设计模式之prototype(原型模型)
以我的理解原型模式的重点就几个字 用于克隆易变对象设计模式主要是为了解决new对象时的耦合问题,这是要克隆某个易变对象时只要直接传入要克隆的对象就可以实现克隆一下是我复制网上的一些代码 摘自《设计模式之美》 Dennis Gao
设计模式之美:Prototype(原型)
索引
别名
- Clone
意图
用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
Specify the kinds of objects to create using a prototypical instance, and create new objects by copying this prototype.
结构
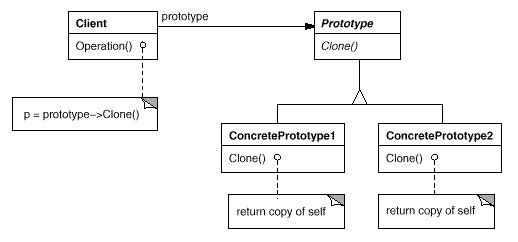
参与者
Prototype
- 声明一个克隆自身的接口。
ConcretePrototype
- 实现一个克隆自身的操作。
Client
- 让一个原型克隆自身从而创建一个新的对象。
适用性
在以下情况下可以使用 Prototype 模式:
- 一个系统要独立于它的产品的创建、构成和表示时。
- 当要实例化的类是在运行时刻指定时,例如:通过动态装载。
- 为了避免创建一个与产品类层次平行的工厂类层次时。
- 当一个类的实例只能有几个不同状态组合中的一种时。建立相应数目的原型并克隆它们可能比每次用合适的状态手工实例化该类更方便一些。
缺点
- 每一个 Prototype 子类都必须实现 Clone 操作。当内部包括一些不支持拷贝或有循环引用的对象时,实现克隆可能也会很困难。
效果
- 它对客户隐藏了具体的产品类,因此减少了客户知道的名字的数目。
- 使客户无需改变即可使用与特定应用相关的类。
- 运行时刻增加和删除产品。
- 改变值以指定新对象。
- 改变结构以指定新对象。
- 减少子类的构造。
- 用类动态配置应用。
相关模式
- Abstract Factory 可以用 Prototype来实现。
- Composite和 Decorator模式的设计也可以从 Prototype 获益。
命名约定
使用命名约定是一个好习惯,例如,总是声明那些实现克隆的操作为 Clone()。
实现
实现方式(一):使用一个原型管理器。
当一个系统中原型数目不固定时,可以保持一个可用原型的注册表,用以存储和检索原型。我们称这个注册表为原型管理器(Prototype Manager)。
客户在克隆一个原型前会先向注册表请求该原型。

namespace PrototypePattern.Implementation1
{
public abstract class AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public int ValueProperty1 { get; set; } public abstract AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone();
} public class ConcretePrototypeProductA : AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public override AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone()
{
return new ConcretePrototypeProductA()
{
ValueProperty1 = this.ValueProperty1,
};
}
} public class ConcretePrototypeProductB : AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public override AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone()
{
return new ConcretePrototypeProductB()
{
ValueProperty1 = this.ValueProperty1,
};
}
} public class ProductPrototypeManager
{
private Dictionary<string, AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct> _registry
= new Dictionary<string, AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct>(); public void Register(string name,
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct prototypeProduct)
{
_registry[name] = prototypeProduct;
} public void Unregister(string name)
{
_registry.Remove(name);
} public AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Retrieve(string name)
{
return _registry[name];
} public bool IsRegisterd(string name)
{
return _registry.ContainsKey(name);
}
} public class Client
{
public void TestCase1()
{
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct prototypeProduct1 = new ConcretePrototypeProductA();
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct prototypeProduct2 = new ConcretePrototypeProductB(); ProductPrototypeManager manager = new ProductPrototypeManager();
manager.Register("PrototypeProduct1", prototypeProduct1);
manager.Register("PrototypeProduct2", prototypeProduct2); AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct clonedProduct1 = manager.Retrieve("PrototypeProduct1").Clone(); if (manager.IsRegisterd("PrototypeProduct2"))
{
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct clonedProduct2 = manager.Retrieve("PrototypeProduct2").Clone();
}
}
}
}

