RecyclerView 缓存机制详解
一 前言
RecyclerView据官方的介绍,该控件用于在有限的窗口中展示大量数据集,其实这样功能的控件我们并不陌生,例如:ListView、GridView。RecyclerView可以用来代替传统的ListView,GridView,更加强大和灵活。RecyclerView的使用网上有非常多案例,这里就不多说了,我们今天主要来看看RecyclerView 的缓存机制。
二 缓存机制Recycler详解
Recycler是RecyclerView的一个内部类。我们来看一下它的主要的成员变量。
- mChangedScrap 表示数据已经改变的ewHolder列表
- mAttachedScrap 未与RecyclerView分离的ViewHolder列表
- mCachedViews ViewHolder缓存列表,其大小由mViewCacheMax决定,默认DEFAULT_CACHE_SIZE为2,可动态设置。
- mViewCacheExtension 开发者可自定义的一层缓存,是虚拟类ViewCacheExtension的一个实例,开发者可实现方法getViewForPositionAndType(Recycler recycler, int position, int type)来实现自己的缓存。
- mRecyclerPool ViewHolder缓存池,在有限的mCachedViews中如果存不下ViewHolder时,就会把ViewHolder存入RecyclerViewPool中。
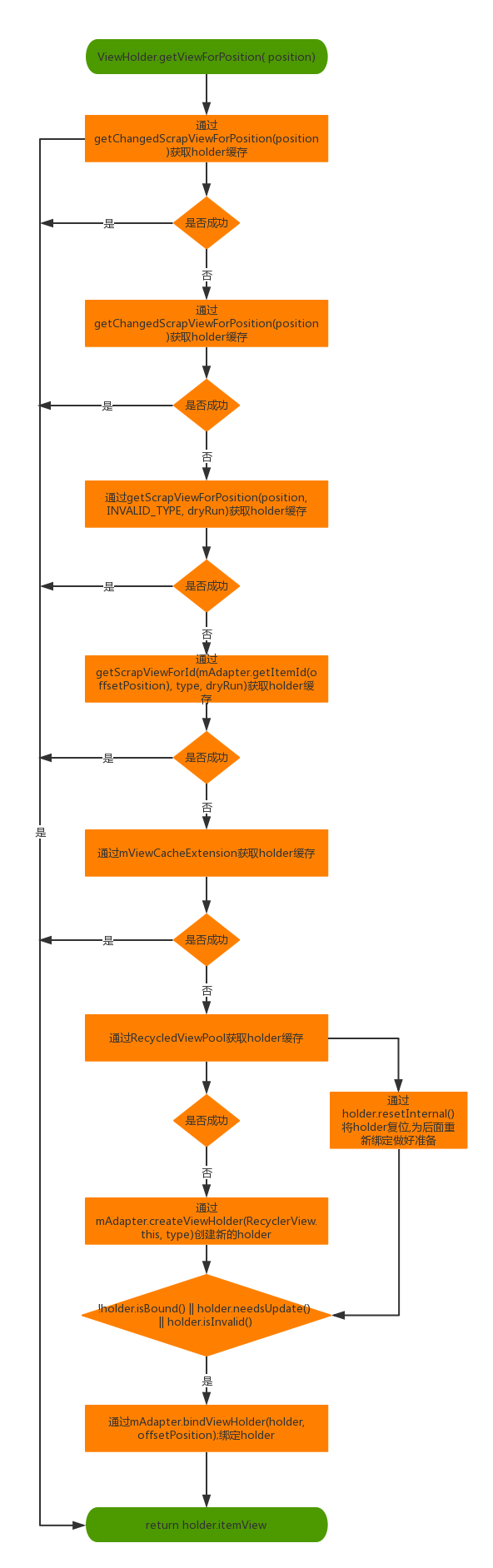
我们来看一张RecyclerView 缓存机制的流程图,如下图
贴上源码,如下。我们根据流程图和源码来分析RecyclerView的缓存机制。
public View getViewForPosition(int position) {
return getViewForPosition(position, false);
}
View getViewForPosition(int position, boolean dryRun) {
if (position < 0 || position >= mState.getItemCount()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Invalid item position " + position
+ "(" + position + "). Item count:" + mState.getItemCount());
}
boolean fromScrap = false;
ViewHolder holder = null;
// 0) If there is a changed scrap, try to find from there
if (mState.isPreLayout()) {
holder = getChangedScrapViewForPosition(position);
fromScrap = holder != null;
}
// 1) Find from scrap by position
if (holder == null) {
holder = getScrapViewForPosition(position, INVALID_TYPE, dryRun);
if (holder != null) {
if (!validateViewHolderForOffsetPosition(holder)) {
// recycle this scrap
if (!dryRun) {
// we would like to recycle this but need to make sure it is not used by
// animation logic etc.
