java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常;java.util.ConcurrentModificationException实战
写代码遇到这个问题,很多博客文章都是在反复的强调理论,而没有对应的实例,所以这里从实例出发,后研究理论:
一、错误产生情况
1 、字符型
(1)添加
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>();
stringList.add("张三毛");
stringList.add("李四");
stringList.add("王五");
stringList.add("钱二");
if (stringList!=null) {
if (!stringList.equals(Collections.EMPTY_LIST.isEmpty())){
for (String s : stringList) {
stringList.add("赵大");
}
}
}
System.out.println(stringList);
}
报错
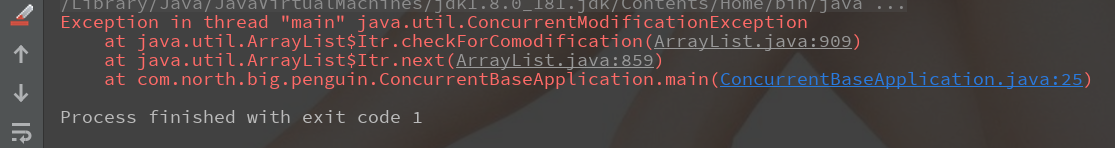
改写为如下即可:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>();
stringList.add("张三毛");
stringList.add("李四");
stringList.add("王五");
stringList.add("钱二");
if (stringList != null) {
if (!stringList.equals(Collections.EMPTY_LIST.isEmpty())) {
stringList.add("赵大");
Iterator<String> it = stringList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
it.next();
}
}
}
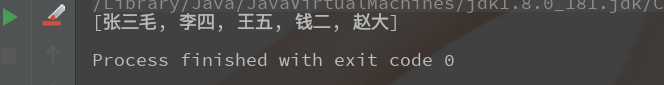
System.out.println(stringList);
}
打印出结果:
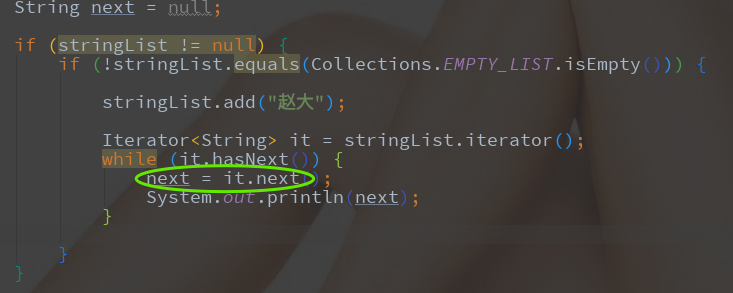
然后我们打印其next,就会发现其循环就是通过it.next()方法将数据添加进去的
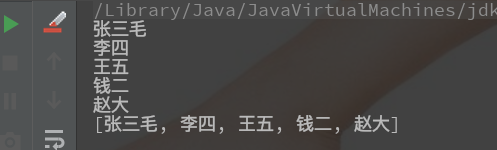
打印:
(2)、删除
错误写法:
private static String key = "钱二";
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>();
stringList.add("张三毛");
stringList.add("李四");
stringList.add("王五");
stringList.add("钱二");
if (stringList != null) {
if (!stringList.equals(Collections.EMPTY_LIST.isEmpty())) {
for (String s : stringList) {
if (key.equals(s)){
stringList.remove(s);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(stringList);
}
报错:
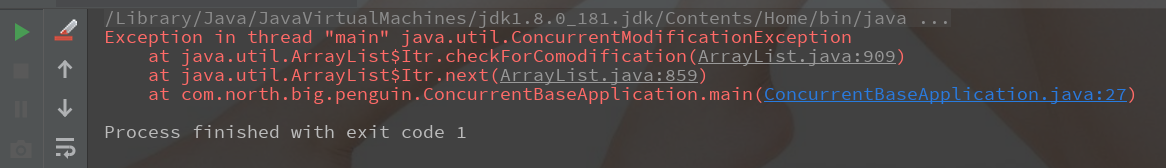
改写为:
private static String key = "钱二";
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>();
stringList.add("张三毛");
stringList.add("李四");
stringList.add("王五");
stringList.add("钱二");
if (stringList != null) {
if (!stringList.equals(Collections.EMPTY_LIST.isEmpty())) {
