机器学习中的权重衰退 —— 深度学习中的权重衰退 —— 权重衰退 —— weight decay
在看代码时看到了这个概念,以前虽然也看到过但是没有太在意,再次看到于是研究了一下。
引自:
https://sota.jiqizhixin.com/models/methods/0bdb8f87-9c05-483e-af49-e1140b9e7d19

直接说答案,weight decay 就是L2 Regularization 。
引自:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/995516301b0a

其实在深度学习框架中的优化器参数中就可以设置weight decay,如:
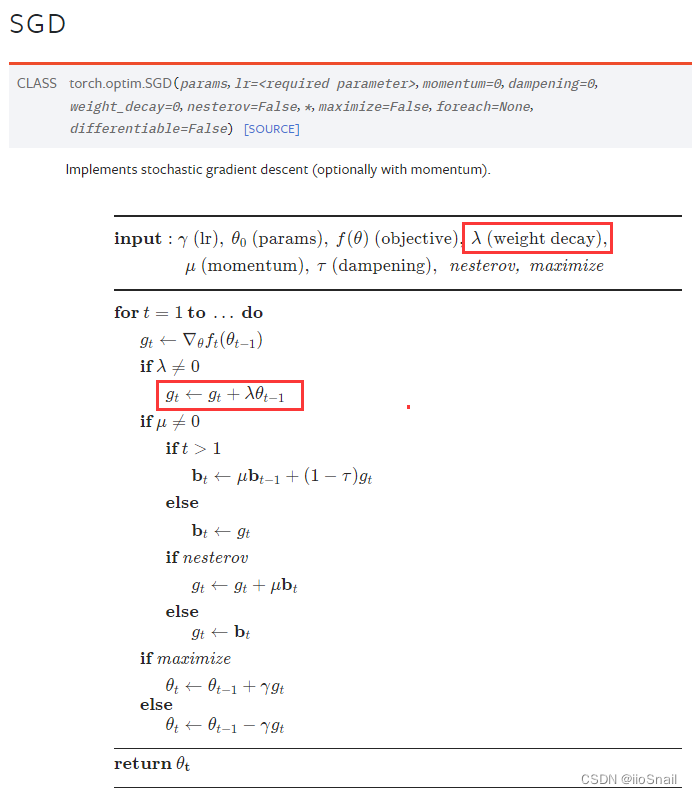
============================================
引自:
https://blog.csdn.net/zhaohongfei_358/article/details/129625803
weight_decay的一些trick:
- weight_decay并没有你想想中的那么好,它的效果可能只有一点点,不要太指望它。尤其是当你的模型很复杂时,权重衰退的效果可能会更小了。
- 通常取1e-3,如果要尝试的话,一般也就是1e-2, 1e-3, 1e-4 这些选项。
- 权重衰退通常不对bias做。但通常bias做不做权重衰退其实效果差不多,不过最好不要做。
- weight_decay取值越大,对抑制模型的强度越大。但这并不说明越大越好,太大的话,可能会导致模型欠拟合。
============================================
给出chainer框架中的实现:(不对bias进行decay,只对weight进行decay)
地址:
https://github.com/chainer/chainerrl/blob/master/chainerrl/optimizers/nonbias_weight_decay.py
class NonbiasWeightDecay(object):
"""Weight decay only for non-bias parameters.
This hook can be used just like chainer.optimizer_hooks.WeightDecay except
that this hook does not apply weight decay to bias parameters.
This hook assumes that all the bias parameters have the name of "b". Any
parameter whose name is "b" is considered as a bias and excluded from
weight decay.
"""
name = 'NonbiasWeightDecay'
call_for_each_param = True
timing = 'pre'
def __init__(self, rate):
self.rate = rate
def __call__(self, rule, param):
if param.name == 'b':
return
p, g = param.array, param.grad
if p is None or g is None:
return
with cuda.get_device_from_array(p) as dev:
if int(dev) == -1:
g += self.rate * p
else:
kernel = cuda.elementwise(
'T p, T decay', 'T g', 'g += decay * p', 'weight_decay')
kernel(p, self.rate, g)
def add_hook(self, hook, name=None, timing='auto'):
"""Adds a hook function. The hook function is called before or after any updates (see the timing
attribute). Args:
hook (callable): Hook function to be added. It takes two
arguments: the update rule object and the parameter variable.
name (str): Name of the hook function. The name attribute of the
hook function is used by default.
timing (str): Specifies when the hook is called. If 'auto', the
timimg property of the hook will decide the timing.
