4-2 线程安全性-原子性-atomic-2
AtomicReference和AtomicLong、AtomicInteger很像,方法也基本上是一样的,然后我们通过引用Integer来做一个简单的例子。
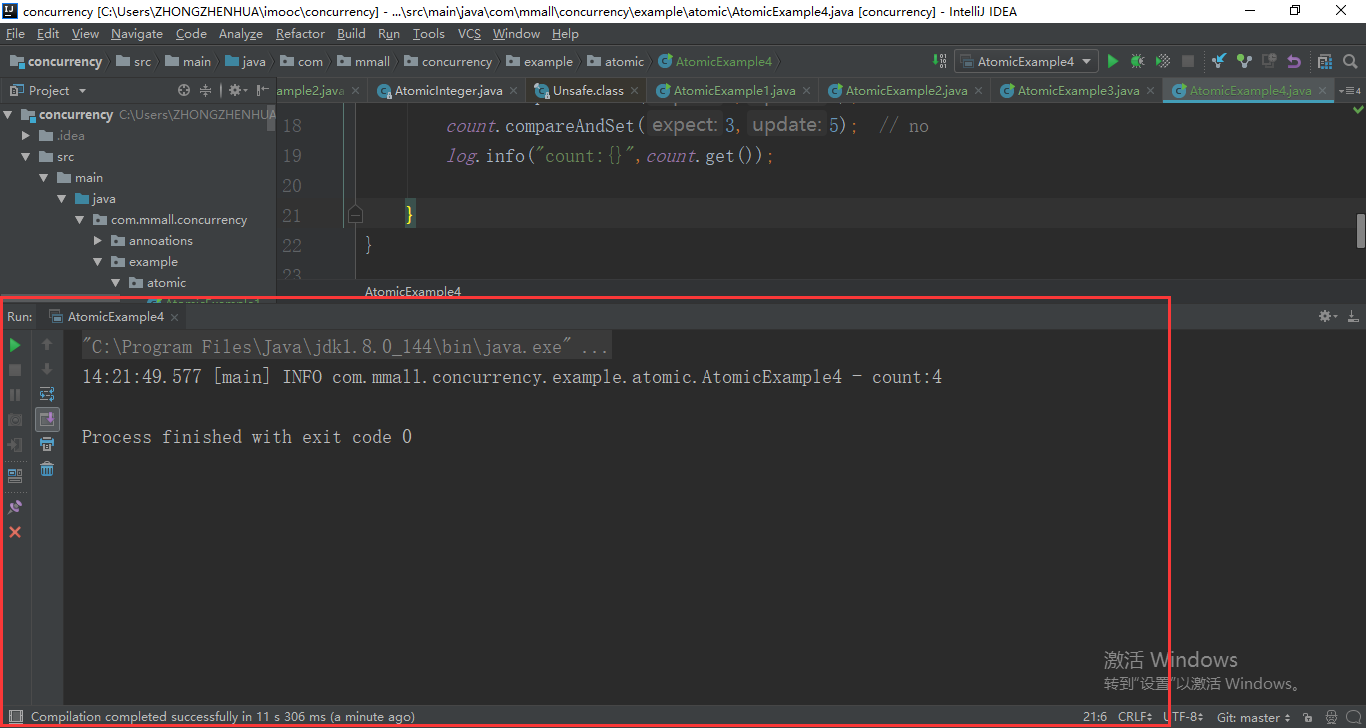
com.mmall.concurrency.example.atomic.AtomicExample4
C:\Users\ZHONGZHENHUA\imooc\concurrency\src\main\java\com\mmall\concurrency\example\atomic\AtomicExample4.java
package com.mmall.concurrency.example.atomic; import com.mmall.concurrency.annoations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference; @Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicExample4 {
private static AtomicReference<Integer> count = new AtomicReference<>(0); public static void main(String args[]){
count.compareAndSet(0,2); //
count.compareAndSet(0,1); // no
count.compareAndSet(1,3); // no
count.compareAndSet(2,4); //
count.compareAndSet(3,5); // no
log.info("count:{}",count.get()); }
}
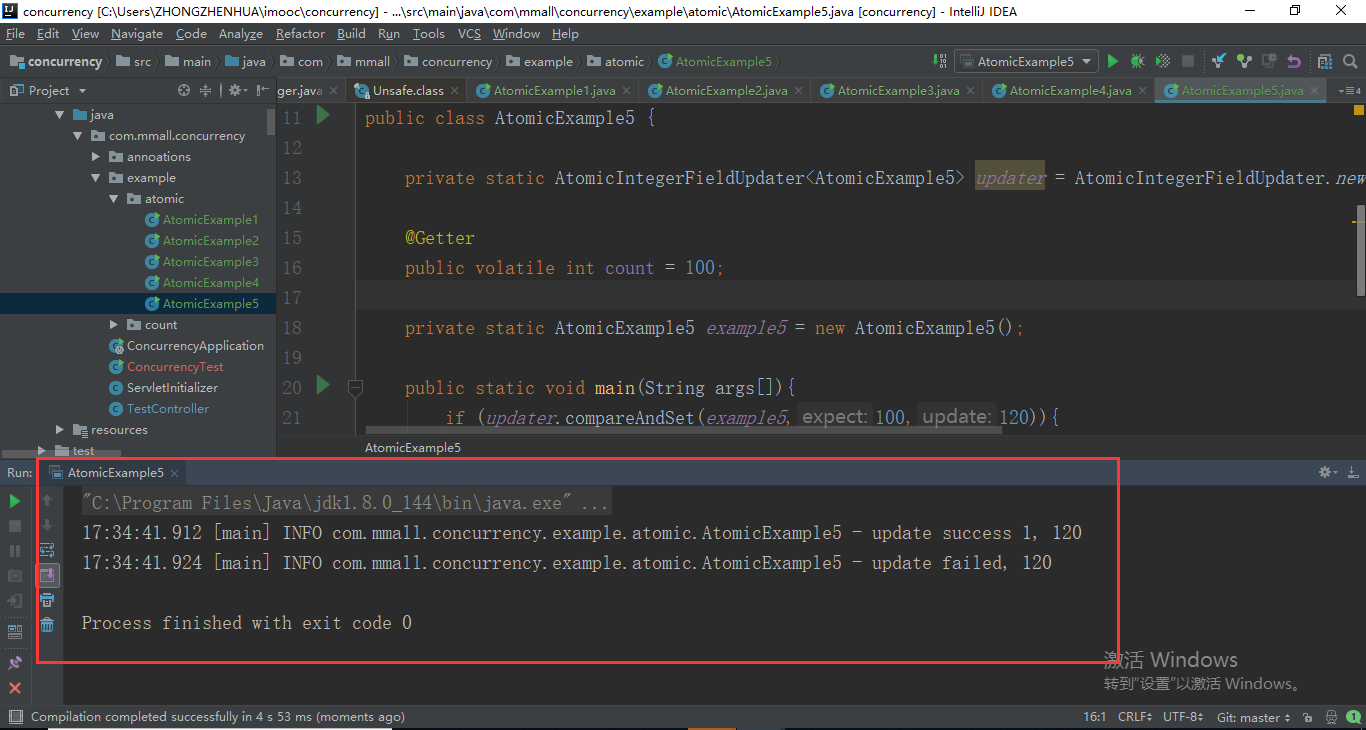 AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater的核心是想原子性去更新某一个类的一个实例,就是我们这里说的example5,选定的某一个字段count,这个count值必须要求是通过特殊关键字修饰才可以,这个类的本质上就是干这个事情的,是原子性的修改。如果当前的这个变量example5对应的这个字段count,expect和update其实是id的版本支持的。如果我这里面传入的值是一个普通的数值,而不是定义好的一个常量值的时候,它就会告诉我当前这个变量是什么名称,这与我当前的id有关系,不是什么特殊的配置。AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater它的核心作用是要更新指定的一个类AtomicExample5的某一个字段的值,而这个字段它要求必须是通过volatile修饰同时还不能是static的字段才可以。这是它的要求,必须是有这个volatile以及非static描述的字段才可以。AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater使用的不多。com.mmall.concurrency.example.atomic.AtomicExample5
