Django基础,Day2 - 编写urls,views,models
编写views
views:作为MVC中的C,接收用户的输入,调用数据库Model层和业务逻辑Model层,处理后将处理结果渲染到V层中去。
polls/views.py:
from django.http import HttpResponse # Create your views here.
def index(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello, world. You're at the polls index.")
编写urls
urls,程序的入口,支持正则匹配访问url,将访问url映射到views中的具体某个函数中。
为了能调用到上面这个views,我们需要将views.index函数映射到URL中。
我们可以创建一个urls.py 在App目录下。
polls/urls.py:
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding=utf-8 from django.conf.urls import url
from . import views urlpatterns = [
url(r'^$', views.index, name='index'),
]
下一步,我们需要将创建的urls.py 添加到全局urls.py中,如
mysite/urls.py:
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from django.contrib import admin urlpatterns = [
url(r'^polls/', include('polls.urls')),
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
]
此时,可以通过访问 http://localhost:8000/polls/ 可以调用到所编写的views
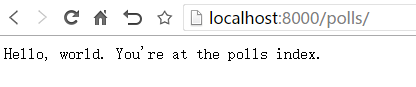
编写models
models与数据库操作相关,是django处理数据库的一个特色之处,它包含你的数据库基本字段与数据。通过一系列封装的api可以直接操作数据库。当然,也支持原生sql。
既然models与数据库相关,那么首先需要配置数据库
1、数据库设置,mysite/settings.py:
这里默认使用内置的sqlite3,配置如下:
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'),
}
}
如果想要改为MYSQL,配置修改如下:
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': MYSQL_DB,
'USER': MYSQL_USER,
'PASSWORD': MYSQL_PASS,
'HOST': MYSQL_HOST_M,
'PORT': MYSQL_PORT,
}
}
2、初始化数据库数据
在pycharm中,首次使用django相关命令,需要做一些配置。如

配置 python manage.py migrate
配置好后便可运行,运行结果如:
$ python manage.py migrate
Operations to perform:
Apply all migrations: admin, auth, contenttypes, sessions
Running migrations:
Applying contenttypes.0001_initial... OK
Applying auth.0001_initial... OK
Applying admin.0001_initial... OK
Applying admin.0002_logentry_remove_auto_add... OK
Applying contenttypes.0002_remove_content_type_name... OK
Applying auth.0002_alter_permission_name_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0003_alter_user_email_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0004_alter_user_username_opts... OK
Applying auth.0005_alter_user_last_login_null... OK
Applying auth.0006_require_contenttypes_0002... OK
Applying auth.0007_alter_validators_add_error_messages... OK
Applying auth.0008_alter_user_username_max_length... OK
Applying sessions.0001_initial... OK
3、创建models
在本实例中,创建两个models:Questions 和 Choice.
polls/models.py:
from __future__ import unicode_literals from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Question(models.Model):
question_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
pub_date = models.DateTimeField('date published') class Choice(models.Model):
question = models.ForeignKey(Question, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
choice_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
votes = models.IntegerField(default=0)
4、激活models
将app包含到project中,我们需要将它的配置类注册到全局配置中的 INSTALLED_APPS 中。它的配置类 PollsConfig 在 polls/apps.py 中,所以它的路径为'polls.apps.PollsConfig'
编辑mysite/settings.py:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'polls.apps.PollsConfig',
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
]
现在,django已经知道包含了polls app。此时,我们需要告诉django,models已经更改。to create migrations for those changes
$ python manage.py makemigrations polls
makemigrations 命令将会生成一些更新sql语句,同样的,为了在pycharm中容易使用,将其配置如:

运行后,控制台输出如:

然后,重新运行 python manage.py migrate,将会在数据库中创建这些models表。to apply those changes to the database.
