Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) E. Breaking Good [Dijkstra 最短路 优先队列]
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Breaking Good is a new video game which a lot of gamers want to have. There is a certain level in the game that is really difficult even for experienced gamers.
Walter William, the main character of the game, wants to join a gang called Los Hermanos (The Brothers). The gang controls the whole country which consists of n cities with m bidirectional roads connecting them. There is no road is connecting a city to itself and for any two cities there is at most one road between them. The country is connected, in the other words, it is possible to reach any city from any other city using the given roads.
The roads aren't all working. There are some roads which need some more work to be performed to be completely functioning.
The gang is going to rob a bank! The bank is located in city 1. As usual, the hardest part is to escape to their headquarters where the police can't get them. The gang's headquarters is in city n. To gain the gang's trust, Walter is in charge of this operation, so he came up with a smart plan.
First of all the path which they are going to use on their way back from city 1 to their headquarters n must be as short as possible, since it is important to finish operation as fast as possible.
Then, gang has to blow up all other roads in country that don't lay on this path, in order to prevent any police reinforcements. In case of non-working road, they don't have to blow up it as it is already malfunctional.
If the chosen path has some roads that doesn't work they'll have to repair those roads before the operation.
Walter discovered that there was a lot of paths that satisfied the condition of being shortest possible so he decided to choose among them a path that minimizes the total number of affected roads (both roads that have to be blown up and roads to be repaired).
Can you help Walter complete his task and gain the gang's trust?
The first line of input contains two integers n, m (2 ≤ n ≤ 105, 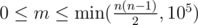 ), the number of cities and number of roads respectively.
), the number of cities and number of roads respectively.
In following m lines there are descriptions of roads. Each description consists of three integers x, y, z (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n, 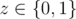 ) meaning that there is a road connecting cities number x and y. If z = 1, this road is working, otherwise it is not.
) meaning that there is a road connecting cities number x and y. If z = 1, this road is working, otherwise it is not.
In the first line output one integer k, the minimum possible number of roads affected by gang.
In the following k lines output three integers describing roads that should be affected. Each line should contain three integers x, y, z (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n, 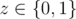 ), cities connected by a road and the new state of a road. z = 1 indicates that the road between cities x and y should be repaired and z = 0 means that road should be blown up.
), cities connected by a road and the new state of a road. z = 1 indicates that the road between cities x and y should be repaired and z = 0 means that road should be blown up.
You may output roads in any order. Each affected road should appear exactly once. You may output cities connected by a single road in any order. If you output a road, it's original state should be different from z.
After performing all operations accroding to your plan, there should remain working only roads lying on some certain shortest past between city 1 and n.
If there are multiple optimal answers output any.
2 1
1 2 0
1
1 2 1
4 4
1 2 1
1 3 0
2 3 1
3 4 1
3
1 2 0
1 3 1
2 3 0
8 9
1 2 0
8 3 0
2 3 1
1 4 1
8 7 0
1 5 1
4 6 1
5 7 0
6 8 0
3
2 3 0
1 5 0
6 8 1
In the first test the only path is 1 - 2
In the second test the only shortest path is 1 - 3 - 4
In the third test there are multiple shortest paths but the optimal is 1 - 4 - 6 - 8
有n个城市,m条边。让你求出来1到n的最短路,但是要求,保证最短路的时候,要求权值最大。
最开始没反应过来是求最短路问题,直接bfs,,,跪惨。。。。
| 9557892 | 2015-01-26 11:37:48 | njczy2010 | E - Breaking Good | GNU C++ | Accepted | 124 ms | 19100 KB |