Iterator<String> it = stringList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String next = it.next();
if (key.equals(next)) {
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(stringList);
}
结果:
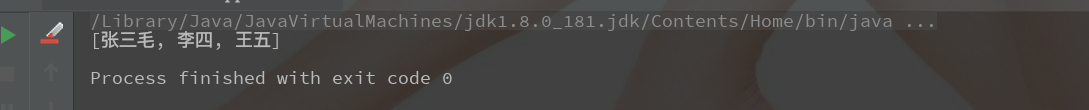
2、整形
正确添加:
public class ConcurrentBaseApplication {
private static String key = "钱二";
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
integerList.add(1);
integerList.add(2);
integerList.add(3);
integerList.add(4);
Integer next=0;
if (integerList != null) {
if (!integerList.equals(Collections.EMPTY_LIST.isEmpty())) {
integerList.add(5);
Iterator<Integer> it = integerList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
next = it.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
}
System.out.println(integerList);
}
}
结果:
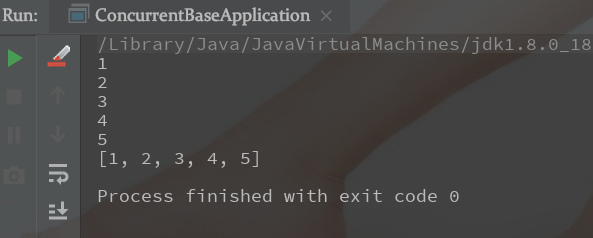
正确删除:
public class ConcurrentBaseApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
integerList.add(1);
integerList.add(2);
integerList.add(3);
integerList.add(4);
if (integerList != null) {
if (!integerList.equals(Collections.EMPTY_LIST.isEmpty())) {
Iterator<Integer> it = integerList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Integer next = it.next();
if("2".equals(next.toString())){
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(integerList);
}
}
结果:

(3) 实体类
创建实体类
Student
package com.north.big.penguin.pojo; import java.io.Serializable; /**
* @author liuyangos8888
*/
public class Student implements Serializable { /**
* 姓名
*/
private String name; /**
* 年龄
*/
private String age; /**
* 标识
*/
private String id; public Student() {
} public Student(String name, String age, String id) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
} public String getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
", id='" + id + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
正确的添加:
