React源码解析之React.Children.map()(五)
一,React.Children是什么?
是为了处理this.props.children(this.props.children表示所有组件的子节点)这个属性提供的工具,是顶层的api之一
二,React.Children.map的结构及举例
结构:React.Children.map(object children,function fn [, object context])
举例如下:
class ChildrenDemo extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<ol>
{
React.Children.map(this.props.children, (child)=> {//child子节点
return <li>{child}</li>
})
}
</ol>
)
}
}
class MessageList extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<ChildrenDemo>
<span>1</span>
<span>2</span>
</ChildrenDemo>
)
}
}
this.props.children值有三种情况
1.如果组件没有节点 值为undefined

2.如果组件有一个节点 值的数据类型为对象

3.如果组件有多个节点 值的数据类型为数组

React.Children.map(this.props.children, child => [child, [child]]):来遍历this.props.children的子节点 多层嵌套的 [child, [child]])通过map之后平铺成一维数组[child,child]
这里两个子节点<span>1</span>和<span>2</span>,这里每一个节点都是数组 通过React.Children.map变成一个一维数组

//children:被遍历的子组件
//func:单个子组件需要执行的函数
//context:func执行时候,this指针指的对象
function mapChildren(children, func, context) {
if (children == null) {
return children;
}
var result = [];
//this.props.children [] null child=>[child,[child]] undefined
mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(children, result, null, func, context);
//执行完mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal方法后 返回result
return result;
}
/*
第一次:children:[child1,child2] array:[] prefix:null func:child=>[child,[child]] context:undefined
第二次:children:[child1,[child1]] array:[] prefix:".0" func:c=>c context:undefined
第三次:children:[child2,[child2]] array:[] prefix:".1" func:c=>c context:undefined
*/
function mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(children, array, prefix, func, context) {
var escapedPrefix = '';
//处理key 如果字符串有多个/ 在匹配的字符串后面加一个/ 一般第二层递归用到 第一层prefix为null
if (prefix != null) {
escapedPrefix = escapeUserProvidedKey(prefix) + '/';
}
//从traverseContextPool里面里面获取一个context
var traverseContext = getPooledTraverseContext(array, escapedPrefix, func, context);
//多个节点 循环每一个节点 将嵌套的数组展平
traverseAllChildren(children, mapSingleChildIntoContext, traverseContext);
//context对象清空然后放回到traverseContextPool里面
releaseTraverseContext(traverseContext);
}
解析:escapeUserProvidedKey()/getPooledTraverseContext()/traverseAllChildren()/releaseTraverseContext()函数的包裹器
escapeUserProvidedKey()
function escapeUserProvidedKey(text) {
//如果字符串中有多个/的话 在匹配的字符后加/
//let a='aa/a/' =>// aa/a//
return ('' + text).replace(userProvidedKeyEscapeRegex, '$&/');
}
//创建一个对象池 复用对象 从而减少对象带来的内存暂用 和性能消耗
var POOL_SIZE = 10; //对象池的最大容量
var traverseContextPool = [];//全局变量 对象池 有多少个数组,就有多少个对象,这就是traverseContextPool设置在这里的含义
function getPooledTraverseContext(mapResult, keyPrefix, mapFunction, mapContext) {
//如果对象池内存在对象 则出队一个对象
if (traverseContextPool.length) {//如果全局变量有子节点
var traverseContext = traverseContextPool.pop();//pop()方法用于删除并返回数组的最后一个元素。
traverseContext.result = mapResult;
traverseContext.keyPrefix = keyPrefix;
