vCenter Single Sign On 5.1 best practices
http://www.virtualizationteam.com/virtualization-vmware/vsphere-virtualization-vmware/vcenter-single-sign-on-5-1-best-practices.html
vCenter Single Sign On 5.1 best practices
Since vCenter Single Sign On was introduced in vSphere 5.1, many questions have been rising around it. There seems to be a very limited amount of resources out there that document best practices related to vCenter Single Sign On, which is the reason for me to develop this post where I will try to combine as many best practices and answers related to vCenter 5.1 Single Sign On as possible.
I have been one of the lucky consultants who has already got to design/implement vSphere 5.1 for quite few enterprise customers where I have got to debate and drive best practices that I used across those implementations. I am sharing them here where others can benefit from them as well to allow a room for others to debate them and contribute their feedback.
Where to install vCenter Single Sign On (Physical vs Virtual)?
Just as the recommendations have always been for vCenter using virtual machine(s) is the best practice to save on cost and benefit of the availability features built in vSphere, that is no difference in vSphere 5.1. You can host all vCenter 5.1 components including SSO on virtual or physical machine, where virtual machine is the recommended practice due to the same reason mentioned earlier. Further, implementing vCenter 5.1 components including Single Sign On in a virtual machine will not limit its scalability by any mean and it still can deliver up to vCenter current maximums of 10,000VMs & 1,000 hosts.
Where to install vCenter Single Sign On (Combine it with vCenter Service & Inventory Service or on its own VM)?
As Single Sign On has became a mandatory requirement when installing vCenter 5.1, & as the option of breaking out the different vCenter components across multiple machines was introduced in vSphere 5.1 this has became the most vCenter Single Sign On related question. Although I titled this article as vCenter Single Sign On best practices, I would like to break in at this question and cover when to combine and when not to combine vCenter Service, vCenter Inventory Service, & SSO.
vCenter Inventory Service: vCenter Inventory Service can be resource intensive at larger environments especially ones that is approaching the 10,000VM/1000hosts vCenter limit. From scalability perspective, you will want to move the inventory service to a separate VM from the one running the vCenter service in environment approaching the vCenter limit (No exact number provided, but I will say anything larger than 8,000VMs/800hosts will fall into that category). In most other environments (>90% of the time), it will make much more sense to keep it running with the vCenter Service on the same VM.
vCenter Single Sign On: Unlike vCenter Inventory Service, SSO is a very light service that is not intense on resources even for the largest environment out there, which leads to scalability not being a concern when combining it with vCenter Service on the same VM.
On the other hand, you will need to decide on whether to place Single Sign On on the same VM as your vCenter service or not based on the importance of its availability & how are you planning to protect it. If your environment is made up of a single vCenter instance & you are quite sure that you will not grow or ever have a reason to have a second vCenter or other service like vCOPs or vCD sharing that same Single Sign On Instance then it is safe to host SSO on the same VM hosting the other vCenter Services. In this scenario, your SSO is only used for a single vCenter instance and it does not matter much if it goes down with it.
On the other hand, if you are having or planning to multiple vCenters in your environment, the importance of SSO is now beyond the importance of any single vCenter as losing it means you can not access any of the other vCenters. Imagine the scenario where you have to carry out maintenance on the vCenter VM hosting your SSO, you will not be only affecting access to that vCenter but every other vCenter & tool that is dependent on that SSO instance. For that in such a case when the availability of SSO is beyond affecting just a single vCenter then you will want to have it on a separate VM and make sure its well protected.
Which vCenter Single Sign On Deployment Mode should I use in my environment?
Before I go through which vCenter Single Sign On Deployment Mode to use in your environment & why, lets recall the vCenter Single Sign On Deployment modes definition as stated in vSphere 5.1 Documentation Center:
Simple mode: installs vCenter Single Sign On, vCenter Inventory Service, and vCenter Server together on a single host machine using the vCenter Server Simple Install option. This option is appropriate for small deployments.
Basic mode: installs a standalone version of vCenter Single Sign-On. Multiple vCenter Server and Inventory Service instances can point to it. If the Single Sign-On server or the virtual machine hosting the server fails, administrators cannot access vCenter Server, but ESXi hosts continue to function normally. Multiple Active Directory and OpenLDAP instances can be added as identity sources.
