Codeforces 626G Raffles(贪心+线段树)
G. Raffles
Johnny is at a carnival which has n raffles. Raffle i has a prize with value pi. Each participant can put tickets in whichever raffles they choose (they may have more than one ticket in a single raffle). At the end of the carnival, one ticket is selected at random from each raffle, and the owner of the ticket wins the associated prize. A single person can win multiple prizes from different raffles.
However, county rules prevent any one participant from owning more than half the tickets in a single raffle, i.e. putting more tickets in the raffle than all the other participants combined. To help combat this (and possibly win some prizes), the organizers started by placing a single ticket in each raffle, which they will never remove.
Johnny bought t tickets and is wondering where to place them. Currently, there are a total of li tickets in the i-th raffle. He watches as other participants place tickets and modify their decisions and, at every moment in time, wants to know how much he can possibly earn. Find the maximum possible expected value of Johnny's winnings at each moment if he distributes his tickets optimally. Johnny may redistribute all of his tickets arbitrarily between each update, but he may not place more than t tickets total or have more tickets in a single raffle than all other participants combined.
The first line contains two integers n, t, and q (1 ≤ n, t, q ≤ 200 000) — the number of raffles, the number of tickets Johnny has, and the total number of updates, respectively.
The second line contains n space-separated integers pi (1 ≤ pi ≤ 1000) — the value of the i-th prize.
The third line contains n space-separated integers li (1 ≤ li ≤ 1000) — the number of tickets initially in the i-th raffle.
The last q lines contain the descriptions of the updates. Each description contains two integers tk, rk (1 ≤ tk ≤ 2, 1 ≤ rk ≤ n) — the type of the update and the raffle number. An update of type 1 represents another participant adding a ticket to raffle rk. An update of type 2 represents another participant removing a ticket from raffle rk.
It is guaranteed that, after each update, each raffle has at least 1 ticket (not including Johnny's) in it.
Print q lines, each containing a single real number — the maximum expected value of Johnny's winnings after the k-th update. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 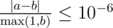 .
.
2 1 3
4 5
1 2
1 1
1 2
2 1
1.666666667
1.333333333
2.000000000
3 20 5
6 8 10
6 6 6
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 3
2 3
12.000000000
12.000000000
11.769230769
12.000000000
12.000000000
In the first case, Johnny only has one ticket to distribute. The prizes are worth 4 and 5, and the raffles initially have 1 and 2 tickets, respectively. After the first update, each raffle has 2 tickets, so Johnny has expected value  of winning by placing his ticket into the second raffle. The second update adds a ticket to the second raffle, so Johnny can win
of winning by placing his ticket into the second raffle. The second update adds a ticket to the second raffle, so Johnny can win  in the first raffle. After the final update, Johnny keeps his ticket in the first raffle and wins
in the first raffle. After the final update, Johnny keeps his ticket in the first raffle and wins  .
.
In the second case, Johnny has more tickets than he is allowed to spend. In particular, after the first update, there are 7, 6, and 6 tickets in each raffle, respectively, so Johnny can only put in 19 tickets, winning each prize with probability  . Also, note that after the last two updates, Johnny must remove a ticket from the last raffle in order to stay under
. Also, note that after the last two updates, Johnny must remove a ticket from the last raffle in order to stay under  the tickets in the third raffle.
the tickets in the third raffle.
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/626/problem/G
题意:
给n个奖池,t张彩票,q次操作。
每个奖池的奖金为pi。
每个奖池现有的彩票的数量为ai,保证ai>=1;
q次操作,每次有两种,第i个奖池的现有彩票数量加一,或减一。
不允许投票的数量多于奖池数量的二分之一。
保证:
n,t,q<=2e5
ai<=1000 pi<=1000
求在采用最佳策略的前提下获得奖金的期望。
思路:
首先要证明贪心的正确性,即把某张票投入某奖池之后其下一张票给期望做出的贡献要小于上一张彩票...
把式子写一下,求导,发现导数是单调递减的...
然后是对于每次操作的处理。
一开始一直纠结如何处理从某奖池拿出的亏损。因为按照贡献差来说第一个和后来的是有区别的,而且还要处理是否超票的问题。
但是看了卿学姐的思路...
