二叉树 & 平衡二叉树 算法(Java实现)
二叉树
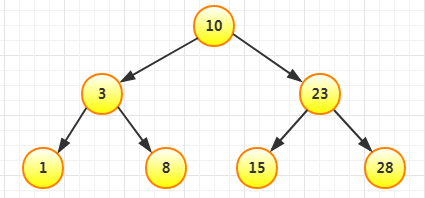
比如我要依次插入10、3、1、8、23、15、28。先插入10作为根节点:

然后插入3,比10小,放在左边:
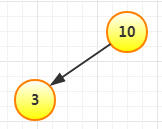
再插入1,比10和3小,放在3左边:

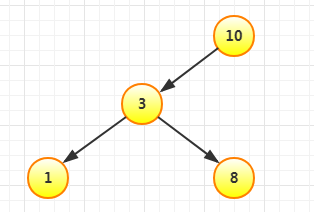
再插入8,比10小,比3大,放在3右边:
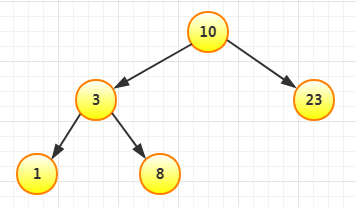
再插入23,比10大,放在10右边:
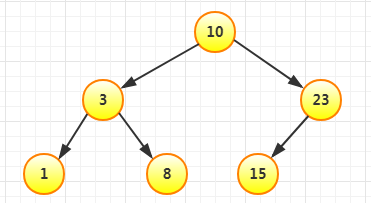
再插入15,比10大,比23小,放在23左边:
最后插入28,比10和23大,放在23右边:
代码实现:
package com.demo.tree; import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { public static void main(String[] args){
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.batchInsert(new int[]{10,3,1,8,23,15,28});
tree.prePrint();
tree.midPrint();
tree.postPrint();
tree.tierPrint();
tree.printDepth();
} private Node root; /**
* 节点
*/
private class Node{
int data; // 数据
Node left; // 左指针
Node right; // 右指针 private Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
} /**
* 插入
* @param data
*/
public void insert(int data){
Node newData = new Node(data);
if (root == null){
root = newData;
}else{
Node parent = root;
while (true){
if (data < parent.data){
// 如果左边为空,那新数据就直接放在这
if (parent.left == null){
parent.left = newData;
break;
}
// 进入左节点
parent = parent.left;
}else{
// 如果右边为空,那新数据就直接放在这
if (parent.right == null){
parent.right = newData;
break;
}
// 进入右节点
parent = parent.right;
}
}
}
} /**
* 批量插入
* @param arr
*/
public void batchInsert(int[] arr){
for (int data : arr){
insert(data);
}
} /**
* 前序遍历
*/
public void prePrint(){
System.out.print("前序遍历\t");
if (root != null){
pre(root);
}
System.out.println();
} private void pre(Node node){
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
pre(node.left);
pre(node.right);
}
} /**
* 中序遍历
*/
public void midPrint(){
System.out.print("中序遍历\t");
if (root != null){
mid(root);
}
System.out.println();
} private void mid(Node node){
if (node != null) {
mid(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
