SpringBoot原理发现(一)
说明:
本系列基于SpringBoot 2.2.9.RELEASE 版本,对SpringBoot的原理进行分析,一共分为四节:
SpringBoot原理发现(一):创建Hello World,对pom依赖以及@SpringBootApplication注解进行分析
SpringBoot原理发现(二):分析SpringBoot自动配置原理
SpringBoot原理发现(三):通过主配置类main方法分析SpringBoot启动配置原理
SpringBoot原理发现(四):了解SpringBoot启动中的几个重要回调机制
Hello World
创建Hello World,主启动类如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
} @RestController
public class HelloController{ @GetMapping("/")
public String helloWorld(){
return "hello world";
}
}
}
1. POM文件
1.1 父POM
<!-- 当前项目pom -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent> <!-- spring-boot-starter-parent 的父pom -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>
可以看出当前项目pom中的parent 依赖了 spring-boot-dependencies,而spring-boot-dependencies中管理的就是SpringBoot应用里面的所有依赖版本。(如果其中没包含,需要自定义在父pom中进行依赖)
<!-- spring-boot-dependencies 部分代码 -->
<properties>
<activemq.version>5.15.13</activemq.version>
<antlr2.version>2.7.7</antlr2.version>
<appengine-sdk.version>1.9.81</appengine-sdk.version>
<artemis.version>2.10.1</artemis.version>
<aspectj.version>1.9.6</aspectj.version>
<assertj.version>3.13.2</assertj.version>
<atomikos.version>4.0.6</atomikos.version>
<awaitility.version>4.0.3</awaitility.version>
<bitronix.version>2.1.4</bitronix.version>
.......
1.2 启动器
SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取成一个个的starter,只需要依赖某个starter,便有了相关依赖信息及功能,这样的starter称之为场景启动器。
可以通过点击官网进行查看包含哪些starter,如下图:
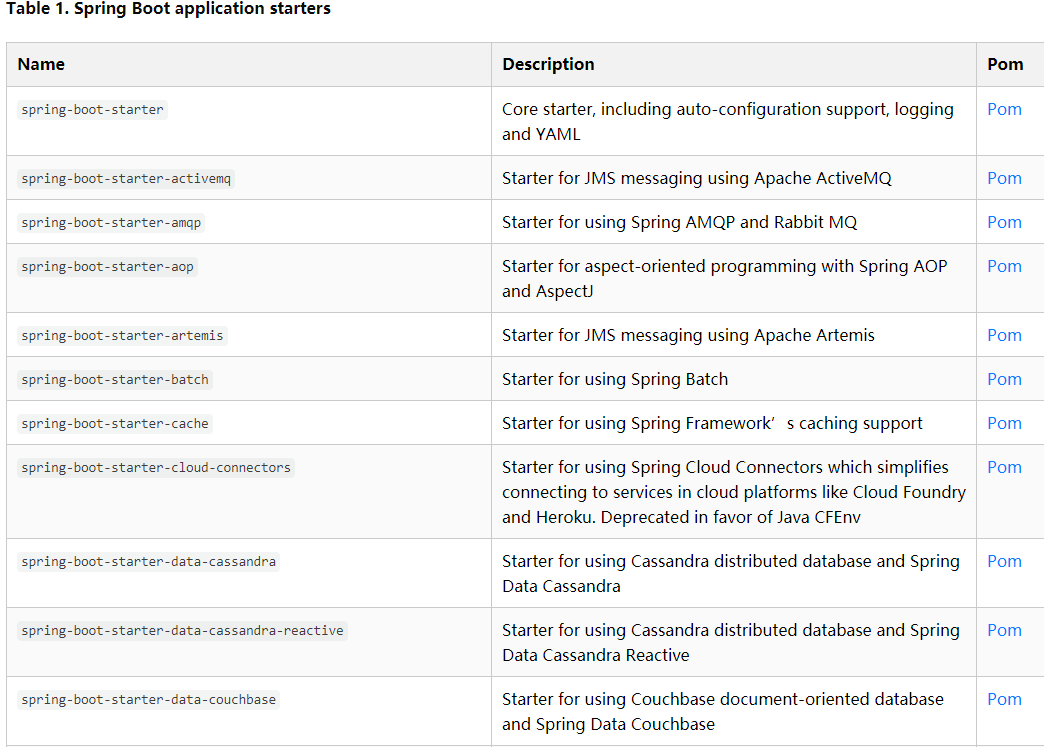
如开发web应用,只需要引入spring-boot-starter-web便有了web模块的相关功能
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency> ......
