重新整理 .net core 实践篇—————中间件[十九]
前言
简单介绍一下.net core的中间件。
正文
官方文档已经给出了中间件的概念图:
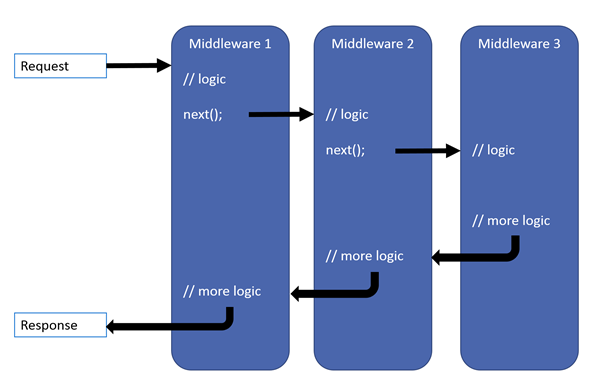
和其密切相关的是下面这两个东西:
IApplicationBuilder 和 RequestDelegate(HttpContext context)
IApplicationBuilder :
public interface IApplicationBuilder
{
IServiceProvider ApplicationServices { get; set; }
IFeatureCollection ServerFeatures { get; }
IDictionary<string, object> Properties { get; }
IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware);
IApplicationBuilder New();
RequestDelegate Build();
}
RequestDelegate:
namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
{
public delegate Task RequestDelegate(HttpContext context);
}
举一个 中间件的例子:
app.Use(async (context, next) => {
await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello word");
});
效果:
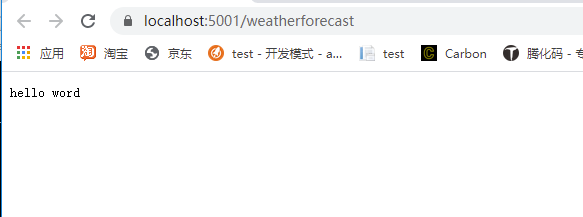
这里我没有执行next,故而在这里就终止了。
来看下这个Use,干了什么:
public static class UseExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder Use(
this IApplicationBuilder app,
Func<HttpContext, Func<Task>, Task> middleware)
{
return app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (next => (RequestDelegate) (context =>
{
Func<Task> func = (Func<Task>) (() => next(context));
return middleware(context, func);
})));
}
}
是的,他是对IApplicationBuilder 的一个扩展。
如果不想使用这个扩展方法,那么你要这么写:
app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (next=> (RequestDelegate)((context)=>
{
Func<Task> func = (Func<Task>)(() => next(context));
Func<HttpContext, Func<Task>, Task> middleware = async (context1, next2) =>
{
await context1.Response.WriteAsync("hello word");
};
return middleware(context, func);
})));
有些人可能看不惯这样写哈,换一种写法:
app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (next =>
{
return (RequestDelegate)((context) =>
{
Func<Task> func = (Func<Task>)(() => next(context));
Func<HttpContext, Func<Task>, Task> middleware = async (context1, next2) =>
{
await context1.Response.WriteAsync("hello word");
};
return middleware(context, func);
});
}));
又或者,这样写:
app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (next =>
{
return (RequestDelegate)((context) =>
{
Func<HttpContext, RequestDelegate, Task> middleware = async (context1, next2) =>
{
await context1.Response.WriteAsync("hello word");
};
return middleware(context, next);
});
}));
还可以这样写:
public async Task WriteAsync(HttpContext context, RequestDelegate requestDelegate)
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello word");
}
app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (next =>
{
return (RequestDelegate)((context) => WriteAsync(context, next));
}));
上面没有用到这个next,那么这个next是干什么的呢?从上面的传参推断出,就是我们的下一步。
如果没有执行下一步,那么下一步是不会执行的。
来看一下IApplicationBuilder的实现类ApplicationBuilder的use方法:
private readonly IList<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>> _components = (IList<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>) new List<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>();
public IApplicationBuilder Use(
Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware)
{
this._components.Add(middleware);
return (IApplicationBuilder) this;
}
会将我们传入的middleware,加入到_components 中。
ApplicationBuilder看下build 方法:
public RequestDelegate Build()
{
RequestDelegate requestDelegate = (RequestDelegate) (context =>