其实思路是很简洁的,大概的内容是维护一个亏损的线段树一个盈利的线段树,亏损的意思是从某一奖池拿出一张票我们期望的减少,盈利的意思是往某一奖池投入一张票期望的增加。其实奖池的投递数量不用限制的,只要把盈利控制为0就可以了。而对于减少某奖池现有彩票的数量,直接对上限和投递数量的数组进行处理,然后更新维护这个奖池的盈利和亏损就可以了。因为亏损和盈利是可以直接根据这两个数据确定的。
下面给出AC代码:【卿学姐的代码,参考一下,待补】
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5+;
inline int read()
{
int x=,f=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<''||ch>''){if(ch=='-')f=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){x=x*+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int x[maxn],y[maxn],p[maxn];
struct treenode
{
int L , R ;
double Up,Down,Max,Min,ans;
void updata()
{
ans=1.0*p[L]*min(1.0*x[L]/(x[L]+y[L]),0.5);
if(x[L]>=y[L])Up=;
else
{
Up=1.0*p[L]*(x[L]+1.0)/(x[L]+y[L]+1.0);
Up-=1.0*p[L]*x[L]/(x[L]+y[L]);
}
if(x[L])
{
if(x[L]>y[L])Down=;
else
{
Down=1.0*p[L]*x[L]/(x[L]+y[L]);
Down-=1.0*p[L]*(x[L]-1.0)/(x[L]-1.0+y[L]);
}
}
else
Down=1e18;
}
};
treenode tree[maxn*];
inline void push_up(int o)
{
tree[o].ans=tree[o<<].ans+tree[o<<|].ans;
tree[o].Up=max(tree[o<<].Up,tree[o<<|].Up);
tree[o].Down=min(tree[o<<].Down,tree[o<<|].Down);
if(tree[o<<].Up>tree[o<<|].Up)
tree[o].Max=tree[o<<].Max;
else
tree[o].Max=tree[o<<|].Max;
if(tree[o<<].Down<tree[o<<|].Down)
tree[o].Min=tree[o<<].Min;
else
tree[o].Min=tree[o<<|].Min;
} inline void build_tree(int L , int R , int o)
{
tree[o].L = L , tree[o].R = R, tree[o].ans=;
if(L==R)
tree[o].Min=tree[o].Max=L,tree[o].updata();
if (R > L)
{
int mid = (L+R) >> ;
build_tree(L,mid,o*);
build_tree(mid+,R,o*+);
push_up(o);
}
} inline void updata(int QL,int o)
{
int L = tree[o].L , R = tree[o].R;
if (L==R)
{
tree[o].updata();
}
else
{
int mid = (L+R)>>;
if (QL <= mid) updata(QL,o*);
else updata(QL,o*+);
push_up(o);
}
}
int main()
{
int n,t,q,mx,mi;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&t,&q);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
p[i]=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
y[i]=read();
build_tree(,n,);
while(t--)mx=tree[].Max,x[mx]++,updata(mx,);
while(q--)
{
int type,r;type=read(),r=read();
if(type==)y[r]++;else y[r]--;
updata(r,);
while()
{
int mx = tree[].Max;
int mi = tree[].Min;
if(tree[].Up<=tree[].Down)break;
x[mx]++,x[mi]--;
updata(mx,);
updata(mi,);
}
printf("%.12f\n",tree[].ans);
}
}
Codeforces 626G Raffles(贪心+线段树)的更多相关文章
- BZOJ4391 High Card Low Card [Usaco2015 dec](贪心+线段树/set库
正解:贪心+线段树/set库 解题报告: 算辣直接甩链接qwq 恩这题就贪心?从前往后从后往前各推一次然后找一遍哪个地方最大就欧克了,正确性很容易证明 (这里有个,很妙的想法,就是,从后往前推从前往后 ...
- Buses and People CodeForces 160E 三维偏序+线段树
Buses and People CodeForces 160E 三维偏序+线段树 题意 给定 N 个三元组 (a,b,c),现有 M 个询问,每个询问给定一个三元组 (a',b',c'),求满足 a ...
- CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树
CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树 题意 就是树上有n个点,然后每个点都有一盏灯,给出初始的状态,1表示亮,0表示不亮,然后有两种操作,第一种是get x,表示你需要输出x的子树和x本身 ...
- [Codeforces 1197E]Culture Code(线段树优化建图+DAG上最短路)
[Codeforces 1197E]Culture Code(线段树优化建图+DAG上最短路) 题面 有n个空心物品,每个物品有外部体积\(out_i\)和内部体积\(in_i\),如果\(in_i& ...
