django视图 CBV 和 FBV
视图 CBV 和 FBV
什么是视图?
一个视图函数(类),简称视图,是一个简单的Python 函数(类),它接受Web请求并且返回Web响应。
响应可以是一张网页的HTML内容,一个重定向,一个404错误,一个XML文档,或者一张图片。放置在项目
(project)或应用程序(app)目录中的名为views.py的文件中。
- 下面是一个以HTML文档的形式返回当前日期和时间的视图:
from django.http import HttpResponse
import datetime
def current_datetime(request):
now = datetime.datetime.now()
html = "<html><body>It is now %s.</body></html>" % now
return HttpResponse(html)
- 让我们来逐行解释下上面的代码:
首先,我们从 django.http模块导入了HttpResponse类,以及Python的datetime库。
接着,我们定义了current_datetime函数。它就是视图函数。每个视图函数都使用HttpRequest对象作为第一个参数,
并且通常称之为request。
注意,视图函数的名称并不重要;不需要用一个统一的命名方式来命名,以便让Django识别它。
我们将其命名为current_datetime,是因为这个名称能够比较准确地反映出它实现的功能。
这个视图会返回一个HttpResponse对象,其中包含生成的响应。每个视图函数都负责返回一个HttpResponse对象。
Django使用请求和响应对象来通过系统传递状态。
当浏览器向服务端请求一个页面时,Django创建一个HttpRequest对象,该对象包含关于请求的元数据。然后,
Django加载相应的视图,将这个HttpRequest对象作为第一个参数传递给视图函数。
每个视图负责返回一个HttpResponse对象。
FBV function based view 基于函数的视图
from app01 import models
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, HttpResponse
import datetime
def mul(request):
now = datetime.datetime.now()
return render(request, 'mul.html',{'now':now})
- 使用 FBV
#urls.py 文件
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^mul', views.mul),
]
CBV class based view 基于类的视图
from app01 import models
from django.views import View
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, HttpResponse
class AddPublisher(View):
def get(self,request):
"""处理get请求"""
return response
def post(self,request):
"""处理post请求"""
return response
#处理求响的逻辑很清晰
- 使用CBV:
#urls.py 文件
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^add_publisher/', views.AddPublisher.as_view()),
]#固定写法注意.as_view()是要加括号的
小技巧
我们写的视图,可以接收,处理8种请求,页面发来的8种请求:
from app01 import views #ctrl+鼠标右击views 查看源码
class View(object):
"""
Intentionally simple parent class for all views. Only implements
dispatch-by-method and simple sanity checking.
"""
http_method_names = ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace']
#可以看到views 默认接收了八种请求'get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace'
#那我在写视图函数是可以重新定义http_method_names = ['get',post]让这个视图,让它只接收get和post请求
- 在CBV 视图中request和self.request效果是一样的
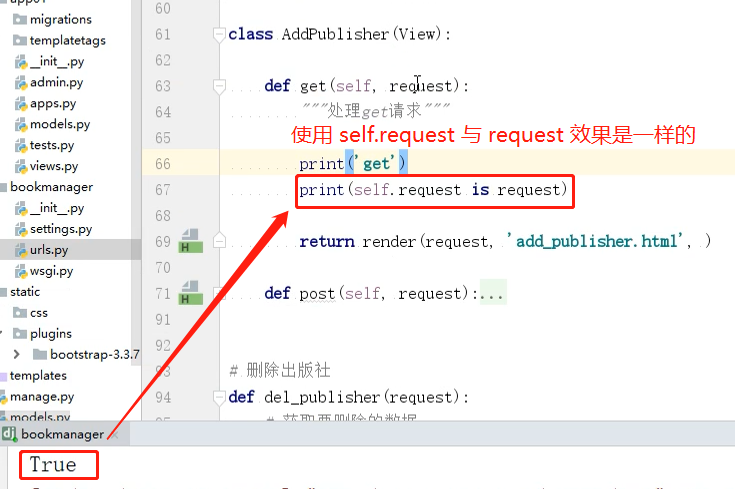
CBV 如何获取页面请求类型,并响应的
1. 项目启动,执行AddPublisher.as_view() ——》 view
url(r'add_publisher/',views.AddPublisher.as_view())
url(r'add_publisher/', view )
2. 请求到来时执行view函数:
1. 实例化AddPublisher ——》 self
2. self.request = reqeust
3. 执行self.dispatch(request,*args,**kwargs)
1. 判断请求方式是否被允许 http_method_names = []
1. 允许
通过反射获取到当前请求方式对应的方法 ——》 handler
2. 不允许
self.http_method_not_allowed ——》 handler
2. 执行handler(request,*args,**kwargs) ——》 返回响应
使用装饰器的 FBV
- FBV本身就是一个函数,所以和给普通的函数加装饰器无差:
def wrapper(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
end_time = time.time()
print("used:", end_time-start_time)
return ret
return inner
# FBV版添加装饰器
@wrapper
def add_class(request):
if request.method == "POST":
class_name = request.POST.get("class_name")
models.Classes.objects.create(name=class_name)
return redirect("/class_list/")
return render(request, "add_class.html")