If 'pre', the hook will be called before any updates.
If 'post', the hook will be called after any updates.
If 'auto' and the timing property of the hook is not
available, timing will default to 'pre'. """
if not callable(hook):
raise TypeError('hook function must be callable')
if timing not in ('pre', 'post', 'auto'):
raise ValueError("timing must be one of ('pre', 'post', 'auto')")
if timing == 'auto':
timing = getattr(hook, 'timing', 'pre') if name is None:
name = getattr(hook, 'name', getattr(hook, '__name__', None))
if name is None:
raise ValueError(
'the name of the hook function is not specified')
if name in self._pre_update_hooks or name in self._post_update_hooks:
raise ValueError('hook "{}" already exists'.format(name)) if timing == 'pre':
self._pre_update_hooks[name] = hook
else:
self._post_update_hooks[name] = hook def remove_hook(self, name):
"""Removes the specified hook function. Args:
name (str): Name of the hook function to be removed. The hook
function registered with this name will be removed. """
try:
del self._pre_update_hooks[name]
except KeyError:
del self._post_update_hooks[name] def update(self, param):
"""Invokes hook functions and updates the parameter. Args:
param (~chainer.Variable): Variable to be updated. """
if not self.enabled:
return self.t += 1 if self._use_fp32_update and param.dtype == numpy.float16:
if self._fp32_param is None:
self._fp32_param = variable.Variable(
param.array.astype(numpy.float32),
name=param.name)
fp32_param = self._fp32_param
fp32_param.grad = param.grad.astype(numpy.float32) if fp32_param.data is not None:
self._prepare(fp32_param)
if param._loss_scale is not None:
fp32_param.grad /= param._loss_scale
for hook in six.itervalues(self._pre_update_hooks):
hook(self, fp32_param)
self.update_core(fp32_param)
for hook in six.itervalues(self._post_update_hooks):
hook(self, fp32_param) param.data = fp32_param.data.astype(param.dtype)
fp32_param.grad = None
else:
if param.data is not None:
self._prepare(param)
if param._loss_scale is not None:
param.grad /= param._loss_scale
for hook in six.itervalues(self._pre_update_hooks):
hook(self, param)
self.update_core(param)
for hook in six.itervalues(self._post_update_hooks):
hook(self, param)
============================================
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/995516301b0a
https://blog.csdn.net/zhaohongfei_358/article/details/129625803
机器学习中的权重衰退 —— 深度学习中的权重衰退 —— 权重衰退 —— weight decay的更多相关文章
- 机器学习之路:tensorflow 深度学习中 分类问题的损失函数 交叉熵
经典的损失函数----交叉熵 1 交叉熵: 分类问题中使用比较广泛的一种损失函数, 它刻画两个概率分布之间的距离 给定两个概率分布p和q, 交叉熵为: H(p, q) = -∑ p(x) log q( ...
- 深度学习中常见的 Normlization 及权重初始化相关知识(原理及公式推导)
Batch Normlization(BN) 为什么要进行 BN 防止深度神经网络,每一层得参数更新会导致上层的输入数据发生变化,通过层层叠加,高层的输入分布变化会十分剧烈,这就使得高层需要不断去重新 ...
- 深度学习中Dropout原理解析
1. Dropout简介 1.1 Dropout出现的原因 在机器学习的模型中,如果模型的参数太多,而训练样本又太少,训练出来的模型很容易产生过拟合的现象. 在训练神经网络的时候经常会遇到过拟合的问题 ...
- 卷积在深度学习中的作用(转自http://timdettmers.com/2015/03/26/convolution-deep-learning/)
卷积可能是现在深入学习中最重要的概念.卷积网络和卷积网络将深度学习推向了几乎所有机器学习任务的最前沿.但是,卷积如此强大呢?它是如何工作的?在这篇博客文章中,我将解释卷积并将其与其他概念联系起来,以帮 ...
- 深度学习中的Normalization模型
Batch Normalization(简称 BN)自从提出之后,因为效果特别好,很快被作为深度学习的标准工具应用在了各种场合.BN 大法虽然好,但是也存在一些局限和问题,诸如当 BatchSize ...
