ospfv3 lsa database
https://www.networkfuntimes.com/ospfv3-the-new-lsa-types-in-ipv6-ospf/
WHY DID THEY CHANGE THE LSAs FOR OSPFv3?
You’ll remember that OSPF has seven link-state advertisement types. Let’s quickly remind ourselves about the first one: Router LSAs, otherwise known as Type 1 LSAs.
Router LSAs advertise the fact that a router is in the area; the links attached to that router; and the IP networks on those links. This means that if an IP address is changed on an interface, or if a link goes down, the router generates a new LSA with the change in topology. This LSA gets flooded throughout the area, and then each router eagerly and hungrily re-runs the SPF algorithm, as if the routers were junkies, but junkies addicted not to meth, but to maths.
In IPv4, a link on a router generally only has one IP network on it, and the address generally stays the same, so it’s not such a big deal for the SPF calculation to have to re-run every time there’s a change. But IPv6 is a bit different, because you can, and often do, have multiple IPv6 prefixes on one link. Which means that every time a new IPv6 prefix is added, the SPF algorithm would need to be run again – even though there’s been no change in the physical topology!
IPv4网络中,一个接口只有一个地址,地址很少变。IPv6中,一个接口可以有很多地址,增加一个地址就会触发SPF计算,开销大。
This seems pretty inefficient. All the routers already know the best path to get to the link. The addition of a new IPv6 prefix shouldn’t generate such unnecessary workload for our routers. Wouldn’t it be better to somehow separate the physical topology information from the IPv6 address information, so we can add IPv6 addresses ?
That’s exactly what some wise boffins did: in OSPFv3, the IP address information has been taken out of the Router LSA, which now exists only to advertise the physical links on a router. Instead, IPv6 address advertisements now happen in the two brand new LSA types: Link LSAs (Type 8), and Intra-Area Prefix LSAs (Type 9).
Here’s a list of all nine OSPFv3 LSAs, next to the equivalent LSA in IPv4 OSPF.
| OSPFv3 LSA TYPE | LSA NAME | OSPFv2 LSA TYPE | LSA NAME |
| 0x2001 | Router LSA | 1 | Router LSA |
| 0x2002 | Network LSA | 2 | Network LSA |
| 0x2003 | Inter-Area Prefix LSA | 3 | Summary LSA |
| 0x2004 | Inter-Area Router LSA | 4 | ASBR Summary LSA |
| 0x4005 | AS-External LSA | 5 | AS-External LSA |
| 0x2006 | Multicast LSA | 6 | Multicast LSA |
| 0x2007 | Not-So-Stubby-Area LSA | 7 | Not-So-Stubby-Area LSA |
| 0x0008 | Link LSA | ||
| 0x2009 | Intra-Area Prefix LSA |
第1个十六进制数是区域:
0 = LINK LOCAL ONLY
2 = AREA ONLY
4 = ENTIRE AUTONOMOUS SYSTEM
用例子描述不同LSA的作用
https://www.networkfuntimes.com/ospfv3-how-to-read-ipv6s-ospf-database/
Router-LSA描述路由器节点之间的拓扑,连接关系
Network-LSA描述某个网络有哪些路由器
Link-LSA和Intra-Prefix描述前缀信息(地址信息)
OSPFv3 – HOW TO READ IPv6’s OSPF DATABASE
So, you’ve read my guide to the new link-state advertisement types in OSPFv3. (If you haven’t, read it now!)
Well, now you know the theory, how about we get hands-on with a little bit of practice? Okay, fine, you’ve twisted my arm: we’ll do it. Stop twisting my arm now. Ow! I said stop! You’re hurting my arm! OW! MUM!! THE BIGGER BOYS ARE TWISTING MY ARM AGAIN!
In this post, we’re going to dig deep into the OSPFv3 database. Put your topology hat on: we’re going exploring.
