2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online
cable cable cable
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2084 Accepted Submission(s): 1348
Now you have M display screens and K different signal sources(K≤M≤232−1). Select K display screens from M display screens, how many cables are needed at least so that **any** K display screens you select can show exactly K different colors.
there is one line contains two integers M and K.
20 15
90
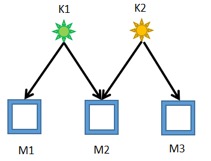
As the picture is shown, when you select M1 and M2, M1 show the color of K1, and M2 show the color of K2.
When you select M3 and M2, M2 show the color of K1 and M3 show the color of K2.
When you select M1 and M3, M1 show the color of K1.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const int N = 1e6+;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int main()
{
ll n,k;
while(cin>>n>>k)
{
cout<<k*(n-k+)<<endl;
}
return ;
}
array array array
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2917 Accepted Submission(s): 1170
Kiddo: "I have an array A and a number k, if you can choose exactly k elements from A and erase them, then the remaining array is in non-increasing order or non-decreasing order, we say A is a magic array. Now I want you to tell me whether A is a magic array. " Conan: "emmmmm..." Now, Conan seems to be in trouble, can you help him?
1≤T≤20
1≤n≤105
0≤k≤n
1≤Ai≤105
4 1
1 4 3 7
5 2
4 1 3 1 2
6 1
1 4 3 5 4 6
A is a magic array.
A is not a magic array.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int a[N],g[N],f[N],b[N],c[N],n,h[N];
int main() {
int t,n,last,l,i,m,x;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
cin>>a[i],h[n-i-]=a[i];
fill(g,g+n,INF);
b[]=;
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
{
int j=lower_bound(g, g+n,a[i])-g;
g[j]=a[i];
b[i]=j;
}
l=lower_bound(g, g+n,INF)-g-;
last=INF;
for(i=n-;i>=;i--)
{
if(l==-)break;
if(b[i]==l&&a[i]<last)
{
last=a[i];
c[l]=last;
l--;
}
}
l=lower_bound(g, g+n,INF)-g;
l=n-l;x=l; fill(g,g+n,INF);
b[]=;
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
{
int j=lower_bound(g, g+n,h[i])-g;
g[j]=h[i];
b[i]=j;
}
l=lower_bound(g, g+n,INF)-g-;
last=INF;
for(i=n-;i>=;i--)
{
if(l==-)break;
if(b[i]==l&&a[i]<last)
{
last=a[i];
c[l]=last;
l--;
}
}
l=lower_bound(g, g+n,INF)-g;
if(x>n-l)
x=n-l; if(x<=m)
puts("A is a magic array.");
else puts("A is not a magic array.");
//printf("%d\n",l); }
return ;
}
number number number
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2021 Accepted Submission(s): 1068
⋅ F0=0,F1=1;
⋅ Fn=Fn−1+Fn−2 (n≥2).
Give you an integer k, if a positive number n can be expressed by
n=Fa1+Fa2+...+Fak where 0≤a1≤a2≤⋯≤ak, this positive number is mjf−good. Otherwise, this positive number is mjf−bad.
Now, give you an integer k, you task is to find the minimal positive mjf−bad number.
The answer may be too large. Please print the answer modulo 998244353.
Each test case includes an integer k which is described above. (1≤k≤109)
找规律+矩阵快速幂
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const long long M =;
struct Matrix
{
long long a[][];
Matrix()
{
memset(a, , sizeof(a));
}
Matrix operator * (const Matrix y)
{
Matrix ans;
for(long long i = ; i <= ; i++)
for(long long j = ; j <= ; j++)
for(long long k = ; k <= ; k++)
ans.a[i][j] += a[i][k]*y.a[k][j];
for(long long i = ; i <= ; i++)
for(long long j = ; j <= ; j++)
ans.a[i][j] %= M;
return ans;
}
void operator = (const Matrix b)
{
for(long long i = ; i <= ; i++)
for(long long j = ; j <= ; j++)
a[i][j] = b.a[i][j];
}
};
long long solve(long long x)
{
Matrix ans, trs;
ans.a[][] = ans.a[][] = ;
trs.a[][] = trs.a[][] = trs.a[][] = ;
while(x)
{
if(x&)
ans = ans*trs;
trs = trs*trs;
x >>= ;
}
return ans.a[][];
}
int main()
{
long long n;
while(~scanf("%lld", &n))
{
cout <<(solve(*n+)-+M)%M << endl;
}
return ;
}
transaction transaction transaction
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 132768/132768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2245 Accepted Submission(s): 682
As we know, the price of this book was different in each city. It is ai yuan in it city. Kelukin will take taxi, whose price is 1yuan per km and this fare cannot be ignored.
