机器学习(六):回归分析——鸢尾花多变量回归、逻辑回归三分类只用numpy,sigmoid、实现RANSAC 线性拟合
[实验1 回归分析]
一、 预备知识
- 使用梯度下降法求解多变量回归问题
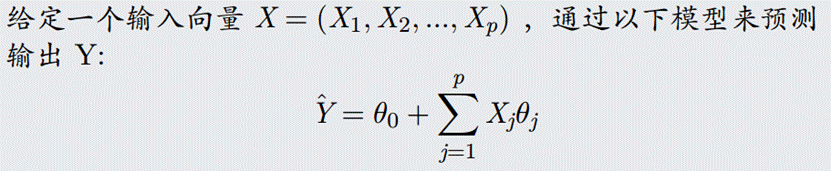
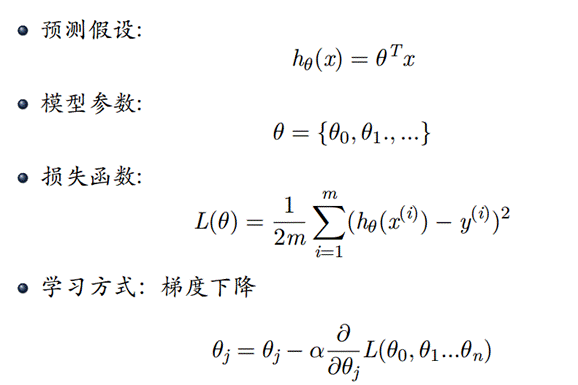
- 数据集
Iris 鸢尾花数据集是一个经典数据集,在统计学习和机器学习领域都经常被用作示例。数据集内包含 3 类共 150 条记录,每类各 50 个数据,每条记录都有 4 项特征:花萼长度、花萼宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度,可以通过这4个特征预测鸢尾花卉属于(iris-setosa, iris-versicolour, iris-virginica)中的哪一品种。
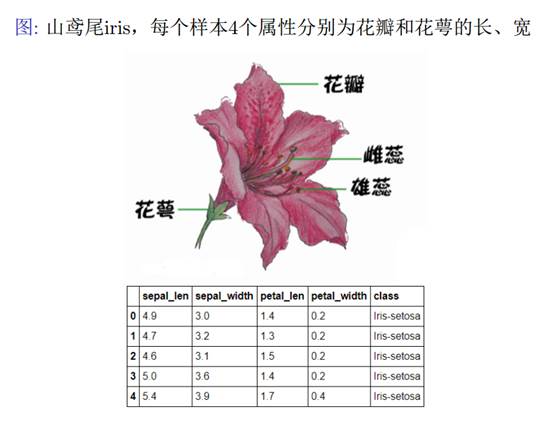
sepal length:花萼长度,单位cm;sepal width:花萼宽度,单位cm
petal length:花瓣长度,单位cm;petal width:花瓣宽度,单位cm
种类:setosa(山鸢尾),versicolor(杂色鸢尾),virginica(弗吉尼亚鸢尾)
我们用100组数据作为训练数据iris-train.txt,50组数据作为测试数据iris-test.txt。
'setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica'
0 1 2
二、 实验目的
掌握梯度下降法的原理及设计;
掌握利用梯度下降法解决回归类问题。
三、 实验内容
数据读取:(前4列是特征x,第5列是标签y)
import numpy as np
train_data = np.loadtxt('iris-train.txt', delimiter='\t')
x_train=np.array(train_data[:,:4])
y_train=np.array(train_data[:,4])
- 设计多变量回归分析方法,利用训练数据iris-train.txt求解参数
思路:首先确定h(x)函数,由于是4个特征,我们可以取5个参数
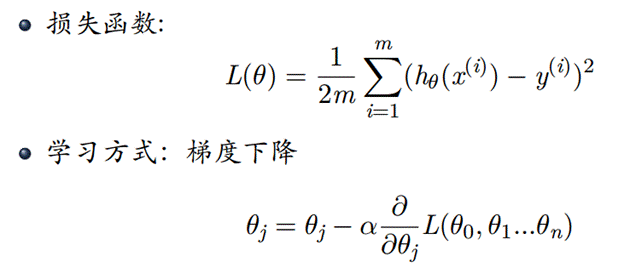
- 设计逻辑回归分析方法,利用训练数据iris-train.txt求解参数
思路:首先确定h(x)函数,由于是4个特征,我们可以取5个参数
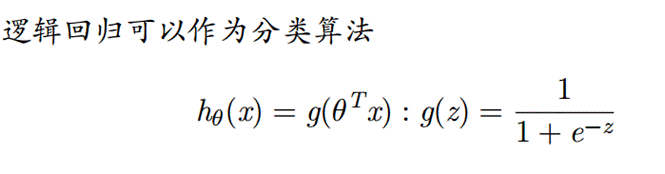
- 利用测试数据iris-test.txt,统计逻辑回归对测试数据的识别正确率 ACC,Precision,Recall。
四、 操作方法和实验步骤
1.对于多变量回归分析:
\]
(1)实现损失函数、h(x)、梯度下降函数等:
def hypothesis(X, theta):
return np.dot(X, theta)
def cost_function(X, y, theta):
m = len(y)
J = np.sum((hypothesis(X, theta) - y) ** 2) / (2 * m)
return J
def gradient_descent(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters):
m = len(y)
J_history = np.zeros(num_iters)
for i in range(num_iters):
theta = theta - (alpha / m) * np.dot(X.T, (hypothesis(X, theta) - y))
J_history[i] = cost_function(X, y, theta)
return theta, J_history