OUR TOPOLOGY
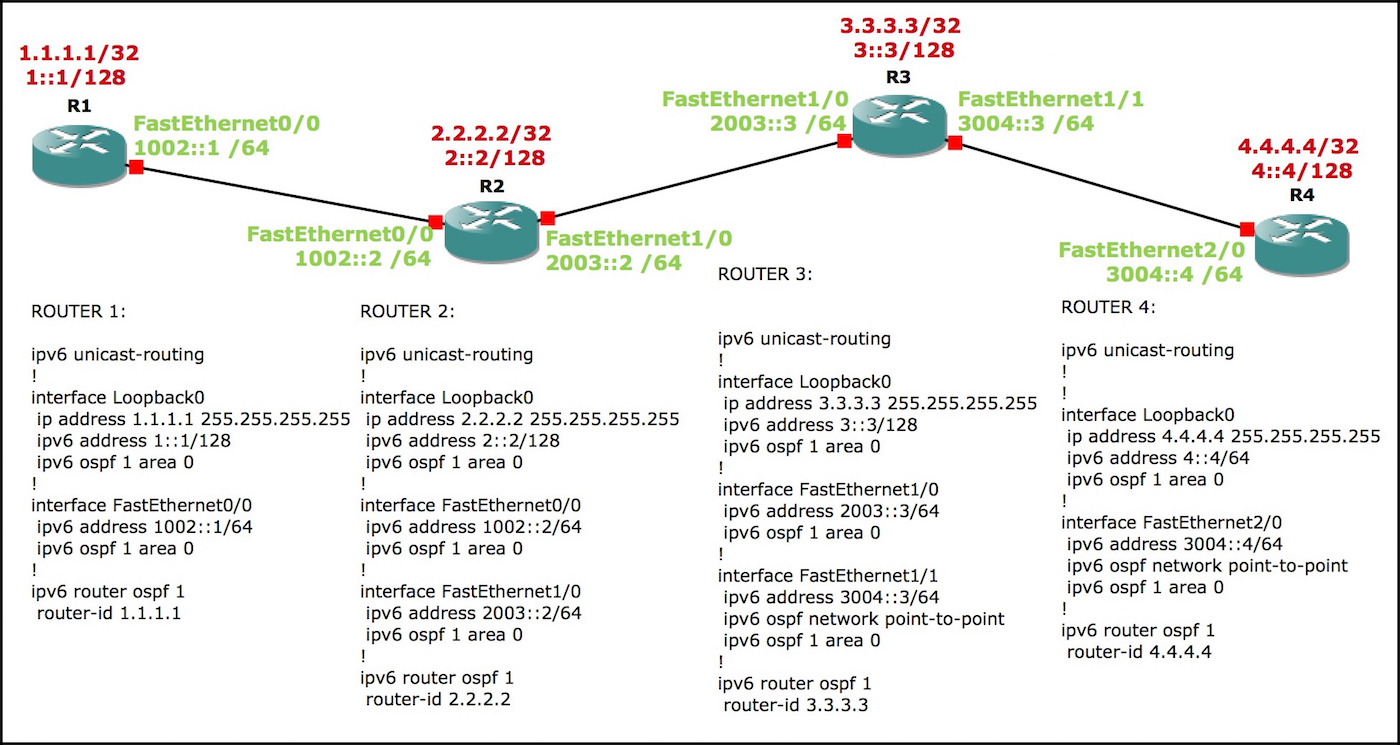 If there’s one thing I know about millennials, it’s that they love a sweet topology. Well, who am I to deny them what they want.
If there’s one thing I know about millennials, it’s that they love a sweet topology. Well, who am I to deny them what they want.
Here’s the topology we’ll be using: four routers, logically numbered.
We’ll be spending most of our time on router 1. Every interface is FastEthernet, which you may know means that the network type defaults to being a transit network, requiring a DR/BDR election. So, to shake things up, the link between routers 3 and 4 has been manually configured to be a point-to-point.
READING THE DATABASE SUMMARY
So, let’s “log on” to Router 1, and “dive in” to our full database, by typing show ipv6 ospf database.
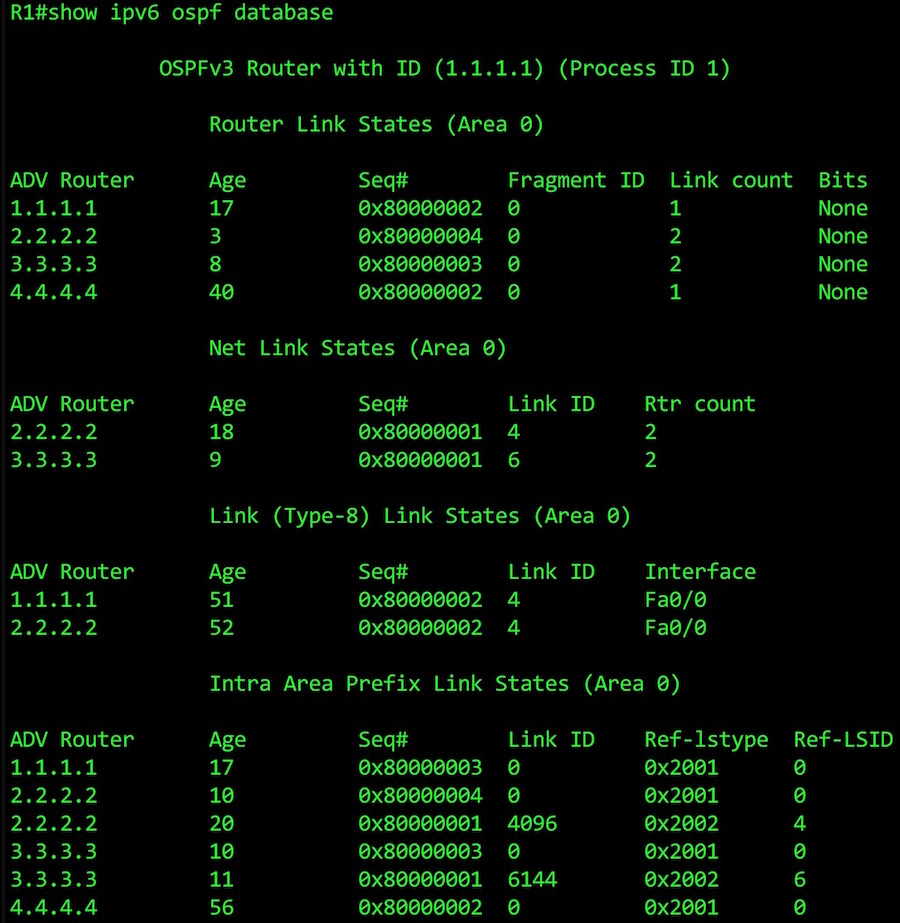
At the top of our LSA database we see four router LSAs, one for each router.