$ python manage.py migrate

注意,每次更改models,都必须重新分别执行
$ python manage.py makemigrations
$ python manage.py migrate
增强models
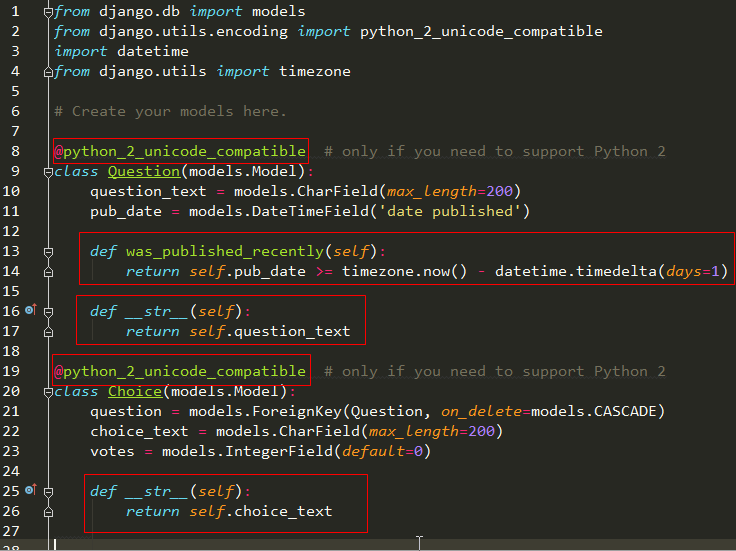
polls/models.py:
from django.db import models
from django.utils.encoding import python_2_unicode_compatible
import datetime
from django.utils import timezone # Create your models here. @python_2_unicode_compatible # only if you need to support Python 2
class Question(models.Model):
question_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
pub_date = models.DateTimeField('date published') def was_published_recently(self):
return self.pub_date >= timezone.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=1) def __str__(self):
return self.question_text @python_2_unicode_compatible # only if you need to support Python 2
class Choice(models.Model):
question = models.ForeignKey(Question, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
choice_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
votes = models.IntegerField(default=0) def __str__(self):
return self.choice_text
修改位置:
通过Database API操作数据
进入django shell 环境:
$ python manage.py shell
执行database API:
>>> from polls.models import Question, Choice # Import the model classes we just wrote. # No questions are in the system yet.
>>> Question.objects.all()
<QuerySet []> # Create a new Question.
# Support for time zones is enabled in the default settings file, so
# Django expects a datetime with tzinfo for pub_date. Use timezone.now()
# instead of datetime.datetime.now() and it will do the right thing.
>>> from django.utils import timezone
>>> q = Question(question_text="What's new?", pub_date=timezone.now()) # Save the object into the database. You have to call save() explicitly.
>>> q.save() # Now it has an ID. Note that this might say "1L" instead of "", depending
# on which database you're using. That's no biggie; it just means your
# database backend prefers to return integers as Python long integer
# objects.
>>> q.id # Access model field values via Python attributes.
>>> q.question_text
"What's new?"
>>> q.pub_date
datetime.datetime(, , , , , , , tzinfo=<UTC>) # Change values by changing the attributes, then calling save().
>>> q.question_text = "What's up?"
>>> q.save() # objects.all() displays all the questions in the database.
# Make sure our __str__() addition worked.
>>> Question.objects.all()
<QuerySet [<Question: What's up?>]> # Django provides a rich database lookup API that's entirely driven by
# keyword arguments.
>>> Question.objects.filter(id=)
<QuerySet [<Question: What's up?>]>
>>> Question.objects.filter(question_text__startswith='What')
<QuerySet [<Question: What's up?>]> # Get the question that was published this year.
>>> from django.utils import timezone
>>> current_year = timezone.now().year
>>> Question.objects.get(pub_date__year=current_year)
<Question: What's up?> # Request an ID that doesn't exist, this will raise an exception.
>>> Question.objects.get(id=)
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
DoesNotExist: Question matching query does not exist. # Lookup by a primary key is the most common case, so Django provides a
# shortcut for primary-key exact lookups.
# The following is identical to Question.objects.get(id=).
>>> Question.objects.get(pk=)
<Question: What's up?> # Make sure our custom method worked.
>>> q = Question.objects.get(pk=)
>>> q.was_published_recently()
True # Give the Question a couple of Choices. The create call constructs a new
# Choice object, does the INSERT statement, adds the choice to the set
# of available choices and returns the new Choice object. Django creates
# a set to hold the "other side" of a ForeignKey relation
# (e.g. a question's choice) which can be accessed via the API.
>>> q = Question.objects.get(pk=) # Display any choices from the related object set -- none so far.
>>> q.choice_set.all()
<QuerySet []> # Create three choices.
>>> q.choice_set.create(choice_text='Not much', votes=)
<Choice: Not much>
>>> q.choice_set.create(choice_text='The sky', votes=)
<Choice: The sky>
>>> c = q.choice_set.create(choice_text='Just hacking again', votes=) # Choice objects have API access to their related Question objects.
>>> c.question
<Question: What's up?> # And vice versa: Question objects get access to Choice objects.
>>> q.choice_set.all()
<QuerySet [<Choice: Not much>, <Choice: The sky>, <Choice: Just hacking again>]>
>>> q.choice_set.count() # The API automatically follows relationships as far as you need.
# Use double underscores to separate relationships.
# This works as many levels deep as you want; there's no limit.
# Find all Choices for any question whose pub_date is in this year
# (reusing the 'current_year' variable we created above).
>>> Choice.objects.filter(question__pub_date__year=current_year)
<QuerySet [<Choice: Not much>, <Choice: The sky>, <Choice: Just hacking again>]> # Let's delete one of the choices. Use delete() for that.
