android 进程/线程管理(一)----消息机制的框架
一:android 进程和线程
进程是程序运行的一个实例。android通过4大主件,弱化了进程的概念,尤其是在app层面,基本不需要关系进程间的通信等问题。
但是程序的本质没有变,尤其是多任务系统,以事件为驱动的软件系统基本模式都是如下:
程序的入口一般是main:
1.初始化:
比如创建窗口,申请资源等。
2.进入while(true)
在循环中处理各种事件,直到进程退出。
四大组件是进程的部分载体,配置进程在androidmanifest.xml里面,android:process 属性。
当然默认所有的都在同一个进程里面,由application里面配置,默认进程为apk的包名。
线程是进程的有机组成部分,是CPU调度的基础。
一般情况下,都有主线程和其他线程之分,只有主线程才可以刷新UI。
应用程序启动后,将创建ActivityThread 主线程。
不同包名的组件可以一定的方式运行在同一个进程中。
一个Activity启动后,至少会有3个线程。一个主线程和2个binder线程。
二:android 进程内的消息驱动机制---Handler,MessageQueue,Runnable,Looper
1.Runnable & MessageQueue:
Runnable 和Message 是消息的2种载体。
消息的行为本质上就是 一段操作Runnable,或者是一段数据Message,包含这操作内容,由handlemessage来判断处理。
他们的操作方式就是:
public final boolean post(Runnable r)
{
return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0);
}
public final boolean postAtTime(Runnable r, long uptimeMillis)
public final boolean postAtTime(Runnable r, Object token, long uptimeMillis)
上面就是Runnable的方法,可以看到Runnable会被分装成Message的形式发送。
private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) {
Message m = Message.obtain();
m.callback = r;
return m;
}
所以本质上,都是以Message的封装方式处理。
最终所有的消息都会放入MessageQueue里面。
MessageQueue并不是一个真正的队列,而是链表。
Looper就是循环在某件事情,类似于while(true)干的事情。
Handler就是真正做事情的。
Looper不断的从MessageQueue从取出数据,然后交给handler来处理。
2.Handler:
framework/base/core/android/os/Handler.java
其实handler的作用,它的注释已经解释的非常清楚。
/**
* A Handler allows you to send and process {@link Message} and Runnable
* objects associated with a thread's {@link MessageQueue}. Each Handler
* instance is associated with a single thread and that thread's message
* queue. When you create a new Handler, it is bound to the thread /
* message queue of the thread that is creating it -- from that point on,
* it will deliver messages and runnables to that message queue and execute
* them as they come out of the message queue.
*
* <p>There are two main uses for a Handler: (1) to schedule messages and
* runnables to be executed as some point in the future; and (2) to enqueue
* an action to be performed on a different thread than your own.
*
* <p>When posting or sending to a Handler, you can either
* allow the item to be processed as soon as the message queue is ready
* to do so, or specify a delay before it gets processed or absolute time for
* it to be processed. The latter two allow you to implement timeouts,
* ticks, and other timing-based behavior.
*/
这个一共三段内容,大意是:
1)handler使用runnable或者message的方式传递,存储在一个thread的messagequeue里面。
当你创建一个新的handler的时候,他会与这个创建它的线程绑定。
对于一个Thread 来说MessageQueue,和Looper只有一个。
2)使用handler一般有2种场景。
希望do runnable或者某种Message 在in the future.
或者把一个action(Runnable or Message)传递到其他线程进行操作。
常见的操作就是在工作线程中使用主线程handler来操作UI。
3)你可以让handler直接操作message内容,或者等待一段时间,这个时间是可以配置的。
handle的2大功能
处理message:
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) 分发消息
public void handleMessage(Message msg) 处理消息,该方法通常情况下,须由子类继承。
Looper.loop()方法会调用dispatchMessage来处理消息。
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
handler的子类通过重载该方法,可以修改handler的消息派发方式。
handler的第二个作用是把message & Runnable分装到MessageQueue里面。
handler,messagequeue,looper目的是什么,目的就是启动消息机制。
MessageQueue:
MessageQueue从哪里得到,从Handler源码看到,是从Looper里面来的。
public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = looper;
mQueue = looper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
Looper:
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
Looper 构造函数就干了2件事。
创建Messagequeue,所以 每个Looper都有唯一的一个MessageQueue与之对应。
得到运行thread。
// sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().