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater的核心是想原子性去更新某一个类的一个实例,就是我们这里说的example5,选定的某一个字段count,这个count值必须要求是通过特殊关键字修饰才可以,这个类的本质上就是干这个事情的,是原子性的修改。如果当前的这个变量example5对应的这个字段count,expect和update其实是id的版本支持的。如果我这里面传入的值是一个普通的数值,而不是定义好的一个常量值的时候,它就会告诉我当前这个变量是什么名称,这与我当前的id有关系,不是什么特殊的配置。AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater它的核心作用是要更新指定的一个类AtomicExample5的某一个字段的值,而这个字段它要求必须是通过volatile修饰同时还不能是static的字段才可以。这是它的要求,必须是有这个volatile以及非static描述的字段才可以。AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater使用的不多。com.mmall.concurrency.example.atomic.AtomicExample5
C:\Users\ZHONGZHENHUA\imooc\concurrency\src\main\java\com\mmall\concurrency\example\atomic\AtomicExample5.java
package com.mmall.concurrency.example.atomic; import com.mmall.concurrency.annoations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater; @Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicExample5 { private static AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AtomicExample5> updater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AtomicExample5.class,"count"); @Getter
public volatile int count = 100; private static AtomicExample5 example5 = new AtomicExample5(); public static void main(String args[]){