There are n−1 roads connecting n cities. Kelukin can choose any city to start his travel. He want to know the maximum money he can get.
For each test case:
first line contains an integer n (2≤n≤100000) means the number of cities;
second line contains n numbers, the ith number means the prices in ith city; (1≤Price≤10000)
then follows n−1 lines, each contains three numbers x, y and z which means there exists a road between x and y, the distance is zkm (1≤z≤1000).
4
10 40 15 30
1 2 30
1 3 2
3 4 10
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+;
vector<pair<int,int> >G[N];
int sell[N],buy[N],ans;
int vis[N];
void dfs(int x)
{
for(int i=;i<(int)G[x].size();i++)
{
int v=G[x][i].first;
int w=G[x][i].second;
if(vis[v])continue;
vis[v]=;
dfs(v);
buy[x]=min(buy[x],buy[v]+w);
sell[x]=max(sell[x],sell[v]-w);
}
ans=max(ans,buy[x]-sell[x]);
ans=max(ans,sell[x]-buy[x]);
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
G[i].clear();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&sell[i]);
buy[i]=sell[i];
}
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
int u,v,w;
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
G[u].push_back({v,w});
G[v].push_back({u,w});
}
ans=;
vis[]=;
dfs();
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
card card card
Time Limit: 8000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2684 Accepted Submission(s): 755
One day, MJF takes a stack of cards and talks to him: let's play a game and if you win, you can get all these cards. MJF randomly assigns these cards into n heaps, arranges in a row, and sets a value on each heap, which is called "penalty value".
Before the game starts, WYJ can move the foremost heap to the end any times.
After that, WYJ takes the heap of cards one by one, each time he needs to move all cards of the current heap to his hands and face them up, then he turns over some cards and the number of cards he turned is equal to the penaltyvalue.
If at one moment, the number of cards he holds which are face-up is less than the penaltyvalue, then the game ends. And WYJ can get all the cards in his hands (both face-up and face-down).
Your task is to help WYJ maximize the number of cards he can get in the end.So he needs to decide how many heaps that he should move to the end before the game starts. Can you help him find the answer?
MJF also guarantees that the sum of all "penalty value" is exactly equal to the number of all cards.
For each test case:
the first line is an integer n (1≤n≤106), denoting n heaps of cards;
next line contains n integers, the ith integer ai (0≤ai≤1000) denoting there are ai cards in ith heap;
then the third line also contains n integers, the ith integer bi (1≤bi≤1000) denoting the "penalty value" of ith heap is bi.
4 6 2 8 4
1 5 7 9 2
For the sample input: + If WYJ doesn't move the cards pile, when the game starts the state of cards is:
4 6 2 8 4
1 5 7 9 2
WYJ can take the first three piles of cards, and during the process, the number of face-up cards is 4-1+6-5+2-7. Then he can't pay the the "penalty value" of the third pile, the game ends. WYJ will get 12 cards.
+ If WYJ move the first four piles of cards to the end, when the game starts the state of cards is:
4 4 6 2 8
2 1 5 7 9
WYJ can take all the five piles of cards, and during the process, the number of face-up cards is 4-2+4-1+6-5+2-7+8-9. Then he takes all cards, the game ends. WYJ will get 24 cards. It can be improved that the answer is 4. **huge input, please use fastIO.**
直接模拟下,但是有个细节就是全部都可以取到
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int a[],b[];
int main()
{
int n,x,i,s,p,y,q,r;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
for(i=;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]),b[i]=a[i];
for(i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
a[i]-=x;
}
s=;p=i;y=;q=;r=;
for(i=;i<n;i++)
{
s+=a[i];
if(s<)
{
if(q<y)
{
q=y,r=p;
}
y=;
s=;
p=i+;
}
y+=b[i];
}
if(p==n)
{
printf("%d\n",r);
continue;
}
for(i=;i<p;i++)
{
s+=a[i];
if(s<)
{
if(q<y)
{
q=y,r=p;
}
break;
}
y+=b[i];
}
if(q<y)
{
q=y,r=p;
}
printf("%d\n",r);
}
}
2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online的更多相关文章
- 2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online spfa+最长路
transaction transaction transaction Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 132768/1 ...