{
Endpoint endpoint = context.GetEndpoint();
if (endpoint?.RequestDelegate != null)
throw new InvalidOperationException("The request reached the end of the pipeline without executing the endpoint: '" + endpoint.DisplayName + "'. Please register the EndpointMiddleware using 'IApplicationBuilder.UseEndpoints(...)' if using routing.");
context.Response.StatusCode = 404;
return Task.CompletedTask;
});
foreach (Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> func in this._components.Reverse<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>())
requestDelegate = func(requestDelegate);
return requestDelegate;
}
这个就是套娃工程,把后面一个的requestDelegate,作为前面一个requestDelegate的参数。最后返回第一个requestDelegate。
断点验证,我打了两个断点,下面是断点的顺序。
第一个断点停留的位置:
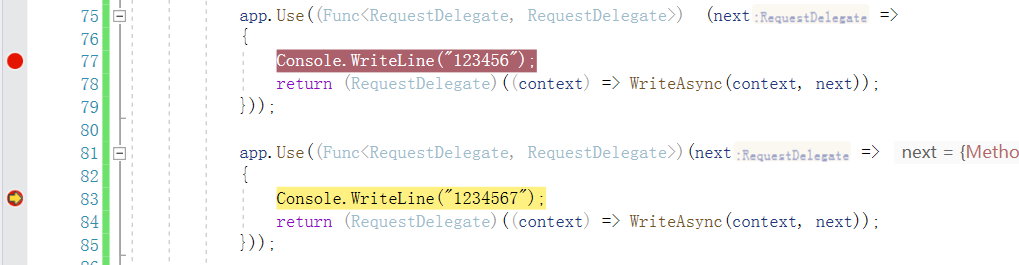
第二个断点停留的位置:
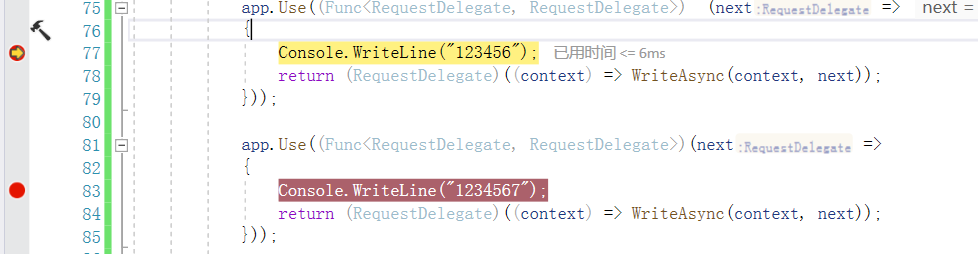
第二个断点里面的next就是第一个断点返回的结果。
因为返回的是第一个中间件的返回的RequestDelegate,那么运行。
那么运行顺序就是第一个返回的RequestDelegate开始运行,且参数是第二个中间件返回的RequestDelegate。
返回的RequestDelegate运行顺序如下:
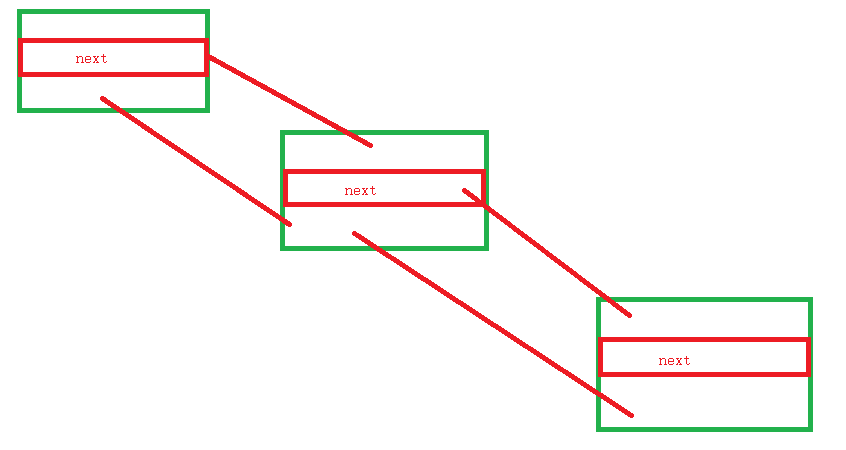
这大概就是中间件的原理了。
下面看一下动态中间件:
app.Map("/abc", builder =>
{
app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>)(next =>
{
return (RequestDelegate)((context) => WriteAsync(context, next));
}));
});
如上面这样,如果匹配到了/abc,那么就走里面的中间件。
看下源码吧,Map的。
public static class MapExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder Map(
this IApplicationBuilder app,
PathString pathMatch,
Action<IApplicationBuilder> configuration)
{
if (app == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (app));
if (configuration == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (configuration));
if (pathMatch.HasValue && pathMatch.Value.EndsWith("/", StringComparison.Ordinal))
throw new ArgumentException("The path must not end with a '/'", nameof (pathMatch));
IApplicationBuilder applicationBuilder = app.New();
configuration(applicationBuilder);
RequestDelegate requestDelegate = applicationBuilder.Build();
MapOptions options = new MapOptions()
{
Branch = requestDelegate,
PathMatch = pathMatch
};
return app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (next => new RequestDelegate(new MapMiddleware(next, options).Invoke)));
}
}
里面做的主要是两件事,一件事是另外 app.New();弄出一条分支出来。然后调用Build()独立走出一条新的中间件链。
New方法如下:
public IApplicationBuilder New()
{
return (IApplicationBuilder) new ApplicationBuilder(this);
}
第二件事就是返回了一个新的中间件RequestDelegate,传入了两个参数一个是next,这个是用来走老的分支,估摸着不匹配的时候走旧的分支。
还有一个参数是options,这个参数有两个属性,一个是Branch 就是新的分支。一个是PathMatch 是匹配字符,那么就是如果是匹配的话,就走新的分支。
事实证明果然如此:
public class MapMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly MapOptions _options;
public MapMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, MapOptions options)
{
if (next == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (next));
if (options == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (options));
this._next = next;
this._options = options;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
if (context == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (context));
PathString matched;
PathString remaining;
if (context.Request.Path.StartsWithSegments(this._options.PathMatch, out matched, out remaining))
{
PathString path = context.Request.Path;
