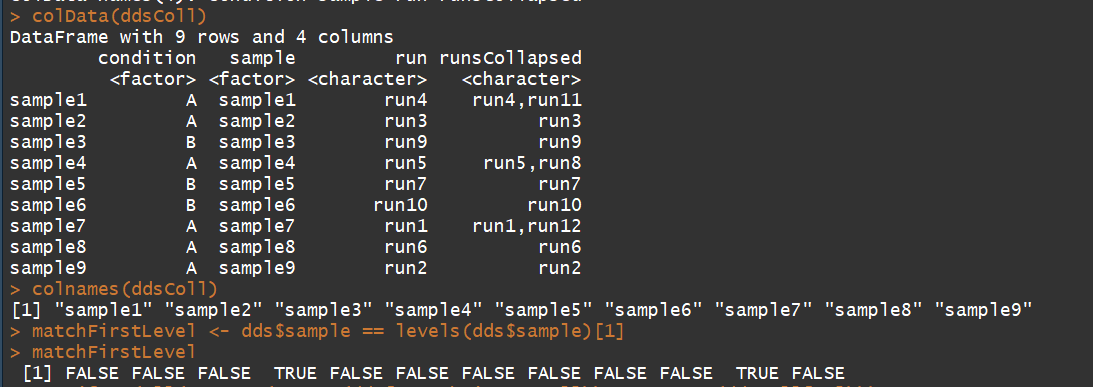
ddsColl <- collapseReplicates(dds, dds$sample, dds$run)
# examine the colData and column names of the collapsed data
colData(ddsColl)
colnames(ddsColl)
# check that the sum of the counts for "sample1" is the same
# as the counts in the "sample1" column in ddsColl
matchFirstLevel <- dds$sample == levels(dds$sample)[1]
stopifnot(all(rowSums(counts(dds[,matchFirstLevel])) == counts(ddsColl[,1])))
3.3)counts:Accessors for the ’counts’ slot of a DESeqDataSet object(对表达矩阵进行统计,)
one row for each observational unit (gene or the like), and one column for each sample(行代表观察值(例如基因),列代表样本(例如肝、脾、肾等))
语法:counts(object, normalized = FALSE,replaced = FALSE)
参数:
object:a DESeqDataSet object(表达矩阵).
normalized:logical indicating whether or not to divide the counts by the size factors or normalization factors before returning (normalization factors always preempt size factors),(即不同量级的数据要不要归一化)
replaced:返回极端值
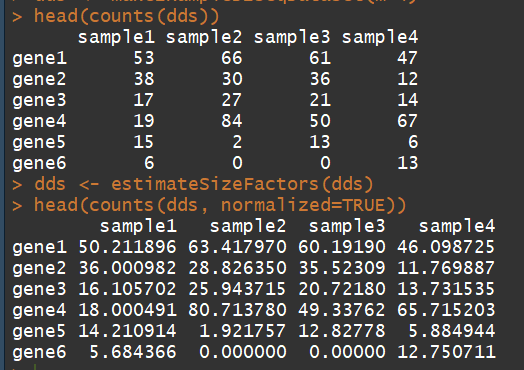
dds <- makeExampleDESeqDataSet(m=4) ##构建一个表达矩阵
head(counts(dds))
dds <- estimateSizeFactors(dds) # run this or DESeq() first
head(counts(dds, normalized=TRUE))
3.4)DESeq:Differential expression analysis based on the Negative Binomial (a.k.a.Gamma-Poisson) distribution(基于负二项分布进行差异分析)
语法:
DESeq(object, test = c("Wald", "LRT"), fitType = c("parametric", "local","mean"), sfType = c("ratio", "poscounts", "iterate"), betaPrior,full = design(object), reduced, quiet = FALSE,minReplicatesForReplace = 7, modelMatrixType, useT = FALSE, minmu = 0.5,
parallel = FALSE, BPPARAM = bpparam())
参数:
object:a DESeqDataSet object(表达矩阵对象)
test:Wald" or "LRT"检验
fitType:either "parametric", "local", or "mean"
sfType:either "ratio", "poscounts", or "iterate" for teh type of size factor estimation.
betaPrior:whether or not to put a zero-mean normal prior on the non-intercept coefficients
reduced:for test="LRT", a reduced formula to compare against
quiet:whether to print messages at each step
minReplicatesForReplace:the minimum number of replicates required
modelMatrixType:either "standard" or "expanded", which describe how the model matrix, X of the GLM formula is formed.
useT:logical, passed to nbinomWaldTest, default is FALSE
minmu:lower bound on the estimated count for fitting gene-wise dispersion
parallel:if FALSE, no parallelization. if TRUE, parallel execution using BiocParallel,
BPPARAM:an optional parameter object passed internally to bplapply when parallel=TRUE.