if (updater.compareAndSet(example5,100,120)){
log.info("update success 1, {}",example5.getCount()); }
if (updater.compareAndSet(example5,100,120)){
log.info("update success 2, {}",example5.getCount());
}else{
log.info("update failed, {}",example5.getCount());
}
}
}
ABA问题它是指在CAS操作的时候,其他线程将变量的值A改成了B,但是又改回了A,本线程使用期望值A与当前变量进行比较的时候,发现A变量没有变,于是CAS就将A值进行了交换操作。这个时候实际上该值已经被其他线程改变过,这与实际思想是不符合的。因此ABA问题的解决思路它是每次变量更新的时候,把变量的版本号加1,那么之前的那个A改成B再改成A,就会变成了A对上1版本,然后改成B变成2版本,再改回A变成3版本。这个时候只要变量被某一个线程修改过,该变量对应的版本号就会发生递增变化,从而解决了ABA问题。
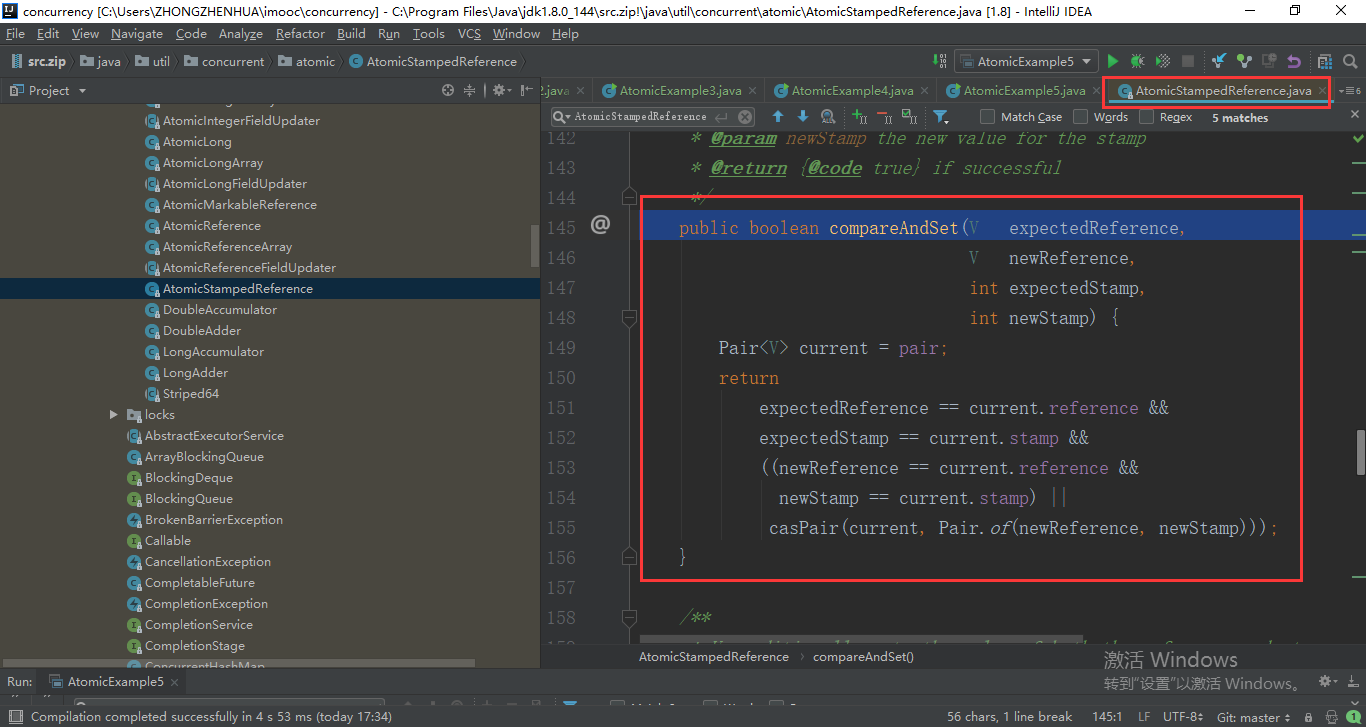
java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference的核心方法是compareAndSet,这个方法里相对于我们之前的java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean的compareAndSet多了一个stamp的比较。stamp的值是由每次更新的时候来维护的,它的使用和我们之前其他Atomic包里面的其他类的用法很相似。
/**
* Atomically sets the value of both the reference and stamp
* to the given update values if the
* current reference is {@code ==} to the expected reference
* and the current stamp is equal to the expected stamp.
*
* @param expectedReference the expected value of the reference
* @param newReference the new value for the reference
* @param expectedStamp the expected value of the stamp
* @param newStamp the new value for the stamp
* @return {@code true} if successful
*/
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