mid(node.right);
}
} /**
* 后序遍历
*/
public void postPrint(){
System.out.print("后序遍历\t");
if (root != null){
post(root);
}
System.out.println();
} private void post(Node node){
if (node != null) {
post(node.left);
post(node.right);
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
}
} /**
* 层序遍历,利用队列先进先出
*/
public void tierPrint(){
if (root != null){
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
System.out.print("层序遍历\t");
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Node temp = queue.remove();
System.out.print(temp.data + "\t");
if (temp.left != null){
// 左节点不为空,放进队列
queue.add(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null){
// 右节点不为空,放进队列
queue.add(temp.right);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
} /**
* 求树高
*/
public void printDepth(){
if (root == null){
System.out.println(0);
}else{
System.out.println("树高\t" + getDepth(root));
}
} private int getDepth(Node node){
if (node == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(getDepth(node.left), getDepth(node.right))+1;
} }
测试:

平衡二叉树
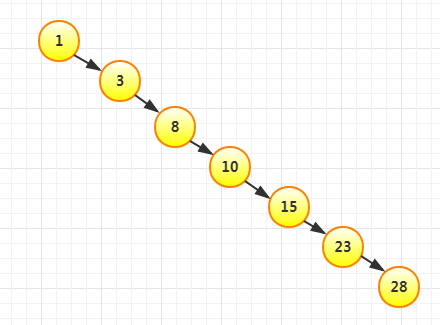
前面的二叉树有个问题,如果我们按照顺序插入,那么这个树就会退化成一个线性链表,这个时候引入平衡二叉树来解决。
平衡二叉树要维持平衡需要旋转操作
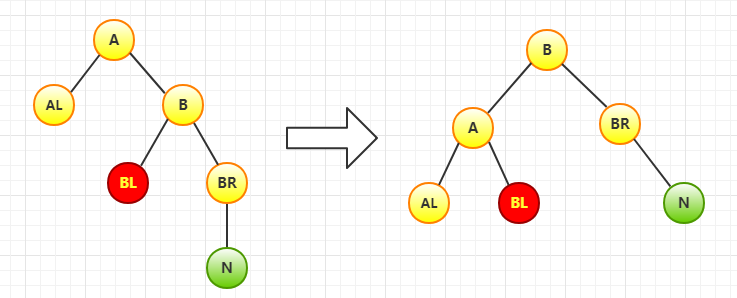
LL型(在A的左孩子(L)的左子树(L)上插入新结点)

过程:
1. 将A的左孩子B提升为根节点
2. 将A降级为B的右孩子
3. 将B的右孩子调整为A的左孩子
RR型(在A的右孩子(R)的右子树(R)上插入新结点)
过程:
1. 将A的右孩子B提升为根节点
2. 将A降级为B的左孩子
3. 将B的左孩子调整为A的右孩子
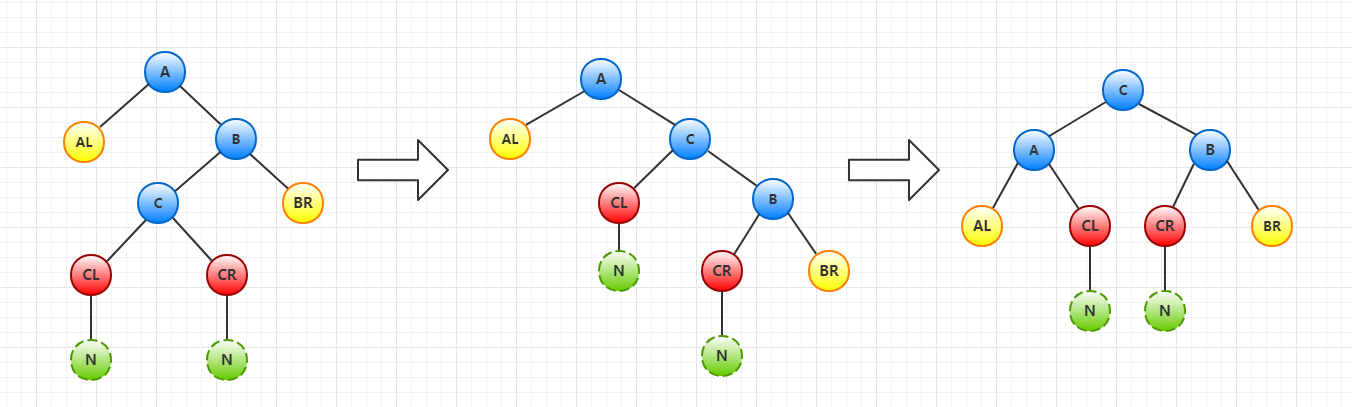
LR型(在A的左孩子(L)的右子树(R)上插入新结点)【插入在C任意一颗子树都可以】

过程:
1. B、C节点左旋。
2. A、C节点右旋。
RL型(在A的右孩子(R)的左子树(L)上插入新结点)【插入在C任意一颗子树都可以】
过程:
1. B、C节点右旋。
2. A、C节点左旋。
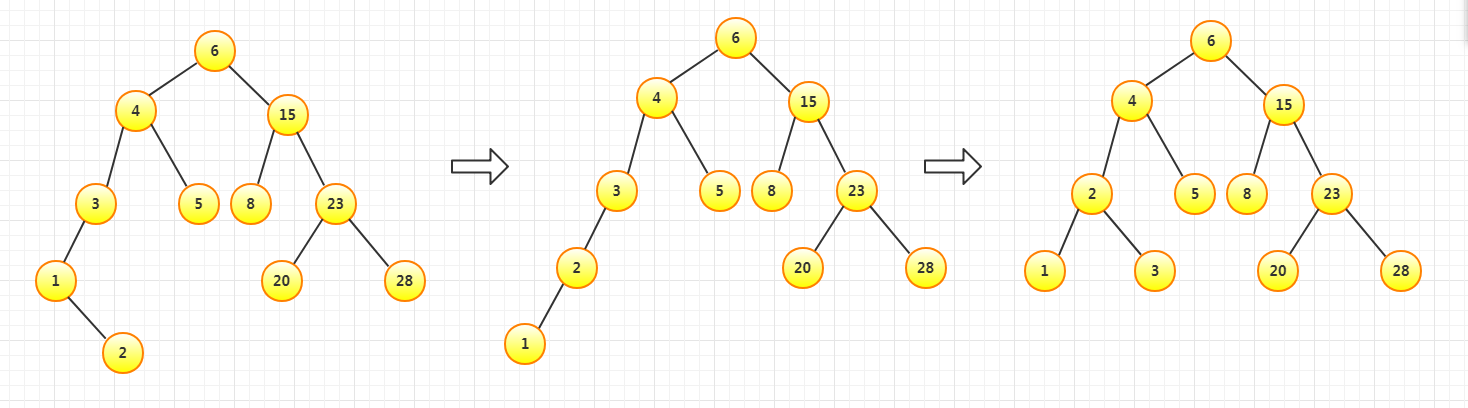
插入步骤图解
平衡二叉树的插入,例如依次插入:8,6,3,4,5,20,15,23,28,1,2
插入8先作为根节点,插入6依然平衡,插入3不平衡,进行一次右旋(LL)
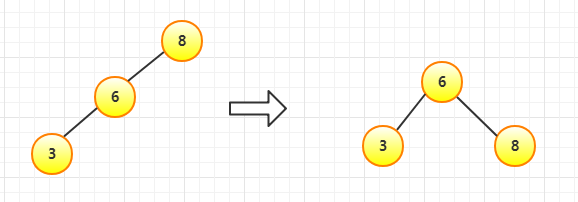
插入4依然平衡,插入5不平衡,进行左旋(RR)
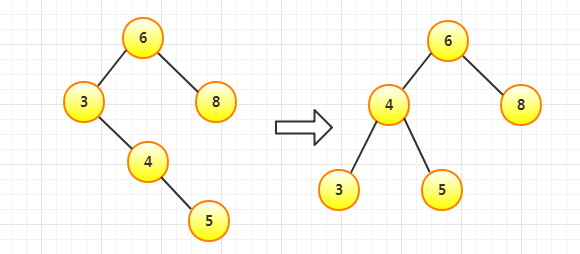
插入20依然平衡,插入15不平衡,先右旋再左旋(RL)
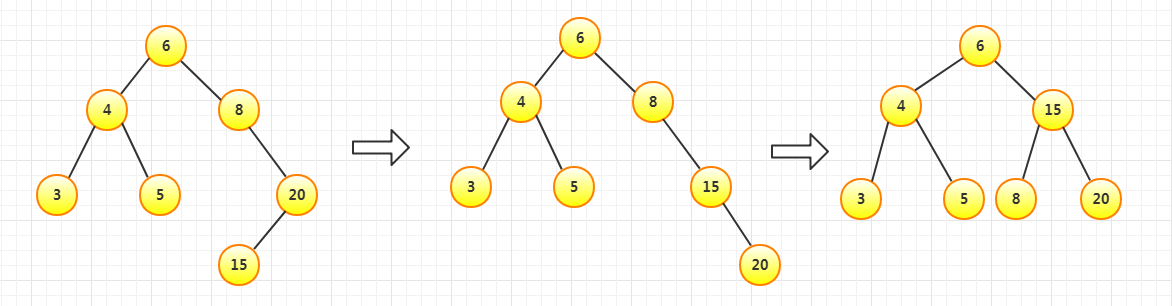
插入23依然平衡,插入28不平衡,进行一次左旋(RR)