例子:
# count tables from RNA-Seq data
cnts <- matrix(rnbinom(n=1000, mu=100, size=1/0.5), ncol=10)
cond <- factor(rep(1:2, each=5)) # object construction
dds <- DESeqDataSetFromMatrix(cnts, DataFrame(cond), ~ cond) # standard analysis
dds <- DESeq(dds)
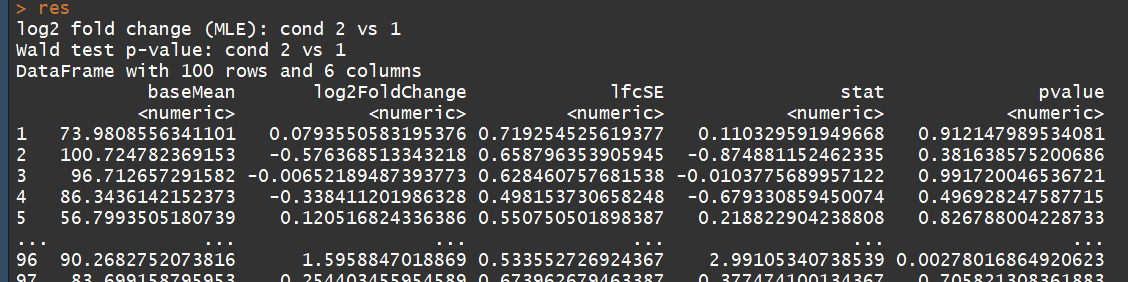
res <- results(dds) # moderated log2 fold changes
resultsNames(dds)
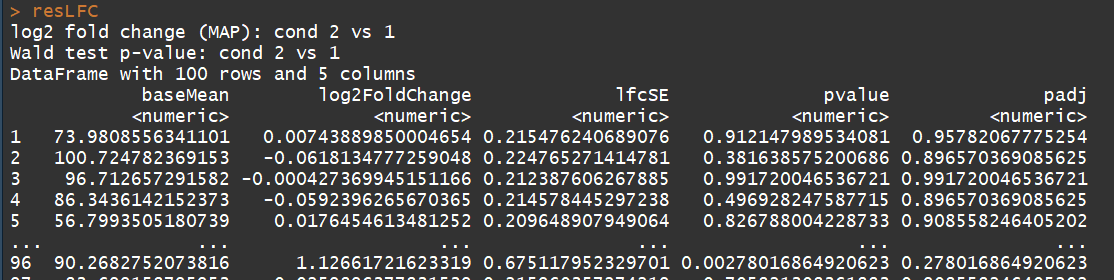
resLFC <- lfcShrink(dds, coef=2, type="apeglm") # an alternate analysis: likelihood ratio test
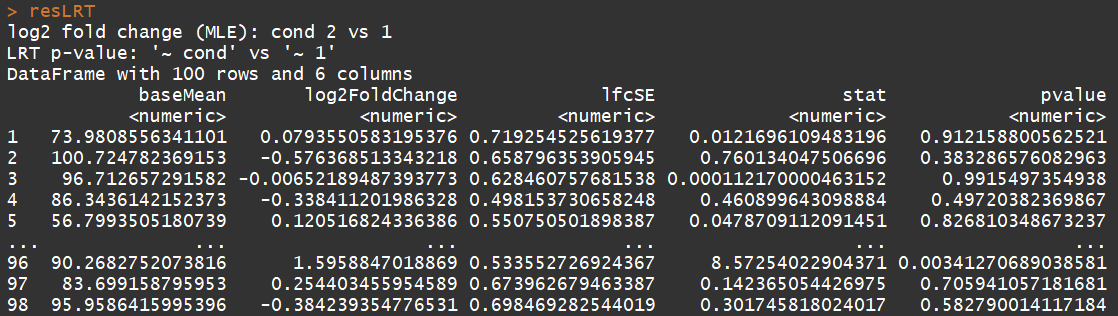
ddsLRT <- DESeq(dds, test="LRT", reduced= ~ 1)
resLRT <- results(ddsLRT)
3.5)DESeqDataSet-class(DESeqDataSet object and constructors)
语法:
DESeqDataSet(se, design, ignoreRank = FALSE)
DESeqDataSetFromMatrix(countData, colData, design, tidy = FALSE,ignoreRank = FALSE, ...)