We also see two network LSAs. 2.2.2.2 won the DR election for the link between routers 1 and 2, while 3.3.3.3 won the election between routers 2 and 3. (Remember that we set the link between 3 and 4 to be a point-to-point, so there’s no network LSA for this link.
Next, we see the first of our two new LSA types, the Type 8 “Link” LSA. Notice that we only see routers 1 and 2 on this list. That makes sense: we wouldn’t see routers 3 and 4, because this LSA only has a link-local scope.
The final section is where the good stuff happens: the new Intra-Area Prefix LSA. Notice that some routers have more than one LSA here. That’s because there’s an LSA for each link, and routers 2 and 3 both have two links on them.
We also see a column called “Ref-lstype”. This refers back to what we talked about in our previous article, about the new LSA Types. We see 0x2001 when the prefix refers to a physical interface advertised in a Router LSA, and 0x2002 when we’re referencing Network LSAs.
Now that you know what’s going on in the database summary, shall we go even deeper? Deeper than we’ve ever been before? Don’t be scared. You can hold my hand, if you like?
READING TYPE 1 ROUTER LSAs IN OSPFv3
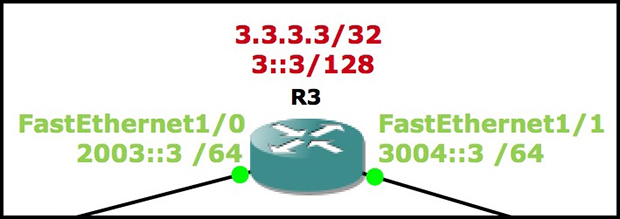 Lets have a look at the Router LSA being generated by 3.3.3.3.Remember, Router 3 has two FastEthernet links. One is manually configured to be a point-to-point. The other is left to its default settings, and is therefore a transit network (ie one that requires a DR/BDR election).
Lets have a look at the Router LSA being generated by 3.3.3.3.Remember, Router 3 has two FastEthernet links. One is manually configured to be a point-to-point. The other is left to its default settings, and is therefore a transit network (ie one that requires a DR/BDR election).
In this article you can always see the full command we’re typing at the top of each screenshot. For example, you can see that below we’re typing show ipv6 ospf database router adv-router 3.3.3.3.
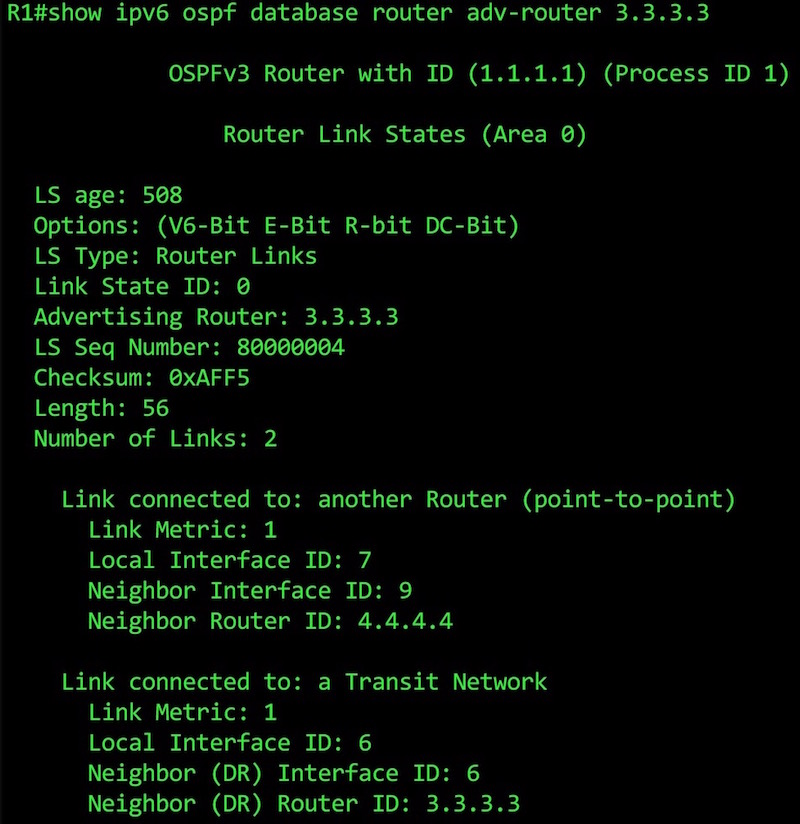 This is what a Type 1 LSA looks like in OSPFv3. It’s so beautiful! Perfection! As if it were made by the gods!
