Docker镜像搭建ubuntu下samba目录共享
第一种方法:(未使用)
yum install docker
// 下载镜像
docker pull dperson/samba
// 启动镜像,具体看文档,但重要的配置是以下的注释
docker run --name samba \
-it -p 139:139 -p 445:445 \
-v /home/technofiend:/home/technofiend \ #共享目录
-d dperson/samba \
-u "www;thisispasswd" \ #访问用户
-s "technofiend;/home/technofiend/;yes;no;no;all;none" #共享配置
// 密码跟本机一致,1001为用户id,具体查看你本机的/etc/passwd文件,设置为共享目录所属用户
docker exec -it samba sed -i 's/1000/1001/g' /etc/passwd
// 组跟本机一致,1001为组id,具体查看你本机的/etc/group文件,设置为共享目录所属组
docker exec -it samba sed -i 's/1000/1001/g' /etc/group
// 替换samba的启动用户,与权限有关
docker exec -it samba sed -i 's/force user = smbuser/force user = www/g' /etc/samba/smb.conf
// 替换samba的启动组,与权限有关
docker exec -it samba sed -i 's/force group = users/force group = www/g' /etc/samba/smb.conf
// 重启samba
docker restart samba 用户id那块看清楚了。但docker实例里面新建的第一个用户是1000.这里跟你主机的用户权限需要一直,所以得替换成同样的id,用户和组也得要
就是新进容器建这个用户
第一种方法
第二种方法:(实验成功)
第一步安装docker:
yum install docker-engine
第二步启动服务:
service docker start
第三步:
docker pull dperson/samba
第四步:
docker run -it --name samba -p 139:139 -p 445:445 -v /home:/mount -d dperson/samba -u "www;overkill" -s "www;/mount/;yes;no;no;all;none"
开放了139和445端口。 用服务器访问即可!
要是想把容器的权限与宿主主机的用户权限一致的话,则只需要把用户和组文件映射到容器里面即可:
docker run -it --name samba -p 139:139 -p 445:445 -v /home:/mount -v /etc/passwd:/etc/passwd -v /etc/group:/etc/group -d dperson/samba -s "www;/mount/;yes;no;no;all;none"
请注意 -s 参数后面的第一个;前面的是现已存在的用户名。
官方使用教程:https://github.com/dperson/samba
三、配置方法
系统:ubuntu16.04
配置文件:/etc/samba/smb.conf
Samba的主配置文件叫smb.conf,默认在/etc/samba/目录下
配置文件详解
# This is the main Samba configuration file. You should read the
# smb.conf() manual page in order to understand the options listed
# here. Samba has a huge number of configurable options (perhaps too
# many!) most of which are not shown in this example
#
# Any line which starts with a ; (semi-colon) or a # (hash)
# is a comment and is ignored. In this example we will use a #
# for commentry and a ; for parts of the config file that you
# may wish to enable
#
# NOTE: Whenever you modify this file you should run the command "testparm"
# to check that you have not made any basic syntactic errors.
#
#======================= Global Settings =====================================
[global] # workgroup = NT-Domain-Name or Workgroup-Name
workgroup = MYGROUP
#设定 Samba Server 所要加入的工作组或者域
# server string is the equivalent of the NT Description field
server string = Samba Server
#设定 Samba Server 的注释,可以是任何字符串,也可以不填。宏%v表示显示Samba的版本号 # This option is important for security. It allows you to restrict
# connections to machines which are on your local network. The
# following example restricts access to two C class networks and
# the "loopback" interface. For more examples of the syntax see
# the smb.conf man page
; hosts allow = 192.168.. 192.168.. .
#表示允许连接到Samba Server的客户端,多个参数以空格隔开。可以用一个IP表示,也可以用一个网段表示。hosts deny 与hosts allow 刚好相反。
# if you want to automatically load your printer list rather
# than setting them up individually then you'll need this
printcap name = /dev/null
load printers = no # It should not be necessary to spell out the print system type unless
# yours is non-standard. Currently supported print systems include:
# bsd, sysv, plp, lprng, aix, hpux, qnx
printing = bsd # Uncomment this if you want a guest account, you must add this to /etc/passwd
# otherwise the user "nobody" is used
; guest account = pcguest # this tells Samba to use a separate log file for each machine
# that connects
log file = /dev/stdout
#日志文件的存储位置以及日志文件名称
# Put a capping on the size of the log files (in Kb).
max log size =
#设置Samba Server日志文件的最大容量,单位为kB,0代表不限制
# Security mode. Most people will want user level security. See
# security_level.txt for details.
security = user
#用户访问Samba Server的验证方式
; password server = <NT-Server-Name> # Password Level allows matching of _n_ characters of the password for
