c#数字图像处理(十二)图像的腐蚀与膨胀
背景知识
腐蚀与膨胀基本原理:就是用一个特定的结构元素来与待处理图像按像素做逻辑操作;可以理解成拿一个带孔的网格板(结构元素矩阵中元素为1的为孔)盖住图像的某一部分,然后按照各种不同的观察方式来确定操作类型。
比如:腐蚀操作就是拿这个结构元素的中心位置(假设参与逻辑计算的元素对应与二维矩阵中元素为1的点,即网格板上的孔),在图像上移动时,如果透过所有的孔都能看到底下的图像,那么这个中心点处的图像就保留,否则去除。
腐蚀
图像腐蚀运算定义
二值图像腐蚀运算的数学表达式为
g(x,y)=erode[f(x, y ), B]=AND[Bf(x,y)]
其中,g(x,y)为腐蚀后的二值图像,f(x,y)为原二值图像,B为结构元素。B(x,y)定义为:
Bf(x,y)={f(x-bx, y-by) ,(bx, by)∈B}
算子AND(x1,…,xn)定义为:当且仅当x1=··=xn=1时,AND(x1,…,xn)等于1;否则为0。
把结构元素B平移a后得到Ba,若Ba包含于X,我们记下这个a点,所有满足上述条件的a点组成的集合称做X被B腐蚀(Erosion)的结果。用公式表示为:E(X)={a| Ba∈X}=XB。原理图如下:
实际使用时示意图:
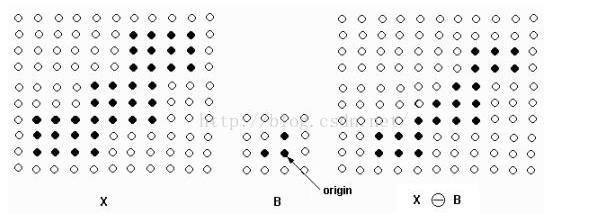
说明:左边是被处理的图象X(二值图象,我们针对的是黑点),中间是结构元素B,那个标有origin的点是中心点,即当前处理元素的位置,我们在介绍模板操作时也有过类似的概念。腐蚀的方法是,拿B的中心点和X上的点一个一个地对比,如果B上的所有点都在X的范围内,则该点保留,否则将该点去掉;右边是腐蚀后的结果。可以看出,它仍在原来X的范围内,且比X包含的点要少,就象X被腐蚀掉了一层。
private void erode_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (curBitmap != null)
{
struction struForm = new struction();
struForm.Text = "腐蚀运算结构元素";
if (struForm.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(, , curBitmap.Width, curBitmap.Height);
BitmapData bmpData = curBitmap.LockBits(rect, ImageLockMode.ReadWrite, curBitmap.PixelFormat);
IntPtr ptr = bmpData.Scan0;
int bytes = curBitmap.Width * curBitmap.Height;
byte[] grayValues = new byte[bytes];
Marshal.Copy(ptr, grayValues, , bytes); //得到结构元素
byte flagStru = struForm.GetStruction; byte[] tempArray = new byte[bytes];
for (int i = ; i < bytes; i++)
{
tempArray[i] = ;
}
switch (flagStru)
{
case 0x11:
//3位水平方向结构元素
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j ++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
}
}
}
break;
case 0x21:
//5位水平方向结构元素
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
}
}
}
break;
case 0x12:
//3位垂直方向结构元素
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x22:
//5位垂直方向结构元素
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x14:
//3位十字形状结构元素
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x24:
//5位十字形状结构元素
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x18:
//3位方形结构元素
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x28:
//5位方形结构元素
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == &&
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
default:
MessageBox.Show("错误的结构元素!");
break;
} grayValues = (byte[])tempArray.Clone();
Marshal.Copy(grayValues, , ptr, bytes);
curBitmap.UnlockBits(bmpData);
} Invalidate();
}
}
#region 关于图像尺寸的说明
//本代码只能处理8位深度的512*512图像。可自行修改,如修改3位水平方向结构元素代码:
//01修改成如下代码即可处理任意尺寸的8位深度的图像
//int bytes = bmpData.Stride * curBitmap.Height;
//for (int i = 0; i < curBitmap.Height; i++)
//{
// for (int j = 1; j < curBitmap.Width - 1; j++)
// {
// if (grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j] == 0 &&
// grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 3] == 0 &&
// grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j - 1] == 0)
// {
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j] = 0;
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 1] = 0;
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 2] = 0;
// }
// }
//}
//02修改成如下代码即可处理任意尺寸的24位深度的图像
//int bytes = bmpData.Stride * curBitmap.Height;
//for (int i = 0; i < curBitmap.Height; i++)
//{
// for (int j = 4; j < curBitmap.Width * 3 - 3; j += 3)
// {
// if (grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j] == 0 &&
// grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 3] == 0 &&
// grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j - 1] == 0)
// {
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j] = 0;
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 1] = 0;
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 2] = 0;
// }
// }
//}
#endregion
膨胀
图像膨胀运算定义
二值图像膨胀运算的数学表达式为:
g(x, y)=dilate[f(x, y), B]=OR[Bf(x,y)]
其中,g(x,y)为膨胀后的二值图像,f(x,y)为原二值图像,B为结构元素。
B(x,y)定义为:
Bf(x,y)={f(x-bx, y-by) ,(bx, by)∈B}