int expectedStamp,
int newStamp) {
Pair<V> current = pair;
return
expectedReference == current.reference &&
expectedStamp == current.stamp &&
((newReference == current.reference &&
newStamp == current.stamp) ||
casPair(current, Pair.of(newReference, newStamp)));
}
java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLongArray 它维护的是一个数组,这个数组我们可以选择性地更新某一个索引对应的值,也是进行原子性操作的。相比于AtomicLong和AtomicInteger它们的方法,它的方法会额外多一个索引值让我们去更新。getAndSet,取出这个索引更新一个值。compareAndSet也是,它这里面相当于举了一个实例之后呢,传入对应是哪个索引的值,告诉我期望是哪个值,更新成哪个值。
java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean的compareAndSet在实际中还是很实用的。
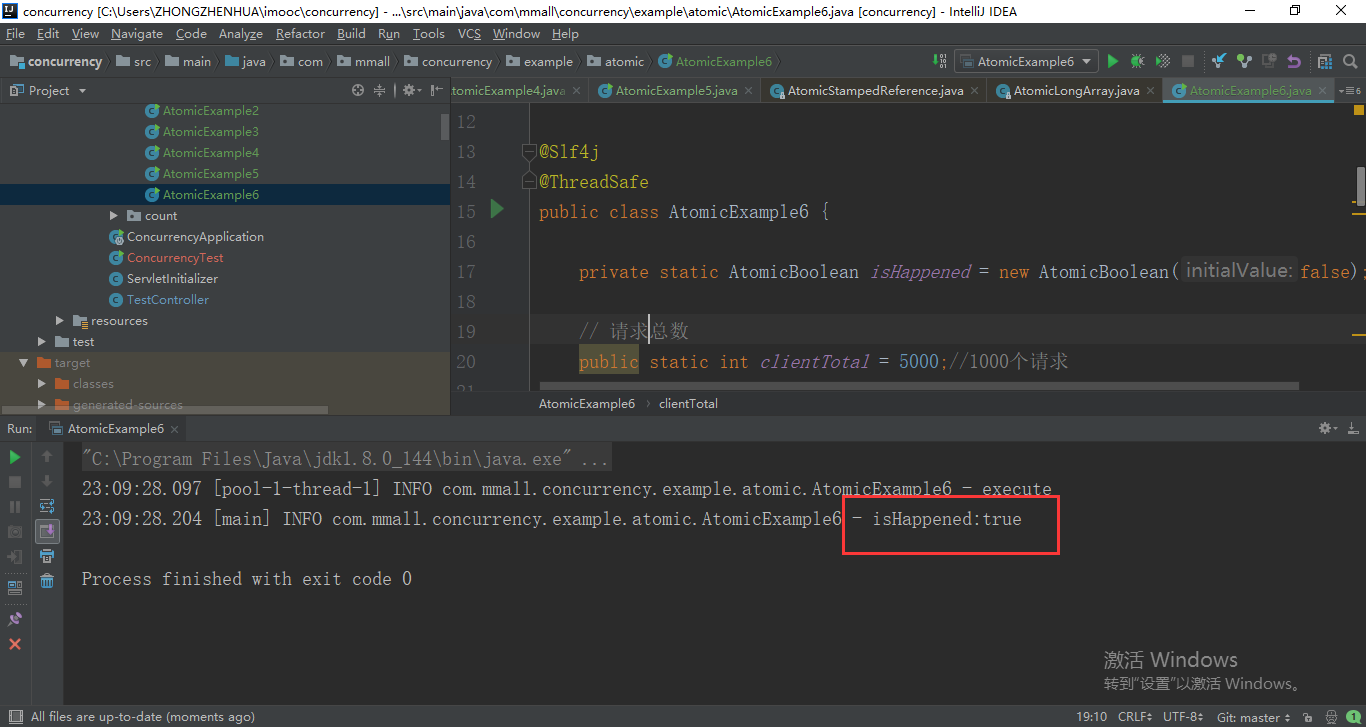

因为它的原子性操作,它可以保证从false变成true只会执行一次,之后的所有4999次,在主要这个函数if(isHappened.compareAndSet(false,true)){判断的时候呢,都是因为它是true没法执行这个动作因此都不会执行。当前这个例子演示了我们如何让某一段代码只执行一次,绝对不会重复,在实际中有的时候会遇到有些流程你只希望某一段代码只执行过一遍就可以参考这个例子来去处理它。
com.mmall.concurrency.example.atomic.AtomicExample6
C:\Users\ZHONGZHENHUA\imooc\concurrency\src\main\java\com\mmall\concurrency\example\atomic\AtomicExample6.java
package com.mmall.concurrency.example.atomic; import com.mmall.concurrency.annoations.ThreadSafe; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean; @Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicExample6 { private static AtomicBoolean isHappened = new AtomicBoolean(false); // 