High Availability Cluster: Cluster mode installs two or more vCenter Single Sign-On instances in high availability mode. All instances use the same database and point to the same identity sources. Single Sign-On administrator users, when connected to vCenter Server through the vSphere Web Client, will see the primary Single Sign-On instance.
Multisite mode: is designed for deployments with multiple physical locations. Installing a Single Sign-On instance at each site allows fast access to local authentication-related services. Each Single Sign-On instance is connected to the local instances of the AD (LDAP) servers and has its own database with local users and groups. In each datacenter, you can install Single Sign-On in standalone or clustered mode, pointing to the identity sources in that location.
Now that we have covered the different SSO deployment modes, let’s discuss which one you should use. The answer in its most diplomatic forms “It depends”. Different modes are used in different scenarios, though below I will talk about the use cases of each:
Simple Mode: This one should only be used for smaller deployments where having all the components on a single VM will not affect their scalability and availability requirements. The next question, I can see running in many people heads is what being regarded a smaller deployment. I have not seen any official statement on this, but it seems 10-25hosts/100-250VMs is where most of the answers I were getting. Something to remember in basic mode, you will be forced to install all your components on a single VM and your SSO availability will be tight to that vCenter instance.
Basic mode: While Basic mode allows you to combine vCenter Service, vCenter Inventory Service, & Single Sign On on the same VM, unlike the Simple Mode it will allow you as well to spread these services across multiple VMs when required for scalability or availability reasons. If vSphere HA or vCenter Heartbeat is your preferred method for protecting your SSO, and you are not planning to use the Multisite mode then Basic mode might be the right deployment mode for you. Unlike Simple mode, Basic mode fit organizations of all sizes and not limited for smaller deployments.
High Availability Cluster: This is my preferred method of deployment (When obtaining vCenter Heartbeat is not an option), even if all you are planning to deploy initially is a single SSO VM, using this method will give you the chance to cluster your SSO without having to re-build it in the future.
Note: SSO HA provides limited availability, The database is a single point of failure (no cluster support) and the administration of SSO unavailable when failed over. vCenter Heartbeat provide better protection and with a simplified configuration of SSO. As you can see vCenter Heartbeat is worth its tag price if you can stretch your budget a bit.
Multisite mode: The only time I would recommend using multisite mode at the moment is if you are planning to use vCenter Linked Mode. In case you missed it, vCenters setup in linked mode must be connected to the same vCenter SSO instance where the goal of Multisite mode is to allow you to have a single vCenter SSO instance spanning across two different physical locations where each site will have its own SSO nodes(Single or clustered). While this sound great in theory, there is few hiccups in there that you should be aware off:
- Multisite mode does not offer any kind off availability across the sites. For example if the SSO server at site A fail while it is setup in a Multisite mode with another SSO server at site B which is working fine, you will still lose access to vCenters dependent on the SSO server in site A. The good news is that you can configure each SSO involved in multisite configuration in High Availability Cluster within the same site to protect against its failure.
- SSO does not currently have any built-in replication to keep the nodes across sites within a Multisite mode in sync, where you will have to script the process of SSO database replication across the sites to achieve such configuration which is required by vCenter Linked mode.
I guess depending on your environment, you will have the choose the deployment mode that fit you best. In my opinion, the safest option and where most medium to large installation will utilize is the Basic mode when vCenter Heartbeat is an option, else High Availability mode even if they set it up with a single SSO node during the initial installation.
Do you recommend vCenter Linked Mode to obtain a single view of your multiple vCenters?
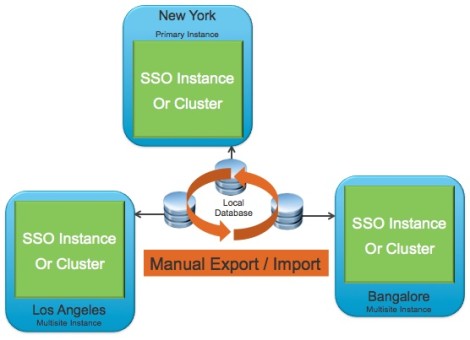
I have recommended vCenter Linked Mode in vSphere 5.1 environment as long all the vCenters involved were on the same site and have LAN like connectivity. I have usually recommended against the Multi-Site(different physical location) vCenter Linked Mode at the moment due to the complexity as well manual work and amount of maintenance required to keep it going in the long run. As I mentioned earlier, setting up vCenter Linked Mode across sites will require you to setup your SSO in a multi-site configuration as well to script a database synchronization between the two sites. Although its currently supported and workable, I am not advising for it unless it is a mandatory requirements. I am confident though this will improve as vCenter SSO evolve.