static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();
Looper有个特殊的变量,ThreadLocal, 这个对象只对自己所在的线程全局,其他的线程无法看到它。
Looper提供了很多static的方法,所以肯定还有一些能都识别“身份“的方法。
这些方法在我们使用looper 的时候,最重要的是如下2个:
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
/**
* Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call
* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.
*/
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; // Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
} // This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
} msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
} // Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
} msg.recycle();
}
}
prepare才是looper创建以及和thread绑定的地方。
looper.loop()方法是整个looper机制启动的地方。
从此thread就会接受消息和处理消息了。
这里有个小问题:
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
一开始的时候,MessageQueue handler没有传递消息进队列,按理说取到的消息是null,这样looper就直接退出了。
这个问题等到分析源码的时候,在解决。
这样handler,messaqequeue,looper, 和thread都关联起来了。
下面还有一个mainlooper的问题。
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
Looper.loop();
}
以上是ActivityThread的部分入口函数main的源码:
可见prepareMainLooper()的方法,是给主线程使用的。
而looper那边的
private static Looper sMainLooper; // guarded by Looper.class
是为了给其他线程应用使用。
这样其他线程可以给主线程发消息。
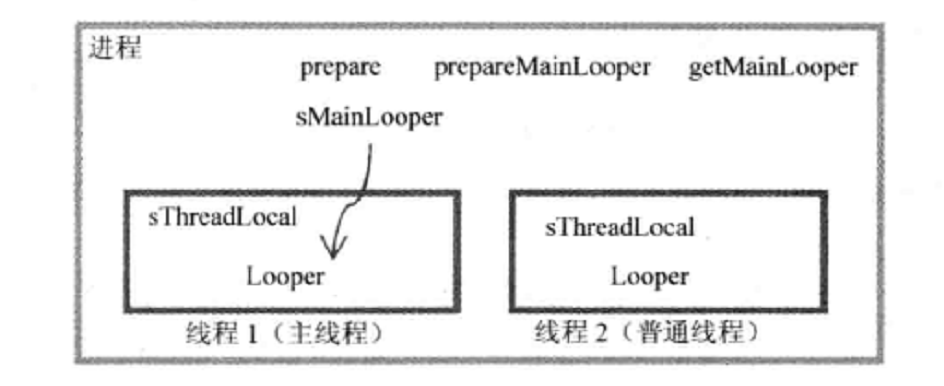
如图所示:主线程的looper将由sMainLooper作为应用,保存在static空间中,其他工作线程可以访问它
至此,整个消息机制的框架已经驱动起来。
本文参考:
1.《深入理解android内核设计思想》林学森
2.《Android内核剖析》
相关文章:
android 进程/线程管理(三)----Thread,Looper / HandlerThread / IntentService
android 进程/线程管理(一)----消息机制的框架的更多相关文章
- android 进程/线程管理(四)续----消息机制的思考(自定义消息机制)
继续分析handler 和looper 先看看handler的 public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) { if (msg.callback != null) ...
- android 进程/线程管理(四)----消息机制的思考(自定义消息机制)
关于android消息机制 已经写了3篇文章了,想要结束这个系列,总觉得少了点什么? 于是我就在想,android为什么要这个设计消息机制,使用消息机制是现在操作系统基本都会有的特点. 可是andro ...
- android 进程/线程管理(二)----关于线程的迷思
一:进程和线程的由来 进程是计算机科技发展的过程的产物. 最早计算机发明出来,是为了解决数学计算而发明的.每解决一个问题,就要打纸带,也就是打点. 后来人们发现可以批量的设置命令,由计算机读取这些命令 ...
- android 进程/线程管理(三)----Thread,Looper / HandlerThread / IntentService
Thread,Looper的组合是非常常见的组合方式. Looper可以是和线程绑定的,或者是main looper的一个引用. 下面看看具体app层的使用. 首先定义thread: package ...