| 9557655 | 2015-01-26 11:12:44 | njczy2010 | E - Breaking Good | GNU C++ | Accepted | 623 ms | 19300 KB |
| 9557440 | 2015-01-26 10:51:36 | njczy2010 | E - Breaking Good | GNU C++ | Wrong answer on test 8 | 31 ms | 6100 KB |
| 9557233 | 2015-01-26 10:29:53 | njczy2010 | E - Breaking Good | GNU C++ | Wrong answer on test 8 | 15 ms | 6200 KB |
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<stack>
#include<string> #define N 100005
#define M 105
#define mod 1000000007
//#define p 10000007
#define mod2 1000000000
#define ll long long
#define LL long long
#define eps 1e-6
#define inf 100000000
#define maxi(a,b) (a)>(b)? (a) : (b)
#define mini(a,b) (a)<(b)? (a) : (b) using namespace std; int n,m;
int x[N],y[N],z[N];
int tot; typedef struct
{
int a,b;
int f;
}AA; AA ans[N]; typedef struct
{
int to;
int f;
int indexb;
}PP; vector<PP>bian[N];
int vis[N];
int Step[N];
int Cnt[N]; struct QQ
{
friend bool operator < (QQ n1,QQ n2)
{
if(n1.step==n2.step){
return n1.cnt>n2.cnt;
}
else{
return n1.step>n2.step;
}
}
int index;
int cnt;
int indexn;
int pre;
int step;
}; void out(QQ te); void ini()
{
int i;
tot=;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
PP te;
for(i=;i<=n;i++){
bian[i].clear();
Step[i]=inf;
Cnt[i]=inf;
}
Step[]=;
Cnt[]=;
for(i=;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&x[i],&y[i],&z[i]);
te.to=y[i];te.f=z[i];te.indexb=i;
bian[ x[i] ].push_back(te);
te.to=x[i];
bian[ y[i] ].push_back(te);
}
} typedef struct
{
int in;
int pre;
}NN; NN node[N*];
int totnode; void bfs()
{
priority_queue <QQ>q;
QQ te,nt;
te.index=;
te.cnt=;
te.step=;
totnode=;
te.indexn=-;
te.pre=-;
q.push(te);
int st;
PP yy;
vector<PP>::iterator it;
while(q.size()>=)
{
te=q.top();
q.pop();
if(te.index==n){
out(te);
return;
}
if(vis[te.index]==) continue;
vis[te.index]=;
st=te.index;
for(it=bian[st].begin();it!=bian[st].end();it++)
{
yy=*it;
if(vis[yy.to]==) continue;
nt.index=yy.to;
nt.cnt=te.cnt;
nt.pre=te.index;
nt.step=te.step+;
if(yy.f==){
nt.cnt++;
}
if(nt.step>Step[nt.index]) continue;
if(nt.step==Step[nt.index] && nt.cnt>Cnt[nt.index]) continue;
Step[nt.index]=nt.step;
Cnt[nt.index]=nt.cnt;
nt.indexn=totnode;
node[totnode].in=yy.indexb;
node[totnode].pre=te.indexn;
totnode++;
q.push(nt);
}
}
} void solve()
{
bfs();
} void out(QQ te)
{
int i;
int vis2[N];
memset(vis2,,sizeof(vis2));
i=te.indexn;
int temp;
while(i!=-)
{
temp=node[i].in;
vis2[temp]=;
i=node[i].pre;
}
for(i=;i<=m;i++){
if(vis2[i]==){
if(z[i]==){
ans[tot].a=x[i];
ans[tot].b=y[i];
ans[tot].f=;
tot++;
}
}
else{
if(z[i]==){
ans[tot].a=x[i];
ans[tot].b=y[i];
ans[tot].f=;
tot++;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",tot);
for(i=;i<tot;i++){
printf("%d %d %d\n",ans[i].a,ans[i].b,ans[i].f);
}
} int main()
{
//freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("data.out","w",stdout);
//scanf("%d",&T);
//for(int ccnt=1;ccnt<=T;ccnt++)
//while(T--)
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
ini();
solve();
// out();
}
return ;
}
一开始wa在test8的代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<stack>
#include<string> #define N 100005
#define M 105
#define mod 1000000007
//#define p 10000007
#define mod2 1000000000
#define ll long long
#define LL long long
#define eps 1e-6
#define inf 100000000
#define maxi(a,b) (a)>(b)? (a) : (b)
#define mini(a,b) (a)<(b)? (a) : (b) using namespace std; int n,m;
int x[N],y[N],z[N];
int tot; typedef struct
{
int a,b;
int f;
}AA; AA ans[N]; typedef struct
{
int to;
int f;
int indexb;
}PP; vector<PP>bian[N];
int vis[N];
int Step[N];
int Cnt[N]; struct QQ
{
friend bool operator < (QQ n1,QQ n2)
{
if(n1.step==n2.step){
return n1.cnt>n2.cnt;
}
else{
return n1.step>n2.step;
}
}
int index;
int cnt;
string s;
int indexn;
int pre;
int step;
}; void out(QQ te); void ini()
{
int i;
tot=;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
PP te;
for(i=;i<=n;i++){
bian[i].clear();
Step[i]=inf;
Cnt[i]=inf;
}
Step[]=;
Cnt[]=;
for(i=;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&x[i],&y[i],&z[i]);
te.to=y[i];te.f=z[i];te.indexb=i;
bian[ x[i] ].push_back(te);
te.to=x[i];
bian[ y[i] ].push_back(te);
}
} typedef struct
{
int in;
int pre;
}NN; NN node[N*];
int totnode; void bfs()
{
priority_queue <QQ>q;
QQ te,nt;
te.index=;
te.cnt=;
te.step=;
te.s="";
totnode=;
te.indexn=-;
te.pre=-;
//vis[1]=1;
q.push(te);
int st;
PP yy;
char ss;