# all combinations of upper and lower case.
; username level = # You may wish to use password encryption. Please read
# ENCRYPTION.txt, Win95.txt and WinNT.txt in the Samba documentation.
# Do not enable this option unless you have read those documents
; encrypt passwords = yes
; smb passwd file = /etc/samba/smbpasswd # The following are needed to allow password changing from Windows to
# update the Linux sytsem password also.
# NOTE: Use these with 'encrypt passwords' and 'smb passwd file' above.
# NOTE2: You do NOT need these to allow workstations to change only
# the encrypted SMB passwords. They allow the Unix password
# to be kept in sync with the SMB password.
unix password sync = no
; passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
; passwd chat = *New*UNIX*password* %n\n *ReType*new*UNIX*password* %n\n *passwd:*all*authentication*tokens*updated*successfully* # Unix users can map to different SMB User names
; username map = /etc/samba/smbusers # Using the following line enables you to customise your configuration
# on a per machine basis. The %m gets replaced with the netbios name
# of the machine that is connecting
; include = /etc/samba/smb.conf.%m # Configure Samba to use multiple interfaces
# If you have multiple network interfaces then you must list them
# here. See the man page for details.
; interfaces = 192.168.12.2/ 192.168.13.2/ # Configure remote browse list synchronisation here
# request announcement to, or browse list sync from:
# a specific host or from / to a whole subnet (see below)
; remote browse sync = 192.168.3.25 192.168.5.255
# Cause this host to announce itself to local subnets here
; remote announce = 192.168.1.255 192.168.2.44 # Browser Control Options:
# set local master to no if you don't want Samba to become a master
# browser on your network. Otherwise the normal election rules apply
; local master = no # OS Level determines the precedence of this server in master browser
# elections. The default value should be reasonable
; os level = # Domain Master specifies Samba to be the Domain Master Browser. This
# allows Samba to collate browse lists between subnets. Don't use this
# if you already have a Windows NT domain controller doing this job
; domain master = yes # Preferred Master causes Samba to force a local browser election on startup
# and gives it a slightly higher chance of winning the election
; preferred master = yes # Use only if you have an NT server on your network that has been
# configured at install time to be a primary domain controller.
; domain controller = <NT-Domain-Controller-SMBName> # Enable this if you want Samba to be a domain logon server for
# Windows95 workstations.
; domain logons = yes # if you enable domain logons then you may want a per-machine or
# per user logon script
# run a specific logon batch file per workstation (machine)
; logon script = %m.bat
# run a specific logon batch file per username
; logon script = %U.bat # Where to store roving profiles (only for Win95 and WinNT)
# %L substitutes for this servers netbios name, %U is username
# You must uncomment the [Profiles] share below
; logon path = \\%L\Profiles\%U # All NetBIOS names must be resolved to IP Addresses
# 'Name Resolve Order' allows the named resolution mechanism to be specified
# the default order is "host lmhosts wins bcast". "host" means use the unix
# system gethostbyname() function call that will use either /etc/hosts OR
# DNS or NIS depending on the settings of /etc/host.config, /etc/nsswitch.conf
# and the /etc/resolv.conf file. "host" therefore is system configuration
# dependant. This parameter is most often of use to prevent DNS lookups
# in order to resolve NetBIOS names to IP Addresses. Use with care!
# The example below excludes use of name resolution for machines that are NOT
# on the local network segment
# - OR - are not deliberately to be known via lmhosts or via WINS.
; name resolve order = wins lmhosts bcast # Windows Internet Name Serving Support Section:
# WINS Support - Tells the NMBD component of Samba to enable it's WINS Server
; wins support = yes # WINS Server - Tells the NMBD components of Samba to be a WINS Client
# Note: Samba can be either a WINS Server, or a WINS Client, but NOT both
; wins server = w.x.y.z # WINS Proxy - Tells Samba to answer name resolution queries on
# behalf of a non WINS capable client, for this to work there must be
# at least one WINS Server on the network. The default is NO.
; wins proxy = yes # DNS Proxy - tells Samba whether or not to try to resolve NetBIOS names
