Notes on Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis (PLSA)
转自:http://www.hongliangjie.com/2010/01/04/notes-on-probabilistic-latent-semantic-analysis-plsa/
I highly recommend you read the more detailed version of http://arxiv.org/abs/1212.3900
Formulation of PLSA
There are two ways to formulate PLSA. They are equivalent but may lead to different inference process.
Let’s see why these two equations are equivalent by using Bayes rule.
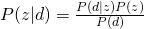
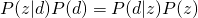
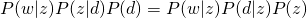
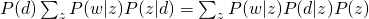
The whole data set is generated as (we assume that all words are generated independently):
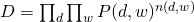
The Log-likelihood of the whole data set for (1) and (2) are:
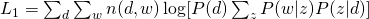
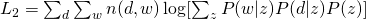
EM
For 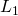 or
or 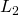 , the optimization is hard due to the log of sum. Therefore, an algorithm called Expectation-Maximization is usually employed. Before we introduce anything about EM, please note that EM is only guarantee to find a local optimum (although it may be a global one).
, the optimization is hard due to the log of sum. Therefore, an algorithm called Expectation-Maximization is usually employed. Before we introduce anything about EM, please note that EM is only guarantee to find a local optimum (although it may be a global one).
First, we see how EM works in general. As we shown for PLSA, we usually want to estimate the likelihood of data, namely 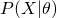 , given the paramter
, given the paramter 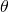 . The easiest way is to obtain a maximum likelihood estimator by maximizing
. The easiest way is to obtain a maximum likelihood estimator by maximizing 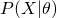 . However, sometimes, we also want to include some hidden variables which are usually useful for our task. Therefore, what we really want to maximize is
. However, sometimes, we also want to include some hidden variables which are usually useful for our task. Therefore, what we really want to maximize is 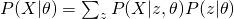 , the complete likelihood. Now, our attention becomes to this complete likelihood. Again, directly maximizing this likelihood is usually difficult. What we would like to show here is to obtain a lower bound of the likelihood and maximize this lower bound.
, the complete likelihood. Now, our attention becomes to this complete likelihood. Again, directly maximizing this likelihood is usually difficult. What we would like to show here is to obtain a lower bound of the likelihood and maximize this lower bound.
We need Jensen’s Inequality to help us obtain this lower bound. For any convex function 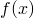 , Jensen’s Inequality states that :
, Jensen’s Inequality states that :
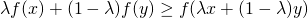
Thus, it is not difficult to show that :
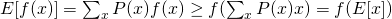
and for concave functions (like logarithm), it is :
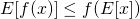
Back to our complete likelihood, we can obtain the following conclusion by using concave version of Jensen’s Inequality :
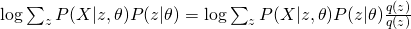
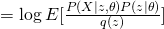
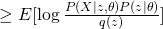
Therefore, we obtained a lower bound of complete likelihood and we want to maximize it as tight as possible. EM is an algorithm that maximize this lower bound through a iterative fashion. Usually, EM first would fix current 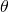 value and maximize
value and maximize 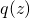 and then use the new
and then use the new 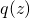 value to obtain a new guess on
value to obtain a new guess on 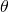 , which is essentially a two stage maximization process. The first step can be shown as follows:
, which is essentially a two stage maximization process. The first step can be shown as follows:
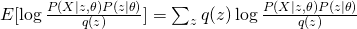
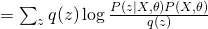
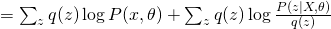
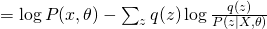
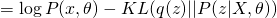
The first term is the same for all  . Therefore, in order to maximize the whole equation, we need to minimize KL divergence between
. Therefore, in order to maximize the whole equation, we need to minimize KL divergence between 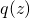 and
and 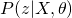 , which eventually leads to the optimum solution of
, which eventually leads to the optimum solution of 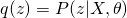 . So, usually for E-step, we use current guess of
. So, usually for E-step, we use current guess of 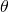 to calculate the posterior distribution of hidden variable as the new update score. For M-step, it is problem-dependent. We will see how to do that in later discussions.
to calculate the posterior distribution of hidden variable as the new update score. For M-step, it is problem-dependent. We will see how to do that in later discussions.