vector<PP>::iterator it;
while(q.size()>=)
{
te=q.top();
// printf(" index=%d cnt=%d",te.index,te.cnt);
// cout<<" s="<<te.s<<endl;
q.pop();
if(te.index==n){
out(te);
return;
}
if(vis[te.index]==) continue;
vis[te.index]=;
st=te.index;
for(it=bian[st].begin();it!=bian[st].end();it++)
{
yy=*it;
if(vis[yy.to]==) continue;
nt.index=yy.to;
ss=yy.indexb+'';
nt.s=te.s+ss;
// vis[yy.indexb]=1;
//vis[nt.index]=1;
nt.cnt=te.cnt;
nt.pre=te.index;
nt.step=te.step+;
if(yy.f==){
nt.cnt++;
}
if(nt.step>Step[nt.index]) continue;
if(nt.step==Step[nt.index] && nt.cnt>Cnt[nt.index]) continue;
Step[nt.index]=nt.step;
Cnt[nt.index]=nt.cnt;
nt.indexn=totnode;
node[totnode].in=yy.indexb;
node[totnode].pre=te.indexn;
totnode++;
q.push(nt); // printf(" index=%d cnt=%d",nt.index,nt.cnt);
// cout<<" s="<<nt.s<<endl;
}
}
} void solve()
{
bfs();
} void out(QQ te)
{
int l=te.s.length();
int i;
int vis2[N];
memset(vis2,,sizeof(vis2));
// cout<<"te.s="<<te.s<<" l="<<l<<endl;
i=te.indexn;
int temp;
while(i!=-)
{
temp=node[i].in;
vis2[temp]=;
i=node[i].pre;
}
// for(i=0;i<l;i++){
// vis2[ te.s[i]-'0' ]=1;
// }
for(i=;i<=m;i++){
if(vis2[i]==){
if(z[i]==){
ans[tot].a=x[i];
ans[tot].b=y[i];
ans[tot].f=;
tot++;
}
}
else{
if(z[i]==){
ans[tot].a=x[i];
ans[tot].b=y[i];
ans[tot].f=;
tot++;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",tot);
for(i=;i<tot;i++){
printf("%d %d %d\n",ans[i].a,ans[i].b,ans[i].f);
}
} int main()
{
//freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("data.out","w",stdout);
//scanf("%d",&T);
//for(int ccnt=1;ccnt<=T;ccnt++)
//while(T--)
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
ini();
solve();
// out();
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) E. Breaking Good [Dijkstra 最短路 优先队列]的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) E. Breaking Good 最短路
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/507/E E. Breaking Good time limit per test2 secondsme ...
- Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) E. Breaking Good 路径记录!!!+最短路+堆优化
E. Breaking Good time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard in ...
- 贪心 Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) A. Amr and Music
题目传送门 /* 贪心水题 */ #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #inclu ...
- Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) C. Guess Your Way Out! 思路
C. Guess Your Way Out! time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- CodeForces Round #287 Div.2
A. Amr and Music (贪心) 水题,没能秒切,略尴尬. #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespac ...
- Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) C. Guess Your Way Out! 水题
C. Guess Your Way Out! time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) B. Amr and Pins 水题
B. Amr and Pins time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inpu ...
- Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) A. Amr and Music 水题
A. Amr and Music time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inp ...
- Codeforces Round #287 (Div. 2) D. The Maths Lecture [数位dp]
传送门 D. The Maths Lecture time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stan ...
随机推荐
- git 添加 ,密匙
转载此处 https://blog.csdn.net/xiayiye5/article/details/79652296
- 实 Jordan 标准型和实 Weyr 标准型
将学习到什么 本节讨论关于实矩阵的实形式的 Jordan 标准型,也讨论关于复矩阵的另外一种形式的 Jordan 标准型,因为它在与交换性有关的问题中很有用. 实 Jordan 标准型 假设 \( ...
- 【page-monitor 前端自动化 中篇】 源码分析
转载文章:来源(靠谱崔小拽) 上篇中初探了page-monitor的一些功能和在前端自动化测试方面的可行性,本篇主要分析下page-monitor的实现方式和源码. mode-module简介 pag ...
- C# 使用Epplus导出Excel [2]:导出动态列数据
C# 使用Epplus导出Excel [1]:导出固定列数据 C# 使用Epplus导出Excel [2]:导出动态列数据 C# 使用Epplus导出Excel [3]:合并列连续相同数据 C# 使用 ...
- HTML 显示和隐藏浏览器滚动条
滚动条和overflow有关 显示: overflow-x:auto; overflow-y:auto; overflow-x:scroll; overflow-y:scroll; 隐藏: overf ...
- js函数arguments与获取css样式方法
函数传参,当参数的个数不定时,可以使用arguments:表示实参集合 arguments.length=实参个数 获得css样式方法: getComputedStyle()方法---->得到的 ...
- django第9天(多表操作)
django第9天 models类 class Book(Model): id = AutoField(primary_key=True) name = CharField(max_length=20 ...
- HDU 2476 区间DP String painter
题解 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm ...
- 练习题,新建数据库anyun
一.新建数据库,数据库名为anyun mysql> create database anyun; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) 二.查看数据库 mysq ...
- POP-一个点击带有放大还原的动画效果
原理 监听屏幕的点击事件 - (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)ev ...
