python3二元Logistics Regression 回归分析(LogisticRegression)
纲要
boss说增加项目平台分析方法:
T检验(独立样本T检验)、线性回归、二元Logistics回归、因子分析、可靠性分析
根本不懂,一脸懵逼状态,分析部确实有人才,反正我是一脸懵
首先解释什么是二元Logistic回归分析吧

官方简介:
链接:https://pythonfordatascience.org/logistic-regression-python/

Logistic regression models are used to analyze the relationship between a dependent variable (DV) and independent variable(s) (IV) when the DV is dichotomous. The DV is the outcome variable, a.k.a. the predicted variable, and the IV(s) are the variables that are believed to have an influence on the outcome, a.k.a. predictor variables. If the model contains IV, then it is a simple logistic regression model, and if the model contains + IVs, then it is a multiple logistic regression model. Assumptions for logistic regression models: The DV is categorical (binary)
If there are more than categories in terms of types of outcome, a multinomial logistic regression should be used
Independence of observations
Cannot be a repeated measures design, i.e. collecting outcomes at two different time points.
Independent variables are linearly related to the log odds
Absence of multicollinearity
Lack of outliers
原文

理解了什么是二元以后,开始找库
需要用的包
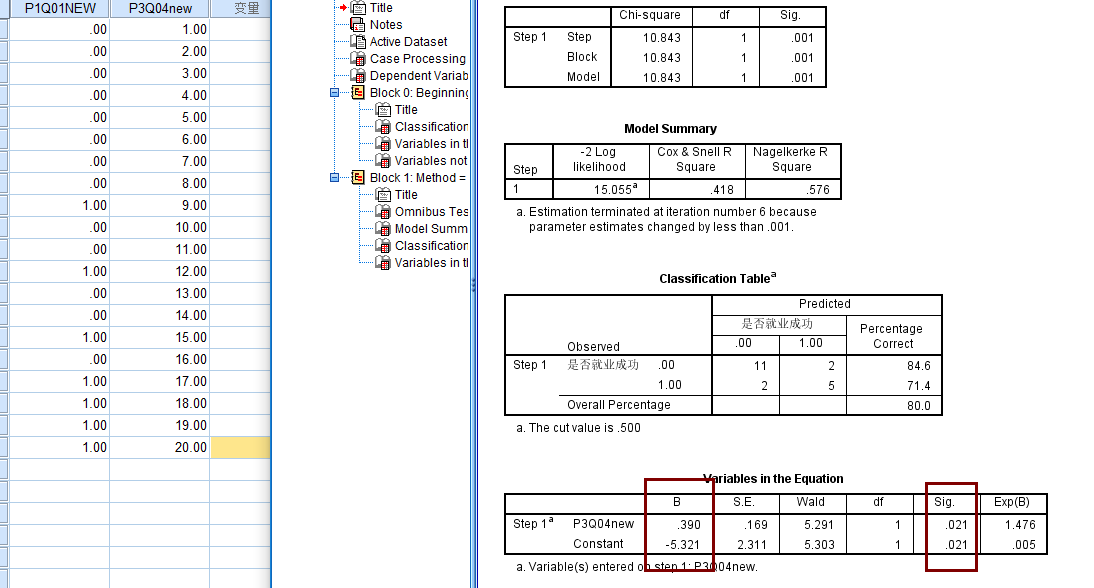
这里需要特别说一下,第一天晚上我就用的logit,但结果不对,然后用机器学习搞,发现结果还不对,用spss比对的值
奇怪,最后没办法,只能抱大腿了,因为他们纠结Logit和Logistic的区别,然后有在群里问了下,有大佬给解惑了
而且也有下面文章给解惑
1. 是 statsmodels 的logit模块
2. 是 sklearn.linear_model 的 LogisticRegression模块
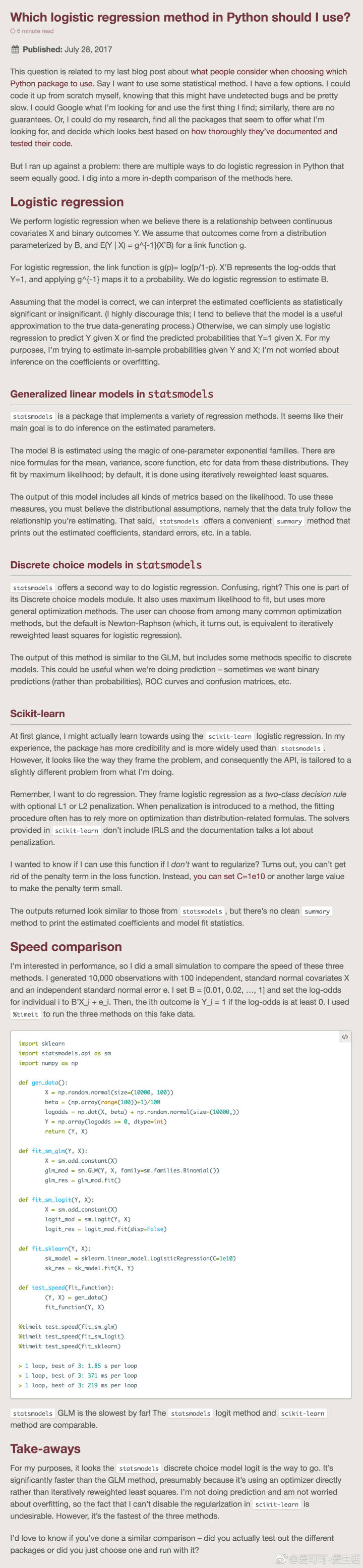
先说第一种方法
首先借鉴文章链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zj360202/article/details/78688070?utm_source=blogxgwz0
解释的比较清楚,但是一定要注意一点就是,截距项,我就是在这个地方出的问题,因为我觉得不重要,就没加
#!/usr/bin/env
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import pandas as pd
import statsmodels.api as sm
import pylab as pl
import numpy as np
from pandas import DataFrame, Series
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn import metrics
from collections import OrderedDict data = {
'y': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1],
'x': [i for i in range(1, 21)],
} df = DataFrame(OrderedDict(data)) df["intercept"] = 1.0 # 截距项,很重要的呦,我就错在这里了 print(df)
print("==================")
print(len(df))
print(df.columns.values) print(df[df.columns[1:]]) logit = sm.Logit(df['y'], df[df.columns[1:]])
#
result = logit.fit()
#
res = result.summary2() print(res)
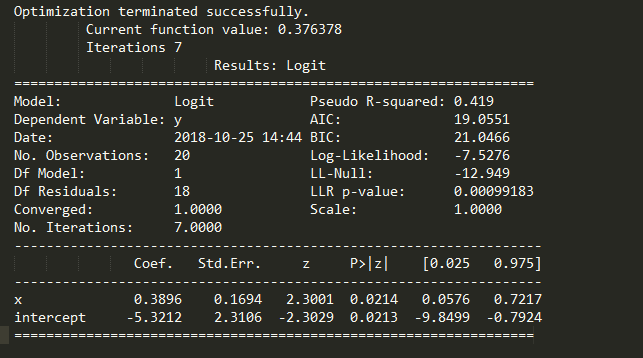
这么写我觉得更好,因为上面那么写执行第二遍的时候总是报错:
statsmodels.tools.sm_exceptions.PerfectSeparationError: Perfect separation detected, results not available
我改成x, y变量自己是自己的,就莫名其妙的好了