public class ConcurrentBaseApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setName("李雷");
student1.setAge("13");
student1.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setName("韩梅梅");
student2.setAge("14");
student2.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
Student student3 = new Student();
student3.setName("李华");
student3.setAge("15");
student3.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
students.add(student1);
students.add(student2);
students.add(student3);
if (students != null) {
if (!students.equals(Collections.EMPTY_LIST.isEmpty())) {
Student student4 = new Student();
student4.setName("小明");
student4.setAge("16");
student4.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
Iterator<Student> it = students.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
// 添加学生
Student next = it.next();
}
}
}
System.out.println(students);
}
}
结果:
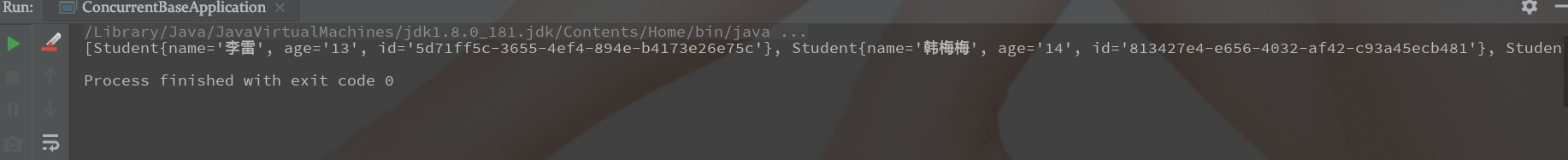
正确的删除:
public class ConcurrentBaseApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setName("李雷");
student1.setAge("13");
student1.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setName("韩梅梅");
student2.setAge("14");
student2.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
Student student3 = new Student();
student3.setName("李华");
student3.setAge("15");
student3.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
students.add(student1);
students.add(student2);
students.add(student3);
if (students != null) {
if (!students.equals(Collections.EMPTY_LIST.isEmpty())) {
Student student4 = new Student();
student4.setName("小明");
student4.setAge("16");
student4.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
Iterator<Student> it = students.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
// 添加学生
Student next = it.next();
Integer integerAge = Integer.valueOf(next.getAge());
if(integerAge>14){