实现方式(二):使用浅拷贝实现克隆(Clone)操作。
Prototype 模式最困难的部分在于正确的实现 Clone 操作。
浅拷贝(Shallow Copy)在拷贝时只复制对象所有字段的值。如果字段是值类型,则复制其值;如果字段是引用类型,则复制引用指针。

namespace PrototypePattern.Implementation2
{
public class ReferencedClass
{
public int ReferencedClassProperty1 { get; set; }
} public abstract class AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public int ValueProperty1 { get; set; }
public ReferencedClass ReferenceProperty2 { get; set; } public abstract AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone();
} public class ConcreteShallowCopyPrototypeProductA
: AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public ConcreteShallowCopyPrototypeProductA()
{
this.ReferenceProperty2 = new ReferencedClass()
{
ReferencedClassProperty1 =
};
} public override AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone()
{
return new ConcreteShallowCopyPrototypeProductA()
{
ValueProperty1 = this.ValueProperty1,
ReferenceProperty2 = this.ReferenceProperty2,
};
}
} public class Client
{
public void TestCase2()
{
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct prototypeProduct1 = new ConcreteShallowCopyPrototypeProductA();
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct clonedProduct1 = prototypeProduct1.Clone();
bool areEqual1 = object.ReferenceEquals(
prototypeProduct1.ReferenceProperty2,
clonedProduct1.ReferenceProperty2);
}
}
}

实现方式(三):使用深拷贝实现克隆(Clone)操作。
深拷贝(Deep Copy)涉及对源对象整个结构的拷贝。
深拷贝在拷贝时复制对象的所有字段的值。如果字段是值类型,则复制其值;如果字段是引用类型,则会将这个引用指针指向的对象也克隆一份。
可以通过序列化和反序列化来实现深拷贝。

namespace PrototypePattern.Implementation3
{
public class ReferencedClass
{
public int ReferencedClassProperty1 { get; set; }
} public abstract class AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public int ValueProperty1 { get; set; }
public ReferencedClass ReferenceProperty2 { get; set; } public abstract AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone();
} public class ConcreteShallowCopyPrototypeProductA
: AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public ConcreteShallowCopyPrototypeProductA()
{
this.ReferenceProperty2 = new ReferencedClass()
{
ReferencedClassProperty1 =
};
} public override AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone()
{
return new ConcreteShallowCopyPrototypeProductA()
{
ValueProperty1 = this.ValueProperty1,
ReferenceProperty2 = this.ReferenceProperty2,
};
}
} public class ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB
: AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB()
{
this.ReferenceProperty2 = new ReferencedClass()
{
ReferencedClassProperty1 =
};
} public override AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone()
{
return new ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB()
{
ValueProperty1 = this.ValueProperty1,
ReferenceProperty2 = new ReferencedClass()
{
ReferencedClassProperty1 =
this.ReferenceProperty2.ReferencedClassProperty1
},
};
}
} public class Client
{
public void TestCase3()
{
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct prototypeProduct1 = new ConcreteShallowCopyPrototypeProductA();
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct clonedProduct1 = prototypeProduct1.Clone();
bool areEqual1 = object.ReferenceEquals(
prototypeProduct1.ReferenceProperty2,
clonedProduct1.ReferenceProperty2); AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct prototypeProduct2 = new ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB();
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct clonedProduct2 = prototypeProduct2.Clone();
bool areEqual2 = object.ReferenceEquals(
prototypeProduct2.ReferenceProperty2,
clonedProduct2.ReferenceProperty2); Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", areEqual1, areEqual2);
}
}
}

实现方式(四):初始化克隆对象。
客户可能会希望使用一些值来初始化该对象的内部状态。
但在 Clone 操作中传递参数会破坏克隆接口的统一性。
原型的类可以在 Clone 操作之后,调用包含初始化参数的 Initialize 方法来设定对象内部状态。

namespace PrototypePattern.Implementation4
{
public class ReferencedClass
{
public int ReferencedClassProperty1 { get; set; }
} public abstract class AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public int ValueProperty1 { get; set; }
public ReferencedClass ReferenceProperty2 { get; set; } public abstract AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone();
} public class ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB
: AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct
{
public ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB()
{
} public void Initialize(int propertyValue)
{
this.ValueProperty1 = propertyValue;
this.ReferenceProperty2.ReferencedClassProperty1 = propertyValue;
} public override AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct Clone()
{
return new ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB()
{
ValueProperty1 = this.ValueProperty1,
ReferenceProperty2 = new ReferencedClass()
{
ReferencedClassProperty1 =
this.ReferenceProperty2.ReferencedClassProperty1
},
};
}
} public class Client
{
public void TestCase4()
{
AbstractOrInterfaceOfPrototypeProduct prototypeProduct2 = new ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB();
ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB clonedProduct2 =
(ConcreteDeepCopyPrototypeProductB)prototypeProduct2.Clone(); clonedProduct2.Initialize();
}
}
}