This is what a Type 1 LSA looks like in OSPFv3. It’s so beautiful! Perfection! As if it were made by the gods!
First we see the high-points of the LSA: its age, type, the advertising router ID, the link-state sequence number, and the number of links.
Below that, we see our two links. It worked! Phew! Everything’s coming up Millhouse.
Notice how there’s no prefix information any more in this LSA. We’ll see that later, in our Type 9 LSA. All we have here is a local interface ID (more info on this in a moment), and either the router’s ID if it’s a point-to-point link, or the DR Router ID if it’s a transit network. Our routers use this information to piece together the jigsaw that is our network.
READING TYPE 2 NETWORK LSAs IN OSPFv3
So, how about the LSAs for segments that require a DR? As you’d expect, there’s just the one LSA, and it’s made by the winner of the DR election:
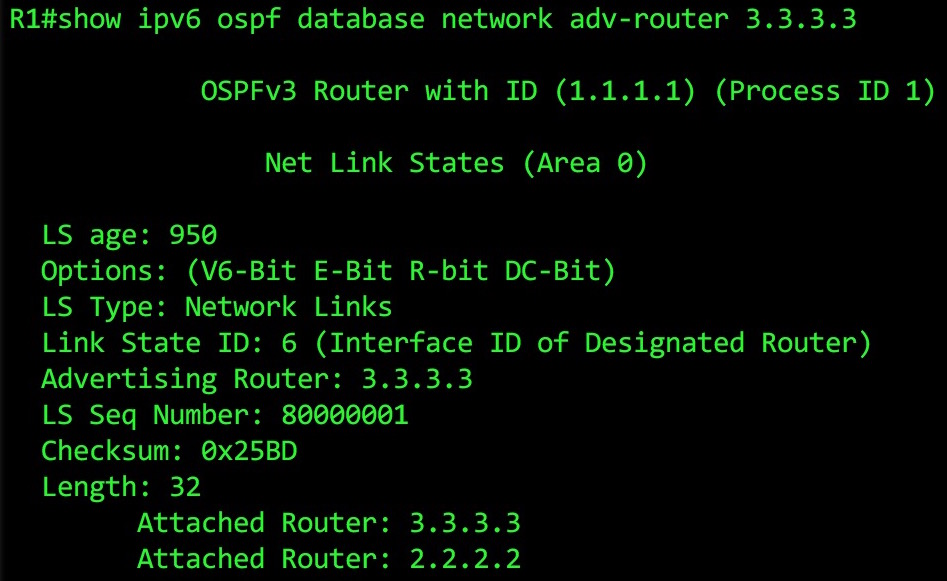 This LSA is nice and simple: we see all the routers in the network segment – and thanks to the info in the Advertising Router section, we know that 3.3.3.3 is the DR for this segment.
This LSA is nice and simple: we see all the routers in the network segment – and thanks to the info in the Advertising Router section, we know that 3.3.3.3 is the DR for this segment.
Again, there’s no prefix information here: in OSPFv3, this LSA’s only function is to tell us about the DR, and the routers on the segment.
What’s this Link State ID we keep seeing? What does “Link State ID: 6 (Interface ID of Designated Router)” mean? For an answer, let’s hop over to Router 3, and type show ipv6 ospf interface brief:
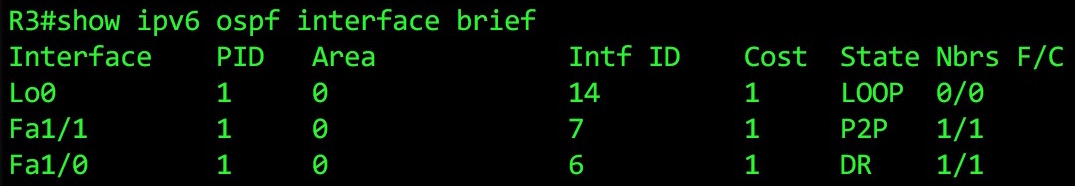
Each interface on a router is given an Intf ID. No, it doesn’t refer to Intifada ID (quick side-note: solidarity with everyone around the world on the streets fighting tyranny). Instead, IntfID refers to the interface ID.
The information you need to build the topology is a bit spread out, but luckily routers are smart enough to be able to piece all of this together, and build the network in its imagination. Good work, Barry Cisco (CEO of Cisco)!
READING TYPE 8 NETWORK LSAs IN OSPFv3
Now, let’s look at the new LSAs – the ones that contain the actual prefix information.