PathString pathBase = context.Request.PathBase;
context.Request.PathBase = pathBase.Add(matched);
context.Request.Path = remaining;
try
{
await this._options.Branch(context);
}
finally
{
context.Request.PathBase = pathBase;
context.Request.Path = path;
}
path = new PathString();
pathBase = new PathString();
}
else
await this._next(context);
}
}
还可以这样自定义:
app.MapWhen(context =>
{
return context.Request.Query.Keys.Contains("abc");
}, builder =>
{
app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>)(next =>
{
return (RequestDelegate)((context) => WriteAsync(context, next));
}));
});
有了上面的简单分析,应该不难理解哈。
我这里直接贴了:
MapWhen:
public static class MapWhenExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder MapWhen(
this IApplicationBuilder app,
Func<HttpContext, bool> predicate,
Action<IApplicationBuilder> configuration)
{
if (app == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (app));
if (predicate == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (predicate));
if (configuration == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (configuration));
IApplicationBuilder applicationBuilder = app.New();
configuration(applicationBuilder);
RequestDelegate requestDelegate = applicationBuilder.Build();
MapWhenOptions options = new MapWhenOptions()
{
Predicate = predicate,
Branch = requestDelegate
};
return app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (next => new RequestDelegate(new MapWhenMiddleware(next, options).Invoke)));
}
}
MapWhenMiddleware:
public class MapWhenMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly MapWhenOptions _options;
public MapWhenMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, MapWhenOptions options)
{
if (next == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (next));
if (options == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (options));
this._next = next;
this._options = options;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
if (context == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (context));
if (this._options.Predicate(context))
await this._options.Branch(context);
else
await this._next(context);
}
}
上面都是异曲同工,就不做解释了。
这里再介绍一个方法,run:
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello word");
});
这个这个Run方法,没有传入next。
如下:
public static void Run(this IApplicationBuilder app, RequestDelegate handler)
{
if (app == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (app));
if (handler == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (handler));
app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (_ => handler));
}
表示这是末端。
那么下面介绍一下,将我们的中间件写入到一个独立的类里面去。
定义一个扩展类:
public static class SelfBuilderExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseSelfSelfMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder app)
{
return app.UseMiddleware<SelfMiddleware>();
}
}
具体的实现:
public class SelfMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public SelfMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
this._next = next;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
Console.WriteLine("request handle");
await this._next(context);
Console.WriteLine("response handle");
}
}
使用:
app.UseSelfSelfMiddleware();