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID);
if (holder.isScrap()) {
removeDetachedView(holder.itemView, false);
holder.unScrap();
} else if (holder.wasReturnedFromScrap()) {
holder.clearReturnedFromScrapFlag();
}
recycleViewHolderInternal(holder);
}
holder = null;
} else {
fromScrap = true;
}
}
}
if (holder == null) {
final int offsetPosition = mAdapterHelper.findPositionOffset(position);
if (offsetPosition < 0 || offsetPosition >= mAdapter.getItemCount()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Inconsistency detected. Invalid item "
+ "position " + position + "(offset:" + offsetPosition + ")."
+ "state:" + mState.getItemCount());
}
final int type = mAdapter.getItemViewType(offsetPosition);
// 2) Find from scrap via stable ids, if exists
if (mAdapter.hasStableIds()) {
holder = getScrapViewForId(mAdapter.getItemId(offsetPosition), type, dryRun);
if (holder != null) {
// update position
holder.mPosition = offsetPosition;
fromScrap = true;
}
}
if (holder == null && mViewCacheExtension != null) {
// We are NOT sending the offsetPosition because LayoutManager does not
// know it.
final View view = mViewCacheExtension
.getViewForPositionAndType(this, position, type);
if (view != null) {
holder = getChildViewHolder(view);
if (holder == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("getViewForPositionAndType returned"
+ " a view which does not have a ViewHolder");
} else if (holder.shouldIgnore()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("getViewForPositionAndType returned"
+ " a view that is ignored. You must call stopIgnoring before"
+ " returning this view.");
}
}
}
if (holder == null) { // fallback to recycler
// try recycler.
// Head to the shared pool.
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "getViewForPosition(" + position + ") fetching from shared "
+ "pool");
}
holder = getRecycledViewPool().getRecycledView(type);
if (holder != null) {
holder.resetInternal();
if (FORCE_INVALIDATE_DISPLAY_LIST) {
invalidateDisplayListInt(holder);
}
}
}
if (holder == null) {
holder = mAdapter.createViewHolder(RecyclerView.this, type);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "getViewForPosition created new ViewHolder");
}
}
}
// This is very ugly but the only place we can grab this information
// before the View is rebound and returned to the LayoutManager for post layout ops.
// We don't need this in pre-layout since the VH is not updated by the LM.
if (fromScrap && !mState.isPreLayout() && holder
.hasAnyOfTheFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_BOUNCED_FROM_HIDDEN_LIST)) {
holder.setFlags(0, ViewHolder.FLAG_BOUNCED_FROM_HIDDEN_LIST);
if (mState.mRunSimpleAnimations) {
int changeFlags = ItemAnimator
.buildAdapterChangeFlagsForAnimations(holder);
changeFlags |= ItemAnimator.FLAG_APPEARED_IN_PRE_LAYOUT;
final ItemHolderInfo info = mItemAnimator.recordPreLayoutInformation(mState,
holder, changeFlags, holder.getUnmodifiedPayloads());
recordAnimationInfoIfBouncedHiddenView(holder, info);
}
}
boolean bound = false;
if (mState.isPreLayout() && holder.isBound()) {
// do not update unless we absolutely have to.
holder.mPreLayoutPosition = position;
} else if (!holder.isBound() || holder.needsUpdate() || holder.isInvalid()) {
if (DEBUG && holder.isRemoved()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Removed holder should be bound and it should"
+ " come here only in pre-layout. Holder: " + holder);
}
final int offsetPosition = mAdapterHelper.findPositionOffset(position);
holder.mOwnerRecyclerView = RecyclerView.this;
mAdapter.bindViewHolder(holder, offsetPosition);
attachAccessibilityDelegate(holder.itemView);
bound = true;
if (mState.isPreLayout()) {
holder.mPreLayoutPosition = position;
}
}
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = holder.itemView.getLayoutParams();
final LayoutParams rvLayoutParams;
if (lp == null) {
rvLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) generateDefaultLayoutParams();
holder.itemView.setLayoutParams(rvLayoutParams);
} else if (!checkLayoutParams(lp)) {
rvLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) generateLayoutParams(lp);
holder.itemView.setLayoutParams(rvLayoutParams);
} else {
rvLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) lp;
}
rvLayoutParams.mViewHolder = holder;
rvLayoutParams.mPendingInvalidate = fromScrap && bound;
return holder.itemView;
}主流程 1
我们来看主流程源码的第14行
holder = getChangedScrapViewForPosition(position);
我们通过position匹配 mChangedScrap 获取holder缓存。
getChangedScrapViewForPosition(position)方法内部通过2种方法获取holder缓存。第一种通过mChangedScrap匹配
position获取holder缓存。第二种通过mChangedScrap匹配id获取holder缓存。源码如下。
ViewHolder getChangedScrapViewForPosition(int position) {
// If pre-layout, check the changed scrap for an exact match.