- [优化]深度学习中的 Normalization 模型
来源:https://www.chainnews.com/articles/504060702149.htm 机器之心专栏 作者:张俊林 Batch Normalization (简称 BN)自从提出 ...
- Hebye 深度学习中Dropout原理解析
1. Dropout简介 1.1 Dropout出现的原因 在机器学习的模型中,如果模型的参数太多,而训练样本又太少,训练出来的模型很容易产生过拟合的现象. 在训练神经网络的时候经常会遇到过拟合的问题 ...
- zz详解深度学习中的Normalization,BN/LN/WN
详解深度学习中的Normalization,BN/LN/WN 讲得是相当之透彻清晰了 深度神经网络模型训练之难众所周知,其中一个重要的现象就是 Internal Covariate Shift. Ba ...
- 模型汇总24 - 深度学习中Attention Mechanism详细介绍:原理、分类及应用
模型汇总24 - 深度学习中Attention Mechanism详细介绍:原理.分类及应用 lqfarmer 深度学习研究员.欢迎扫描头像二维码,获取更多精彩内容. 946 人赞同了该文章 Atte ...
- 深度学习中正则化技术概述(附Python代码)
欢迎大家关注我们的网站和系列教程:http://www.tensorflownews.com/,学习更多的机器学习.深度学习的知识! 磐石 介绍 数据科学研究者们最常遇见的问题之一就是怎样避免过拟合. ...
随机推荐
- SRE Google 运维解密读书笔记一:SRE 方法论概述
SRE Google 运维解密,是 SRE 领域的启蒙之作,讲述了 Google 的 SRE 实践,SRE 就是从 Google 流传出来的.本文是读书笔记,第一篇,概述 SRE 方法论.帮大家把书读 ...
- 使用腾讯元宝+markmap生成思维导图
AI可以帮助我们进行提炼和总结, 节省了大量搜索资料和查阅的时间,像上图这张思维导图,就是使用腾讯元宝大模型进行内容提炼,再使用markmap生成思维导图,下面讲解下详细实现步骤: 一.工具准备 腾讯 ...
- 增补博客 第四篇 python 中文级联菜单
from pypinyin import pinyin, Style # 定义菜单项和对应的子菜单 menu = { "文件": { "新建": {}, &qu ...
- #PowerBi 1分钟学会,用PowerBi获取数据库最近90天的数据(DATE_SUB)
在powerbi报表中,我们往往会对数据源进行日常刷新,powerbi链接了数据库的情况下,根据日期灵活取数是我们必须掌握的一个技能. 在本文中,我们将介绍如何使用 SQL 的 DATE_SUB 函数 ...
- golang如何使用指针灵活操作内存?unsafe包原理解析
Hi 你好,我是k哥.一个大厂工作6年,还在继续搬砖的后端程序员. 我们都知道,C/C++提供了强大的万能指针void*,任何类型的指针都可以和万能指针相互转换.并且指针还可以进行加减等算数操作.那么 ...
- 15-容器简介与Docker安装
传统企业应用构建 应用被直接部署在操作系统之上,并且操作系统直接安装于硬件之上应用被操作系统绑定 操作系统被硬件绑定 缺点 部署非常慢(启动应用的速度非常慢) 成本非常高(原有服务器的操作系统不支持这 ...
- 实验2.ARP实验
# 实验2.ARP实验 本实验用于验证arp以及arp表,arp缓存的使用,测试ping包时arp表的更新机制. 实验组 PC1 10.68.57.10 255.255.255.0 00-00-00- ...
- libevent之evbuffer
目录 Evbuffers:缓冲 IO 的实用程序功能 简介 创建或释放 evbuffer Evbuffers 和线程安全 检查 evbuffer 向 evbuffer 添加数据:基础知识 将数据从一个 ...
- 【Python】基于动态规划和K聚类的彩色图片压缩算法
引言 当想要压缩一张彩色图像时,彩色图像通常由数百万个颜色值组成,每个颜色值都由红.绿.蓝三个分量组成.因此,如果我们直接对图像的每个像素进行编码,会导致非常大的数据量.为了减少数据量,我们可以尝试减 ...
- MFC基于对画框工程笔记->更改窗口图标以及生成的.exe图标
一.前言 继前一篇生成MFC基于对话框工程->新建MFC对话框后,开始改动对话框图标以及生成的.exe图标. 原对话框图标以及.exe图标: 在菜单栏中选择生成目录为Release 打开Rele ...