# via DNS nslookups. The built-in default for versions 1.9. is yes,
# this has been changed in version 1.9. to no.
dns proxy = no # Case Preservation can be handy - system default is _no_
# NOTE: These can be set on a per share basis
preserve case = yes
short preserve case = yes
# Default case is normally upper case for all DOS files
default case = lower
# Be very careful with case sensitivity - it can break things!
; case sensitive = no pam password change = yes
map to guest = bad user
usershare allow guests = yes
create mask =
force create mode =
directory mask =
force directory mode =
# force user = www
# force group = www
follow symlinks = yes
load printers = no
printing = bsd
printcap name = /dev/null
disable spoolss = yes
socket options = TCP_NODELAY
strict locking = no
vfs objects = recycle
recycle:keeptree = yes
recycle:versions = yes
min protocol = SMB2 [公共文件]
path = /home/technofiend/public
browsable = yes #用来指定该共享是否可以浏览
read only = no
guest ok = no #将设置客户端以该游客账号来访问共享
veto files = /._*/.apdisk/.AppleDouble/.DS_Store/.TemporaryItems/.Trashes/desktop.ini/ehthumbs.db/Network Trash Folder/Temporary Items/Thumbs.db/
delete veto files = yes
valid users = @public
[网络开发文件]
comment = group-web #对该共享的描述,可以是任意字符串
path = /home/technofiend/group/web #共享目录路径
public = yes #用来指定该共享是否允许guest账户访问
writable = yes #用来指定该共享路径是否可写
printable = no
valid users = @web #允许访问该共享的用户,组就用“@+组名”表示
[引擎开发文件]
comment = ue4
path = /home/technofiend/group/editor
public = yes #用来指定该共享是否允许guest账户访问
writable = yes #用来指定该共享路径是否可写
printable = no
valid users = @editor
[设计内部文件]
comment = group public
path = /home/technofiend/group/public
public = yes writable = yes #用来指定该共享路径是否可写
printable = no
valid users = @seji #允许访问该共享的用户,组就用“@+组名”表示
service smb restart 重启服务
检查语法是否正确:testparm -v
思路方法:
1)创建组:添加用户组
groupadd public 创建用户组
useradd -s /sbin/nologin -G web,public,group-public webtest1 添加到多个用户组
usermod -g seji cesiyonghu 添加到组
注意:useradd和adduser区别
useradd与adduser都是创建新的用户
在CentOs下useradd与adduser是没有区别的都是在创建用户,在home下自动创建目录,没有设置密码,需要使用passwd命令修改密码。
而在Ubuntu下useradd与adduser有所不同
、useradd在使用该命令创建用户是不会在/home下自动创建与用户名同名的用户目录,而且不会自动选择shell版本,也没有设置密码,那么这个用户是不能登录的,需要使用passwd命令修改密码。
、adduser在使用该命令创建用户是会在/home下自动创建与用户名同名的用户目录,系统shell版本,会在创建时会提示输入密码,更加友好。
userdel 删除用户,
userdel只能删除用户,并不会删除相关的目录文件。userdel -r 可以删除用户及相关目录。
2)变更文件夹的用户和用户组权限
chown -R :web group/web #表示所有web组
3)把用户添加到samba中
smbpasswd -a share #设置密码
4)激活用户
smbpasswd -e share
5)window下使用; 运行----输入\\ip地址
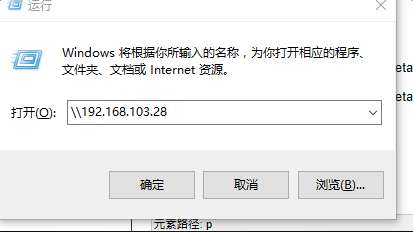
文章出处:
http://blog.csdn.net/technofiend/article/details/52346303 主要转载这篇
http://blog.csdn.net/technofiend/article/details/51066262
更多注释详解:http://blog.csdn.net/dhgao38/article/details/43567403
Docker镜像搭建ubuntu下samba目录共享的更多相关文章
- Docker镜像搭建Linux下samba共享目录
Samba 是 SMB/CIFS 网络协议的重新实现, 它作为 NFS 的补充使得在 Linux.OS/2.DOS 和 Windows 系统中进行文件共享.打印机共享更容易实现.SMB协议是客户机/服 ...
- python开发笔记-Python3.7+Django2.2 Docker镜像搭建
目标镜像环境介绍: 操作系统:ubuntu16.04 python版本:python 3.7.4 django版本:2.2 操作步骤: 1. 本地安装docker环境(略)2. 拉取ubunut指定 ...
- 搭建Ubuntu下c/c++编译环境【转】
1. 安装Ubuntu. 2. 安装gcc 方法一: sudo apt-get install build-essential 安装完了可以执行 gcc--version的 ...