DESeqDataSetFromHTSeqCount(sampleTable, directory = ".", design,ignoreRank = FALSE, ...)
DESeqDataSetFromTximport(txi, colData, design, ...)
例子:
countData <- matrix(1:100,ncol=4)
condition <- factor(c("A","A","B","B"))
dds <- DESeqDataSetFromMatrix(countData, DataFrame(condition), ~ condition)
3.6)DESeqResults-class:DESeqResults object and constructor
语法:DESeqResults(DataFrame, priorInfo = list())
参数:
DataFrame:a DataFrame of results, standard column names are: baseMean, log2FoldChange,lfcSE, stat, pvalue, padj.
priorInfo:a list giving information on the log fold change prior
3.7)DESeqTransform-class(DESeqTransform object and constructor)
语法:DESeqTransform(SummarizedExperiment)
参数:SummarizedExperiment a RangedSummarizedExperiment
3.8)rlog Apply a ’regularized log’ transformation
用法:
rlog(object, blind = TRUE, intercept, betaPriorVar, fitType = "parametric")
rlogTransformation(object, blind = TRUE, intercept, betaPriorVar,fitType = "parametric")
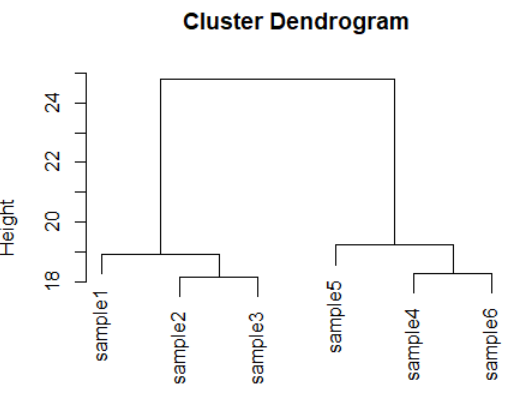
dds <- makeExampleDESeqDataSet(m=6,betaSD=1)
rld <- rlog(dds)
dists <- dist(t(assay(rld)))
plot(hclust(dists))
3.9)plotPCA(Sample PCA plot for transformed data)
用法:plotPCA(object, intgroup = "condition",ntop = 500, returnData = FALSE)
参数:
object:a DESeqTransform object, with data in assay(x), produced for example by either rlog or varianceStabilizingTransformation.
intgroup: interesting groups: a character vector of names in colData(x) to use for grouping
ntop:number of top genes to use for principal components, selected by highest row variance
returnData:should the function only return the data.frame of PC1 and PC2 with intgroup covariates for custom plotting
# using rlog transformed data:
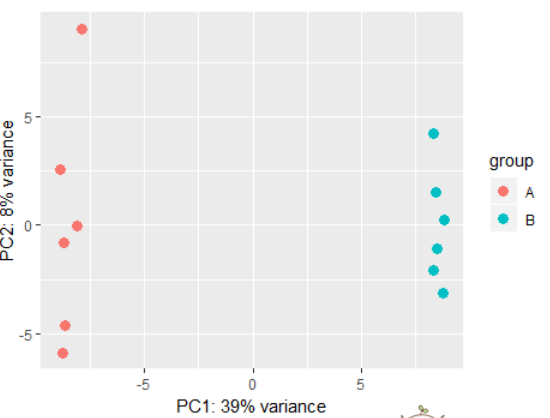
dds <- makeExampleDESeqDataSet(betaSD=1)
rld <- rlog(dds)
plotPCA(rld) # also possible to perform custom transformation:
dds <- estimateSizeFactors(dds)
# shifted log of normalized counts
se <- SummarizedExperiment(log2(counts(dds, normalized=TRUE) + 1),
colData=colData(dds))
# the call to DESeqTransform() is needed to
# trigger our plotPCA method.
plotPCA( DESeqTransform( se ) )
3.10)
DESeq2包的更多相关文章
- 简单使用DESeq2/EdgeR做差异分析
简单使用DESeq2/EdgeR做差异分析 Posted: 五月 07, 2017 Under: Transcriptomics By Kai no Comments DESeq2和EdgeR都 ...
- airway之workflow
1)airway简介 在该workflow中,所用的数据集来自RNA-seq,气道平滑肌细胞(airway smooth muscle cells )用氟美松(糖皮质激素,抗炎药)处理.例如,哮喘患 ...