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(students);
}
}
结果:
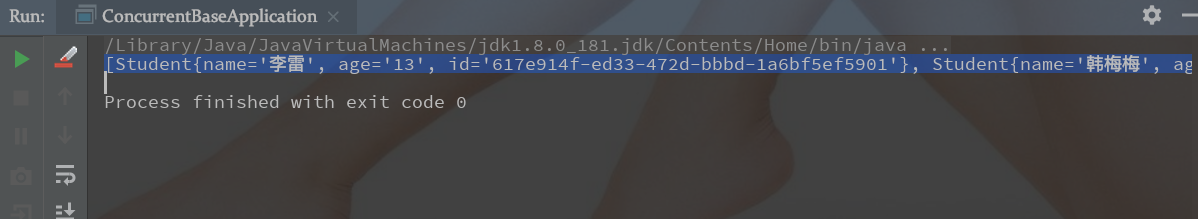
结果集:
[Student{name='李雷', age='13', id='617e914f-ed33-472d-bbbd-1a6bf5ef5901'}, Student{name='韩梅梅', age='14', id='cb804e43-4846-4fc6-84c8-9e4a6b17d7f1'}]
二、原理补充
继承关系图
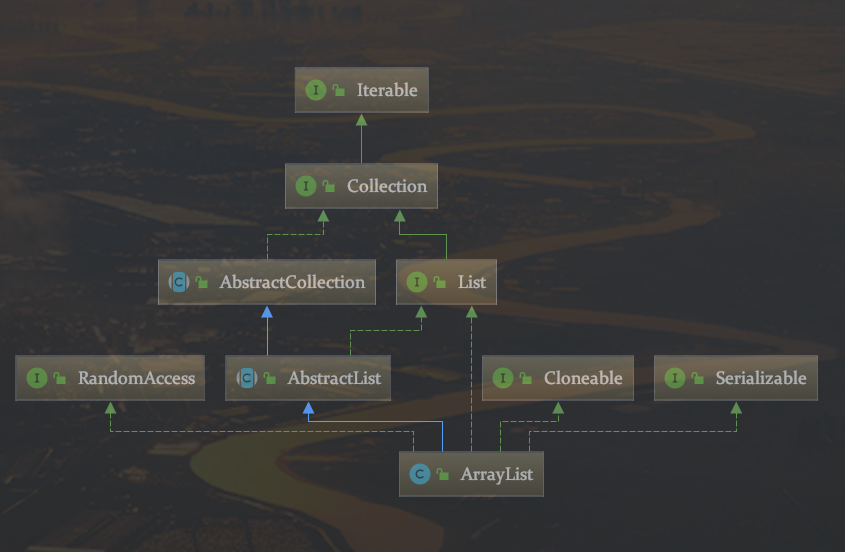
根据错误我们知道是Itr出错了

根据添加class,可以看到它跟ArrayList的关系
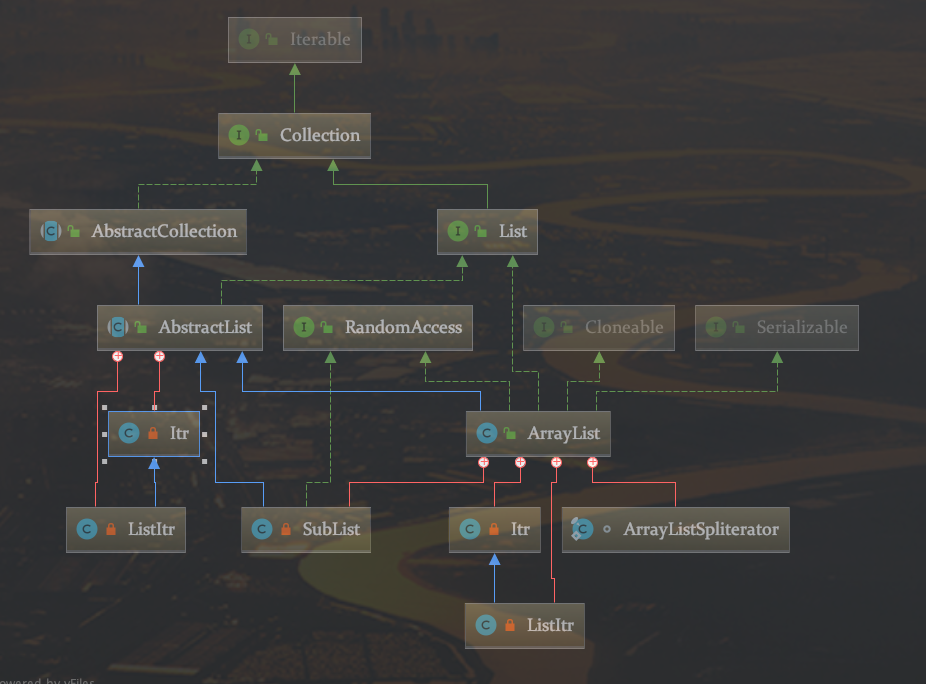
Itr是一个内部类,还实现了Iterator

其源码
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
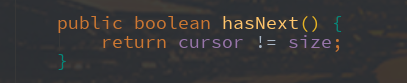
int expectedModCount = modCount; Itr() {} public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
} public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification(); try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} @Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
} final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
想要调用iteror转化ArrayList就要找iterator方法
Itr参数解析
| 参数 | 含义 |
| cursor | 一个索引,代表下一个要访问的元素的索引 |
| astRet | 表示上一个访问的元素的索引 |
| expectedModCount | 表示修改次数的 |
| modCount | 表示对List的修改次数 |
其方法主要是hasNext()和next()两个方法,
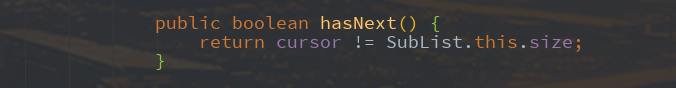
用其判断是否还有元素未被访问,代码中
while(iter.hasNext()){
}
如果下一个访问的元素下标不等于ArrayList的大小,就表示有元素需要访问,这个很容易理解,如果下一个访问元素的下标等于ArrayList的大小,则肯定到达末尾了。
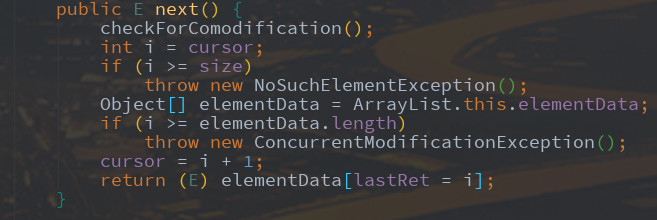
首先在next()方法中会调用checkForComodification()方法,然后根据cursor的值获取到元素,接着将cursor的值赋给lastRet,并对cursor的值进行加1操作。初始时,cursor为0,lastRet为-1,那么调用一次之后,cursor的值为1,lastRet的值为0。注意此时,modCount为0,expectedModCount也为0。
当判断当前元素的值是否为2,若为2,则调用list.remove()方法来删除该元素。
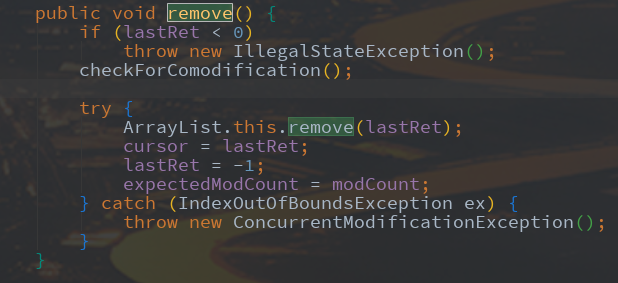
ArrayList中的remove
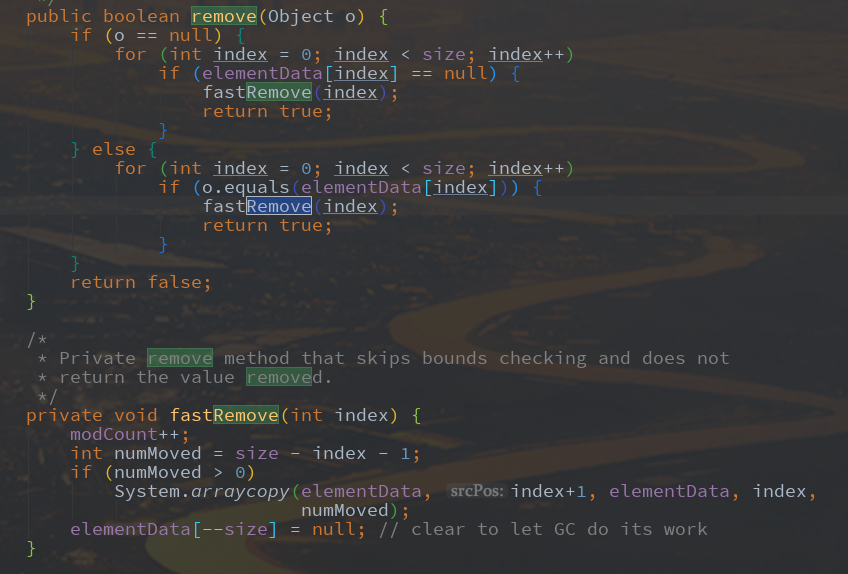
通过remove方法删除元素最终是调用的fastRemove()方法,在fastRemove()方法中,首先对modCount进行加1操作(因为对集合修改了一次),然后接下来就是删除元素的操作,最后将size进行减1操作,并将引用置为null以方便垃圾收集器进行回收工作。
执行完删除操作后,继续while循环,调用hasNext方法()判断,由于此时cursor为1,而size为0,那么返回true,所以继续执行while循环,然后继续调用iterator的next()方法.