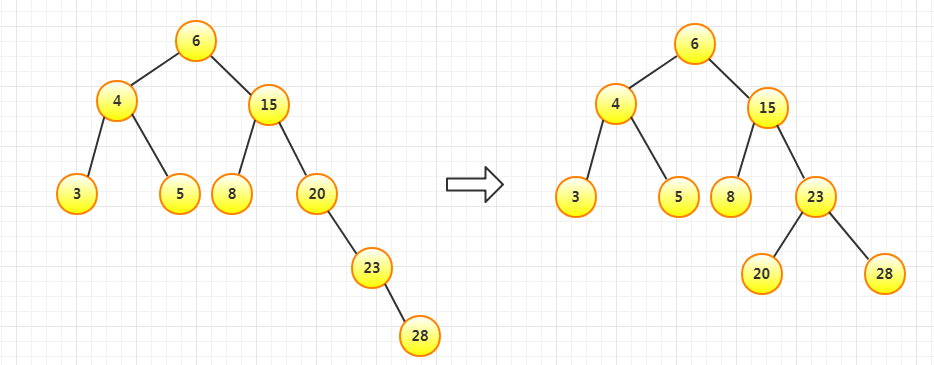
插入1依然平衡,插入2不平衡,先左旋再右旋(LR)
代码
package com.demo.tree; import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue; public class BalancedBinaryTree { public static void main(String[] args){
BalancedBinaryTree tree = new BalancedBinaryTree();
tree.batchInsert(new int[]{8,6,3,4,5,20,15,23,28,1,2});
tree.tierPrint();
} private Node root; /**
* 节点
*/
private class Node{
int data; // 数据
Node left; // 左指针
Node right; // 右指针 private Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
} /**
* 右旋操作(左孩子的左子树插入节点)
* @param p
*/
private Node rightRotate(Node p){
Node temp = p.left; // temp指向p的左子树
p.left = temp.right; // p的左子树指向temp的右子树
temp.right = p;
return temp;
} /**
* 左旋操作(右孩子的右子树插入节点)
* @param p
*/
private Node leftRotate(Node p){
Node temp = p.right; // temp指向p的右子树
p.right = temp.left; // p的右子树指向temp的左子树
temp.left = p;
return temp;
} /**
* 先左旋再右旋(左孩子的右子树插入节点)
* @param p
*/
private Node leftRightRotate(Node p){
p.left = leftRotate(p.left);
return rightRotate(p);
} /**
* 先右旋再左旋(右孩子的左子树插入节点)
* @param p
*/
private Node rightLeftRotate(Node p){
p.right = rightRotate(p.right);
return leftRotate(p);
} /**
* 树高
* @param node
* @return
*/
private int getDepth(Node node){
if (node == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(getDepth(node.left), getDepth(node.right))+1;
} /**
* 平衡因子(左高:>1 等高:0 右高:<-1)
* @return
*/
public int balanceFactor(Node node){
if (node == null){
return 0;
}
return getDepth(node.left) - getDepth(node.right);
} /**
* 插入
* @param node
* @param data
*/
public Node insert(Node node, int data){
Node newData = new Node(data);
if (node == null){
return newData;
}
if (data < node.data){
node.left = insert(node.left, data);
}else if (data > node.data){
node.right = insert(node.right, data);
}else{
return node;
}
int bf = balanceFactor(node); if (bf > 1 && data < node.left.data){
// LL
System.out.println("LL" + data);