spring-boot-starter-web:管理了web模块需要引用的依赖文件,如下图:
<!-- spring-boot-starter-web.pom部分依赖-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
2.主程序分析
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
} @RestController
public class HelloController{ @GetMapping("/")
public String helloWorld(){
return "hello world";
}
}
}
2.1 @SpringBootApplication
该注解标注在某个类上,说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类,SpringBoot应用应该使用这个类的main方法进行启动。
进入该注解,可以看到@SpringBootApplication是一个组合注解,代码如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
2. 1.1 @SpringBootConfiguration
SpringBoot的配置类。进去会发现其实就是一个Spring的配置类@Configuration,而@Configuration其实就是一个组件@Component。
@SpringBootConfiguration是SpringBoot提供的,而@Configuration是Spring提供的
代码如下:
/**
* SpringBootConfiguration
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration { ..... /**
* Configuration
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {
2 .2 @EnableAutoConfiguration
作用:开启自动配置功能
所谓开启自动配置:以前需要提供各种配置文件,如包扫描等,现在使用@EnableAutoConfiguration标注,SpringBoot就会开启自动配置功能。
点开这个注解,会发现它同样是组合注解,如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
2.2.1 @AutoConfigurationPackage
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage { }
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class):向容器中导入一个组件,组件由@Import后面传入的类指定
AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class 关键代码如下:
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName());
}
通过debug可以查看该注解是标注是在主启动类上,获取主启动类所在的包位置路径,将该路径下面的所有包扫描注入到容器中。类似spring配置文件xml中 <context:component-scan base-package="xx.yyy" />功能。
@AutoConfigurationPackage 其实就是自动获取主配置类下面的所有包并扫描注入进IOC容器中。
2.2.2 @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
同样是往IOC容器中导入AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class中指定的组件。
AutoConfigurationImportSelector主要代码:
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
通过debug可以看出,它会返回各种XXXAutoConfiguration。而有了这些XXXAutoConfiguration,就不需要我们在手动去编写相关场景的注入功能组件等工作,如下图:
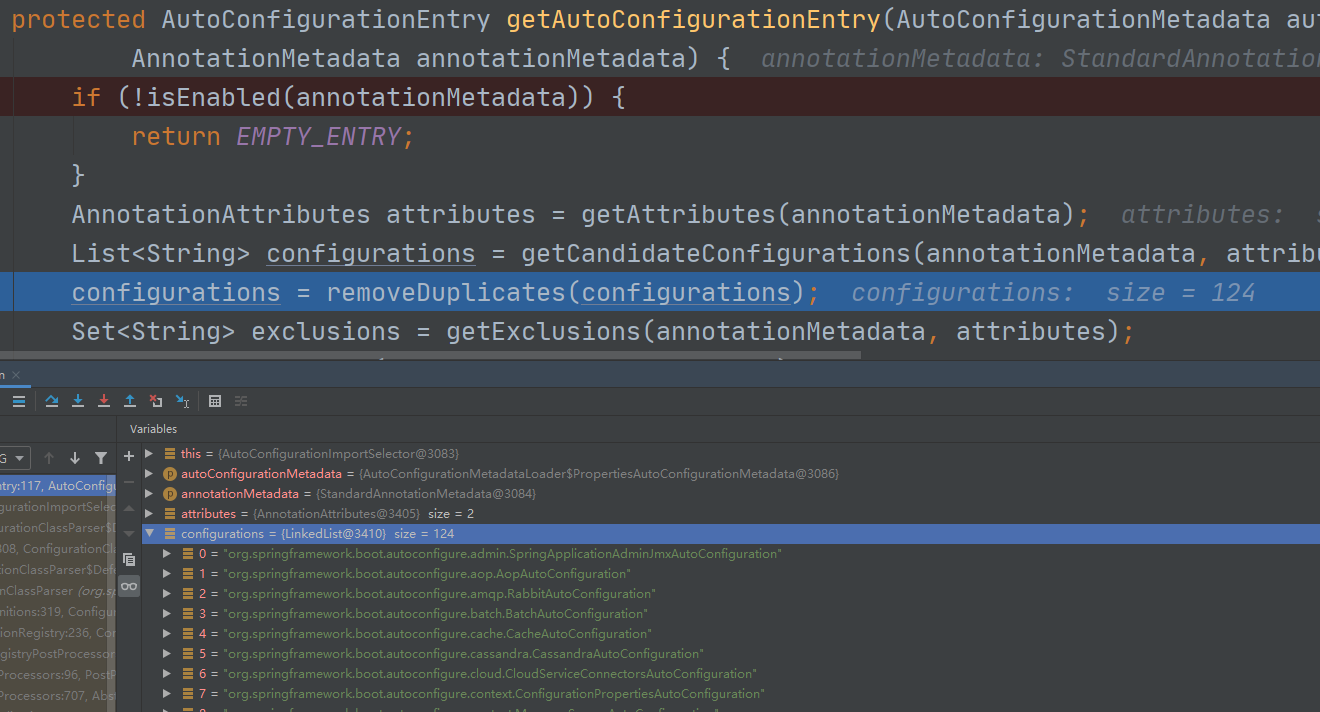
这些XXXAutoConfiguration又是从何而来呢?
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
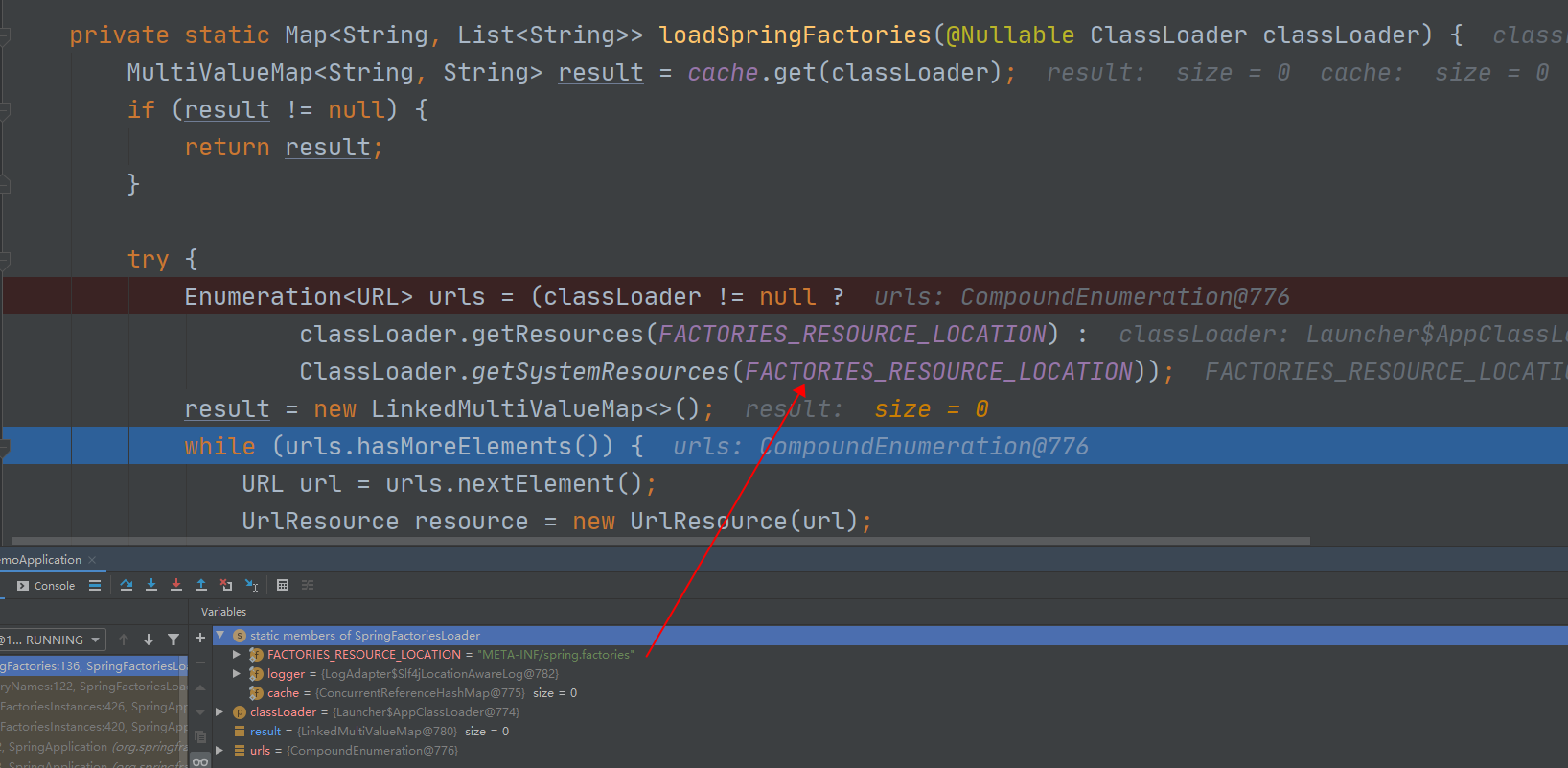
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),getBeanClassLoader())
第一个参数:EnableAutoConfiguration.class