(2)处理输出X并开始计算
X_train_hat= np.hstack((np.ones((X_train.shape[0], 1)), X_train))
X_train= X_train_hat
theta = np.ones(X_train.shape[1])
alpha = 0.0005
num_iters = 120
theta, J_history = gradient_descent(X_train, y_train, theta, alpha, num_iters)
print("Parameter vector: ", theta)
print("Final cost: ", J_history[-1])
- 对于逻辑回归分析
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
train_data = np.loadtxt("iris/iris-train.txt", delimiter="\t")
X_train = train_data[:, 0:4]
y_train = train_data[:, 4]
encoder = LabelEncoder()
y_train = encoder.fit_transform(y_train) # Convert class labels to 0, 1, 2
X_train_hat = np.hstack((np.ones((X_train.shape[0], 1)), X_train))
X_train = X_train_hat
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def cost_function(X, y, theta):
m = len(y)
epsilon = 1e-5
h = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta))
J = (-1 / m) * np.sum(y * np.log(h+epsilon) + (1 - y) * np.log(1 - h+epsilon))
grad = (1 / m) * np.dot(X.T, (h - y))
return J, grad
def gradient_descent(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters):
m = len(y)
J_history = np.zeros(num_iters)
for i in range(num_iters):
J, grad = cost_function(X, y, theta)
theta = theta - (alpha * grad)
J_history[i] = J
return theta, J_history
def logistic_regression(X, y, alpha, num_iters):
theta = np.ones((X_train.shape[1], 3))
# Perform gradient descent to minimize the cost function for each class
for i in range(3):
y_train_i = (y_train == i).astype(int)
theta_i, J_history_i = gradient_descent(X_train, y_train_i, theta[:, i], alpha, num_iters)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(J_history_i)
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.title('Cost function'+str(i))