First, we’ll look at the Link LSA, which contains information only about the prefixes on local links. We’re still on Router 1, so let’s see what it gets from its link-local neighbor, 2.2.2.2:
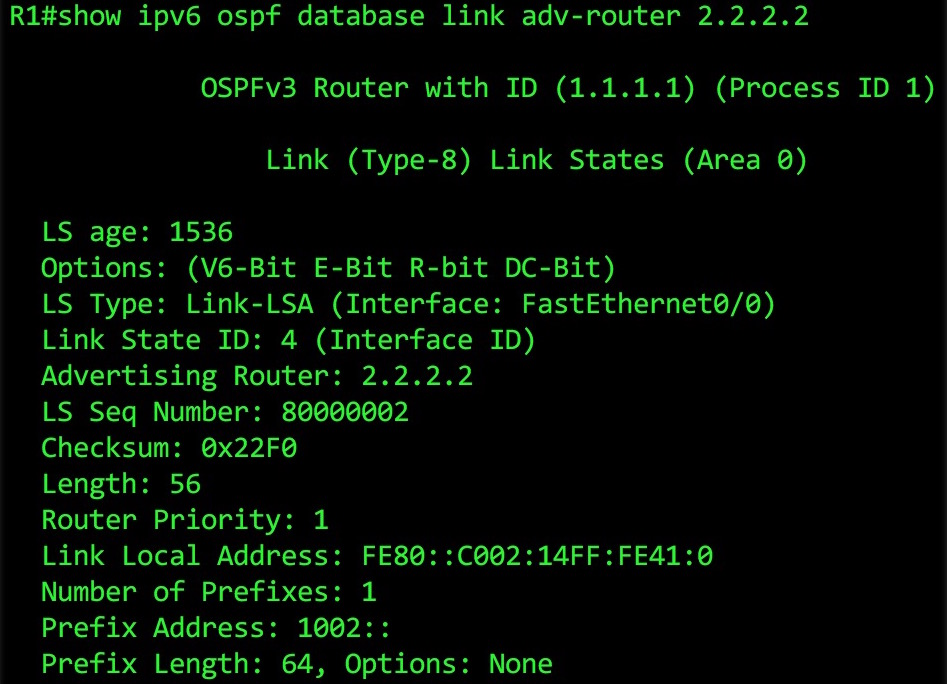 Near the bottom you can see what we’re looking for: the Link Local Address. We also see any global prefixes configured on the link, and the prefix length. This info is repeated in the Type 9 LSA. But remember: nothing in this LSA is passed on to any neighbors. It stays link local, like a blood pact between sisters who have sworn to keep a secret until the day they die.
Near the bottom you can see what we’re looking for: the Link Local Address. We also see any global prefixes configured on the link, and the prefix length. This info is repeated in the Type 9 LSA. But remember: nothing in this LSA is passed on to any neighbors. It stays link local, like a blood pact between sisters who have sworn to keep a secret until the day they die.
You can combine the Advertising Router with the Link State ID (aka the Interface ID) to work out exactly where this is in the topology.
READNG TYPE 9 INTRA-AREA PREFIX LSAs
Finally, we get to the best one. Let’s just remind ourself what we saw in Router 1’s database summary:
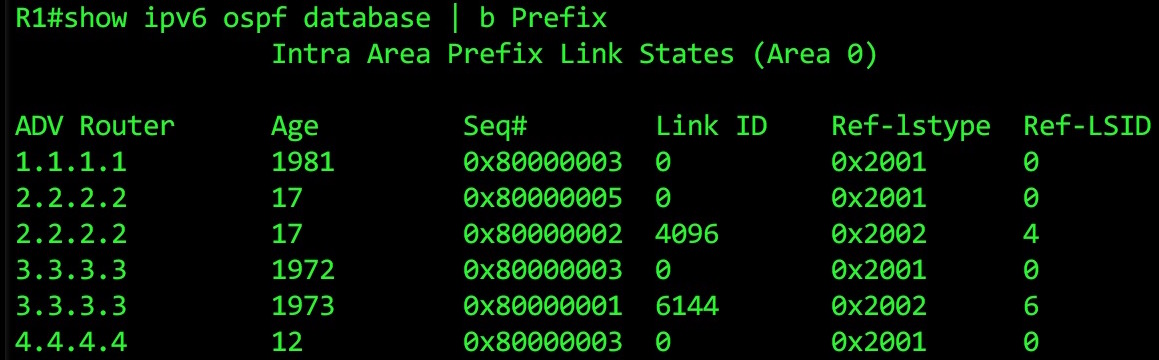
What we see here is one link-state advertisement for every link on each router. That’s why 2.2.2.2 and 3.3.3.3 appear twice: they have two links on them. (Fun fact: loopbacks aren’t classed as “links”, so keep an eye out below for where that prefix information is stored.)