- 傲视Kubernetes(二):Docker镜像搭建与本地Kubernetes环境搭建
主要内容: 1.Docker与Kubernetes的关系 2.SpringBoot微服务的Docker镜像创建 3.Kubernetes本地环境搭建 一.Docker与Kubernetes的关系 在说 ...
- PyCharm使用之利用Docker镜像搭建Python开发环境
在我们平时使用PyCharm的过程中,一般都是连接本地的Python环境进行开发,但是如果是离线的环境呢?这样就不好搭建Python开发环境,因为第三方模块的依赖复杂,不好通过离线安装包的方式安装 ...
- Docker+STF在ubuntu下测试环境搭建(详细搭建步骤及踩坑记录)
一.什么是OpenSTF? STF又称OpenSTF,它是一个手机设备管理平台,可以对手机进行远程管理.调试.远程手机桌面监控等操作.这个系统类似于目前很流行的云测服务比如Testin,虽然网页上提供 ...
- Ubuntu杂记——Ubuntu下用虚拟机共享上网
由于最近把自己电脑环境换成了Ubuntu,但学校的网络是电信的闪讯,大学里用过的人都知道这货有多坑,而且没有Linux客户端,上网都是问题,怪不得国内用Linux的人那么少,特别是高校的学生(让我瞎逼 ...
- TensorFlow(1):使用Docker镜像搭建TensorFlow环境
1,关于TensorFlow TensorFlow 随着AlphaGo的胜利也火了起来. google又一次成为大家膜拜的大神了.google大神在引导这机器学习的方向. 同时docker 也是一个非 ...
- Ubuntu12.04下samba服务器共享配置
1 . 前置工作 首先保证你的Ubuntu能上网:虚拟机网络连接方式为NAT:虚拟机雨物理机互ping可通: 2. 安装samba sudo apt-get insall samba sudo apt ...
随机推荐
- Tomcat 输出日志出现中文乱码
Tomcat 输出日志出现中文乱码 解决方案: 打开到tomcat安装目录下的conf/文件夹 修改logging.properties文件,找到 java.util.logging.ConsoleH ...
- Man手册--nmap
目录 nmap使用手册 附录: nmap使用手册 附录: NMAP(1) Nmap Reference Guide NMAP(1) NAME nmap - Network exploration to ...
- TLV320AIC3268寄存器读写
该芯片支持I2C和SPI读写寄存器,本人用的是SPI1接口. 以下是对手册中SPI接口读写寄存器相关内容的翻译(英文版可以看手册的94页~) 在SPI控制模式下,TLV320AIC3268使用SCL_ ...
- 《设计模式之美》 <03>面向对象、设计原则、设计模式、编程规范、重构,这五者有何关系?
面向对象 现在,主流的编程范式或者是编程风格有三种,它们分别是面向过程.面向对象和函数式编程.面向对象这种编程风格又是这其中最主流的.现在比较流行的编程语言大部分都是面向对象编程语言.大部分项目也都是 ...
- Nagios4.x安装配置总结
1. Nagios介绍 Nagios是一个监视系统运行状态和网络信息的监视系统.Nagios能监视所指定的本地或远程主机以及服务,同时提供异常通知功能等. Nagios可运行在Linux/Unix平 ...
- python爬取豆瓣电影信息数据
题外话+ 大家好啊,最近自己在做一个属于自己的博客网站(准备辞职回家养老了,明年再战)在家里 琐事也很多, 加上自己 一回到家就懒了(主要是家里冷啊! 广东十几度,老家几度,躲在被窝瑟瑟发抖,) 由于 ...
- java--mybatis的实现原理
动态代理? 需要调试下,看下源码,再研究下……
- 遍历二叉树 - 基于递归的DFS(前序,中序,后序)
上节中已经学会了如何构建一个二叉搜索数,这次来学习下树的打印-基于递归的DFS,那什么是DFS呢? 有个概念就行,而它又分为前序.中序.后序三种遍历方式,这个也是在面试中经常会被问到的,下面来具体学习 ...
- python+Appium自动化:TouchAction九宫格实战
TouchAction Touch Action包含一系列操作,比如按压.长按.点击.移动.暂停. 使用TochAction需要先导入对应的模块 from appium.webdriver.commo ...
- ak-1
最近研究ak,网上也有很多这方面的资料,就不重复叙述了,本次记录就是自己在做适应时的一些记录. 本次环境 中标麒麟 金蝶apusic 人大金仓 先说说东西从哪下载怎么来的 基本都是通过官网打电话申请 ...