plt.show()
theta[:, i] = theta_i
print(f"Class {i} parameter vector: {theta_i}")
print(f"Class {i} final cost: {J_history_i[-1]}")
return theta
def predict(test_data, theta):
X_test = test_data[:, 0:4]
X_test_hat = np.hstack((np.ones((X_test.shape[0], 1)), X_test))
X_test = X_test_hat
y_test = test_data[:, 4]
y_test = encoder.transform(y_test) # Convert class labels to 0, 1, 2
y_pred = np.zeros(X_test.shape[0])
for i in range(3):
sigmoid_outputs = sigmoid(np.dot(X_test, theta[:, i]))
threshold = np.median(sigmoid_outputs[y_test == i])#不采用统一的阈值,而是采用每个类别的中位数作为阈值
y_pred_i = (sigmoid_outputs >= threshold).astype(int)
y_pred[y_pred_i == 1] = i
y_pred = encoder.inverse_transform(y_pred.astype(int)) # Convert class labels back to original values
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
test_data = np.loadtxt("iris/iris-test.txt", delimiter="\t")
theta = logistic_regression(X_train, y_train, 0.0005, 5000)
predict(test_data, theta)
实验结果和分析
1.对于多变量回归分析的实验结果:
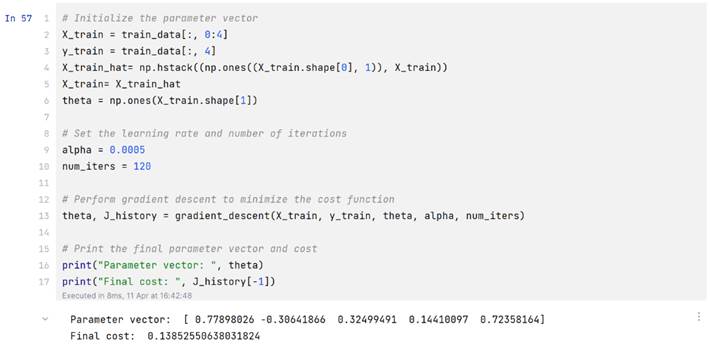
代价曲线:
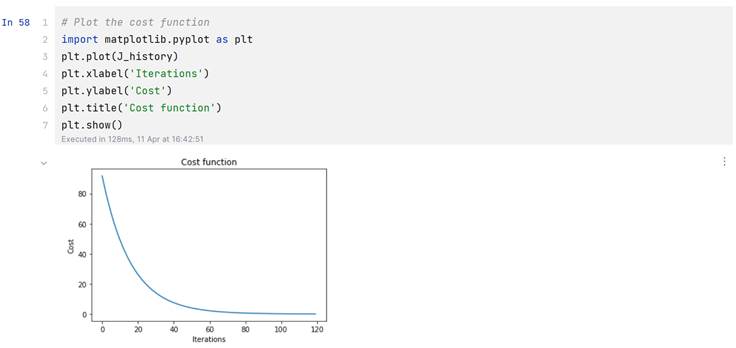
那么计算函数也就是:
\]
2.对于逻辑回归分析的实验结果
代价曲线:
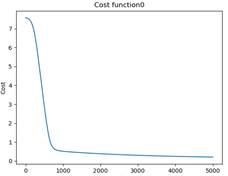
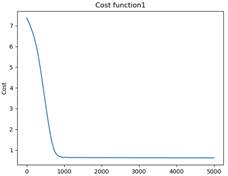
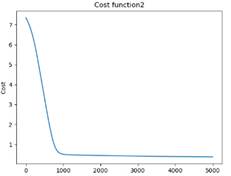
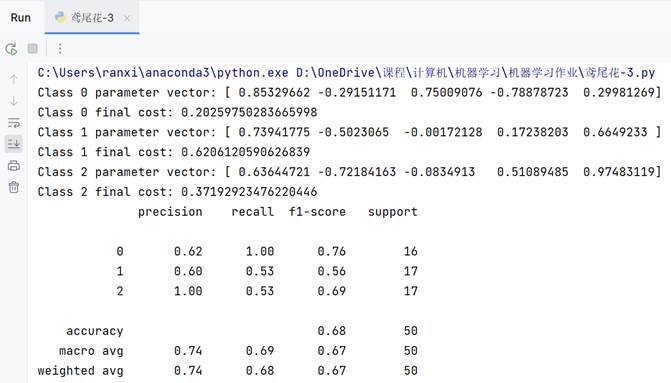
利用测试数据iris-test.txt,统计逻辑回归对测试数据的识别正确率 ACC,Precision,Recall:
通过sigmoid函数实现的逻辑回归只能处理二分类,我是通过分别计算三个二分类实现的。【猜测:预测1时把0和2归为同一类会对模型产生误导】
由于实现方法是One VS One.效果并不是很好,而且得到如下结果还是在处理sigmoid函数结果时还修改了原本0.5的阈值,有泄露结果的嫌疑。
(不采用统一的阈值,而是采用每个类别的h函数结果中位数作为阈值)
五、 思考题
给出 RANSAC 线性拟合的 python 实现
import random
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def ransac_line_fit(data, n_iterations, threshold):
"""
RANSAC algorithm for linear regression.