Let’s take a look at what information Router 1 knows about Router 3, using the command show ipv6 ospf database prefix adv-router 3.3.3.3:
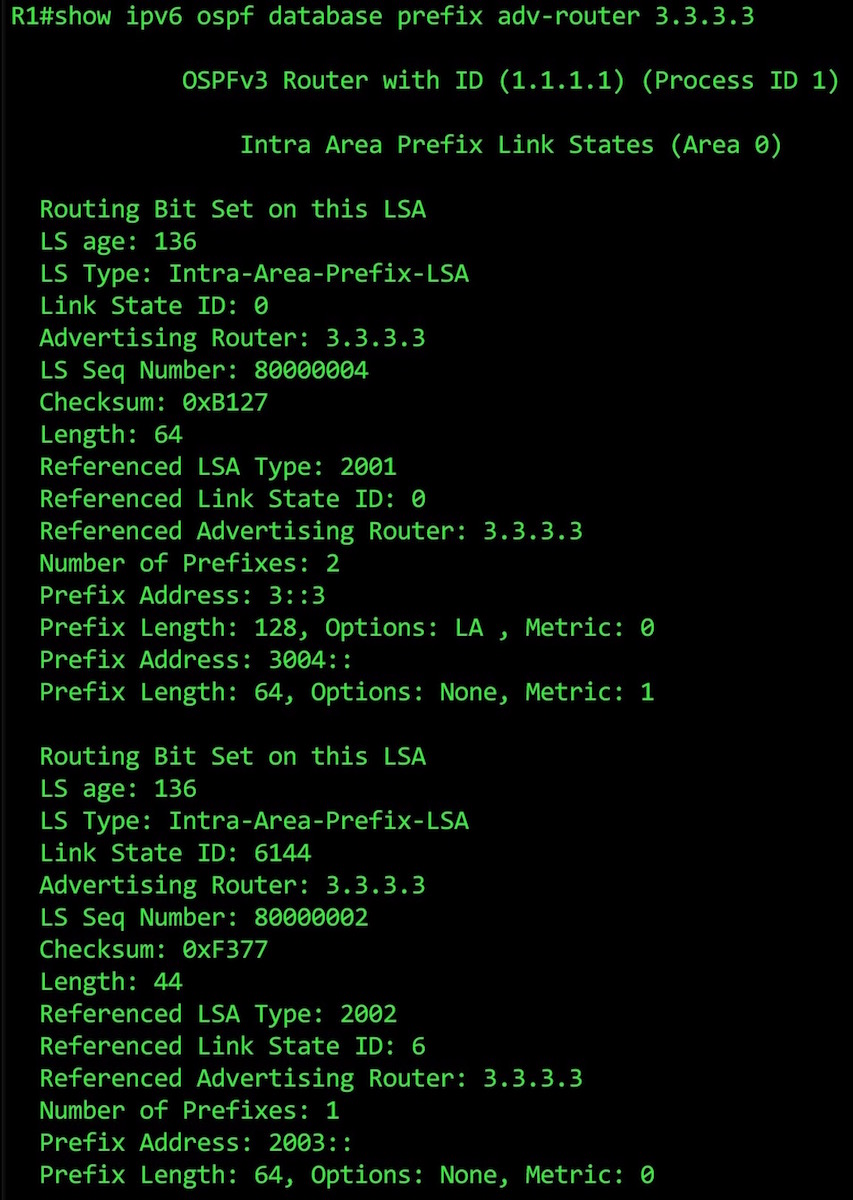 This command gives us the details about the two Type 9 LSAs that Router 3 is generating.
This command gives us the details about the two Type 9 LSAs that Router 3 is generating.
In the first one, we see the prefix info on the link between routers 3 and 4. I know this because I cleverly chose IPv6 addresses that start with the numbers of the two routers, hence the output “Prefix Address: 3004::“.
Of course, in the real world things won’t be this easy to read. In a production environment, it will probably be a LOT harder to work out precisely which link you’re looking at: you’ll need to log on to the Advertising Router, and do a show ipv6 ospf interface brief to find the interface’s Link State ID.
Staying on the first LSA, notice that it contains not only the 3004::/64 network, but also our loopback address, 3::3/128! What?? That’s surely not right? 3::3/128 is on its own loopback interface. It’s not on the same FastEthernet interface as the 3004:/64 network. What’s going on??
Well, it turns out that OSPFv3 doesn’t advertise loopbacks as links. So, to get around this, OSPFv3 attaches the prefix to a different link instead. Notice the section that says “Options: LA“. LA stands for Local Address, and when the LA bit is set on a prefix, it means it’s a local address on the router.
(I’ll be honest with you: I don’t know why the router chooses to attach the Loopback prefix to Router 3’s FastEthernet1/1 link, and not its FastEthernet 1/0 link. I did a lot of Googling, and no-one on the internet seems to know either! Do comment if you know the answer!)
Under that, we see the second LSA. It’s broadly the same, but refers just to the 2003::/64 network. Both of these LSA also contain information that allows the router to attach these prefix to links, such as the “Advertising Router” and the “Link State ID”.
There is one interesting quirk you need to be aware of when you’re looking at your Intra-Area Prefix LSAs. Let’s look at Router 1’s own Intra-Area Prefix LSA:
 Okay, we see the 1::1/128 loopback prefix… but what about the 1002::/64 network??
Okay, we see the 1::1/128 loopback prefix… but what about the 1002::/64 network??
Well, as it happens, if a router is connected to a segment that requires a DR election, the prefix information won’t appear anywhere other than in the DR’s Type 9 LSA.