简单看一下UseMiddleware这个方法:
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware<TMiddleware>(
this IApplicationBuilder app,
params object[] args)
{
return app.UseMiddleware(typeof (TMiddleware), args);
}
继续看app.UseMiddleware:
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware(
this IApplicationBuilder app,
Type middleware,
params object[] args)
{
if (typeof (IMiddleware).GetTypeInfo().IsAssignableFrom(middleware.GetTypeInfo()))
{
if (args.Length != 0)
throw new NotSupportedException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareExplicitArgumentsNotSupported((object) typeof (IMiddleware)));
return UseMiddlewareExtensions.UseMiddlewareInterface(app, middleware);
}
IServiceProvider applicationServices = app.ApplicationServices;
return app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (next =>
{
MethodInfo[] array = ((IEnumerable<MethodInfo>) middleware.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public)).Where<MethodInfo>((Func<MethodInfo, bool>) (m => string.Equals(m.Name, "Invoke", StringComparison.Ordinal) || string.Equals(m.Name, "InvokeAsync", StringComparison.Ordinal))).ToArray<MethodInfo>();
if (array.Length > 1)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddleMutlipleInvokes((object) "Invoke", (object) "InvokeAsync"));
if (array.Length == 0)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoInvokeMethod((object) "Invoke", (object) "InvokeAsync", (object) middleware));
MethodInfo methodInfo = array[0];
if (!typeof (Task).IsAssignableFrom(methodInfo.ReturnType))
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNonTaskReturnType((object) "Invoke", (object) "InvokeAsync", (object) "Task"));
ParameterInfo[] parameters = methodInfo.GetParameters();
if (parameters.Length == 0 || parameters[0].ParameterType != typeof (HttpContext))
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoParameters((object) "Invoke", (object) "InvokeAsync", (object) "HttpContext"));
object[] objArray = new object[args.Length + 1];
objArray[0] = (object) next;
Array.Copy((Array) args, 0, (Array) objArray, 1, args.Length);
object instance = ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance(app.ApplicationServices, middleware, objArray);
if (parameters.Length == 1)
return (RequestDelegate) methodInfo.CreateDelegate(typeof (RequestDelegate), instance);
Func<object, HttpContext, IServiceProvider, Task> factory = UseMiddlewareExtensions.Compile<object>(methodInfo, parameters);
return (RequestDelegate) (context =>
{
IServiceProvider serviceProvider = context.RequestServices ?? applicationServices;
if (serviceProvider == null)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareIServiceProviderNotAvailable((object) "IServiceProvider"));
return factory(instance, context, serviceProvider);
});
}));
}
一段一段分析:
if (typeof (IMiddleware).GetTypeInfo().IsAssignableFrom(middleware.GetTypeInfo()))
{
if (args.Length != 0)
throw new NotSupportedException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareExplicitArgumentsNotSupported((object) typeof (IMiddleware)));
return UseMiddlewareExtensions.UseMiddlewareInterface(app, middleware);
}
如果middleware 继承IMiddleware,那么将会调用UseMiddlewareExtensions.UseMiddlewareInterface.