Can you recommend on sizing for the SSO VM?
KB2021202 has provided a great sizing recommendation for vCenter components & I referred to it consistently when I started working with vSphere 5.1 & I believe you should give it a look. It has actually recommended a minimum of (2vCPU, 3GB of RAM, 2GB of disk) for vCenter Single Sign On VM. In practice, what I have usually used and recommend for the SSO VM size is (2vCPU, 4GB of RAM, 20GB of disk).
Where Do I install vCenter SSO Database?
This question has been popping up quite often lately. Do I actually install vCenter Single Sign on database with it on the same VM, or on the DB Server hosting my vCenter DB? While both options work pretty well, consider the below recommendations when making your choice:
- If vCenter DB is hosted on the vCenter VM, & you have decided to host SSO on a separate VM for availability perspective then you should not host your SSO DB next your vCenter DB on that VM. It just does not make sense, as you will be tying your SSO availability again to vCenter and that is the reason you decided to host SSO on a separate VM from vCenter in the first place.
- If you have a production SQL Server setup and maintained by your DBAs and it is not running on your vCenter VM & maintained separately from it then this might be your best place to install your SSO DB as this will give you the advantage of your DBA maintaining & backing up the DB for you.
- If you like to have a self contained SSO server & not being dependent on any external DB or you don’t have a production DB server that is well maintained and centralize, then your best option will be to host your SSO on an SQL Express Database server that get installed on the vCenter Single Sign On VM it self.
How to size my vCenter Single Sign On DB?
I hear this question a lot as VMware has not published any numbers on the size of the Single Sign On DB beside saying it is small. Actually after digging it a bit, I have found it to be small enough for most customers that sizing for it can almost be ignored. I have to still see a customer who use even close to 100MB of db size for vCenter Single Sign On. That have been said, I would actually keep a capacity of 1GB for the vCenter Single Sign On just to give you a lot of cushions in case you forget to trim your logs or so on, but in general you will not be using much of space for it at all as it only store the below three main items:
- Identity Source Configurations
- Users & Groups membership
- Password Policies for SSO Users.
Will Microsoft SQL Express be sufficient for my vCenter Single Sign On DB?
Unlike vCenter which is limited to support 5 hosts & 50 VM if you are using Microsoft SQL Express to host its DB, SSO can grow to support the maximums of your vCenter 5.1 (10,000VMs/1,000 hosts) while running on Microsoft SQL Express which make it definitely an option specially if you are planning to install the SSO DB on the same VM as your SSO to keep it self contained and ease image backup and restore of it.
Additional vCenter Single Sign On Resources:
While in this article I have tried to addressed few of the best practice questions that keep popping up in the field, there is quite valuable resources out there that I thought would be useful to point out in here:
- Preparing the Database for Single Sign On installation
- vCenter 5.1 Installation(Part 2) – Single Sign On Installation(Step by Step)
- VMware vSphere 5.1 new vCenter architecture & Single Sign on
- Frequently Asked Questions: VMware vCenter Single Sign On 5.1
- vCenter Single Sign-On FAQ (2034918)
- VMware SSO Blog
Feedback:
I am really interested in hearing your feedback, thoughts, what best practices that should have been on this list and needed to be added. Anything that you agree with or disagree with. Please keep those productive feedback comings so we can improve this list for everyone benefits.
vCenter Single Sign On 5.1 best practices的更多相关文章
- 在shiro-cas中实现 Jasig-cas的Single Sign Out 功能
1 Single Sign Out 功能 即单点登出功能.也就是在任意子系统进行登出操作后,其他子系统会自动登出. 实际CAS登出的步骤为 所以每个子系统都需要实现一个sso登出响应. cas-cli ...
- 源代码解读Cas实现单点登出(single sign out)功能实现原理
关于Cas实现单点登入(single sing on)功能的文章在网上介绍的比较多,想必大家多多少少都已经有所了解,在此就不再做具体介绍.如果不清楚的,那只能等我把single sign on这块整理 ...