如果modCount不等于expectedModCount,则抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
此时modCount为1,而expectedModCount为0,因此程序就抛出了ConcurrentModificationException异常。
java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常;java.util.ConcurrentModificationException实战的更多相关文章
- java.io.InvalidClassException 异常解决, 实现Serializable接口的注意事项
解决方案: 在类中显式指定 private static final long serialVersionUID = 42L; 类实现序列化接口, 进行序列化反序列化的时候, 抛出 java.io.I ...
- java集合--java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常
ConcurrentModificationException 异常:并发修改异常,当方法检测到对象的并发修改,但不允许这种修改时,抛出此异常.一个线程对collection集合迭代,另一个线程对Co ...
- java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 异常问题详解
环境:JDK 1.8.0_111 在Java开发过程中,使用iterator遍历集合的同时对集合进行修改就会出现java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常, ...
- java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常原因及解决方法
在java语言中,ArrayList是一个很常用的类,在编程中经常要对ArrayList进行删除操作,在使用remove方法对ArrayList进行删除操作时,报java.util.Concurren ...
- java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常分析
Java在操作ArrayList.HashMap.TreeMap等容器类时,遇到了java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常.以ArrayList为例,如下 ...
- java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 异常解决的方法及原理
近期在修程序的bug,发现后台抛出下面异常: Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationExceptio ...
- java foreach循环抛出异常java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
代码如下: for (Iterator<String> iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) { if (Integer.parseInt(i ...
- java.util.ConcurrentModificationException(如何避免ConcurrentModificationException)
java.util.ConcurrentModificationException is a very common exception when working with java collecti ...
- Java ConcurrentModificationException异常原因和解决方法
Java ConcurrentModificationException异常原因和解决方法 在前面一篇文章中提到,对Vector.ArrayList在迭代的时候如果同时对其进行修改就会抛出java.u ...
随机推荐
- [LeetCode] 727. Minimum Window Subsequence 最小窗口序列
Given strings S and T, find the minimum (contiguous) substring W of S, so that T is a subsequence of ...
- JAVA主动抛异常的几种方式及捕捉结果输出对比
测试代码: /** * 测试异常抛出及捕捉 */ @Test public void test() { try { this.testA(); } catch (Exception ex) { Sys ...
- 微信企业号消息接口PHP SDK
微信企业号消息接口PHP SDK及Demo <?php /* 方倍工作室 http://www.fangbei.org/ CopyRight 2015 All Rights Reserved * ...
- kubernetes实战(九):k8s集群动态存储管理GlusterFS及使用Heketi扩容GlusterFS集群
1.准备工作 所有节点安装GFS客户端 yum install glusterfs glusterfs-fuse -y 如果不是所有节点要部署GFS管理服务,就在需要部署的节点上打上标签 [root@ ...
- Python 中把一个list 列表分组/分块
比如:将list:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]按照下标顺序分成3组:[1,2,3] [4,5,6] [7,8,9]或分成5组:[1,2,] [3, 4] [5,6] [7, 8] [ 9 ] ...
- Java8 新特性 Stream 无状态中间操作
无状态中间操作 Java8 新特性 Stream 练习实例 中间无状态操作,可以在单个对单个的数据进行处理.比如:filter(过滤)一个元素的时候,也可以判断,比如map(映射)... 过滤 fil ...
- 五、Hexo静态博客背景及界面显示优化配置
示例预览:我的主页 背景图片添加 自动切换背景 静态本地背景 首先将已选定的背景图片放到博客根目录下的\source\images下 示例:D:\Blog\source\images\backgr ...
- 前端学习:JS面向对象知识学习(图解)
前端学习:JS面向对象知识学习(图解) 前端学习:JS(面向对象)代码笔记 JS面向对象图解知识全览 创建类和对象 方式1:使用Object()函数 方式2:使用自变量 方式3:使用工厂函数 创建多个 ...
- 排序算法Java代码实现(六)—— 堆排序
本片内容: 堆排序 堆排序 最大堆: 二叉堆是完全二叉树或者是近似完全二叉树, 当父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最大堆.(父节点大于任何一个子节点) 算法思想: 把n个元素建立最大 ...
- VS报错,Metadata file 'xxx.dll' could not be found
错误提示“Metadata file 'xxx.dll' could not be found”步骤如下:1.右键单击解决方案,然后单击“属性”.2.单击左侧的配置.3.确保选中了它找不到的项目的“生 ...