请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;//1000个请求 // 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;//允许并发的线程数是50 //public static AtomicBoolean count = new AtomicBoolean(false); public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) {
executorService.execute(()-> {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
//add();
test();
semaphore.release();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
//log.info("count:{}",count);
//log.info("count:{}",count.get());
log.info("isHappened:{}",isHappened.get()); }
public static void test(){
if(isHappened.compareAndSet(false,true)){
log.info("execute"); }
}
}

使用Atomic包下面的AtomicInteger的类可以实现线程安全,在这个基础之上呢跟大家说明了CAS原理,以及实现的时候借助于UnSafe的compareAndSwapInt这个方法。AtomicLong和LongAdder这两个类的使用以及它们的对比,它们的优势和缺点。AtomicReference和AtomicReferenceUpdater两个类的使用。AtomicStampReference来解决掉CAS的ABA问题。AtomicLongArray这个类的使用,AtomicBoolean的compareAndSet方法在实际中的应用。
4-2 线程安全性-原子性-atomic-2的更多相关文章
- 并发与高并发(七)-线程安全性-原子性-atomic
一.线程安全性定义 定义:当多个线程访问某个类时,不管运行时环境采用何种调度方式或者这些线程将如何交替执行,并且在主调代码中不需要任何额外的同步或协同,这个类都能表现出正确的行为,那么就称这个类是线程 ...
- Java并发编程入门与高并发面试(三):线程安全性-原子性-CAS(CAS的ABA问题)
摘要:本文介绍线程的安全性,原子性,java.lang.Number包下的类与CAS操作,synchronized锁,和原子性操作各方法间的对比. 线程安全性 线程安全? 线程安全性? 原子性 Ato ...
- 线程安全性-原子性之Atomic包
先了解什么是线程安全性:当多个线程访问某个类时,不管运行时环境采用何种调度方式或者这些进程将如何交替执行,并且在主调代码中不需要任何额外的同步或协同,这个类都能表现出正确的行为,那么就称为这个类是线程 ...