使用装饰器的CBV
类中的方法与独立函数不完全相同,因此不能直接将函数装饰器应用于类中的方法 ,我们需要先将其转换为方法装饰器。
Django中提供了method_decorator装饰器用于将函数装饰器转换为方法装饰器。
装饰器加在类方法上
# 装饰器加在类方法上
import tinme
from django.views import View
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator #导入method_decorator装饰器
def timer(func):
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
ret = func(request, *args, **kwargs)
print("函数执行的时间是{}".format(time.time() - start))
return ret
return inner
class AddClass(View):
@method_decorator(timer)#只有get请求装饰器才生效
def get(self, request):
return render(request, "add_class.html")
def post(self, request):
class_name = request.POST.get("class_name")
models.Classes.objects.create(name=class_name)
return redirect("/class_list/")
dispatch()加装饰器
# 使用CBV时要注意,请求过来后会先执行dispatch()这个方法,如果需要批量对具体的请求处理方法,如get,
post等做一些操作的时候,这里我们可以手动改写dispatch方法,这个dispatch方法就和在FBV上加装饰器的效果一样。
import tinme
from django.views import View
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator #导入方法装饰器
def timer(func):
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
ret = func(request, *args, **kwargs)
print("函数执行的时间是{}".format(time.time() - start))
return ret
return inner
class Login(View):
@method_decorator(timer) #相当于给get,post请求都加上了装饰器
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
obj = super(Login,self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
return obj
def get(self,request):
return render(request,'login.html')
def post(self,request):
print(request.POST.get('user'))
return HttpResponse('Login.post')
装饰器加在类上
#装饰器加在类上
import tinme
from django.views import View
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator #导入方法装饰器
def timer(func):
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
ret = func(request, *args, **kwargs)
print("函数执行的时间是{}".format(time.time() - start))
return ret
return inner
@method_decorator(timer,name = 'get') #相当于给get请求,加上了装饰器
@method_decorator(timer,name = 'post')#相当于给post请求,加上了装饰器
class Login(View):
def get(self,request):
return render(request,'login.html')
def post(self,request):
print(request.POST.get('user'))
return HttpResponse('Login.post')
使用method_decorator与不使用的区别:
"""
def timer(func):
pritn(func)
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
print(args)
start = time.time()
ret = func(request, *args, **kwargs)
print("函数执行的时间是{}".format(time.time() - start))
return ret
"""
不使用用method_decorator
func ——》 <function AddPublisher.get at 0x000001FC8C358598>
args ——》 (<app01.views.AddPublisher object at 0x000001FC8C432C50>, <WSGIRequest: GET '/add_publisher/'>)
使用method_decorator之后:
func ——》 <function method_decorator.<locals>._dec.<locals>._wrapper.<locals>.bound_func at 0x0000015185F7C0D0>
args ——》 (<WSGIRequest: GET '/add_publisher/'>,)
django视图 CBV 和 FBV的更多相关文章
- Django(视图 CBV、FBV)
day67 参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/liwenzhou/articles/8305104.html CBV和FBV 我们之前写过的都是基于函数的view,就叫FBV.还可以 ...
- python测试开发django-73.django视图 CBV 和 FBV
前言 FBV(function base views) 就是在视图里使用函数处理请求,这一般是学django入门的时候开始使用的方式. CBV(class base views) 就是在视图里使用类处 ...