- 2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online(部分题解)
HDU 6197 array array array 题意 输入n和k,表示输入n个整数和可以擦除的次数k,如果至多擦除k次能是的数组中的序列是不上升或者是不下降序列,就是魔力数组,否则不是. 解题思 ...
- HDU 6205(尺取法)2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online
题目链接 emmmm...思路是群里群巨聊天讲这题是用尺取法.....emmm然后就没难度了,不过时间上3000多,有点.....盗了个低配本的读入挂发现就降到2800左右, 翻了下,发现神犇Clar ...
- HDU 6198(2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online)
思路:找规律发现这个数是斐波那契第2*k+3项-1,数据较大矩阵快速幂搞定. 快速幂入门第一题QAQ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h& ...
- 2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online array array array
2017-09-15 21:05:41 writer:pprp 给出一个序列问能否去掉k的数之后使得整个序列不是递增也不是递减的 先求出LIS,然后倒序求出最长递减子序列长度,然后判断去k的数后长度是 ...
- 2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online card card card
题意:看后面也应该知道是什么意思了 解法: 我们设置l,r,符合条件就是l=起始点,r=当前点,不符合l=i+1 学习了一下FASTIO #include <iostream> #incl ...
- 2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online transaction transaction transaction
Problem Description Kelukin is a businessman. Every day, he travels around cities to do some busines ...
- 2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online number number number
题意:求n个斐波那契数列组合都无法得到的最小数字 解法: 1 我们先暴力的求出前面几个数字 2 然后再暴力的求递推 3 接着矩阵快速幂(没写错吧?) /*#include<bits/stdc++ ...
- 2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online cable cable cable
Problem Description Connecting the display screen and signal sources which produce different color s ...
随机推荐
- CodeSmith Generator 7.0.2
[工具]CodeSmith Generator 7.0.2激活步骤 只看楼主 收藏 回复 M炎骫毒逆天T c#攻城狮 8 学过三层的人应该认识CodeSmith Generator吧, ...
- Java设计模式开篇
在所有的设计模式开篇中,总是说一个好的架构,或多或少都会有设计模式的出现.当然或多或少也会使用设计模式的相关原则: SOLID+迪米尔原则 1.优化代码的第一步:单一职责原则 S:单一职责链原则:英文 ...
- CF1072B Curiosity Has No Limits
思路: 对于序列t,只要第一个数确定了,后续的数也随之确定了.枚举四种情况即可.实现: #include <iostream> #include <vector> using ...
- JavaScript中的this陷阱
当有人问起你JavaScript有什么特点的时候,你可能立马就想到了单线程.事件驱动.面向对象等一堆词语,但是如果真的让你解释一下这些概念,可能真解释不清楚.有句话这么说:如果你不能向一个6岁小孩解释 ...
- Android 检查内存溢出
工具网址:https://github.com/square/leakcanary 中文版说明地址:http://www.liaohuqiu.net/cn/posts/leak-canary-read ...
- mongo ServerSelectionTimeoutError: localhost:27017: [Errno 111] Connection refused
解决方法 rm /var/lib/mongodb/mongod.lock
- UVA1001 Say Cheese (dijkstra)
如果没有洞,那么任意两点的最短距离就是直线距离,洞里是瞬间的,所以看成一个点就行了(其实点也可以当作半径为0的洞来处理),洞到洞的最短距离都是圆心距离减去半径.剩下的就是求单源最短路径,是完全图,用不 ...
- python在d盘,robotframework引入seleniumlibrary报错
在*** setting*** 中引入库 Library SeleniumLibrary 报错 unknown seleniumlibrary library ,try to use quic ...
- MySQL查询当天数据以及大量查询时提升速度
select * from 表名 where to_days(字段名) = to_days(now()) 一.数据库设计方面1.对查询进行优化,应尽量避免全表扫描,首先应考虑在 where 及 ord ...
- 如何查看 JAR 包的源代码
ava 项目的编译文件经常被打包成 JAR(Java Archive,Java 归档文件)文件,当然,作为学习,有时候也非常想看到这个 JAR 被打包前的源代码是怎么样的. 下面提供几种查看 JAR ...