final int changedScrapSize;
if (mChangedScrap == null || (changedScrapSize = mChangedScrap.size()) == 0) {
return null;
}
// 第一种 通过 position来查找
for (int i = 0; i < changedScrapSize; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = mChangedScrap.get(i);
if (!holder.wasReturnedFromScrap() && holder.getLayoutPosition() == position) {
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP);
return holder;
}
}
//第二种 通过 id来查找
if (mAdapter.hasStableIds()) {
final int offsetPosition = mAdapterHelper.findPositionOffset(position);
if (offsetPosition > 0 && offsetPosition < mAdapter.getItemCount()) {
final long id = mAdapter.getItemId(offsetPosition);
for (int i = 0; i < changedScrapSize; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = mChangedScrap.get(i);
if (!holder.wasReturnedFromScrap() && holder.getItemId() == id) {
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP);
return holder;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}主流程 2
我们看一下主流程第19行代码。
holder = getScrapViewForPosition(position, INVALID_TYPE, dryRun);
通过position查找废弃的holder,我们来看一下getScrapViewForPosition方法内部实现,主要通过3种方法获取holder缓存。
第一种从mAttachedScrap中通过匹配position获取holder缓存。
第二种通过ChildHelper找到隐藏但是没有被移除的View,通过getChildViewHolderInt(view)方法获取holder缓存。
第三种从mCachedViews中通过匹配position获取holder缓存。
getScrapViewForPosition源码如下
ViewHolder getScrapViewForPosition(int position, int type, boolean dryRun) {
final int scrapCount = mAttachedScrap.size();
// 第一种从mAttachedScrap中通过匹配position获取holder缓存。
for (int i = 0; i < scrapCount; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = mAttachedScrap.get(i);
if (!holder.wasReturnedFromScrap() && holder.getLayoutPosition() == position
&& !holder.isInvalid() && (mState.mInPreLayout || !holder.isRemoved())) {
if (type != INVALID_TYPE && holder.getItemViewType() != type) {
Log.e(TAG, "Scrap view for position " + position + " isn't dirty but has" +
" wrong view type! (found " + holder.getItemViewType() +
" but expected " + type + ")");
break;
}
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP);
return holder;
}
}
//通过ChildHelper找到隐藏但是没有被移除的View,通过getChildViewHolderInt(view)方法获取holder缓存。
if (!dryRun) {
View view = mChildHelper.findHiddenNonRemovedView(position, type);
if (view != null) {
// This View is good to be used. We just need to unhide, detach and move to the
// scrap list.
final ViewHolder vh = getChildViewHolderInt(view);
mChildHelper.unhide(view);
int layoutIndex = mChildHelper.indexOfChild(view);
if (layoutIndex == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION) {
throw new IllegalStateException("layout index should not be -1 after "
+ "unhiding a view:" + vh);
}
mChildHelper.detachViewFromParent(layoutIndex);
scrapView(view);
vh.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP
| ViewHolder.FLAG_BOUNCED_FROM_HIDDEN_LIST);
return vh;
}
}
// Search in our first-level recycled view cache.
