Scrapy命令行详解
官方文档:https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/
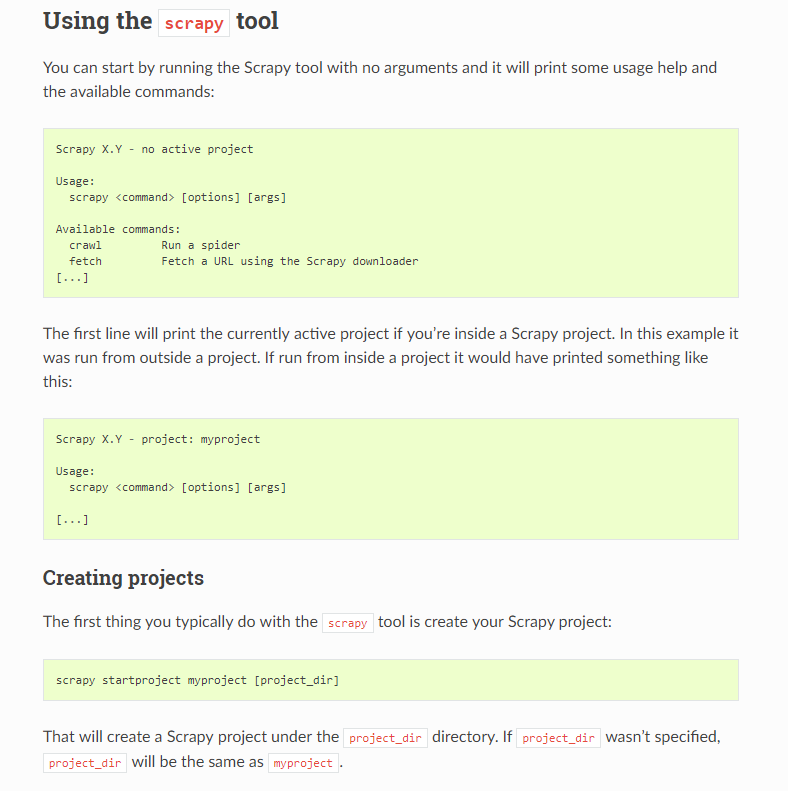
Global commands:
Project-only commands: 在项目目录下才可以执行
startproject
- Syntax:
scrapy startproject <project_name> [project_dir] - Requires project: no
Creates a new Scrapy project named project_name, under the project_dir directory. If project_dir wasn’t specified, project_dirwill be the same as project_name.
Usage example:
$ scrapy startproject myproject
genspider
- Syntax:
scrapy genspider [-t template] <name> <domain> - Requires project: no
Create a new spider in the current folder or in the current project’s spiders folder, if called from inside a project. The <name> parameter is set as the spider’s name, while <domain> is used to generate the allowed_domains and start_urls spider’s attributes.
Usage example:
$ scrapy genspider -l
Available templates:
basic
crawl
csvfeed
xmlfeed $ scrapy genspider example example.com
Created spider 'example' using template 'basic' $ scrapy genspider -t crawl scrapyorg scrapy.org
Created spider 'scrapyorg' using template 'crawl'
This is just a convenience shortcut command for creating spiders based on pre-defined templates, but certainly not the only way to create spiders. You can just create the spider source code files yourself, instead of using this command.
crawl
- Syntax:
scrapy crawl <spider> - Requires project: yes
Start crawling using a spider.
Usage examples:
$ scrapy crawl myspider
[ ... myspider starts crawling ... ]
check
- Syntax:
scrapy check [-l] <spider> - Requires project: yes
Run contract checks.
Usage examples:
$ scrapy check -l
first_spider
* parse
* parse_item
second_spider
* parse
* parse_item $ scrapy check
[FAILED] first_spider:parse_item
>>> 'RetailPricex' field is missing [FAILED] first_spider:parse
>>> Returned 92 requests, expected 0..4
list
- Syntax:
scrapy list - Requires project: yes
List all available spiders in the current project. The output is one spider per line.
Usage example:
$ scrapy list
spider1
spider2
edit
- Syntax:
scrapy edit <spider> - Requires project: yes
Edit the given spider using the editor defined in the EDITORenvironment variable or (if unset) the EDITOR setting.