- 4-3 线程安全性-原子性-synchronized
原子性它提供了互斥访问,同一时刻只能有一个线程来对它进行操作.能保证同一时刻只有一个线程来对其进行操作的,除了Atomic包之外,还有锁.JDK提供锁主要分两种,synchronized是一个Java ...
- 线程安全性-原子性之synchronized锁
原子性提供了互斥访问:同一时刻只能有一个线程进行操作: 除了Atomic包类之外,还有锁可以实现此功能: synchronized: java关键字,依赖于jvm实现锁功能,被此关键字所修饰的,都是 ...
- 4-1 线程安全性-原子性-atomic-1
我们发现在不做任何同步的情况下,我们计算的累加结果是错误的. com.mmall.concurrency.example.count.CountExample2 C:\Users\ZHONGZHENH ...
- 并发与高并发(八)-线程安全性-原子性-synchronized
前言 闲暇时刻,谈一下曾经在多线程教程中接触的同步锁synchronized,相当于复习一遍吧. 主要介绍 synchronized:依赖JVM Lock:依赖特殊的CPU指令,代码实现,Reetra ...
- Java线程安全性-原子性工具对比
synchronized 不可中断锁,适合竞争不激烈的场景,可读性好,竞争激烈时性能下降很快 Lock 可中断锁,多样化同步,竞争激烈时能维持常态 Atomic 竞争激烈时能维持常态,比Lock性能还 ...
- Java并发编程 (四) 线程安全性
个人博客网:https://wushaopei.github.io/ (你想要这里多有) 一.线程安全性-原子性-atomic-1 1.线程安全性 定义: 当某个线程访问某个类时,不管运行时环境 ...
随机推荐
- CallKit iOS 教程
原文:CallKit Tutorial for iOS 作者:József Vesza 译者:kmyhy 对 VoIP App 开发者来说,iOS 的支持并不友好.尤其是它的通知发送这一块,太糙了.你 ...
- Lua基础---循环语句
Lua的循环和C语言的循环的语法其实差不多,所以,理解起来就很好理解的啦,所以实现也很简单,跟C没什么两样,都差不多. 案例如下: test1.lua -- 1.while循环 --[[ 理解为C语言 ...
- Python判断unicode是汉字,数字,英文,或者其他字符
功能: 判断unicode是否是汉字,数字,英文,或者是否是(汉字,数字和英文字符之外的)其他字符. 全角.半角符号相互转换. 全角.半角? 全角--指一个字符占用两个标准字符位置. 汉字字符和规定了 ...
- 使用sqlmap执行SQL注入攻击
sqlmap是开源的SQL注入自动攻击工具,它可以自动的探测SQL注入点并且进一步控制网站的数据库. Kali Linux默认安装了这个工具. 找到潜在的攻击目标 第一步是找到有SQL注入漏洞的网站. ...
- 关于this指向问题的总结【转自秘密花园】
this 的工作原理 JavaScript 有一套完全不同于其它语言的对 this 的处理机制. 在五种不同的情况下 ,this 指向的各不相同. 第一种:全局范围内 this; 当在全部范围内使用 ...
- SQL语句优化方法30例
1. /*+ALL_ROWS*/ 表明对语句块选择基于开销的优化方法,并获得最佳吞吐量,使资源消耗最小化. 例如: SELECT /*+ALL+_ROWS*/ EMP_NO,EMP_NAM,DAT_I ...
- Ajax异步调用http接口后刷新页面
使用Ajax的目的就是提高页面响应速度,无需同步调用,无需整个页面刷新.这里直接在html中使用js来实现: 先获取XMLHttpRequest对象 var xmlHttp; //创建一个xmlHtt ...
- 如何在已经安装好的Nginx上增加新模块
学习资源: https://blog.csdn.net/dxm2025/article/details/41149865 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36663951/artic ...
- 关于urlDecode和tomcat一些源码
1. 看下面源码,找到%号,每次加2,然后将16进制转换为int,也就是%号后两位加2得到16进制,转换为int ) < numChars) && (c=='%')) { ,i+ ...
- Fiddler2 模拟文件上传
最近遇到一个需求,需要上传音频文件, 服务端使用webService 通过spring3 进行文件上传.代码完成后使用 html 通过post 方式请求接口成功了,但不知道如何使用Fiddler2工具 ...