- [Codeforces 1199D]Welfare State(线段树)
[Codeforces 1199D]Welfare State(线段树) 题面 给出一个长度为n的序列,有q次操作,操作有2种 1.单点修改,把\(a_x\)修改成y 2.区间修改,把序列中值< ...
- [Codeforces 316E3]Summer Homework(线段树+斐波那契数列)
[Codeforces 316E3]Summer Homework(线段树+斐波那契数列) 顺便安利一下这个博客,给了我很大启发(https://gaisaiyuno.github.io/) 题面 有 ...
- 【题解】P1712 [NOI2016]区间(贪心+线段树)
[题解]P1712 [NOI2016]区间(贪心+线段树) 一个observe是,对于一个合法的方案,将其线段长度按照从大到小排序后,他极差的来源是第一个和最后一个.或者说,读入的线段按照长度分类后, ...
- Codeforces 626G Raffles 【贪心】【线段树】
题意: 给n个奖池,t张彩票,q次操作. 每个奖池的奖金为pi. 每个奖池现有的彩票的数量为ai,保证ai>=1: q次操作,每次有两种,第i个奖池的现有彩票数量加一,或减一. 不允许投票的数量 ...
- codeforces 626 G. Raffles(线段树+思维+贪心)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/626/problem/G 题解:这题很明显买彩票肯定要买贡献最大的也就是说买p[i]*(num[i]+1)/(num[i]+a[ ...
随机推荐
- iOS tableViewCell 在自定义高度方法中遇到的问题,cell高度为0,cell显示不出来,cell直接显示第几个而不是...cell显示个数不对
遇到以上问题可以看看你的cell高度中是否有,自定的高度,有了继续看,没有了继续百度... 在文字排版中,少不了自适应文字高度,行间距什么的:显然cell的高度时不固定的,如果复用自定义的cell的话 ...
- Intellij IDEA 像eclipse那样给maven添加依赖
打开pom.xml,在它里面使用快捷键:ALT+Insert ---->点击dependency 再输入想要添加的依赖关键字,比如:输个spring 出现下图: 根据需求选择版本,完成以后 ...
- 如何检测mvc性能和sql语句
mvc中使用linq如何检测sql语句 .net中使用mvc开发已经是一种趋势,不仅仅是.net ,java 等越来越多的开发者更倾向于mvc这种开发模式,在.net mvc 使用linq非常方便,各 ...
- 【WebGL】《WebGL编程指南》读书笔记——第4章
一.前言 今天继续第四章的学习内容,开始学习复合变换的知识. 二.正文 Example1: 复合变换 在书中,作者为我们封装了一套用于变换的矩阵对象:Matrix4对象.它 ...
- Java 包装类Integer的值比较
对于包装类型Integer的值比较与int的值比较是不同的: public class Java_Val_Compare { public static void main(String[] ar ...
- ssh简明安全规划
禁止使用口令只允许使用密钥建立 SSH 连接 1.创建 SSH KEY 使用ssh-keygen生成一个密钥对,并且将公钥注册到服务器的 $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys 文件. ...
- Webpack 2 视频教程 013 - 自动分离 CSS 到独立文件
原文发表于我的技术博客 这是我免费发布的高质量超清「Webpack 2 视频教程」. Webpack 作为目前前端开发必备的框架,Webpack 发布了 2.0 版本,此视频就是基于 2.0 的版本讲 ...
- Django_form
Django的Form主要具有一下几大功能: 生成HTML标签 验证用户数据(显示错误信息) HTML Form提交保留上次提交数据 初始化页面显示内容 1.创建Form类 # 创建一个类 from ...
- PHP进阶,使用交互模式进行快速测试实验?
额,那啥,PHP很强,大家都知道哈.不过呢,在搞PHP里的人中,自然也要分高下的.当然了,我更喜欢用好玩来形容了. 什么叫做快速开发?我觉得,快就得快到随手写几个字,就能让代码跑起来!那么,PHP能做 ...
- 微信终端开发团队:新年新语言,WCDB Swift
欢迎大家前往云+社区,获取更多腾讯海量技术实践干货哦~ 作者:sanhuazhang,此文发布在微信终端开发团队的专栏 WCDB 作为微信的终端数据库,从 2017.6 开源至今,共迭代了 5 个版本 ...