This command is provided only as a convenience shortcut for the most common case, the developer is of course free to choose any tool or IDE to write and debug spiders.
Usage example:
$ scrapy edit spider1
fetch
- Syntax:
scrapy fetch <url> - Requires project: no
Downloads the given URL using the Scrapy downloader and writes the contents to standard output.
The interesting thing about this command is that it fetches the page how the spider would download it. For example, if the spider has a USER_AGENT attribute which overrides the User Agent, it will use that one.
So this command can be used to “see” how your spider would fetch a certain page.
If used outside a project, no particular per-spider behaviour would be applied and it will just use the default Scrapy downloader settings.
Supported options:
--spider=SPIDER: bypass spider autodetection and force use of specific spider--headers: print the response’s HTTP headers instead of the response’s body--no-redirect: do not follow HTTP 3xx redirects (default is to follow them) #有重定向的连接时候使用这个参数
Usage examples:
$ scrapy fetch --nolog http://www.example.com/some/page.html
[ ... html content here ... ] $ scrapy fetch --nolog --headers http://www.example.com/
{'Accept-Ranges': ['bytes'],
'Age': ['1263 '],
'Connection': ['close '],
'Content-Length': ['596'],
'Content-Type': ['text/html; charset=UTF-8'],
'Date': ['Wed, 18 Aug 2010 23:59:46 GMT'],
'Etag': ['"573c1-254-48c9c87349680"'],
'Last-Modified': ['Fri, 30 Jul 2010 15:30:18 GMT'],
'Server': ['Apache/2.2.3 (CentOS)']}
view
- Syntax:
scrapy view <url> - Requires project: no
Opens the given URL in a browser, as your Scrapy spider would “see” it. Sometimes spiders see pages differently from regular users, so this can be used to check what the spider “sees” and confirm it’s what you expect.
Supported options:
--spider=SPIDER: bypass spider autodetection and force use of specific spider--no-redirect: do not follow HTTP 3xx redirects (default is to follow them)
Usage example:
$ scrapy view http://www.example.com/some/page.html
[ ... browser starts ... ]
shell
- Syntax:
scrapy shell [url] - Requires project: no
Starts the Scrapy shell for the given URL (if given) or empty if no URL is given. Also supports UNIX-style local file paths, either relative with ./ or ../ prefixes or absolute file paths. See Scrapy shell for more info.
Supported options:
--spider=SPIDER: bypass spider autodetection and force use of specific spider-c code: evaluate the code in the shell, print the result and exit--no-redirect: do not follow HTTP 3xx redirects (default is to follow them); this only affects the URL you may pass as argument on the command line; once you are inside the shell,fetch(url)will still follow HTTP redirects by default.
Usage example:
$ scrapy shell http://www.example.com/some/page.html
[ ... scrapy shell starts ... ] $ scrapy shell --nolog http://www.example.com/ -c '(response.status, response.url)'
(200, 'http://www.example.com/') # shell follows HTTP redirects by default
$ scrapy shell --nolog http://httpbin.org/redirect-to?url=http%3A%2F%2Fexample.com%2F -c '(response.status, response.url)'
(200, 'http://example.com/') # you can disable this with --no-redirect
# (only for the URL passed as command line argument)
$ scrapy shell --no-redirect --nolog http://httpbin.org/redirect-to?url=http%3A%2F%2Fexample.com%2F -c '(response.status, response.url)'
(302, 'http://httpbin.org/redirect-to?url=http%3A%2F%2Fexample.com%2F')
parse
- Syntax:
scrapy parse <url> [options] - Requires project: yes
Fetches the given URL and parses it with the spider that handles it, using the method passed with the --callback option, or parse if not given.
