HDU 2815 Mod Tree (扩展 Baby Step Giant Step )
Mod Tree |
| Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) |
| Total Submission(s): 96 Accepted Submission(s): 38 |
|
Problem Description
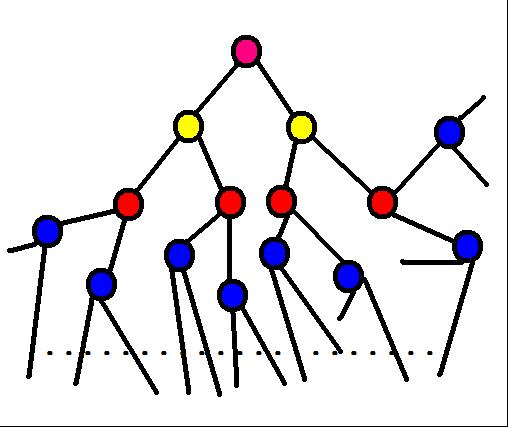 The picture indicates a tree, every node has 2 children. The depth of the nodes whose color is blue is 3; the depth of the node whose color is pink is 0. Now out problem is so easy, give you a tree that every nodes have K children, you are expected to calculate the minimize depth D so that the number of nodes whose depth is D equals to N after mod P. |
|
Input
The input consists of several test cases.
Every cases have only three integers indicating K, P, N. (1<=K, P, N<=10^9) |
|
Output
The minimize D.
If you can’t find such D, just output “Orz,I can’t find D!” |
|
Sample Input
3 78992 453 |
|
Sample Output
Orz,I can’t find D! |
|
Author
AekdyCoin
|
证明来自:
http://hi.baidu.com/aekdycoin/item/236937318413c680c2cf29d4
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL ;
const int N = ; struct B
{
LL num , id ;
bool operator < ( const B &a ) const{
if( num != a.num ) return num < a.num;
else return id < a.id ;
}
}baby[N]; LL n , k , p ;
int tot ;
void e_gcd( LL &x , LL &y , LL &d , LL a , LL b ){
if( b == ){ x = , y = ; d = a ; return ; }
e_gcd( y , x , d , b , a%b );
y -= x* (a/b) ;
} int inv( LL a, LL b ,LL n )
{
LL d,e,x,y ;
e_gcd(x,y,d,a,n);
e = ( x * b ) % n ;
return e < ? e + n : e;
} inline LL gcd(LL a, LL b ){ return b == ? a : gcd( b , a % b ) ; } LL quick_mod( LL a , LL b ,LL mod )
{
LL res = ;
while( b )
{
if( b & ) res = res * a % mod ;
a = a * a % mod ;
b >>= ;
}
return res ;
} int find( LL n )
{
int l = , r = tot - ;
while( l <= r ){
int m = (l + r) >> ;
if( baby[m].num == n){
return baby[m].id;
}
else if( baby[m].num < n )
l = m + ;
else
r = m - ;
}
return -;
} void run()
{
if( p <= n ){
puts("Orz,I can’t find D!");
return ;
}
LL temp = % p ;
for( int i = ; i < ; ++i ) {
if( temp == n ){
printf("%d\n",i);
return ;
}
temp = temp * k % p ;
} LL d = , kk = % p ;
while( ( temp = gcd( k , p ) ) != ){
if( n % temp ) {
puts("Orz,I can’t find D!");
return ;
}
d ++ ;
p /= temp;
n /= temp;
kk = k / temp * kk % p ;
}
int m = ( int ) ceil( sqrt( (double)p ) );
baby[].num = , baby[].id = ;
for( int i = ; i <= m ; ++i ){
baby[i].num = baby[i-].num * k % p ;
baby[i].id = i ;
}
sort( baby , baby + m + ) ;
tot = ;
for( int i = ; i <= m ; ++i ){
if(baby[i].num != baby[tot-].num ){
baby[tot++] = baby[i];
}
} LL am = quick_mod( k , m , p ); for( int j = ; j <= m ; ++j ){
temp = inv(kk,n,p);
if( temp < ){
continue ;
}
int pos = find( temp );
if( pos != - ){
printf("%d\n", m * j + d + pos );
return ;
}
kk = kk * am % p ;
}
puts("Orz,I can’t find D!");
}
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
#endif // LOCAL
while( scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&k,&p,&n) != EOF ) run();
}
HDU 2815 Mod Tree (扩展 Baby Step Giant Step )的更多相关文章
- HDU 2815 Mod Tree 离散对数 扩张Baby Step Giant Step算法
联系:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2815 意甲冠军: watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQ ...
