Linux graphics stack
2D图形架构
早期Linux图形系统的显示全部依赖X Server,X Client调用Xlib提供的借口向 X Server发送渲染命令,X Server根据 X Client的命令请求向硬件设备绘制图形,X Client与X Server之间通过X11协议通讯。通过这种方式,X Server屏蔽了所有的硬件差异,保证同一个X程序能够在不同的硬件设备上运行。
X Server需要与多种多样的硬件打交道,每个硬件提供自己的DDX驱动程序,X Server最后调用DDX的接口将图形发送给硬件设备。

3D图形架构
通过3D硬件执行3D加速能够大大提高绘制效率,根据不同的模式有两种架构:
Indirect Rendering
这种模式下,仅仅X Server能够访问3D硬件设备,X Client需要绘图时通过X11扩展协议将3D命令发送给X Server,然后由X Server控制3D硬件设备执行,这种模式称为“非直接渲染”。
这种模式与2D模式类似。
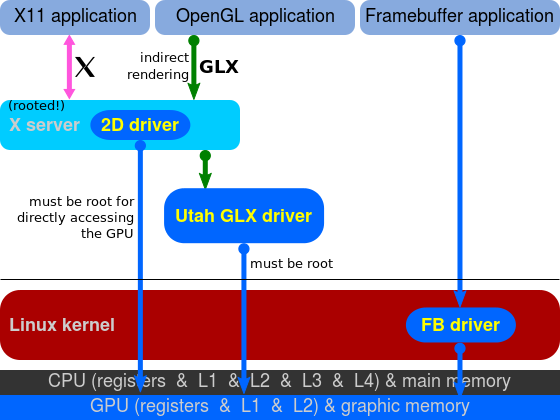
但是这种模式无法发挥出3D硬件的效率
Direct Rendering
DRI(Direct Rendering Infrastructure)架构允许X Client直接控制3D硬件设备,所以这种模式下要求X Client与X Server必须位于同一个设备上。
DRM(Direct Rendering Manager)是DRI架构下的Kernel实现,DRM负责:hardware locking, access synchronization, video memory and more.
DRM also provides userspace with an API that it can use to submit commands and data in a format that is adequate for modern GPUs, which effectively allows userspace to communicate with the graphics hardware.
Notice that many of these things have to be done specifically for the target hardware so there are different DRM drivers for each GPU.
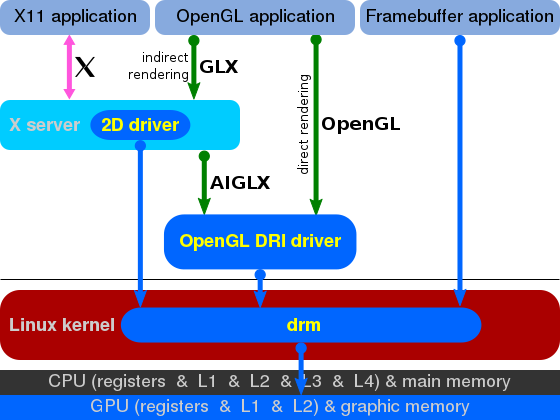
DRI/DRM provide the building blocks that enable userspace applications to access the graphics hardware directly in an efficient and safe manner, but in order to use OpenGL we need another piece of software that, using the infrastructure provided by DRI/DRM, implements the OpenGL API while respecting the X server requirements.
Mesa
Mesa is a free software implementation of the OpenGL specification, and as such, it provides a libGL.so, which OpenGL based programs can use to output 3D graphics in Linux. Mesa can provide accelerated 3D graphics by taking advantage of the DRI architecture to gain direct access to the underlying graphics hardware in its implementation of the OpenGL API.