traverseContext.func = mapFunction;
traverseContext.context = mapContext;
traverseContext.count = 0;
return traverseContext;//其实就是用来记录的对象
} else {//如果没有 就返回一个新对象
return {
result: mapResult,
keyPrefix: keyPrefix,
func: mapFunction,
context: mapContext,
count: 0
};
}
}
解析:创建一个对象池 复用对象 从而减少对象带来的内存暂用 和性能消耗
//traverseAllChildrenImpl的触发器
function traverseAllChildren(children, callback, traverseContext) {
if (children == null) {
return 0;
} return traverseAllChildrenImpl(children, '', callback, traverseContext);
}
解析:traverseAllChildrenImpl的触发器
releaseTraverseContext()
//将对象属性清空并且重新放入对象池中
function releaseTraverseContext(traverseContext) {
traverseContext.result = null;
traverseContext.keyPrefix = null;
traverseContext.func = null;
traverseContext.context = null;
traverseContext.count = 0;
if (traverseContextPool.length < POOL_SIZE) {
traverseContextPool.push(traverseContext);
}
}
解析:将对象属性清空并且重新放入对象池中
traverseAllChildrenImpl()
//核心递归函数 目的为展平数组
//对于可以循环的children 都会重复调用traverseAllChildrenImpl 直到一个节点 然后调用callback
function traverseAllChildrenImpl(children, nameSoFar, callback, traverseContext) {
var type = typeof children; if (type === 'undefined' || type === 'boolean') {
//undefined null都被认为为null
children = null;
}
//调用fun的flag
var invokeCallback = false; if (children === null) {
invokeCallback = true;
} else {
switch (type) {
case 'string':
case 'number':
invokeCallback = true;
break;
//如果props.children单个ReactElement/PortalElement
//递归traverAllChildenTml时 <span>1</span>和<span>2</span>作为child
//必会invokeCallback=true
case 'object':
switch (children.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE:
invokeCallback = true;
} }
} if (invokeCallback) {
callback(traverseContext, children, // If it's the only child, treat the name as if it was wrapped in an array
// so that it's consistent if the number of children grows.
//如果只有一个节点 直接调用callback 把它放到数组中处理
//<span>1</span> key=".0"
nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR + getComponentKey(children, 0) : nameSoFar);
return 1;
} var child;
var nextName;
//有多个子节点
var subtreeCount = 0; // Count of children found in the current subtree. var nextNamePrefix = nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR : nameSoFar + SUBSEPARATOR; if (Array.isArray(children)) {//如果是多个节点
for (var i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {//循环遍历多个节点
child = children[i];
//不手动设置key的话 第一层第一个时。0 第二个。1
nextName = nextNamePrefix + getComponentKey(child, i);
//把child作为参数 进行递归 直到为单个节点的时候 去调用callback
subtreeCount += traverseAllChildrenImpl(child, nextName, callback, traverseContext);
}
} else {
var iteratorFn = getIteratorFn(children); if (typeof iteratorFn === 'function') {
{
// Warn about using Maps as children
if (iteratorFn === children.entries) {
!didWarnAboutMaps ? warning$1(false, 'Using Maps as children is unsupported and will likely yield ' + 'unexpected results. Convert it to a sequence/iterable of keyed ' + 'ReactElements instead.') : void 0;