//第三种从mCachedViews中通过匹配position获取holder缓存。
final int cacheSize = mCachedViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < cacheSize; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = mCachedViews.get(i);
// invalid view holders may be in cache if adapter has stable ids as they can be
// retrieved via getScrapViewForId
if (!holder.isInvalid() && holder.getLayoutPosition() == position) {
if (!dryRun) {
mCachedViews.remove(i);
}
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "getScrapViewForPosition(" + position + ", " + type +
") found match in cache: " + holder);
}
return holder;
}
}
return null;
}主流程 3
我们看一下主流程第52行代码。
holder = getScrapViewForId(mAdapter.getItemId(offsetPosition), type, dryRun);
通过id获取holder缓存,getScrapViewForId方法内部主要通过2种方法获取holder缓存。
第一种从mAttachedScrap中通过匹配id获取holder缓存。
第二种从mCachedViews中通过匹配id获取holder缓存。
getScrapViewForId方法源码如下。
ViewHolder getScrapViewForId(long id, int type, boolean dryRun) {
//第一种从mAttachedScrap中通过匹配id获取holder缓存。
// Look in our attached views first
final int count = mAttachedScrap.size();
for (int i = count - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final ViewHolder holder = mAttachedScrap.get(i);
if (holder.getItemId() == id && !holder.wasReturnedFromScrap()) {
if (type == holder.getItemViewType()) {
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP);
if (holder.isRemoved()) {
// this might be valid in two cases:
// > item is removed but we are in pre-layout pass
// >> do nothing. return as is. make sure we don't rebind
// > item is removed then added to another position and we are in
// post layout.
// >> remove removed and invalid flags, add update flag to rebind
// because item was invisible to us and we don't know what happened in
// between.
if (!mState.isPreLayout()) {
holder.setFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE, ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE |
ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID | ViewHolder.FLAG_REMOVED);
}
}
return holder;
} else if (!dryRun) {
// if we are running animations, it is actually better to keep it in scrap
// but this would force layout manager to lay it out which would be bad.
// Recycle this scrap. Type mismatch.
mAttachedScrap.remove(i);
removeDetachedView(holder.itemView, false);
quickRecycleScrapView(holder.itemView);
}
}
}
//第二种从mCachedViews中通过匹配id获取holder缓存。
// Search the first-level cache
final int cacheSize = mCachedViews.size();
for (int i = cacheSize - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final ViewHolder holder = mCachedViews.get(i);
if (holder.getItemId() == id) {
if (type == holder.getItemViewType()) {
if (!dryRun) {
mCachedViews.remove(i);
}
return holder;
} else if (!dryRun) {
recycleCachedViewAt(i);
}
}
}
return null;
}主流程 4
我们看一下主流程第62行代码。
通过mViewCacheExtension.getViewForPositionAndType获取view,通过getChildViewHolder(view)获取holder缓存。源码如下
final View view = mViewCacheExtension
.getViewForPositionAndType(this, position, type);
if (view != null) {
holder = getChildViewHolder(view);
if (holder == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("getViewForPositionAndType returned"
+ " a view which does not have a ViewHolder");
} else if (holder.shouldIgnore()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("getViewForPositionAndType returned"
+ " a view that is ignored. You must call stopIgnoring before"
+ " returning this view.");
}
}
主流程 5
我们看一下主流程第83行代码。
holder = getRecycledViewPool().getRecycledView(type);
通过RecyclerView 的ViewHolder缓存池获取holder。
通过holder.resetInternal();方法将holder复位,为后续重新绑定做好准备。
主流程 6
我们看一下主流程第92行代码。
holder = mAdapter.createViewHolder(RecyclerView.this, type);创建新的holder
主流程 7
我们看一下主流程第119行代码。
if (!holder.isBound() || holder.needsUpdate() || holder.isInvalid())
判断是否要重新绑定ViewHolder。
主流程就是这样了。
三 总结
经过上面的分析,我们可以看出RecyclerView 缓存机制(Recycler)大致可以分为5级。
第一级 通过mChangedScrap匹配 position或者id获取holder缓存。
第二级 从mAttachedScrap中通过匹配position获取holder缓存,或者通过ChildHelper找到隐藏但是没有被移除的View,通过getChildViewHolderInt(view)方法获取holder缓存,或者
从mCachedViews中通过匹配position获取holder缓存。
第三级 从mAttachedScrap中通过匹配id获取holder缓存,或者
从mCachedViews中通过匹配id获取holder缓存。
第四级 从ViewCacheExtension获取holder缓存。
第五级 通过RecyclerView 的ViewHolder缓存池获取holder。
最后有什么理解不对的地方请大家多多指教。谢谢。
RecyclerView 缓存机制详解的更多相关文章
- 浏览器 HTTP 协议缓存机制详解
最近在准备优化日志请求时遇到了一些令人疑惑的问题,比如为什么响应头里出现了两个 cache control.为什么明明设置了 no cache 却还是发请求,为什么多次访问时有时请求里带了 etag, ...