- android学习-进程/线程管理-完整
我们知道,应用程序的主入口都是main函数--"它是一切事物的起源" main函数工作也是千篇一律的, 初始化 比如ui的初始化,向系统申请资源等. 进入死循环 再循环中处理各种事 ...
- Android 面试收集录5 消息机制
1.消息机制概述 1.1.消息机制的简介 在Android中使用消息机制,我们首先想到的就是Handler. 没错,Handler是Android消息机制的上层接口. Handler的使用过程很简单, ...
- 【转载】每个 Android 开发者必须知道的消息机制问题总结
Android的消息机制几乎是面试必问的话题,当然也并不是因为面试,而去学习,更重要的是它在Android的开发中是必不可少的,占着举足轻重的地位,所以弄懂它是很有必要的.下面就来说说最基本的东西. ...
- Android消息机制:Looper,MessageQueue,Message与handler
Android消息机制好多人都讲过,但是自己去翻源码的时候才能明白. 今天试着讲一下,因为目标是讲清楚整体逻辑,所以不追究细节. Message是消息机制的核心,所以从Message讲起. 1.Mes ...
- Android线程管理之ThreadLocal理解及应用场景
前言: 最近在学习总结Android的动画效果,当学到Android属性动画的时候大致看了下源代码,里面的AnimationHandler存取使用了ThreadLocal,激起了我很大的好奇心以及兴趣 ...
随机推荐
- C#的变迁史 - C# 2.0篇
在此重申一下,本文仅代表个人观点,如有不妥之处,还请自己辨别. 第一代的值类型装箱与拆箱的效率极其低下,特别是在集合中的表现,所以第二代C#重点解决了装箱的问题,加入了泛型.1. 泛型 - 珍惜生命, ...
- go语言操作mysql范例(增删查改)
http://blog.csdn.net/jesseyoung/article/details/40398321 go语言连接mysql简介 go官方仅提供了database package,d ...
- windows下用eclipse+goclipse插件+gdb搭建go语言开发调试环境
windows下用eclipse+goclipse插件+gdb搭建go语言开发调试环境 http://rongmayisheng.com/post/windows%E4%B8%8B%E7%94%A ...
- Mybatis if test中字符串比较
<if test=" name=='你好' "> <if> 这样会有问题,换成 <if test=' name=="你好" '&g ...
- IT男常用软件网站整理
1. 猎豹免费WiFI. 属于wifi共享软件. 360免费wifi.. 2. 悟空VPN, 免费VPN.http://www.wkdaili.net/ 3. PLSQL. 4. WinSCP, ...
- psql 命令行使用
如果觉得直接打开数据库修改繁琐,那么使用终端命令行是方便而又高大上的.下面来看看有哪些命令行: 说明:如果是正式的服务器则需要进行一个操作在执行下面的命令 ssh name @主机地址 -- name ...
- Visual C++中的一些编程小技巧
在应用程序的任意地方实现窗体的最大化.最小化.正常窗口等功能 // 设置Windows窗体的状态void CMinWindowsDlg::SetWindowState(int nWindowSize) ...
- LR常见问题整理
1.LoadRunner录制脚本时为什么不弹出IE浏览器? 当一台主机上安装多个浏览器时,LoadRunner录制脚本经常遇到不能打开浏览器的情况,可以用下面的方法来解决. LR11 无法弹出ie浏览 ...
- Ajax+PHP+MySQL 登陆示例
PHP是一门很好的语言,可以很方便的开发web应用程序,下面介绍一下PHP如何通过AJAX方式实现登录功能: 1 login.php 登录界面中,javascript脚本用ajax方式异步请求dolo ...
- 移动 Web 开发必备!时尚的 Off Canvas 导航
这里向大家分享一组创新的 Off Canvas 导航效果.Off Canvas 导航在一些移动应用程序中被广泛使用.当你点击汉堡按钮(一般是三条横线组成)时,在左侧或者右侧拉出一个菜单,这样可以充分利 ...