didWarnAboutMaps = true;
}
} var iterator = iteratorFn.call(children);
var step;
var ii = 0; while (!(step = iterator.next()).done) {
child = step.value;
nextName = nextNamePrefix + getComponentKey(child, ii++);
subtreeCount += traverseAllChildrenImpl(child, nextName, callback, traverseContext);
}
} else if (type === 'object') {
//如果是纯对象
var addendum = ''; {
addendum = ' If you meant to render a collection of children, use an array ' + 'instead.' + ReactDebugCurrentFrame.getStackAddendum();
} var childrenString = '' + children; {
{
throw Error("Objects are not valid as a React child (found: " + (childrenString === '[object Object]' ? 'object with keys {' + Object.keys(children).join(', ') + '}' : childrenString) + ")." + addendum);
}
}
}
} return subtreeCount;
}
解析:核心递归函数 目的为展平数组,对于可以循环的children 都会重复调用traverseAllChildrenImpl 直到一个节点 然后调用callback也就是mapSingleChildIntoContext
mapSingleChildIntoContext()
//复制除了key以外的属性 替换key属性 将其放到result中 bookKeeping:context对象
function mapSingleChildIntoContext(bookKeeping, child, childKey) {
var result = bookKeeping.result,
keyPrefix = bookKeeping.keyPrefix,
func = bookKeeping.func,
context = bookKeeping.context;
//调用fun
var mappedChild = func.call(context, child, bookKeeping.count++);
//对每一个节点 如果是数组 进行递归
if (Array.isArray(mappedChild)) { //如果返回一个数组 这里返回的是[child,[child]]是一维数组
//大递归 这次 不再调用fun 如果调用fun则无限循环 所以直接返回c
mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(mappedChild, result, childKey, function (c) {
return c;
});
} else if (mappedChild != null) {
if (isValidElement(mappedChild)) {//isValidElement 判断是否是合理的reactElement元素
mappedChild = cloneAndReplaceKey(mappedChild, // Keep both the (mapped) and old keys if they differ, just as
// traverseAllChildren used to do for objects as children
keyPrefix + (mappedChild.key && (!child || child.key !== mappedChild.key) ? escapeUserProvidedKey(mappedChild.key) + '/' : '') + childKey);
}
//替换一下key推入到result中
result.push(mappedChild);
}
}
解析: mapSingleChildIntoContext这个方法其实就是调用React.Children.map(children, callback)这里的callback,就是我们传入的第二个参数,并得到map之后的结果。注意重点来了,如果map之后的节点还是一个数组,那么再次进入mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal,那么这个时候我们就会再次从pool里面去context了,而pool的意义大概也就是在这里了,如果循环嵌套多了,可以减少很多对象创建和gc的损耗,而如果不是数组并且是一个合规的ReactElement,就触达顶点了,替换一下key就推入result了
cloneAndReplaceKey()
//返回一个新的reactElement 替换了newKey 其他的都是老得reactElement
function cloneAndReplaceKey(oldElement, newKey) {
var newElement = ReactElement(oldElement.type, newKey, oldElement.ref, oldElement._self, oldElement._source, oldElement._owner, oldElement.props);
return newElement;
}
解析:返回一个新的reactElement 替换了newKey 其他的都是老得reactElement
流程图如下
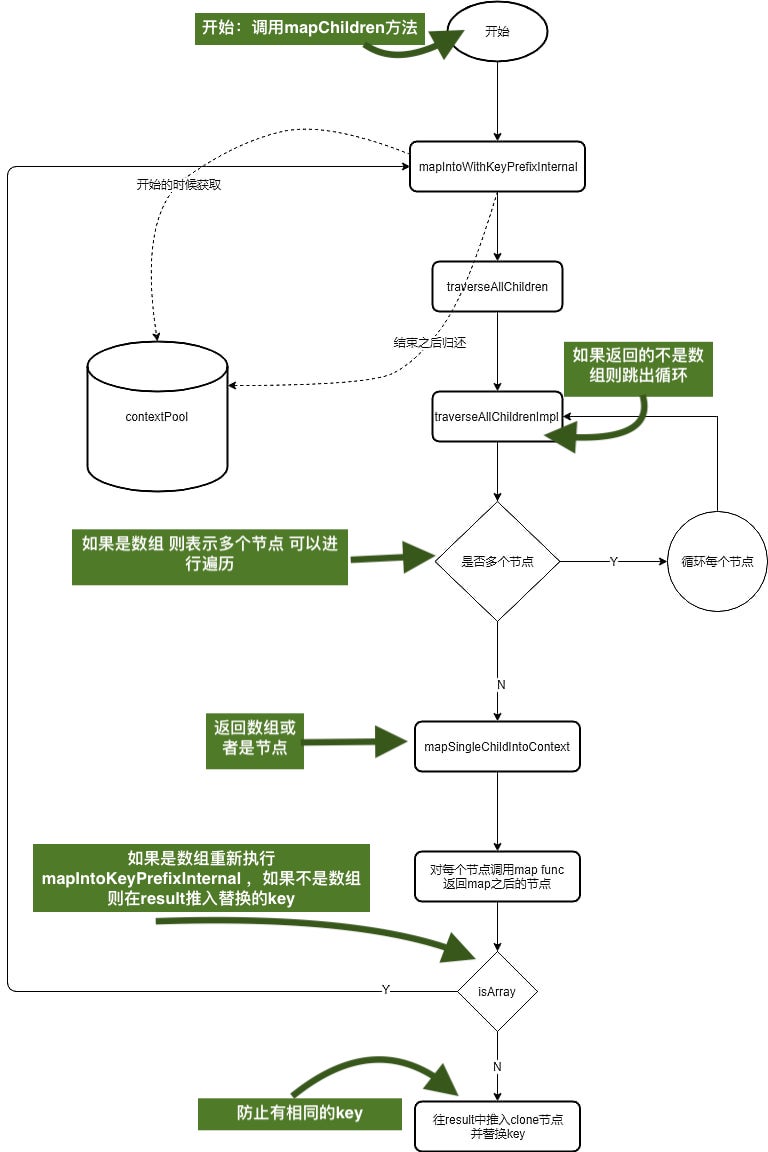
React源码解析之React.Children.map()(五)的更多相关文章
- [源码解析]为什么mapPartition比map更高效
[源码解析]为什么mapPartition比map更高效 目录 [源码解析]为什么mapPartition比map更高效 0x00 摘要 0x01 map vs mapPartition 1.1 ma ...