Parameters:
data (list): list of tuples representing the data points
n_iterations (int): number of iterations to run RANSAC
threshold (float): maximum distance a point can be from the line to be considered an inlier
Returns:
tuple: slope and y-intercept of the best fit line
"""
best_slope, best_intercept = None, None
best_inliers = []
for i in range(n_iterations):
# Randomly select two points from the data
sample = random.sample(data, 2)
x1, y1 = sample[0]
x2, y2 = sample[1]
# Calculate slope and y-intercept of line connecting the two points
slope = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
intercept = y1 - slope * x1
# Find inliers within threshold distance of the line
inliers = []
outliers = []
for point in data:
x, y = point
distance = abs(y - (slope * x + intercept))
distance = distance / np.sqrt(slope ** 2 + 1)
if distance <= threshold:
inliers.append(point)
else:
outliers.append(point)
# If the number of inliers is greater than the current best, update the best fit line
if len(inliers) > len(best_inliers):
best_slope = slope
best_intercept = intercept
best_inliers = inliers
outliers = [point for point in data if point not in best_inliers]
# Plot the data points, best fit line, and inliers and outliers
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# ax.scatter([x for x, y in data], [y for x, y in data], color='black')
ax.scatter([x for x, y in best_inliers], [y for x, y in best_inliers], color='green')
ax.scatter([x for x, y in outliers], [y for x, y in outliers], color='black')
x_vals = np.array([-5,5])
y_vals = best_slope * x_vals + best_intercept
ax.plot(x_vals, y_vals, '-', color='red')
# threshold_line = best_slope * x_vals + best_intercept + threshold*np.sqrt((1/best_slope) ** 2 + 1)
threshold_line = best_slope * x_vals + best_intercept + threshold * np.sqrt(best_slope ** 2 + 1)
ax.plot(x_vals, threshold_line, '--', color='blue')
# threshold_line = best_slope * x_vals + best_intercept - threshold*np.sqrt((1/best_slope) ** 2 + 1)
threshold_line = best_slope * x_vals + best_intercept - threshold * np.sqrt(best_slope ** 2 + 1)
ax.plot(x_vals, threshold_line, '--', color='blue')
# ax.set_xlim([-10, 10])
ax.set_ylim([-6, 6])
plt.show()
return best_slope, best_intercept
import numpy as np
# Generate 10 random points with x values between 0 and 10 and y values between -5 and 5
data = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(np.random.uniform(-5, 5, 10), np.random.uniform(-5, 5, 10))]
print(data)
# Fit a line to the data using RANSAC
slope, intercept = ransac_line_fit(data, 10000, 1)
print(slope, intercept)
结果:
机器学习(六):回归分析——鸢尾花多变量回归、逻辑回归三分类只用numpy,sigmoid、实现RANSAC 线性拟合的更多相关文章
- 一小部分机器学习算法小结: 优化算法、逻辑回归、支持向量机、决策树、集成算法、Word2Vec等
优化算法 先导知识:泰勒公式 \[ f(x)=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{f^{(n)}(x_0)}{n!}(x-x_0)^n \] 一阶泰勒展开: \[ f(x)\approx ...
- 机器学习(1)- 概述&线性回归&逻辑回归&正则化
根据Andrew Ng在斯坦福的<机器学习>视频做笔记,已经通过李航<统计学习方法>获得的知识不赘述,仅列出提纲. 1 初识机器学习 1.1 监督学习(x,y) 分类(输出y是 ...
- stanford coursera 机器学习编程作业 exercise 3(逻辑回归实现多分类问题)
本作业使用逻辑回归(logistic regression)和神经网络(neural networks)识别手写的阿拉伯数字(0-9) 关于逻辑回归的一个编程练习,可参考:http://www.cnb ...