return rightRotate(node);
}else if (bf < -1 && data > node.right.data){
// RR
System.out.println("RR" + data);
return leftRotate(node);
}else if (bf > 1 && data > node.left.data){
// LR
System.out.println("LR" + data);
return leftRightRotate(node);
}else if (bf < -1 && data < node.right.data){
// RL
System.out.println("RL" + data);
return rightLeftRotate(node);
}
return node;
} /**
* 批量插入
* @param arr
*/
public void batchInsert(int[] arr){
for (int data : arr){
root = insert(root, data);
}
} /**
* 前序遍历
*/
public void prePrint(){
System.out.print("前序遍历\t");
if (root != null){
pre(root);
}
System.out.println();
} private void pre(Node node){
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
pre(node.left);
pre(node.right);
}
} /**
* 中序遍历
*/
public void midPrint(){
System.out.print("中序遍历\t");
if (root != null){
mid(root);
}
System.out.println();
} private void mid(Node node){
if (node != null) {
mid(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
mid(node.right);
}
} /**
* 后序遍历
*/
public void postPrint(){
System.out.print("后序遍历\t");
if (root != null){
post(root);
}
System.out.println();
} private void post(Node node){
if (node != null) {
post(node.left);
post(node.right);
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
}
} /**
* 层序遍历,利用队列先进先出
*/
public void tierPrint(){
if (root != null){
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
System.out.print("层序遍历\t");
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Node temp = queue.remove();
System.out.print(temp.data + "\t");
if (temp.left != null){
// 左节点不为空,放进队列
queue.add(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null){
// 右节点不为空,放进队列
queue.add(temp.right);
}
}
}
} }
二叉树 & 平衡二叉树 算法(Java实现)的更多相关文章
- 找出 int 数组的平衡点 & 二叉树 / 平衡二叉树 / 满二叉树 / 完全二叉树 / 二叉查找树
找出 int 数组的平衡点 左右两边和相等, 若存在返回平衡点的值(可能由多个); 若不存在返回 -1; ``java int [] arr = {2,3,4,2,4}; ```js const ar ...