Supported options:
--spider=SPIDER: bypass spider autodetection and force use of specific spider--a NAME=VALUE: set spider argument (may be repeated)--callbackor-c: spider method to use as callback for parsing the response--metaor-m: additional request meta that will be passed to the callback request. This must be a valid json string. Example: –meta=’{“foo” : “bar”}’--pipelines: process items through pipelines--rulesor-r: useCrawlSpiderrules to discover the callback (i.e. spider method) to use for parsing the response--noitems: don’t show scraped items--nolinks: don’t show extracted links--nocolour: avoid using pygments to colorize the output--depthor-d: depth level for which the requests should be followed recursively (default: 1)--verboseor-v: display information for each depth level
Usage example:
$ scrapy parse http://www.example.com/ -c parse_item
[ ... scrapy log lines crawling example.com spider ... ] >>> STATUS DEPTH LEVEL 1 <<<
# Scraped Items ------------------------------------------------------------
[{'name': 'Example item',
'category': 'Furniture',
'length': '12 cm'}] # Requests -----------------------------------------------------------------
[]
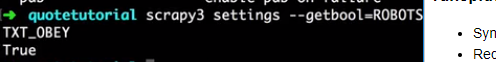
settings
- Syntax:
scrapy settings [options] - Requires project: no
Get the value of a Scrapy setting.
If used inside a project it’ll show the project setting value, otherwise it’ll show the default Scrapy value for that setting.
Example usage:
$ scrapy settings --get BOT_NAME
scrapybot
$ scrapy settings --get DOWNLOAD_DELAY
0


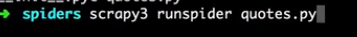
runspider
- Syntax:
scrapy runspider <spider_file.py> - Requires project: no #全局执行
Run a spider self-contained in a Python file, without having to create a project.
Example usage:
$ scrapy runspider myspider.py
[ ... spider starts crawling ... ]
version
- Syntax:
scrapy version [-v] - Requires project: no
Prints the Scrapy version. If used with -v it also prints Python, Twisted and Platform info, which is useful for bug reports.

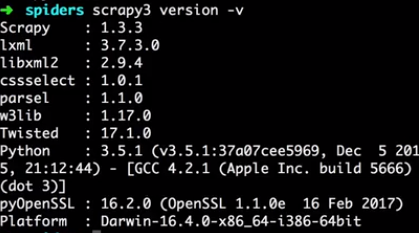
bench
New in version 0.17.
- Syntax:
scrapy bench - Requires project: no
Run a quick benchmark test. Benchmarking.
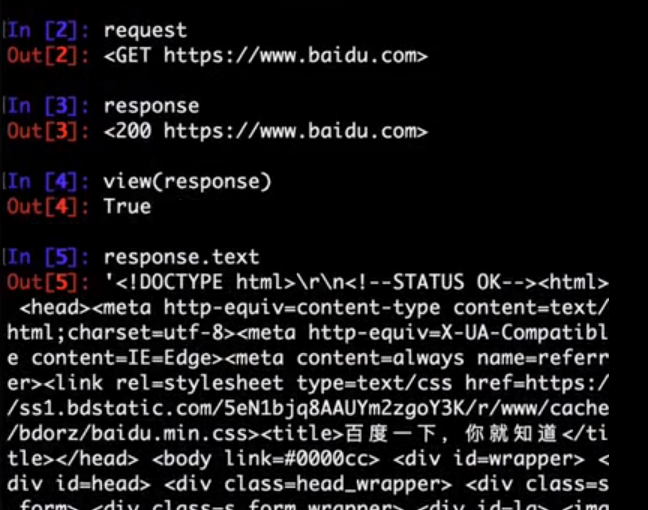
Scrapy命令行详解的更多相关文章
- 爬虫(十):scrapy命令行详解
建爬虫项目 scrapy startproject 项目名例子如下: localhost:spider zhaofan$ scrapy startproject test1 New Scrapy pr ...
- Scrapy框架的命令行详解【转】
Scrapy框架的命令行详解 请给作者点赞 --> 原文链接 这篇文章主要是对的scrapy命令行使用的一个介绍 创建爬虫项目 scrapy startproject 项目名例子如下: loca ...
- [转载]OpenSSL中文手册之命令行详解(未完待续)
声明:OpenSSL之命令行详解是根据卢队长发布在https://blog.csdn.net/as3luyuan123/article/details/16105475的系列文章整理修改而成,我自己 ...