Another explanation of EM is in terms of optimizing a so-called Q function. We devise the data generation process as 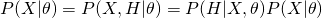 . Therefore, the complete likelihood is modified as:
. Therefore, the complete likelihood is modified as:
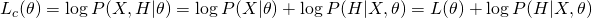
Think about how to maximize 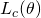 . Instead of directly maximizing it, we can iteratively maximize
. Instead of directly maximizing it, we can iteratively maximize 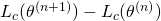 as :
as :
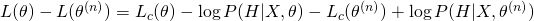
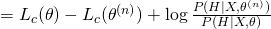
Now take the expectation of this equation, we have:

The last term is always non-negative since it can be recognized as the KL-divergence of 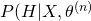 and
and 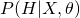 . Therefore, we obtain a lower bound of Likelihood :
. Therefore, we obtain a lower bound of Likelihood :
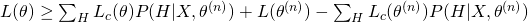
The last two terms can be treated as constants as they do not contain the variable 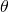 , so the lower bound is essentially the first term, which is also sometimes called as “Q-function”.
, so the lower bound is essentially the first term, which is also sometimes called as “Q-function”. 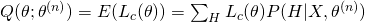
EM of Formulation 1
In case of Formulation 1, let us introduce hidden variables 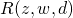 to indicate which hidden topic
to indicate which hidden topic  is selected to generated
is selected to generated 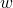 in
in 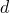 (
(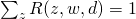 ). Therefore, the complete likelihood can be formulated as :
). Therefore, the complete likelihood can be formulated as :
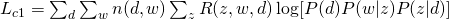
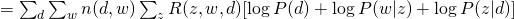
From the equation above, we can write our Q-function for the complete likelihood 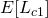 :
:
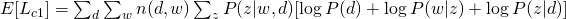
For E-step, simply using Bayes Rule, we can obtain:
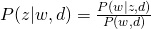
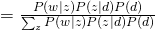
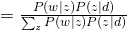
For M-step, we need to maximize Q-function, which needs to be incorporated with other constraints:
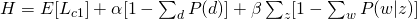

and take all derivatives:
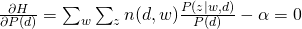
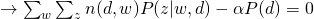
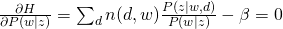
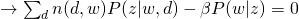
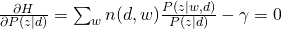
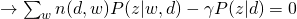
Therefore, we can easily obtain:
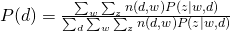
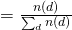
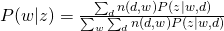
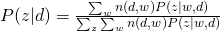
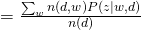
EM of Formulation 2
Use similar method to introduce hidden variables to indicate which  is selected to generated
is selected to generated 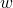 and
and 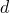 and we can have the following complete likelihood :
and we can have the following complete likelihood :
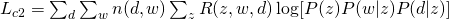
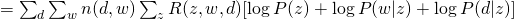
Therefore, the Q-function 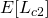 would be :
would be :
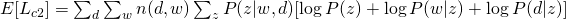
For E-step, again, simply using Bayes Rule, we can obtain:
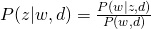
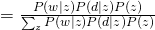
For M-step, we maximize the constraint version of Q-function:
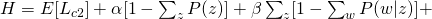
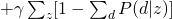
and take all derivatives:
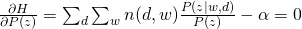
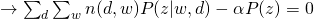
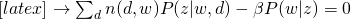
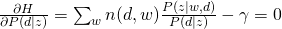
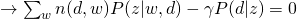
Therefore, we can easily obtain:
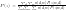
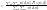
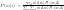
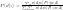
Notes on Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis (PLSA)的更多相关文章
- NLP —— 图模型(三)pLSA(Probabilistic latent semantic analysis,概率隐性语义分析)模型
LSA(Latent semantic analysis,隐性语义分析).pLSA(Probabilistic latent semantic analysis,概率隐性语义分析)和 LDA(Late ...