IMiddleware如下:
public interface IMiddleware
{
Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context, RequestDelegate next);
}
然后UseMiddlewareExtensions.UseMiddlewareInterface:
private static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddlewareInterface(
IApplicationBuilder app,
Type middlewareType)
{
return app.Use((Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>) (next => (RequestDelegate) (async context =>
{
IMiddlewareFactory middlewareFactory = (IMiddlewareFactory) context.RequestServices.GetService(typeof (IMiddlewareFactory));
if (middlewareFactory == null)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoMiddlewareFactory((object) typeof (IMiddlewareFactory)));
IMiddleware middleware = middlewareFactory.Create(middlewareType);
if (middleware == null)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareUnableToCreateMiddleware((object) middlewareFactory.GetType(), (object) middlewareType));
try
{
await middleware.InvokeAsync(context, next);
}
finally
{
middlewareFactory.Release(middleware);
}
})));
上面的大意就是封装一个中间件,里面调用的方法就InvokeAsync。这个很好理解。
MethodInfo[] array = ((IEnumerable<MethodInfo>) middleware.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public)).Where<MethodInfo>((Func<MethodInfo, bool>) (m => string.Equals(m.Name, "Invoke", StringComparison.Ordinal) || string.Equals(m.Name, "InvokeAsync", StringComparison.Ordinal))).ToArray<MethodInfo>();
if (array.Length > 1)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddleMutlipleInvokes((object) "Invoke", (object) "InvokeAsync"));
if (array.Length == 0)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoInvokeMethod((object) "Invoke", (object) "InvokeAsync", (object) middleware));
获取Invoke和InvokeAsync方法。
如果这两个方法同时存在,抛出异常。
如果一个都没有抛出异常。
if (!typeof (Task).IsAssignableFrom(methodInfo.ReturnType))
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNonTaskReturnType((object) "Invoke", (object) "InvokeAsync", (object) "Task"));
ParameterInfo[] parameters = methodInfo.GetParameters();
if (parameters.Length == 0 || parameters[0].ParameterType != typeof (HttpContext))
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoParameters((object) "Invoke", (object) "InvokeAsync", (object) "HttpContext"));
object[] objArray = new object[args.Length + 1];
objArray[0] = (object) next;
Array.Copy((Array) args, 0, (Array) objArray, 1, args.Length);
如果返回结果不是一个Task报错。
如果里面的第一个参数不是HttpContext 报错。
object[] objArray = new object[args.Length + 1];
objArray[0] = (object) next;
Array.Copy((Array) args, 0, (Array) objArray, 1, args.Length);
object instance = ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance(app.ApplicationServices, middleware, objArray);
if (parameters.Length == 1)
return (RequestDelegate) methodInfo.CreateDelegate(typeof (RequestDelegate), instance);
Func<object, HttpContext, IServiceProvider, Task> factory = UseMiddlewareExtensions.Compile<object>(methodInfo, parameters);
return (RequestDelegate) (context =>
{
IServiceProvider serviceProvider = context.RequestServices ?? applicationServices;
if (serviceProvider == null)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareIServiceProviderNotAvailable((object) "IServiceProvider"));
return factory(instance, context, serviceProvider);
});
上面表示含义是实例化函数的第一个参数应该是RequestDelegate。
然后通过反射生成具体的对象。
如果Invoke或者InvokeAsync 只有一个参数的话,也就是只有HttpContext参数,直接通过CreateDelegate,创建委托。
如果不止的话,就通过一系列操作进行转换,这里就不介绍了,细节篇介绍了。毕竟是实践篇。
结
以上只是个人整理,如果有错误,望请指点。
下一节异常处理中间件。
重新整理 .net core 实践篇—————中间件[十九]的更多相关文章
- ASP.NET Core 2.2 十九. 你扔过来个json,我怎么接
原文:ASP.NET Core 2.2 十九. 你扔过来个json,我怎么接 前文说道了Action的激活,这里有个关键的操作就是Action参数的映射与模型绑定,这里即涉及到简单的string.in ...
- 重新整理 .net core 实践篇————配置应用[一]
前言 本来想整理到<<重新整理.net core 计1400篇>>里面去,但是后来一想,整理 .net core 实践篇 是偏于实践,故而分开. 因为是重新整理,那么就从配置开 ...
- 重新整理 .net core 实践篇————依赖注入应用[二]
前言 这里介绍一下.net core的依赖注入框架,其中其代码原理在我的另一个整理<<重新整理 1400篇>>中已经写了,故而专门整理应用这一块. 以下只是个人整理,如有问题, ...