- 7Z命令行详解
7z.exe在CMD窗口的使用说明如下: 7-Zip (A) 4.57 Copyright (c) 1999-2007 Igor Pavlov 2007-12-06 Usage: 7za <co ...
- 7-zip命令行详解
一.简介 7z,全称7-Zip, 是一款开源软件.是目前公认的压缩比例最大的压缩解压软件. 主要特征: # 全新的LZMA算法加大了7z格式的压缩比 # 支持格式: * 压缩 / 解压缩:7z, XZ ...
- Python爬虫从入门到放弃(十三)之 Scrapy框架的命令行详解
这篇文章主要是对的scrapy命令行使用的一个介绍 创建爬虫项目 scrapy startproject 项目名例子如下: localhost:spider zhaofan$ scrapy start ...
- Python之爬虫(十五) Scrapy框架的命令行详解
这篇文章主要是对的scrapy命令行使用的一个介绍 创建爬虫项目 scrapy startproject 项目名例子如下: localhost:spider zhaofan$ scrapy start ...
- gcc命令行详解
介绍] ----------------------------------------- 常见用法: GCC 选项 GCC 有超过100个的编译选项可用. 这些选项中的许多你可能永远都不会用到, 但 ...
- [转]TFS常用的命令行详解
本文转自:http://blchen.com/tfs-common-commands/ 微软的TFS和Visual Studio整合的非常好,但是在开发过程中,很多时候只用GUI图形界面就会发现一些复 ...
随机推荐
- 这可能是最low的发布dotnet core站点到centos7教程
前言 不得不说:我在chrome上写了好长一段,贴了23张图,然后一个crash..我想说我电脑上的chrome已经crash太多次了 以后一定要搞离线编辑的. 正文 什么是.net core,bal ...
- Go语言系列文章
这个系列写的不是很好,未来重构. Go基础系列 Go基础 Go基础 1.Go简介 2.Go数据结构struct 3.构建Go程序 4.import导包和初始化阶段 5.array 6.Slice详解 ...
- 【转载】Windows Server 2012服务器删除IIS方法
在Windows Server2012版本的服务器系统中,我们可以通过服务器管理器中的"添加角色和功能"来添加IIS的Web服务器,当我们不再使用IIS功能时候,我们也可以通过删除 ...
- VS2017 启动调试报错无法启动程序 当前状态中非法
昨天还可以使用,今天就莫名报了这个错误,百度了一下: 1. 第一种尝试方法是右击解决方案中的项目(图标有带球的),打开属性选择“WEB”选项,修改特定页为Home,结果还是报错. 2.我又关闭Wind ...
- SQL Server表名为添加中括号[]执行出错
执行SQL语句: Update Check Set EOBTypeID=102 where E0BID='123344' 结果竟然报错,给表名添加中括号,写成这样: Update [Check] Se ...
- C#单例模式的几种实现方式
一.多线程不安全方式实现 public sealed class SingleInstance { private static SingleInstance instance; private S ...
- mysql 随机数 rand使用
生成随机数 生成0-3的随机数 SELECT RAND() * 最大不会超过3, SELECT FLOOR(RAND() * ) 上面生成整数的值是0,1,2,3生成的随机整数是1,2,3的话,语句如 ...
- 文件类型解析漏洞防御与攻击(PHP)
简介: 解析漏洞主要是一些特殊文件被iis.Apache.Nginx等服务在某种情况下解释成脚本文件格式并得以执行而产生的漏洞,一般的思路都是用图片木马来欺骗服务器,上传webshell,达到提权的目 ...
- 广州.NET微软技术俱乐部 微信群有用信息集锦
考虑到广州.NET微软技术俱乐部 微信群 十分活跃. 有用信息很有可能被淹没. 所以建立此贴. 首先群的活跃是十分重要的. 所以我是不可能把群搞得像技术论坛和github一样, 因为微信群的定位我在& ...
- github、git软件安装、pycharm下使用git配置、git GUI相关
1.GitHub: 官网:直接搜索,排名很靠前,需要注册: 注册完之后,会有指引.新建项目两个选项(看不懂的问YOUDAO等翻译软件啦,大段复制进去就行) 2.Git安装: (https://git- ...