- 主题模型之概率潜在语义分析(Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis)
上一篇总结了潜在语义分析(Latent Semantic Analysis, LSA),LSA主要使用了线性代数中奇异值分解的方法,但是并没有严格的概率推导,由于文本文档的维度往往很高,如果在主题聚类 ...
- Latent semantic analysis note(LSA)
1 LSA Introduction LSA(latent semantic analysis)潜在语义分析,也被称为LSI(latent semantic index),是Scott Deerwes ...
- 主题模型之潜在语义分析(Latent Semantic Analysis)
主题模型(Topic Models)是一套试图在大量文档中发现潜在主题结构的机器学习模型,主题模型通过分析文本中的词来发现文档中的主题.主题之间的联系方式和主题的发展.通过主题模型可以使我们组织和总结 ...
- Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) Tutorial 潜语义分析LSA介绍 一
Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) Tutorial 译:http://www.puffinwarellc.com/index.php/news-and-articles/a ...
- 潜语义分析(Latent Semantic Analysis)
LSI(Latent semantic indexing, 潜语义索引)和LSA(Latent semantic analysis,潜语义分析)这两个名字其实是一回事.我们这里称为LSA. LSA源自 ...
- 潜在语义分析Latent semantic analysis note(LSA)原理及代码
文章引用:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_62a9902f0101cjl3.html Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA)也被称为Latent S ...
- 海量数据挖掘MMDS week4: 推荐系统之隐语义模型latent semantic analysis
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/49256457 海量数据挖掘Mining Massive Datasets(MMDs) -Jure Le ...
- Latent Semantic Analysis(LSA/ LSI)原理简介
LSA的工作原理: How Latent Semantic Analysis Works LSA被广泛用于文献检索,文本分类,垃圾邮件过滤,语言识别,模式检索以及文章评估自动化等场景. LSA其中一个 ...
随机推荐
- css3用AnimationEnd判断动画是否完成, css3在动画完成后执行事件
用css3的animation完成一个动画,当只有这个动画完成时才执行令一个事件,比如让动画保持在终止的状态或其他一些事件.我们该怎么办呢. 第一种方法: 用计时器,设定一个和动画时长一样的time, ...
- Android 编程下两种方式注册广播的区别
常驻型广播 常驻型广播,当你的应用程序关闭了,如果有广播信息来,你写的广播接收器同样的能接收到,它的注册方式就是在你应用程序的AndroidManifast.xml 中进行注册,这种注册方式通常又被称 ...
- 正则化,数据集扩增,Dropout
正则化方法:防止过拟合,提高泛化能力 在训练数据不够多时,或者overtraining时,常常会导致overfitting(过拟合).其直观的表现如下图所示,随着训练过程的进行,模型复杂度增加,在tr ...
- python练习程序(c100经典例12)
题目: 判断101-200之间有多少个素数,并输出所有素数. for i in range(101,201): flag=0; for j in range(2,int(i**(1.0/2))): i ...
- Nodejs学习之一 下载安装与部署nodejs
1,下载nodejs 访问nodejs官网 www.nodejs.org/download/ 下载与机器相匹配的版本 2,安装nodejs 下载下来的msi包一直点击下一步即可 3,部署环 ...
- 使用git自动将子工程发布到百度开放云上
我的项目中包含多个子工程,如web工程.python工程等.我在项目的根目录下建立了git管理,因此如果使用git push只能把整个项目推送上去,但我只想推送web工程目录.因此,编写了cmd脚本如 ...
- String定义与方法
//5种构造方法 public void Con(){ String str = "sfaj"; String str1 = new String("sfajdf&quo ...
- git/github初级运用自如(zz)
----//git/github环境配置 一 . github上创建立一个项目 用户登录后系统,在github首页,点击页面右下角“New Repository” 填写项目信息: project n ...
- JavaScript对象(document对象 图片轮播)
图片轮播: 需要注意的HTML需要img标签,他和input标签一样,是非封闭的标签 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Tran ...
- PHPSTORM 与 Xdebug 配合调试
基本的配置可以参考网上的文档, 浏览器中装插件(xdebug)或直接在请求中加上如下的参数也可启动调试 ?XDEBUG_SESSION_START=PHPSTORM