- hdu 2815 : Mod Tree 【扩展BSGS】
题目链接 直接用模板好了.实在不行,反正有队友啊~~~~ #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL ...
- hdu 2815 Mod Tree (exBSGS)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2815 //解 K^D ≡ N mod P #include<map> #include<cma ...
- hdu 2815 Mod Tree 高次方程,n不为素数
Accepted 406MS 8576K 2379 B C++/** 这里加了一点限制,,大体还是一样的,, **/ #include <iostream> #include <cs ...
- HDU 2815 Mod Tree
不会,先搁着…… http://blog.csdn.net/acm_cxlove/article/details/7832197
- HDU 2815 扩展baby step giant step 算法
题目大意就是求 a^x = b(mod c) 中的x 用一般的baby step giant step 算法会超时 这里参考的是http://hi.baidu.com/aekdycoin/item/2 ...
- 解高次同余方程 (A^x=B(mod C),0<=x<C)Baby Step Giant Step算法
先给出我所参考的两个链接: http://hi.baidu.com/aekdycoin/item/236937318413c680c2cf29d4 (AC神,数论帝 扩展Baby Step Gian ...
- POJ 3243 Clever Y (求解高次同余方程A^x=B(mod C) Baby Step Giant Step算法)
不理解Baby Step Giant Step算法,请戳: http://www.cnblogs.com/chenxiwenruo/p/3554885.html #include <iostre ...
- [置顶] hdu2815 扩展Baby step,Giant step入门
题意:求满足a^x=b(mod n)的最小的整数x. 分析:很多地方写到n是素数的时候可以用Baby step,Giant step, 其实研究过Baby step,Giant step算法以后,你会 ...
随机推荐
- C#windows向窗体传递泛型类
修改窗体代码文件*.cs public partial class FormName<T> : Form partial说明此类还有一半在另外的cs文件中,正是系统替你写好的*.desig ...
- Python Web开发:Django+BootStrap实现简单的博客项目
创建blog的项目结构 关于如何创建一个Django项目,请查看[Python Web开发:使用Django框架创建HolleWorld项目] 创建blog的数据模型 创建一个文章类 所有开发都是数据 ...
- lvm相关
LVM 概念:PV(单个硬件)--VG(组合)--LV(分区) pv打头的:代表pv相关的命令vg带头的:代表vg相关的命令lv带头的: 代表lv相关的命令 create:创建相关remove:移除相 ...
- zabbix基础之环境搭建
zabbix入门 环境部署 安装mysql #安装MySQL,官方的MySQL的repo源地址:http://repo.mysql.com/ #选择指定的MySQL版本,我这里选mysql5.7的版本 ...
- 6层PCB设计技巧和步骤
6层PCB设计技巧和步骤 一.原理图的编辑 6层板由于PCB板中可以有两层地,所以可以将模拟地和数字地分开.对于统一地还是分开地,涉及到电磁干扰中信号的最小回流路径问题,绘制完原理图,别忘检查错误和 ...
- Git--02 Devops介绍及git安装部署
目录 1. Devops介绍 01. 运维介绍 02. Devops是什么 03. Devops能干嘛 04. Devops如何实现 2. Git版本控制系统 01. 版本控制系统简介 02. 为什么 ...
- mysql sqlyog提示2058错误或者用Navicat连接本机Docker的Mysql 和一些问题的解决方案
1. 下载Mysql的Docker镜像: [plain] view plain copy$ docker search mysql (搜索mysql镜像) $ docker pull mysql ( ...
- loadRunner函数之lr_set_debug_message
lr_set_debug_message:选择性开启扩展日志 vuser_init: vuser_init() { ; } Action: Action() { ExtendedLog(); // 开 ...
- spring-boot整合Cxf的webservice案例
1.运行环境 开发工具:intellij idea JDK版本:1.8 项目管理工具:Maven 4.0.0 2.Maven Plugin管理 <?xml version="1.0&q ...
- 31 July
P1005 矩阵取数游戏 高精度不能更坑-- #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> struct INT { long long h, l; ...