- 重新整理 .net core 实践篇——— 权限中间件源码阅读[四十六]
前言 前面介绍了认证中间件,下面看一下授权中间件. 正文 app.UseAuthorization(); 授权中间件是这个,前面我们提及到认证中间件并不会让整个中间件停止. 认证中间件就两个作用,我们 ...
- 重新整理 .net core 实践篇—————异常中间件[二十]
前言 简单介绍一下异常中间件的使用. 正文 if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } 这样写入中间件哈,那么在env环 ...
- 重新整理 .net core 实践篇——— UseEndpoints中间件[四十八]
前言 前文已经提及到了endponint 是怎么匹配到的,也就是说在UseRouting 之后的中间件都能获取到endpoint了,如果能够匹配到的话,那么UseEndpoints又做了什么呢?它是如 ...
- 重新整理 .net core 实践篇—————领域事件[二十九]
前文 前面整理了仓储层,工作单元模式,同时简单介绍了一下mediator. 那么就mediator在看下领域事件启到了什么作用吧. 正文 这里先注册一下MediatR服务: // 注册中间者:Medi ...
- 重新整理 .net core 实践篇————重定向攻击[三十九]
前言 简单介绍一下重定向攻击. 正文 攻击思路: 看着上面挺复杂的,其实是一些很简单的步骤. 攻击者通过某些手段,让用户打开了一个好站点,打开的这个地址里面带有重定向信息,重定向信息就是自己伪造的站点 ...
- 重新整理 .net core 实践篇—————服务与配置之间[十一二]
前言 前面基本介绍了,官方对于asp .net core 设计配置和设计服务的框架的一些思路.看下服务和配置之间是如何联系的吧. 正文 服务: public interface ISelfServic ...
随机推荐
- c# p/invoke 无法加载指定的dll 找不到指定的模块 解决方法
写的程序本来开始好好的,不知道怎么突然就出现了以上这个问题,纠结了好久,网上找了各种方法,比如什么嵌入dll,在system32下面放入dll等等,均宣告失败 下面把我的解决方法写出来,以后只要是这个 ...
- apache-tomcat-7.0.92
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1wnTSjTknYfaeDV_pakrC9g 提取码:see7
- 基于linux信号的timeout装饰器
在做基于ray的分布式任务处理时,偶尔遇到由于ray集群不稳定导致的长时间连接不上,进而导致程序卡死,无法向后端返回任务状态的情况.但是ray的初始化函数本身未实现超时机制,因此设计基于多线程+信号的 ...
- 全套visio版本安装教程及下载地址
1:visio 2003 安装教程及下载地址 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vhJUagKBz3vM-Dru0cwYow 2:visio 2007 安装教程及下载地址 http ...
- TortoiseGit生成.PPK拓展名的密钥
在TortoiseGit 运行目录下找到puttygen.exe 工具 运行puttygen.exe genertate :代表动态生成新的内容 load :导入旧的密钥 save private k ...
- Python分支结构你真的搞定了吗?
分支结构 分支结构能够让计算机像人一样进行思考,应对不同的场景做出不同的回应. Python中不支持switch语法,目前仅支持if/else形式,但是在Python3.10的测试版本中,貌似支持了s ...
- c++逆向分析----返回对象
对象不使用默认析构函数 class Test { public: char cNum1; int iNum2; int* pInt; }; Test _ReturnObject() { Test st ...
- 逆向工程初步160个crackme-------2
有了第一个crackme的经验后,这个crackme用了半个小时就验证成功了.(思路和第一个crackme相似) 动态调试工具:ollydbg (2.10) 文件分析工具:PEID (0.95) 同样 ...
- $(cd "$(dirname "$0")",pwd) 解析
xx.sh 文件内容如下: #!/bin/bash BIN_FOLDER=$(cd "$(dirname "$0")";pwd) echo $BIN_FOLDE ...
- teprunner测试平台定时任务这次终于稳了
teprunner测试平台已经有一个多月没有更新了,主要原因是定时任务不够稳定,经过反复试错,找到了解决办法,这次终于稳定了. 本文开发内容 作为测试平台而言,定时任务算是必备要素了,只有跑起来的自动 ...