- Django之CBV和FBV
Django之CBV和FBV CBV和FBV是C和F的区别: C是Class,F是Function 在请求中,有GET请求和POST请求. 在写CBV时,url是可以对应一个类的,在类中,分别写出GE ...
- django补充CBV和FBV模式
django补充CBV和FBV模式FBV模式---函数:经常用的方式CBV模式---类CBV中url连接时函数名后面要接.as_view()class index(views.View): @... ...
- Django的CBV与FBV
FBV FBV(function base views) 就是在视图里使用函数处理请求. 在之前django的学习中,我们一直使用的是这种方式,所以不再赘述. CBV CBV(class base v ...
- Django的 CBV和FBV
FBV CBV 回顾多重继承和Mixin 回到顶部 FBV FBV(function base views) 就是在视图里使用函数处理请求. 在之前django的学习中,我们一直使用的是这种方式,所以 ...
- 062.Python前段框架Django视图CBV
一 CBV与FBV CBV:Class Based View FBV:Function Based View 之前写过的都是基于函数的view,就叫FBV.还可以把view写成基于类的,那就是CBV. ...
- Django之 CBV和FBV
FBV FBV(function base views) 就是在视图里使用函数处理请求. CBV CBV(class base views) 就是在视图里使用类处理请求. Python是一个面向对象的 ...
- Django视图函数之FBV与CBV模式
FBV模式: FBV(function base views) 就是在视图里使用函数处理请求. 一般直接用函数写的都属于是FBV模式. veiws.py from django.shortcuts i ...
随机推荐
- Android 虚拟机 程序安装目录
Android应用安装涉及到如下几个目录:system/app系统自带的应用程序,无法删除.data/app用户程序安装的目录,有删除权限.安装时把apk文件复制到此目录.data/data存放应用程 ...
- Python网络编程--Echo服务
Python网络编程--Echo服务 学习网络编程必须要练习的三个小项目就是Echo服务,Chat服务和Proxy服务.在接下来的几篇文章会详细介绍. 今天就来介绍Echo服务,Echo服务是最基本的 ...
- golang字符串拼接性能对比
对比 +(运算符).strings.Join.sprintf.bytes.Buffer对字符串拼接的性能 package main import ( "bytes" "f ...
- 程序猿老公去米国参加 WWDC,顺便想带渡老婆蜜月,如何办签证?
这个问题要拆开描述比较好:1. 老公是苹果开发者,抽中了2014 WWDC购票机会,打算自费去参加.如果自己成行,应该办何种签证?2. 顺带,两人新婚半年还未安排蜜月,打算提前几天过去先游览一下西海岸 ...
- LeetCode-5:Longest Palindromic Substring(最长回文子字符串)
描述:给一个字符串s,查找它的最长的回文子串.s的长度不超过1000. Input: "babad" Output: "bab" Note: "aba ...
- JSP常见知识点
false 7.8 磅 0 2 false false false false EN-US ZH-CN X-NONE /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTa ...
- “libgomp.so.1: version `GOMP_4.0' not found” || “libstdc++.so.6: version `CXXABI_1.3.8' not found”错误
类似问题还有 'ImportError ../lib/libstdc++.so.6: version `CXXABI_1.3.7' not found (required by xxx)'. ...
- 查看linux连接进程占用的实时流量 -nethogs
1.安装nethogs yum -y install nethogs 2.安装完成后,就可以执行命令 nethogs 3.实时查看进程流量,来个图显示 图中会显示当前的nginx产生的流量有多少都会清 ...
- MySQL 数据底部出现总计字样 第二种办法 纵向合并 20161103
上次在博客http://www.cnblogs.com/Mr-Cxy/p/5923375.html 我们使用了group by with rollup 函数 field自定义排序 来实现添加底部总计字 ...
- poj1637 Sightseeing tour[最大流+欧拉回路]
混合图的欧拉回路定向问题. 顺便瞎说几句,有向图定欧拉回路的充要条件是每个点入度等于出度,并且图联通.无向图的话只要联通无奇点即可. 欧拉路径的确定应该是无向图联通且奇点数0个或2个,有向图忘了,好像 ...