- 无向图的最短路径算法JAVA实现
一,问题描述 给出一个无向图,指定无向图中某个顶点作为源点.求出图中所有顶点到源点的最短路径. 无向图的最短路径其实是源点到该顶点的最少边的数目. 本文假设图的信息保存在文件中,通过读取文件来构造图. ...
- 无向图的最短路径算法JAVA实现(转)
一,问题描述 给出一个无向图,指定无向图中某个顶点作为源点.求出图中所有顶点到源点的最短路径. 无向图的最短路径其实是源点到该顶点的最少边的数目. 本文假设图的信息保存在文件中,通过读取文件来构造图. ...
- 归并排序算法 java 实现
归并排序算法 java 实现 可视化对比十多种排序算法(C#版) [直观学习排序算法] 视觉直观感受若干常用排序算法 算法概念 归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Di ...
- 快速排序算法 java 实现
快速排序算法 java 实现 快速排序算法Java实现 白话经典算法系列之六 快速排序 快速搞定 各种排序算法的分析及java实现 算法概念 快速排序是C.R.A.Hoare于1962年提出的一种划分 ...
- 堆排序算法 java 实现
堆排序算法 java 实现 白话经典算法系列之七 堆与堆排序 Java排序算法(三):堆排序 算法概念 堆排序(HeapSort)是指利用堆积树(堆)这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法,可以利用数组的特 ...
- Atitit 电子商务订单号码算法(java c# php js 微信
Atitit 电子商务订单号码算法(java c# php js 微信 1.1. Js版本的居然钱三爷里面没有..只好自己实现了. 1.2. 订单号标准化...长度16位 1.3. 订单号的结构 前 ...
- 关于Leetcode上二叉树的算法总结
二叉树,结构很简单,只是比单链表复杂了那么一丢丢而已.我们先来看看它们结点上的差异: /* 单链表的结构 */ struct SingleList{ int element; struct Singl ...
- 基于FP-Tree的关联规则FP-Growth推荐算法Java实现
基于FP-Tree的关联规则FP-Growth推荐算法Java实现 package edu.test.ch8; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util ...
随机推荐
- iOS开发工具:Alcatraz、SVGKit、Lin以及Transformifier等
转自:http://www.cocoachina.com/applenews/devnews/2013/0606/6352.html Alcatraz:Xcode包管理器 Alcatraz是一个开源的 ...
- 金蝶BOS元模型分析
对一些需求变化多样的产品而言,做好可变性设计是非常重要的.国外做得好的有Siebel,国内有金蝶的BOS,实际上金蝶的BOS很多理念跟Siebel是相似的,呵呵...他们都是采用MDD的方式来解决可变 ...
- testNG结果入库
一.使用IReporter接口 https://blog.csdn.net/oqqJohn1234567890/article/details/80900511 此文章中将结果数据打印成文本.
- Android 工作流提交审批填写审批意见PopWindow工具类
公司的项目中几乎都会有走工作流这个环节,为了提高效率,现在特意把弹出的填写审批意见PopWindow改转成工具类,提高效率,免得下次又得整.先看运行效果.
- WorkFlow三:CLASS事件触发工作流
1.创建关键字段结构.这里没有新建,使用前面创建的结构: 2.SE24创建类:保存激活. 3.接口里添加IF_WORKFLOW并激活.(其他两个激活就出现了,不用管) 4.在属性页签中定义两个属性,其 ...
- idea使用过程中的一些常见问题,做个笔记
:当实现这个接口方法时重载是不允许的. 首先我相信我的代码肯定没问题,因为我实现的接口确实有这个方法.在编程阶段就提示这个错误,于是我有理由相信应该是编译错误!通过google,解决办法so easy ...
- C# 连接数据操作的时候抛异常,连接超时
先说说我的业务.我在发送优惠券的时候,同时给6千多个会员发送优惠券,执行了update 和insert语句,这写语句都是通过字符串拼接而来的.update和insert语句加起来一共是一万多条语句.在 ...
- js 字符串 有没有 像C# @ 那种 换行也可以显示的方法 \
- eclipse 工作空间配置UTF-8编码格式
配置前端页面编码格式 1. Windows-->preferences 2. web-->jsp file-->Encoding 3. OK保存 配置java文件编码格式 1. W ...
- Linux服务管理之SSH
Linux服务SSH ssh服务: 管理服务器的方式: 本地管理类 (安装系统,故障修复) SHH远程连接方式 ...