In other words, you’d need to look at the Intra-Area Prefix LSA for Router 2 to see the prefix information.
This does make sense when you think about it. The DR will always be the authority for information on a segment, after all.
Let’s look at Router 2’s Intra-Area Prefix LSA:
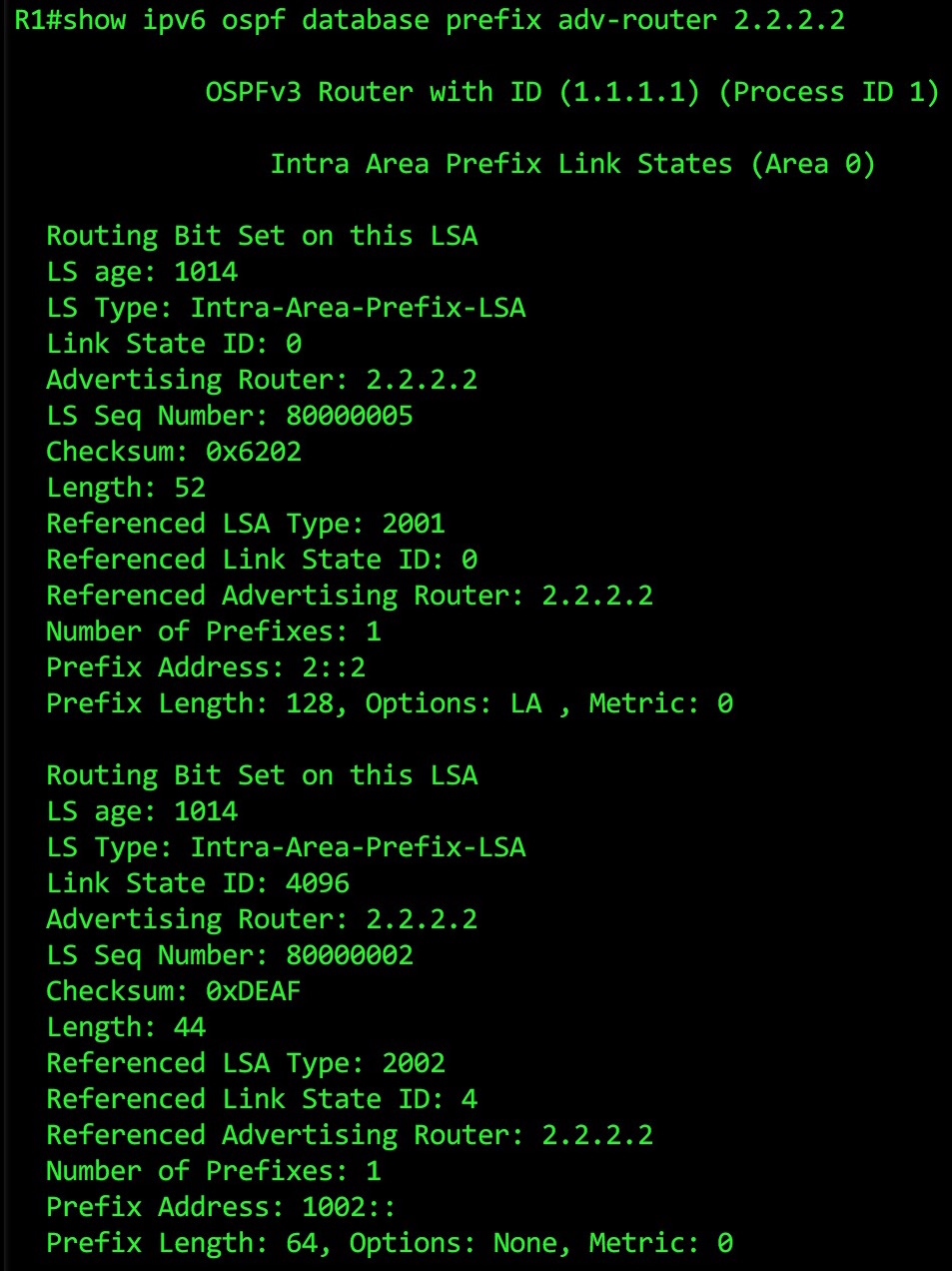 It’s worth going through what’s actually happening here: to build the topology, a router will see the prefix, then see that the “Referenced LSA Type” is 2002 (ie a Network LSA). This tells the router to look at that Network LSA for 2.2.2.2, where it’ll find the list of routers in the segment, combine it with link information from its Type 1 Router LSAs, and build the topology from there.
It’s worth going through what’s actually happening here: to build the topology, a router will see the prefix, then see that the “Referenced LSA Type” is 2002 (ie a Network LSA). This tells the router to look at that Network LSA for 2.2.2.2, where it’ll find the list of routers in the segment, combine it with link information from its Type 1 Router LSAs, and build the topology from there.
Blimey! It takes a few steps, but it works. Personally I’d find it hard to do in my brain. Luckily, routers are more cleverer than me. Although they can’t speak Japanese, so they’re not that clever. (I also can’t speak Japanese.)