第二个参数:ClassLoader
进入loadFactoryNames方法,SpringBoot会扫描类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories 文件中定义的数据,并返回第一个参数EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值,并将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,
在后续该方法会经常出现,用于扫描spring.factories中定义的值,如下图:
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudServiceConnectorsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\ ......
至此基本上可以看出SpringBoot是如何进行加载且工作的。说到底spring的配置文件一个也没少,只是SpringBoot底层将我们的配置文件进行自动配置到容器中了,少了手动编写大量的组件配置。
SpringBoot原理发现(一)的更多相关文章
- 深入springboot原理——动手封装一个starter
从上一篇文章<深入springboot原理——一步步分析springboot启动机制(starter机制)> 我们已经知道springboot的起步依赖与自动配置的机制.spring-bo ...
- 深入springboot原理——一步步分析springboot启动机制(starter机制)
前言 使用过springboot的同学应该已经知道,springboot通过默认配置了很多框架的使用方式帮我们大大简化了项目初始搭建以及开发过程.本文的目的就是一步步分析springboot的启动过程 ...
- Spring-boot原理(附带实现一个spring-boot-starter实例和代码下载)
(我就是个封面) Spring-boot自出现后,到现在火的很,大家貌似都在用,连招聘里面也要求会这个.但是说实话,spring-boot无外乎想实现一种可插拔的编程方式,说是简化配置,其实并没有 ...
- SpringBoot原理讲解
一.问题的引入 首先我们来看一个最简单的例子. 我们先创建一个SpringBoot的工程,如何创建一个SpringBoot工程就不说了,不会请自行解决.然后写一个controller类,通过请求路径, ...