obj = TwoDimensionalLogisticRegressionModel()
data_x = obj.SelectVariableSql( UserID, ProjID, QuesID, xVariable, DatabaseName, TableName, CasesCondition)
data_y = obj.SelectVariableSql( UserID, ProjID, QuesID, yVariable, DatabaseName, TableName, CasesCondition)
if len(data_x) != len(data_y):
raise MyCustomError(retcode=4011)
obj.close() df_X = DataFrame(OrderedDict(data_x))
df_Y = DataFrame(OrderedDict(data_y)) df_X["intercept"] = 1.0 # 截距项,很重要的呦,我就错在这里了
logit = sm.Logit(df_Y, df_X)
result = logit.fit()
res = result.summary() data = [j for j in [i for i in str(res).split('\n')][-3].split(' ') if j != ''][1:] return data
允许二分数值虚拟变量的使用,修改后
obj = TwoDimensionalLogisticRegressionModel()
data_x = obj.SelectVariableSql( UserID, ProjID, QuesID, xVariable, DatabaseName, TableName, CasesCondition)
data_y = obj.SelectVariableSql( UserID, ProjID, QuesID, yVariable, DatabaseName, TableName, CasesCondition)
if len(data_x) != len(data_y):
raise MyCustomError(retcode=)
obj.close() df_X = DataFrame(data_x)
df_Y = DataFrame(data_y) # 因变量,, df_X["intercept"] = 1.0 # 截距项,很重要的呦,我就错在这里了 YColumnList = list(df_Y[yVariable].values)
setYColumnList = list(set(YColumnList))
if len(setYColumnList) > or len(setYColumnList) < :
raise MyCustomError(retcode=)
else:
if len(setYColumnList) == and [,] != [int(i) for i in setYColumnList]:
newYcolumnsList = []
for i in YColumnList:
if i == setYColumnList[]:
newYcolumnsList.append()
else:
newYcolumnsList.append()
df_Y = DataFrame({yVariable:newYcolumnsList})
logit = sm.Logit(df_Y, df_X)
result = logit.fit()
res = result.summary() data = [j for j in [i for i in str(res).split('\n')][-].split(' ') if j != ''] return data[:]
再次更新后
def TwoDimensionalLogisticRegressionDetail(UserID, ProjID, QuesID, xVariableID, yVariableID, CasesCondition):
two_obj = TwoDimensionalLogisticModel()
sql_data, xVarName, yVarName = two_obj.showdatas(UserID, ProjID, QuesID, xVariableID, yVariableID, CasesCondition) two_obj.close() df_dropna = DataFrame(sql_data).dropna()
df_X = DataFrame()
df_Y = DataFrame() # 因变量,0, 1 df_X[xVarName] = df_dropna[xVarName]
df_Y[yVarName] = df_dropna[yVarName] df_X["intercept"] = 1.0 # 截距项,很重要的呦,我就错在这里了 YColumnList = list(df_Y[yVarName].values)
setYColumnList = list(set(YColumnList)) # print(setYColumnList)
if len(setYColumnList) > 2 or len(setYColumnList) < 2:
raise MyCustomError(retcode=4015)
# else:
if len(setYColumnList) == 2 and [0, 1] != [int(i) for i in setYColumnList]:
newYcolumnsList = []
for i in YColumnList:
if i == setYColumnList[0]:
newYcolumnsList.append(0)
else:
newYcolumnsList.append(1)
df_Y = DataFrame({yVarName: newYcolumnsList})
logit = sm.Logit(df_Y, df_X)
res = logit.fit()
res_all = res.summary()
LogLikelihood = [i.strip() for i in str(res_all).split("\n")[6].split(" ") if i][3]
# 没找到具体参数, 只能这么分割
index_var = [i.strip() for i in str(res_all).split("\n")[12].split(" ") if i]
intercept = [i.strip() for i in str(res_all).split("\n")[13].split(" ") if i]
std_err = [index_var[2], intercept[2]]
z = [index_var[3], intercept[3]]
P_z = [index_var[4], intercept[4]] # 显著性
interval_25 = [index_var[5], intercept[5]]
interval_975 = [index_var[6], intercept[6]]
Odds_Ratio = [math.e ** i for i in list(res.params)]
return {
"No_Observations": res.nobs,#No. Observations
"Pseudo_R": res.prsquared,# Pseudo R^2
"Log_Likelihood": LogLikelihood, # LogLikelihood
"LLNull": res.llnull,
"llr_pvalue": res.llr_pvalue, #llr显著性
"coef": list(res.params), # 系数
"std_err": std_err,
"Odds_Ratio": Odds_Ratio,
"z": z,
"P": P_z, #显著性
"interval_25": interval_25, # 区间0.025
"interval_975": interval_975
}
第二种方法,机器学习
参考链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34217858
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from collections import OrderedDict
import pandas as pd examDict = {
'学习时间': [i for i in range(1, 20)],
'通过考试': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1]
} examOrderDict = OrderedDict(examDict)
examDF = pd.DataFrame(examOrderDict)
# print(examDF.head()) exam_X = examDF.loc[:, "学习时间"]
exam_Y = examDF.loc[:, "通过考试"] print(exam_X)
# print(exam_Y) from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split X_train,X_test,y_train, y_test = train_test_split(exam_X,exam_Y, train_size=0.8) # print(X_train.values)
print(len(X_train.values))
X_train = X_train.values.reshape(-1, 1)
print(len(X_train))
print(X_train)
X_test = X_test.values.reshape(-1, 1) from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression module_1 = LogisticRegression()
module_1.fit(X_train, y_train) print("coef:", module_1.coef_) front = module_1.score(X_test,y_test)
print(front) print("coef:", module_1.coef_)
print("intercept_:", module_1.intercept_) # 预测
pred1 = module_1.predict_proba(3)
print("预测概率[N/Y]", pred1) pred2 = module_1.predict(5)
print(pred2)
但是,机器学习的这个有问题,就是只抽取了15个值
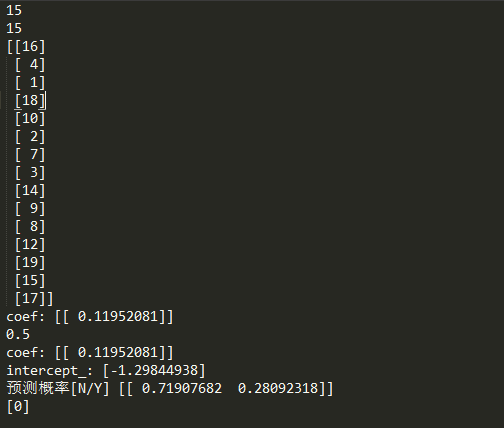
statsmodels的库链接
Statsmodels:http://www.statsmodels.org/stable/index.html

python3二元Logistics Regression 回归分析(LogisticRegression)的更多相关文章
- 1.2、Logistics Regression算法实践
1.1.Logistics Regression算法实践 有了上篇博客的理论准备后,接下来,我们用以及完成的函数,构建Logistics Regression分类器.我们利用线性可分的数据作为训练样 ...