So, that’s it! Now you know exactly as much about OSPFv3’s Link-State Database as I do. I’m looking forward to using OSPFv3 much more in a real production environment, so I can get this stuff burned into my brain.
If you enjoyed this post, I’d love you to share it with nerdy friends and colleagues, either by emailing them the link directly, or by sharing it around on your social media of choice. Thank you so much for reading!
ospfv3 lsa database的更多相关文章
- NTSTATUS Values
By combining the NTSTATUS into a single 32-bit numbering space, the following NTSTATUS values are de ...
- 《OSPF和IS-IS详解》
<OSPF和IS-IS详解> 基本信息 作者: (美)Jeff Doyle 译者: 孙余强 出版社:人民邮电出版社 ISBN:9787115347886 上架时间:2014-4-25 出版 ...
- OSPF详解
OSPF 详解 (1) [此博文包含图片] (2013-02-04 18:02:33) 转载 ▼ 标签: 端的 第二 以太 第一个 正在 目录 序言 初学乍练 循序渐进学习OSPF 朱皓 入门之前 了 ...
- PatentTips - Highly-available OSPF routing protocol
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION FIG. 1A is a simplified block diagram schematically representing a typic ...
- Latent semantic analysis note(LSA)
1 LSA Introduction LSA(latent semantic analysis)潜在语义分析,也被称为LSI(latent semantic index),是Scott Deerwes ...
- OSPF LSA的详解
LSA类型的配置与查看 1基本配置 R1(config)#NO IP DO LO R1(config)#NO ENAble PAssword R1(config)#LINe COnsole 0 R1( ...
- 第三组 通信一班 030 OSPFv2、OSPFv3综合实验
一. 实验目的 掌握 OSPFv2. OSPFv3 的配置方法 掌握在帧中继环境下OSPFv2. OSPFv3 的配置方法 掌握 OSPFv2. OSPFv3 NSSA 的配置方法 ...
- OSPF - 3,OSPF区域和LSA
1,四种末端区域骨干区域和标准区域:1,2,3,4,5,包含5类LSA,为了减少某些普通区域的LSA(主要就是4类和5类,有时做绝到连3类也不要了),引入了末梢区域.同时为了确保数据能出去,一般ABR ...
- ospf 提升 二 ---LSA
ospf ABR和ASBR的区别 官方建议中大型网络的规模参考 根据spf算法 而不是路由器的硬件性能强弱 a ABR最多关联3个区域 b 单区域内路由器最多50台 c 一台运行ospf的路由 ...
随机推荐
- C#实现DataTable转.CSV文件
将DataTable转换成CSV文件是一种常见的转换形式,主要通过遍历Table的每行,再对每行遍历每列,实现对数据的读取,然后用分隔符分隔Table的每个栏位数据,把读取的字符写入到CSV文件中.这 ...
- express项目创建
npm install express-generator -g 全局安装express生成器 express -h 帮助中心 express 项目名 npm i 安装依赖 nod ...
- AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'sorted'
效果图: 解决办法: 原因: AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'sorted' 属性错误: list对象没有sorted属性方法. sor ...
- python的input()函数
# input()函数 # 作用: 获取用户的输入,返回输入的内容 ,也可以用于暂停程序的运行 # 影响: 调用此函数,程序会立即暂停,等待用户输入 # 注意:input()的返回值是一个字符串 # ...
- nginx服务无法停止(Windows)
本人一般停止nginx服务都是通过Windows自带的任务管理器来强制结束nginx进程实现的,如图 2.但是 这次我通过同样的方法来结束nginx服务,发现nginx的进程无法结束 3.首先我要 ...
- 《企业IT架构转型之道:阿里巴巴中台战略思想与架构实战》-总结
一.什么是业务中台 概念来自于阿里,介于前台和后台(此后台指的是云计算.数据库.消息队列.缓存等基础服务) 采用共享式架构设计解决以往烟囱式架构设计的资源浪费.重复造轮.试错成本高的问题 阿里的中 ...
- Oauth2的使用(第三方授权登录)
例子: 京东商城 ,微博 ,用户三者之间的关系 第一方:用户 第二方:京东商城 第三方:微博 用户不希望在京东商城上注册,可以授权微博使用微博上的用户信息进行登录京东商城. 授权流程: 地址一:授权页 ...
- final与 static的区别;static代码块以及嵌套类介绍
本篇文章主要分为两个模块进行介绍:1.final,staic,static final之间的异同:2. static 模块:3.嵌套类的概念 1.final,staic,static final之间的 ...
- TensorFlow or PyTorch
既然你已经读到了这篇文章,我就断定你已经开始了你的深度学习之旅了,并且对人造神经网络的研究已经有一段时间了:或者也许你正打算开始你的学习之旅.无论是哪一种情况,你都是因为发现你陷入了困惑中,才找到了这 ...
- ASENET MVC 5 with Bootstrap and Knockout.js 第一弹
A Basic Example Now that the Knockout library is installed, let’s get right to an example of using ...