- SpringBoot原理分析与配置
1.1 起步依赖原理分析 1.1.1 分析spring-boot-starter-parent 按住Ctrl点击pom.xml中的spring-boot-starter-parent,跳转到了spri ...
- SpringBoot原理—分析SpringBoot启动机制(starter机制)
一:前言使用过springboot的同学应该已经知道,springboot通过默认配置了很多框架的使用方式帮我们大大简化了项目初始搭建以及开发过程.本文的目的就是一步步分析springboot的启动过 ...
- SpringBoot原理深入及源码剖析(一) 依赖管理及自动配置
前言 传统的Spring框架实现一个Web服务需要导入各种依赖jar包,然后编写对应的XML配置文件等,相较而言,SpringBoot显得更加方便.快捷和高效.那么,SpringBoot究竟是如何做到 ...
- Springboot原理
1. SpringBoot特点 一个starter导入所有 依赖管理 父项目做依赖管理:声明了所需依赖的版本号 依赖管理 <parent> <groupId>org.sprin ...
- Spring-Boot原理及应用布署
一.Spring Boot的理念 从最根本上来讲,Spring Boot就是一些库的集合,它能够被任意项目的构建系统所使用.简便起见,该框架也提供了命令行界面,它可以用来运行和测试Boot应用.框架的 ...
随机推荐
- JS中的DOM对象
DOM对象 1. DOM树 当网页被加载时,浏览器会创建页面的文档对象模型(Document Object Model),通过 HTML DOM对象,可访问 JavaScript HTML 文档的所有 ...
- Python-local variable 'raw_password' referenced before assignment
where? 执行Python程序的时候,报这个错 why? 变量作用域问题,在分支中定义的变量,当满足条件的时候则可以正确得到变量,当不满足条件的时候则报这个错 way? 把变量从分支中抽离到分支上 ...
- [VBA原创源代码] excelhome 汇总多工作表花名册
生病了,一点一滴的积累,慢慢康复,今年十月,我就 2 周岁了. 以下代码完成了excelhome中留的作业 http://club.excelhome.net/forum.php?mod=viewth ...
- 016 01 Android 零基础入门 01 Java基础语法 02 Java常量与变量 10 布尔类型和字符串的字面值
016 01 Android 零基础入门 01 Java基础语法 02 Java常量与变量 10 布尔类型和字符串的字面值 本文知识点:字面值 关于字面值的概念,需要注意:很多地方,我们可能就把字面值 ...
- 如何使用微软提供的TCHAR.H头文件?
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/flyingspark/archive/2012/03/16/2399788.html 如何使用微软提供的TCHAR.H头文件? 如果你现在写的代 ...
- P5322 排兵布阵解题报告
本想在洛谷上交篇题解的,结果发现交不了,所以只能在这边写了... 作为一个蒟蒻,看到省选题,第一眼考虑怎么打暴力 我们可以分情况考虑 当\(s==1\)的时候 我们可以把他当成一个\(01\)背包,背 ...
- 【题解】CF413C Jeopardy!
\(\color{blue}{Link}\) \(\text{Solution:}\) 首先,显然的策略是把一定不能翻倍的先加进来.继续考虑下一步操作. 考虑\(x,y\)两个可以翻倍的物品,且\(a ...
- 列举python的可变类型和不可变类型
可变的# unhashable type: 'list'# unhashable type: 'dict'# unhashable type: 'set'# 不可变# hashable type:st ...
- ASP。NET Web表单模型,部分呈现和事件
下载EventExample.zip - 41.33 KB 下载EventandAjaxExample.zip - 41.94 KB 介绍 通过参考ASP获得Web应用程序环境及其约束的概述.NET ...
- 抓包工具Charles使用
设置Reason:最近接触一个APP后台项目,但是不知道APP各个操作访问对应的是后台的哪个接口,迫切需要使用一个抓包工具one by one Charles Free 简单上手快,首选 下载:h ...