- nginx平台初识(二) 浏览器 HTTP 协议缓存机制详解
1.缓存的分类 缓存分为服务端侧(server side,比如 Nginx.Apache)和客户端侧(client side,比如 web browser). 服务端缓存又分为 代理服务器缓存 和 反 ...
- PHP缓存机制详解
一,PHP缓存机制详解 我们可以使用PHP自带的缓存机制来完成页面静态化,但是仅靠PHP自身的缓存机制并不能完美的解决页面静态化,往往需要和其他静态化技术(通常是伪静态技术)结合使用. output ...
- 二,PHP缓存机制详解
一,PHP缓存机制详解 我们可以使用PHP自带的缓存机制来完成页面静态化,但是仅靠PHP自身的缓存机制并不能完美的解决页面静态化,往往需要和其他静态化技术(通常是伪静态技术)结合使用. output ...
- hibernate缓存机制详解
hiberante面试题—hibernate缓存机制详解 这是面试中经常问到的一个问题,可以按照我的思路回答,准你回答得很完美.首先说下Hibernate缓存的作用(即为什么要用缓存机制),然后再 ...
- 浏览器 HTTP 协议缓存机制详解--网络缓存决策机制流程图
1.缓存的分类 2.浏览器缓存机制详解 2.1 HTML Meta标签控制缓存 2.2 HTTP头信息控制缓存 2.2.1 浏览器请求流程 2.2.2 几个重要概念解释 3.用户行为与缓存 4.Ref ...
- IOS缓存机制详解
资料均来自互联网,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 .作者信息和本声明.否则将追究法律责任. 人魔七七:http://www.cnblogs.com/qiqibo/ 为什么要有缓存 应用需要 ...
- 【转】IOS缓存机制详解
人魔七七:http://www.cnblogs.com/qiqibo/ 为什么要有缓存 应用需要离线工作的主要原因就是改善应用所表现出的性能.将应用内容缓存起来就可以支持离线.我们可以用两种不同的缓存 ...
- MySQL缓存机制详解(一)
本文章拿来学习用||参考资料:http://www.2cto.com/database/201308/236361.html 对MySql查询缓存及SQL Server过程缓存的理解及总结 一.M ...
随机推荐
- CCF CSP 201403-3 命令行选项
CCF计算机职业资格认证考试题解系列文章为meelo原创,请务必以链接形式注明本文地址 CCF CSP 201403-3 命令行选项 问题描述 请你写一个命令行分析程序,用以分析给定的命令行里包含哪些 ...
- 成功实施的APS项目故事分享---我们数据治理的心路历程
一.故事背景 A企业是易普优APS重要客户之一,是某行业的龙头企业:APS项目历时7个月顺利上线,十个月验收!通过易普优APS的顺利实施,建成了集团的精益计划管控运营平台,树立计划的权威与指挥棒作用, ...
- Python djangorestframework安装库报错SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED
Python djangorestframework 安装库报错SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED 问题描述 使用pip按照virtualenv报错,如下: pip inst ...
- python之web框架(1):完成静态页面web服务器
python的web框架(1) 1.首先写一个最简单的web服务器,只能给客户回应一个固定的hello world的页面. from socket import * from multiprocess ...
- Jersey入门三:创建一个JavaEE的Web项目
1.在终端中输入如下命令,创建一个名为的simple-service-webapp项目: mvn archetype:generate -DarchetypeArtifactId=jersey-qui ...
- ThinkPHP导入第三方类库Vendor
详情查看ThinkPHP3.2手册 架构 > 自动加载 章节 vendor('Uploader','','.class.php')
- CODEVS 4655 序列终结者-splay(区间更新、区间翻转、区间最值)
4655 序列终结者 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目等级 : 大师 Master 题解 题目描述 Description 网上有许多题,就是给定一个序列,要 ...
- [CodeForces - 848B] Rooter's Song 思维 找规律
大致题意: 有一个W*H的长方形,有n个人,分别站在X轴或Y轴,并沿直线向对面走,第i个人在ti的时刻出发,如果第i个人与第j个人相撞了 那么则交换两个人的运动方向,直到走到长方形边界停止,问最后每个 ...
- merge into issue
ORA-30926: unable to get a stable set of rows in the source tables 一.经检查,这个错误是由于数据来源表(即语句中,using后面的f ...
- python opencv3 人脸识别的例子
一个人脸识别的例子 程序中用到了公共数据集, 欢迎去我的git上下载源码,源码里带有数据集 git:https://github.com/linyi0604/Computer-Vision 脚本中一个 ...