- 1.1、Logistics Regression模型
1.线性可分VS线性不可分 对于一个分类问题,通常可以分为线性可分与线性不可分两种 .如果一个分类问题可以使用线性判别函数正确的分类,则称该问题为线性可分.如图所示为线性可分,否则为线性不可分: 下图 ...
- logistics regression
logistics regression用于解决一些二分类问题.比如(纯假设)网上购物时,网站会判断一个人退货的可能性有多大,如果该用户退货的可能性很大,那么网站就不会推荐改用户购买退费险.反之,如果 ...
- Popular generalized linear models|GLMM| Zero-truncated Models|Zero-Inflated Models|matched case–control studies|多重logistics回归|ordered logistics regression
============================================================== Popular generalized linear models 将不同 ...
- python进行数据分析
1. python进行数据分析----线性回归 2. python进行数据分析------相关分析 3. python进行数据分析---python3卡方 4. 多重响应分析,多选题二分法思路 5. ...
- Logistic Regression Vs Decision Trees Vs SVM: Part I
Classification is one of the major problems that we solve while working on standard business problem ...
- logistics回归简单应用(二)
警告:本文为小白入门学习笔记 网上下载的数据集链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1NwSXJOCzgihPFZfw3NfnfA 密码: jmwz 不知道这个数据集干什么用的,根据直 ...
- 2.1、Softmax Regression模型
Softmax Regression模型 由于Logistics Regression算法复杂度低,容易实现等特点,在工业中的到广泛的使用,但是Logistics Regression算法主要用于处理 ...
- 【R语言进行数据挖掘】回归分析
1.线性回归 线性回归就是使用下面的预测函数预测未来观测量: 其中,x1,x2,...,xk都是预测变量(影响预测的因素),y是需要预测的目标变量(被预测变量). 线性回归模型的数据来源于澳大利亚的C ...
随机推荐
- loj#2013. 「SCOI2016」幸运数字 点分治/线性基
题目链接 loj#2013. 「SCOI2016」幸运数字 题解 和树上路径有管...点分治吧 把询问挂到点上 求出重心后,求出重心到每个点路径上的数的线性基 对于重心为lca的合并寻味,否则标记下传 ...
- java中哪些数值不能被初始化
main方法中的变量不能被初始化 final修饰的变量不能被初始化·
- zabbix 添加被监控主机
点击 configured > host > create host 主机名:输入主机名,允许使用字母数字,空格,点,破折号和下划线 组:从右侧选择框中选择一个或多个组,然后单击 « 将其 ...
- Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException', reason: '*** -[__NSPlaceholderDictionary initWithObjects:forKeys:count:]: attempt to insert nil object from objects[0]'
报错: Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException', reason: '*** -[__NSPlace ...
- Unity3D引擎中特殊的文件夹
Editor Editor文件夹可以在根目录下,可以在子目录里,只要名是Editor就可以./xxx/xxx/Editor 和 /Editor 是一样的,多少个叫Editor的文件夹都可以.Edit ...
- xtrabackup备份MySQL并主从同步
为什么要使用xtarbackup? mysqldump备份数据库的时候,会锁库锁表,导致业务服务的暂时停滞,数据库数量小还没有感觉,当数据超过几个G的时候,使用mysqldump会严重影响服务器性能, ...
- __Linux__文件和目录
Linux 目录 /:根目录,一般根目录下只存放目录,在Linux下有且只有一个根目录.所有的东西都是从这里开始.当你在终端里输入“/home”,你其实是在告诉电脑,先从/(根目录)开始,再进入到ho ...
- strcpy和memcpy的差别
strcpy和memcpy都是标准C库函数.它们有以下的特点. strcpy提供了字符串的复制. 即strcpy仅仅用于字符串复制.而且它不仅复制字符串内容之外,还会复制字符串的结束符,strcpy_ ...
- oracle 常用 sql
判断字段值是否为空( mysql 为 ifnull(,)): nvl (Withinfocode,'') as *** 两字段拼接: (1)concat(t.indate, t.intime) as ...
- Redis进阶之redis的生命周期
D:\Redis-x64-3.2.100>redis-cli.exe -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379127.0.0.1:6379> set aa "123"( ...