>>> c = q.choice_set.filter(choice_text__startswith='Just hacking')
>>> c.delete()
***微信扫一扫,关注“python测试开发圈”,了解更多测试教程!***
Django基础,Day2 - 编写urls,views,models的更多相关文章
- Django基础之路由(urls)层
目录 Django基础之路由(urls)层 无名分组与有名分组 无名分组 有名分组 反向解析 前段解析 后端解析 无名分组反向解析 前段解析 后端解析 有名分组的反向解析 前段解析 后端解析 路由分发 ...
- Django基础(一)_URLconf、Views、template、ORM
一 什么是web框架? 框架,即framework,特指为解决一个开放性问题而设计的具有一定约束性的支撑结构,使用框架可以帮你快速开发特定的系统,简单地说,就是你用别人搭建好的舞台来做表演. 对于所有 ...
- django复习笔记3:urls/views/templates三板斧
0.先看看文件结构 mysite/ mysite/ ├── __pycache__ │ └── manage.cpython-.pyc ├── blog │ ├── __init__.py │ ...
- Django基础知识MTV
Django简介 Django是使用Python编写的一个开源Web框架.可以用它来快速搭建一个高性能的网站. Django也是一个MVC框架.但是在Django中,控制器接受用户输入的部分由框架自行 ...
- Django基础--Django基本命令、路由配置系统(URLconf)、编写视图、Template、数据库与ORM
web框架 框架,即framework,特指为解决一个开放性问题而设计的具有一定约束性的支撑结构. 使用框架可以帮你快速开发特定的系统. 简单地说,就是你用别人搭建好的舞台来做表演. 尝试搭建一个简单 ...
- Django基础之视图(views)层、模板层
目录 Django基础之视图(views)层.模板层 JsonResponse 向前端返回一个json格式字符串的两种方式 重写Django中的json的某个方法 form表单上传文件 FBV与CBV ...
- Django基础之模型(models)层(上)
目录 Django基础之模型(models)层 单表查询 必知必会13条 神奇的双下划线查询 多表查询 外键的字段的增删改查 表与表之间的关联查询 基于双下划线的跨表查询(连表查询) 补充知识 Dja ...
- Django基础之安装配置
安装配置 一 MVC和MTV模式 著名的MVC模式:所谓MVC就是把web应用分为模型(M),控制器(C),视图(V)三层:他们之间以一种插件似的,松耦合的方式连接在一起. 模型负责业务对象与数据库的 ...
- Django基础(一)
Django基础(一) 知识预览 Django基本命令 二 路由配置系统(URLconf) 三 编写视图 四 Template 五 数据库与ORM admin的配置 一 什么是web框架? 框架,即f ...
随机推荐
- mac 抓包工具charles v3.9.3 安装破解步骤
一.下载 先到它的官网http://www.charlesproxy.com/可下载到最新版本,这个下载有点慢,我已经将它放到网盘中了:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1skTXRIl ...
- AngularJS 系列 02 - 模块
引导目录: AngularJS 系列 学习笔记 目录篇 前言: 其实,在上篇文章介绍数据绑定的时候,我们的HelloWorld的代码案例中就已经使用了模块(module).哈哈. 本篇就着重介绍一下a ...
- oracle调用JAVA类的方法
导入jar包 在oracle中导入需要的jar包,我们把编辑好的java类打成jar包,直接在oarcle里面写简单的调用就可以了, 1.操作系统需要拥有支持loadjava命令的jdk. 2.加 ...
- nginx 虚拟主机基于端口的搭建
首先配置nginx.conf [root@localhost conf]# cat nginx.confworker_processes 1;user nginx nginx;error_log /a ...
- 树莓派 连接wifi与路由器ip绑定
先推荐几个手机软件 在酷安网里应该能找到 1.JuiceSSH 橘子ssh软件 手机连上路由器 就可以控制局域网内的树莓派 2.VNC Viewer 远程桌面软件VNC 也是连接局域网的树莓派 ...
- Linux NFS服务器的安装与配置
一.NFS服务简介 NFS 是Network File System的缩写,即网络文件系统.一种使用于分散式文件系统的协定,由Sun公司开发,于1984年向外公布.功能是通过网络让不同的机器.不同的操 ...
- Practical oral English
1.如果你继续发烧,我就去请医生过来If your fever continues, I'll send for the doctor.2.在这么大的停车场里,我是永远都找不到我的车的I'll nev ...
- Spring基础
一.Spring作用:管理项目中各种业务Bean(service类.Dao类.Action类),实例化类,属性赋值 二.Spring IOC(Inversion of Control )控制反转,也被 ...
- 原生Ajax
使用原生Ajax 验证用户名是否被注册 创建出注册信息: <h1>注册信息</h1><input type="text" name="txt ...
- 深入C#编程
1.NET框架 1.1.NET框架结构 VB.NET C# F# lronruby others.... .NET FrameWork(FCL) 公共语言进行时(CLR) 操作系统 .NET框架具有两 ...