《设计模式之美》为 Dennis Gao 发布于博客园的系列文章
二.下面介绍另外一种方法主要介绍this.memberwiseclone()的使用
设计模式之prototype(原型模型)的更多相关文章
- 设计模式(1)--Prototype(原型模式)--创建型
1.模式定义: 原型模式就是用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过复制这些原型创建新的对象. 2.使用场景: 在原型模式中我们可以利用过一个原型对象来指明我们所要创建对象的类型,然后通过复制这个对象的 ...
- Java设计模式:Prototype(原型)模式
概念定义 使用原型实例指定待创建对象的种类,并通过拷贝该原型来创建新的对象.Prototype模式允许一个原型对象克隆(复制)出多个与其相同的对象,而无需知道任何如何创建的细节. 应用场景 对象的创建 ...
- 设计模式:Prototype 原型模式 - 同学你抄过别人的作业么?-clone()方法的使用
原型模式: 通过某个类的实例来创建对象 使用原型模式的好处: 好处是什么呢?当我们需要多次重复的创建一个类的示例的时候,我们可以使用new但是,new不仅仅耗费内存而且,如果new 某个类的构造方法中 ...
- JScript中的prototype(原型)属性研究
今天看到同事使用js中的Prototype,感觉很是新鲜.由此想深入学习一下prototype(英['prəʊtətaɪp] 美['protə'taɪp]n. 原型:标准,模范),在学习prototy ...
- Java设计模式(三)原型模型 适配器型号
(五岁以下儿童)原型模型 Prototype 样机模型旨在复制一个现有对象来创建新对象.而不是通过的方式的实例.原型模式须要实现 Cloneable 接口.覆写clone方法,复制分为浅复制.深复制. ...
- 设计模式05: Prototype 原型模式(创建型模式)
Prototype 原型模式(创建型模式) 依赖关系的倒置抽象不应该依赖于实现细节,细节应该依赖于抽象.对所有的设计模式都是这样的. -抽象A直接依赖于实现细节b -抽象A依赖于抽象B,实现细节b依赖 ...
- 原型设计模式(prototype
# 什么是原型设计模式 > 这里与软件工程中的原型开发模式有那么一点类似的地方,我们首先需要构建出一个原型,这个原型可以在现实开发中抽象出来的具体类型,但是这个类型与具体的类又不同,需要抽取公共 ...
- 一天一个设计模式——Prototype 原型模式
一.模式说明 看了比较多的资料,对原型模式写的比较复杂,个人的理解就是模型复制,根据现有的类来直接创建新的类,而不是调用类的构造函数. 那为什么不直接调用new方法来创建类的实例呢,主要一个原因是如果 ...
- C++设计模式-Prototype原型模式
作用: 用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象. Prototype模式提供了一个通过已存在对象进行新对象创建的接口(Clone), Clone()实现和具体的语言相关,在C+ ...
- 设计模式学习笔记——Prototype原型模式
原型模型就是克隆. 还有深克隆.浅克隆,一切听上去都那么耳熟能详.
随机推荐
- python学习之RabbitMQ-----消息队列
RabbitMQ队列 首先我们在讲rabbitMQ之前我们要说一下python里的queue:二者干的事情是一样的,都是队列,用于传递消息 在python的queue中有两个一个是线程queue,一个 ...
- c++官方文档-按值传递和按引用传递
#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<queue> #include<map> #include& ...
- jar包双击执行引用外部包问题
大家都知道一个java应用项目可以打包成一个jar,当然你必须指定一个拥有main函数的main class作为你这个jar包的程序入口. 具体的方法是修改jar包内目录META-INF下的MANIF ...
- hive 使用笔记(partition; HDFS乱码;日期函数)
6. insert 语句 1) 因为目标表有partition, 所以刚开始我使用的语句是 insert overwrite table sa_r_item_sales_day_week_month ...
- sitemap
sitemap对于网站就像是字典的索引目录,而这个目录的读者则是搜索引擎的爬虫.网站有了sitemap,有助于搜索引擎“了解”网站,这样会有助于站点的内容被收录. sitemap是一个由google主 ...
- Delegate 改变指向
import mx.utils.Delegate; nowWordSound.onSoundComplete =Delegate.create(this, playOver); function pl ...
- UI5-文档-4.37-Content Density
在本演练教程的这一步中,我们将根据用户的设备调整内容密度.SAPUI5包含不同的内容密度,允许您为支持触摸的设备显示更大的控件,为鼠标操作的设备显示更小.更紧凑的设计.在我们的app中,我们将检测设备 ...
- Gulp的安装与配置
http://blog.csdn.net/itlsx/article/details/49981459
- Linux下基于官方源代码RPM包构建自定义MySQL RPM包
rpmbuild时不要以root用户执行! 方法一: 1.首先安装rpmbuild #yum install rpm-build gcc gcc-c++ cmake bison ncurses-dev ...
- cobbler配置解析
1.Cobbler命令说明: 命令名称 命令用途 cobbler check 检查cobbler配置 cobbler list 列出所有的cobbler元素 cobbler report 列出元素的详 ...