- [吴恩达机器学习笔记]12支持向量机1从逻辑回归到SVM/SVM的损失函数
12.支持向量机 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~Follow Me 参考资料 斯坦福大学 2014 机器学习教程中文笔记 by 黄海广 12.1 SVM损失函数 从逻辑回归到支持向量机 为了描述 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 2——逻辑回归
作业说明 Exercise 2,Week 3,使用Octave实现逻辑回归模型.数据集 ex2data1.txt ,ex2data2.txt 实现 Sigmoid .代价函数计算Computing ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 6_Logistic Regression 逻辑回归
Lecture6 Logistic Regression 逻辑回归 6.1 分类问题 Classification6.2 假设表示 Hypothesis Representation6.3 决策边界 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—Week 3 习题—Logistic Regression 逻辑回归
课上习题 [1]线性回归 Answer: D A 特征缩放不起作用,B for all 不对,C zero error不对 [2]概率 Answer:A [3]预测图形 Answer:A 5 - x1 ...
- Logistic回归 逻辑回归 练习——以2018建模校赛为数据源
把上次建模校赛一个根据三围将女性分为四类(苹果型.梨形.报纸型.沙漏)的问题用逻辑回归实现了,包括从excel读取数据等一系列操作. Excel的格式如下:假设有r列,则前r-1列为数据,最后一列为类 ...
- Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(三)logistic regression(逻辑回归)
# 逻辑回归 ## 逻辑回归处理二元分类 %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #显示中文 from matplotlib.font_m ...
- 机器学习之LinearRegression与Logistic Regression逻辑斯蒂回归(三)
一 评价尺度 sklearn包含四种评价尺度 1 均方差(mean-squared-error) 2 平均绝对值误差(mean_absolute_error) 3 可释方差得分(explained_v ...
随机推荐
- ajax的重新学习,以及axios
首先在这次学习之前已经又过了简单的入门,并且在上学期vue的开发中对其中的ajax语法以及方法有所认识,但是还有很多别的框架不同种的写法,因此我需要掌握原生ajax的知识 一.对ajax的简单认识 a ...
- django_应用及分布式路由
一.应用的定义 1.应用在Django中是一个独立的业务模块,可以包含自己的路由.视图.模板.模型. 例如如下图所示,一个资讯类网站中会有不同的模块,如果所有的模块共用一个views.py文件,则会导 ...
- 【内存管理】ION内存管理器浅析(system contig heap)
system contig heap与system heap 从代码中我们看到system contig heap与system heap同属一个文件中,ion_system_heap.c 相同点:它 ...
- bigNumber.js的简单使用
sum 计算传入的参数和,参数类型可以是 String,Number // 两数之和 var x = BigNumber.sum('11', 23) x.toNumber() // 34 // 多个参 ...
- 京东薅羊毛脚本-Docker
一.安装好docker,然后创建容器: 注1:如果是旁路由,建议用--network host \代替-p 5678:5678 \这一行. 注2:如果想要看到lxk0301大佬的js脚本,并且重新部署 ...
- 2.javaweb-begin
1.回顾前端知识 1.CSS 1) CSS的角色:页面显示的美观风格 2) CSS的基础语法:标签样式:类样式:ID样式:组合样式:嵌入式样式表:内部样式表:外部样式表 3) 盒子模型:border. ...
- 2022.07.13 vue3下pinia的简单使用及持久化
使用前说明: 当前demo使用了vue3 + vite + typescript + pinia搭建的简单项目,主要介绍了在单文件组件(sfc)基础上使用pinia的用法,懒得看api的兄弟们,来这瞅 ...
- 118、商城业务---分布式事务---RabbitMQ延时队列定时关单模拟
1.使用RabbitMq实现延时队列方法1 2.基于我们的业务我们使用下面这种方式实现延时队列 1.导入依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springf ...
- VMware安装Rocky Linux8服务器系统并执行优化,包括修改安装镜像源、ssh免密等等
1. https://blog.csdn.net/DCTANT/article/details/125430461?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-tas ...
- Conda 创建、激活、克隆、删除虚拟环境 - 搬运
Conda 创建.激活.克隆.删除虚拟环境 转自 :https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/547724114 风影忍着 通常来说,对于每一个新的项目,我们都需要创建一个新的环境 ...