- React源码解析:setState
先来几个例子热热身: ......... constructor(props){ super(props); this.state = { index: 0 } } componentDidMount ...
- React源码解析:ReactElement
ReactElement算是React源码中比较简单的部分了,直接看源码: var ReactElement = function(type, key, ref, self, source, owne ...
- React源码解析——ReactAPI
一.API背景 api的具体转化关系 可以通过到https://babeljs.io/repl/网站去将我们创建的Jsx进行实时的转译 const React = { Children: { map, ...
- React源码解析-Virtual DOM解析
前言:最近一直在研究React,看了陈屹先生所著的深入React技术栈,以及自己使用了这么长时间.对React应该说有比较深的理解了,正好前阵子也把两本关于前端设计模式的书看完了,总感觉有一种知识错综 ...
- React源码解析——创建更新过程
一.ReactDOM.render 创建ReactRoot,并且根据情况调用root.legacy_renderSubtreeIntoContainer或者root.render,前者是遗留的 API ...
- jQuery 源码解析(六) $.each和$.map的区别
$.each主要是用来遍历数组或对象的,例如: var arr=[11,12,13,14]; $.each(arr,function(element,index){ //遍历arr数组 console ...
- React躬行记(16)——React源码分析
React可大致分为三部分:Core.Reconciler和Renderer,在阅读源码之前,首先需要搭建测试环境,为了方便起见,本文直接采用了网友搭建好的环境,React版本是16.8.6,与最新版 ...
- 源码解读 Golang 的 sync.Map 实现原理
简介 Go 的内建 map 是不支持并发写操作的,原因是 map 写操作不是并发安全的,当你尝试多个 Goroutine 操作同一个 map,会产生报错:fatal error: concurrent ...
随机推荐
- Pi和e的积分
Evaluate integral $$\int_{0}^{1}{x^{-x}(1-x)^{x-1}\sin{\pi x}dx}$$ Well,I think we have $$\int_{0}^{ ...
- Linux下tomcat端口被占用
首先查看占用端口的程序 netstat -alnp | grep 8080 然后出现 tcp6 2 0 :::8080 :: LISTEN 1392/java 杀死端口号 kill -9 1392(进 ...
- flask入门(三)
表单 request.form 能获取POST 请求中提交的表单数据.但是这样不太安全,容易受到恶意攻击.对此,flask有一个flask-wtf扩展,用于避免这一情况 在虚拟环境下用pip inst ...
- SpringBoot整合WEB开发--(七)注册拦截器
1.创建一个拦截器类实现HandlerInterceptor接口,重写其中的3个方法,这拦截器中方法的执行顺序为:preHandle--Controller--postHandle--afterCom ...
- 【C/C++】最短路径
BFS求无权图的最短路径 用book数组的值表示路径长度即可,省略 Floyd算法(允许负边) Floyd算法可以一次性求出所有节点之间的最短距离,且代码简单,但是时间复杂度达到了n^3,因此只适用于 ...
- setUserData
node.setUserData();//设置每个节点的datanode.getUserData();
- Win10激活工具 —— HWIDGen的使用方法
一:引言 众所周知,Windows系统在安装完成之后,第一步就是激活系统,网上的一些激活方法大多数都是KMS激活,激活持续时间为半年. 因此,我找到了一个可以永久激活的工具:HWIDGen,它可以数字 ...
- AcWing 891. Nim游戏
//a1 ^ a2 ^ ··· ^ an = 0 –>先手必败: //a1 ^ a2 ^ ··· ^ an != 0 –>先手必胜: #include<iostream> us ...
- 关于微信小程序
1.设置了tabBar的页面,好像用navigator跳不过去.
- 第四篇,JavaScript面试题汇总
JavaScript是一种属于网络的脚本语言,已经被广泛用于web实用开发,常用来为网页添加各种各样的动态功能,为用户提供更流畅美观的浏览效果.通常JavaScript脚本是通过嵌入在HTML中来实现 ...