- miRAN 分析以及mRNA分析
一些参考资料 http://www.360doc.com/content/17/0528/22/19913717_658086490.shtml https://www.cnblogs.com/tri ...
- Error in library(DESeq2) : 不存在叫‘DESeq2’这个名字的程辑包
Error in read.dcf(file.path(pkgname, "DESCRIPTION"), c("Package", "Type&quo ...
- DESeq2 install --- 如何安装R包("RcppArmadillo")?
安装R包("RcppArmadillo")失败,导致依赖该包的DESeq2 无法使用: 首先对gcc,g++升级至4.7, 但依然报错,还是安装不了RcppArmadillo: 报 ...
- R包安装的正确方式
options("repos" = c(CRAN="https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/CRAN/")) if(! req ...
- Npm包的开发
个人开发包的目录结构 ├── coverage //istanbul测试覆盖率生成的文件 ├── index.js //入口文件 ├── introduce.md //说明文件 ├── lib │ ...
- Windows server 2012 添加中文语言包(英文转为中文)(离线)
Windows server 2012 添加中文语言包(英文转为中文)(离线) 相关资料: 公司环境:亚马孙aws虚拟机 英文版Windows2012 中文SQL Server2012安装包,需要安装 ...
- 如何在nuget上传自己的包+搭建自己公司的NuGet服务器(新方法)
运维相关:http://www.cnblogs.com/dunitian/p/4822808.html#iis 先注册一个nuget账号https://www.nuget.org/ 下载并安装一下Nu ...
随机推荐
- SQL Server存储过程 对数组参数的循环处理
方法一 分割 例:通过SQL Server存储过程传送数组参数删除多条记录 eg. ID 值为'1,2,3' 以下存储过程就是删除表中id号为1,2,3的记录: CREATE PROCEDURE De ...
- JSSDK微信自定义分享朋友圈
服务项目 新手技术咨询 企业技术咨询 定制开发 服务说明 QQ有问必答 QQ.微信.电话 微信开发.php开发,网站开发,系统定制,小程序开发 价格说明 200元/月 1000/月 商议 ...
- 从Qt谈到C++(一):关键字explicit与隐式类型转换
转载:果冻虾仁 提出疑问 当我们新建了一个Qt的widgets应用工程时.会自动生成一个框架,包含了几个文件. 其中有个mainwindow.h的头文件.就是你要操纵的UI主界面了.我们看看其中的一段 ...
- [转]利用C#自带组件强壮程序日志
利用C#自带组件强壮程序日志 在项目正式上线后,如果出现错误,异常,崩溃等情况 我们往往第一想到的事就是查看日志 所以日志对于一个系统的维护是非常重要的 声明 正文中的代码只是一个栗子,一个非常简 ...
- wp模版强制用CSS空两格的问题
之前我写过一篇文章<关于模板该不该用css强制编辑器文本开头空两格>,里面有说到一个观点,模版作者设计的时候,不要控制文章段落空两格,但是我用久了wp,我才慢慢发现,做wp模版的时候,确实 ...
- Ubuntu 11.10 H3C iNode 客户端安装
下载客户端,放到桌面 双击打开,点击解压缩 Ctrl+Alt+T打开终端,依次输入以下代码并回车 代码: cd 桌面sudo cp iNodeClient /usr -Rcd /usr/iNodeCl ...
- 理解Storm Metrics
在hadoop中,存在对应的counter计数器用于记录hadoop map/reduce job任务执行过程中自定义的一些计数器,其中hadoop任务中已经内置了一些计数器,例如CPU时间,GC时间 ...
- 由一条普通的link引用引发的无数问号,大家能回答的帮忙回答回答吧.
<link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="1.css" /> 对于前台工作者来说 ...
- 安装phoenix时,执行命令./sqlline.py hostname1,hostname2.hostname3..... 时报错 ImportError: No module named argparse
问题描述: 怎么解决呢: 网上看了好多方法,但是本屌丝表示看不懂啊,没理解人家的博客的博大精深,好吧我们回到正题!! 先切换到root用户下安装这个东西 yum install python-a ...
- solr亿万级索引优化实践(四)
本篇是这个系类的最后一篇,但优化方案不仅于此,需要后续的研究与学习,本篇主要从schema设计的角度来做一些实践. schema.xml 这个文件的作用是定义索引数据中的域的,包括域名称,域类型,域是 ...