算子OR(x1…xn)定义为:当且仅当x1=…=xn=0时,OR(x1,…xn)等于0;否则为1
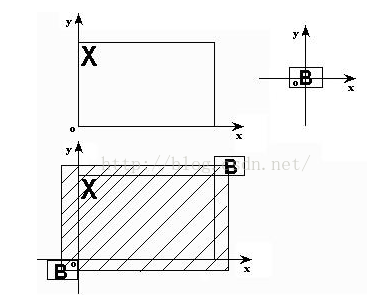
膨胀(dilation)可以看做是腐蚀的对偶运算,其定义是:把结构元素B平移a后得到Ba,若Ba击中X,我们记下这个a点。所有满足上述条件的a点组成的集合称做X被B膨胀的结果。用公式表示为:D(X)={a | Ba↑X}=X  B,如图6.13所示。图6.13中X是被处理的对象,B是结构元素,不难知道,对于任意一个在阴影部分的点a,Ba击中X,所以X被B膨胀的结果就是那个阴影部分。阴影部分包括X的所有范围,就象X膨胀了一圈似的,这就是为什么叫膨胀的原因。原理图如下:
B,如图6.13所示。图6.13中X是被处理的对象,B是结构元素,不难知道,对于任意一个在阴影部分的点a,Ba击中X,所以X被B膨胀的结果就是那个阴影部分。阴影部分包括X的所有范围,就象X膨胀了一圈似的,这就是为什么叫膨胀的原因。原理图如下:
实际使用时示意图:
说明:左边是被处理的图象X(二值图象,我们针对的是黑点),中间是结构元素B。膨胀的方法是,拿B的中心点和X上的点及X周围的点一个一个地对,如果B上有一个点落在X的范围内,则该点就为黑;右边是膨胀后的结果。可以看出,它包括X的所有范围,就象X膨胀了一圈似的。
private void dilate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (curBitmap != null)
{
struction struForm = new struction();
struForm.Text = "膨胀运算结构元素";
if (struForm.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(, , curBitmap.Width, curBitmap.Height);
BitmapData bmpData = curBitmap.LockBits(rect, ImageLockMode.ReadWrite, curBitmap.PixelFormat);
IntPtr ptr = bmpData.Scan0;
int bytes = curBitmap.Width * curBitmap.Height;
byte[] grayValues = new byte[bytes];
Marshal.Copy(ptr, grayValues, , bytes); byte flagStru = struForm.GetStruction; byte[] tempArray = new byte[bytes];
for (int i = ; i < bytes; i++)
{
tempArray[i] = ;
} switch (flagStru)
{
case 0x11:
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x21:
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x12:
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x22:
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x14:
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x24:
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x18:
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
case 0x28:
for (int i = ; i < curBitmap.Height - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < curBitmap.Width - ; j++)
{
if (grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[(i - ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[i * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j - ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == ||
grayValues[(i + ) * curBitmap.Width + j + ] == )
{
tempArray[i * curBitmap.Width + j] = ;
} }
}
break;
default:
MessageBox.Show("错误的结构元素!");
break;
} grayValues = (byte[])tempArray.Clone(); System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.Copy(grayValues, , ptr, bytes);
curBitmap.UnlockBits(bmpData);
} Invalidate();
}
}
#region 关于图像尺寸的说明
//本代码只能处理8位深度的512*512图像。可自行修改,例如修改3位水平方向结构元素代码:
//01修改成如下代码即可处理任意尺寸的8位深度的图像
//int bytes = bmpData.Stride * curBitmap.Height;
//for (int i = 0; i < curBitmap.Height; i++)
//{
// for (int j = 1; j < curBitmap.Width - 1; j++)
// {
// if (grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j] == 0 ||
// grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 3] == 0 ||
// grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j - 1] == 0)
// {
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j] = 0;
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 1] = 0;
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 2] = 0;
// }
// }
//}
//02修改成如下代码即可处理任意尺寸的24位深度的图像
//int bytes = bmpData.Stride * curBitmap.Height;
//for (int i = 0; i < curBitmap.Height; i++)
//{
// for (int j = 4; j < curBitmap.Width * 3 - 3; j += 3)
// {
// if (grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j] == 0 ||
// grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 3] == 0 ||
// grayValues[i * bmpData.Stride + j - 1] == 0)
// {
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j] = 0;
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 1] = 0;
// tempArray[i * bmpData.Stride + j + 2] = 0;
// }
// }
//}
#endregion
c#数字图像处理(十二)图像的腐蚀与膨胀的更多相关文章
- Win8MetroC#数字图像处理--2.2图像二值化函数
原文:Win8MetroC#数字图像处理--2.2图像二值化函数 [函数代码] /// <summary> /// Binary process. /// </summary> ...
- Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.2图像方差计算
原文:Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.2图像方差计算 /// <summary> /// /// </summary>Variance computing. / ...
- Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.3图像直方图计算
原文:Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.3图像直方图计算 /// <summary> /// Get the array of histrgram. /// </sum ...
- Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.4图像信息熵计算
原文:Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.4图像信息熵计算 [函数代码] /// <summary> /// Entropy of one image. /// </su ...
- Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.5图像形心计算
原文:Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.5图像形心计算 /// <summary> /// Get the center of the object in an image. ...
- Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.1图像均值计算
原文:Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--3.1图像均值计算 /// <summary> /// Mean value computing. /// </summary> ...
- Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--2.74图像凸包计算
原文:Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--2.74图像凸包计算 /// <summary> /// Convex Hull compute. /// </summary> ...
- Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--2.68图像最小值滤波器
原文:Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--2.68图像最小值滤波器 /// <summary> /// Min value filter. /// </summary> ...
- Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--2.52图像K均值聚类
原文:Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--2.52图像K均值聚类 [函数名称] 图像KMeans聚类 KMeansCluster(WriteableBitmap src,i ...
- Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--2.45图像雾化效果算法
原文:Win8 Metro(C#)数字图像处理--2.45图像雾化效果算法 [函数名称] 图像雾化 AtomizationProcess(WriteableBitmap src,i ...
随机推荐
- html5中的audio和video属性和事件汇总
<audio> 标签属性: src:音乐的URL preload:预加载 autoplay:自动播放 loop:循环播放 controls:浏览器自带的控制 <video> 标 ...
- C++中常量成员函数的含义
C++中常量成员函数的含义 本文内容来源:<C++必知必会> 使用常量成员函数可以改变对象的逻辑状态,虽然对象的物理状态没有发生改变.考虑如下代码,它定义了一个类X: class X{ p ...
- STM32 命名方法
1.STM32型号的说明:以STM32F103RBT6这个型号的芯片为例,该型号的组成为7个部分,其命名规则如下: STM32 ST公司生产的Cortex-M内核的32位微控制器 F F代表产品类型 ...
- 定位、识别;目标检测,FasterRCNN
定位: 针对分类利用softmax损失函数,针对定位利用L2损失函数(或L1.回归损失等) 人关节点检测 针对连续变量和离散变量需要采用不同种类的损失函数. 识别: 解决方案: 1.利用滑动窗口,框的 ...
- The fifth day of Crawler learning
使用mongoDB 下载地址:https://www.mongodb.com/dr/fastdl.mongodb.org/win32/mongodb-win32-x86_64-2008plus-ssl ...
- 【他山之石】mysql编码问题总结
有些问题可能比较基础,但是没有经过系统学习还是可能会出错,记录下. 这次是mysql的编码问题. 背景是部署新的测试环境,给了一台服务器还有在另一个环境下的mysql,配置过程中发现mysql编码有问 ...
- 【题解】有标号的DAG计数2
[HZOI 2015] 有标号的DAG计数 II \(I\)中DP只有一个数组, \[ dp_i=\sum{i\choose j}2^{j(i-j)}dp_{i-j}(-1)^{j+1} \] 不会. ...
- win服务器管理工具,服务器vps管理
win系列服务器,vps桌面如何管理?用这个工具: IIS7远程桌面批量管理,同时管理上千台vps,服务器,3389远程端口.
- Linux学习之路--简介
1 Linux简介 UNIX与Linux发展史 Unix在1969年,美国贝尔实验室的肯汤普森在DEC PDP-7机器上开发出了UNIX系统.Linux出现于1991年,是由芬兰赫尔辛基大学学生李纳斯 ...
- webpack 实时编译typescript与scss
webpack.config.js const path = require('path'); const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plug ...