- VMware系统运维(五)安装SSO vCenter Single Sign-On
1.前面我们做了很多准备工作,安装了很多需求部件,这时候再安装,必备条件无,这是简单安装,即自动安装,点击"安装". 2.简单安装,提示内存不足,需要4GB以上,加内存,重新安装. ...
- 源代码解读Cas实现单点登出(single sign out)功能实现原理--转
关于Cas实现单点登入(single sing on)功能的文章在网上介绍的比较多,想必大家多多少少都已经有所了解,在此就不再做具体介绍.如果不清楚的,那只能等我把single sign on这块整理 ...
- sso(single sign on)
sso系统使用 https://www.cnblogs.com/shuai-server/p/8987070.html 一:什么是sso(single sign on) ? sso(单点登录系统)简单 ...
- 单点登录(Single Sign On)解决方案
单点登录(Single Sign On)解决方案 需求 多个应用系统中,用户只需要登录一次就可以访问所有相互信任的应用系统. A 网站和 B 网站是同一家公司的关联服务.现在要求,用户只要在其中一个网 ...
- Salesforce Admin篇(四) Security 之Two-Factor Authentication & Single Sign On
本篇参考: https://c1.sfdcstatic.com/content/dam/web/en_us/www/documents/white-papers/2fa-admin-rollout-g ...
- java:sso(单点登录(single sign on),jsp文件动静态导入方式,session跨域)
1.jsp文件导入: 2.session跨域: 3.sso(单点登录(single sign on): sso Maven Webapp: LoginController.java: package ...
- SSO & Single Sign On
SSO & Single Sign On 单点登录 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_sign-on https://cloud.google.com/ ...
随机推荐
- Idea2018激活破解
原文:https://www.imsxm.com/2018/07/idea-2018-1-5-crack-patcher.html 最近更新了Intellij IDEA到2018.1.5之后,使用之前 ...
- 将 nginx 安装成 windows 的方法
服务器这几天不稳定,经常性的重启(硬件问题),而且是windows环境,在其上跑了nginx,每次重启后需要手动启动nginx方能是整个系统正常. 所以就查找了下一种方法,能否将nginx做成wind ...
- 【nginx】配置Nginx实现负载均衡
一文中已经提到,企业在解决高并发问题时,一般有两个方向的处理策略,软件.硬件,硬件上添加负载均衡器分发大量请求,软件上可在高并发瓶颈处:数据库+web服务器两处添加解决方案,其中web服务器前面一层最 ...
- Occlusion Culling遮挡剔除理解设置和地形优化应用
这里使用的是unity5.5版本 具体解释网上都有,就不多说了,这里主要说明怎么使用,以及参数设置和实际注意点 在大场景地形的优化上,但也不是随便烘焙就能降低帧率的,必须结合实际情况来考虑,当然还有透 ...
- 基于Memcached的tomcat集群session共享所用的jar
多个tomcat各种序列化策略配置如下:一.java默认序列化tomcat配置conf/context.xml添加<Manager className="de.javakaffee.w ...
- SharePoint Online 创建和使用视图
前言 本文介绍如何在Office 365中创建和使用视图. 正文 首先,解释一下什么是SharePoint站点视图,所谓视图,就是列表的一个呈现形式,包含特定的栏.排序.筛选.分组等特性,我们通常创建 ...
- ExtJS 4.2 教程-06:服务器代理(proxy)
转载自起飞网,原文地址:http://www.qeefee.com/extjs-course-6-server-proxy ExtJS 4.2 教程-01:Hello ExtJS ExtJS 4.2 ...
- [Web 前端] webstorm 快速搭建react项目
cp from : https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39207948/article/details/79467144 前端新手如何安装webstorm ,初步搭建react项目 下 ...
- caffe中的学习率的衰减机制
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/Julialove102123/article/details/79200158 根据 caffe/ ...
- Guava Enums
概述 Enums提供了几个操作Enum的便利方法 常用方法 Field getField(Enum<?> enumValue): 返回变量名为enumValue变量值的Field < ...