When our 3D application runs in an X11 environment it will output its graphics to a surface (window) allocated by the X server. Notice, however, that with DRI this will happen without intervention of the X server, so naturally there is some synchronization to do between the two, since the X server still owns the window Mesa is rendering to and is the one in charge of displaying its contents on the screen. This synchronization between the OpenGL application and the X server is part of DRI. Mesa’s implementation of GLX (the extension of the OpenGL specification that addresses the X11 platform) uses DRI to talk to the X server and accomplish this.
Mesa also has to use DRM for many things. Communication with the graphics hardware happens by sending commands (for example “draw a triangle”) and data (for example the vertex coordinates of the triangle, their color attributes, normals, etc). This process usually involves allocating a bunch of buffers in the graphics hardware where all these commands and data are copied so that the GPU can access them and do its work. This is enabled by the DRM driver, which is the one piece that takes care of managing video memory and which offers APIs to userspace (Mesa in this case) to do this for the specific target hardware. DRM is also required whenever we need to allocate and manage video memory in Mesa, so things like creating textures, uploading data to textures, allocating color, depth or stencil buffers, etc all require to use the DRM APIs for the target hardware.
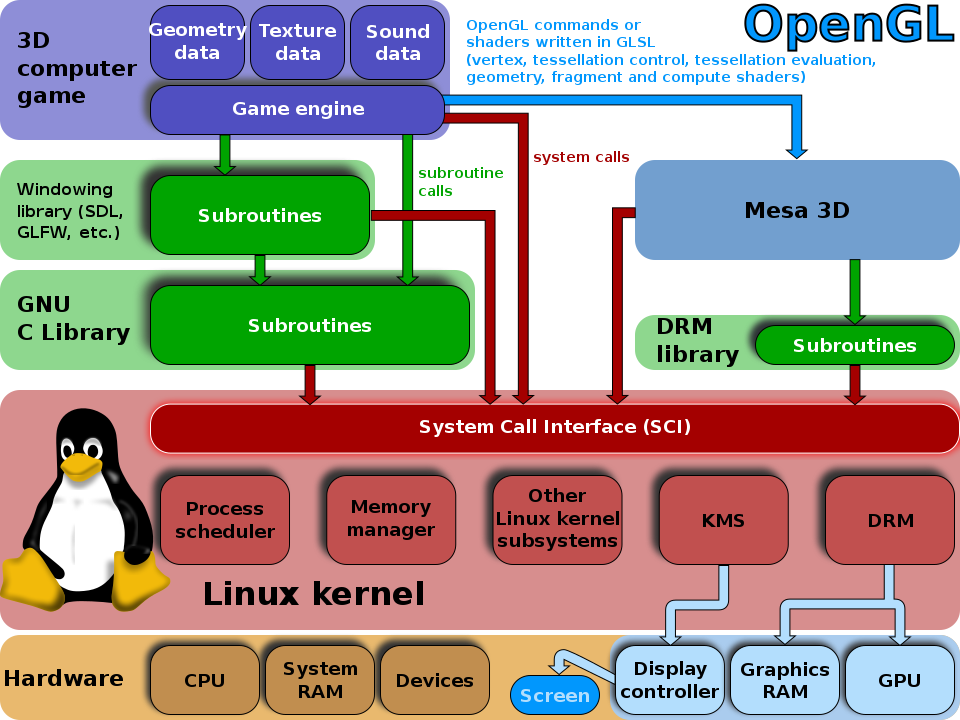
引用原文:https://blogs.igalia.com/itoral/2014/07/29/a-brief-introduction-to-the-linux-graphics-stack/
Linux graphics stack的更多相关文章
- Monitoring and Tuning the Linux Networking Stack: Receiving Data
http://blog.packagecloud.io/eng/2016/06/22/monitoring-tuning-linux-networking-stack-receiving-data/ ...
- Queueing in the Linux Network Stack !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
https://www.coverfire.com/articles/queueing-in-the-linux-network-stack/ Queueing in the Linux Networ ...
- Linux Storage Stack Diagram存储堆栈图
这是一个描述非常好的存储栈,版本为:Linux Storage Stack Diagram v4.10,我在这里转载下图片,可以提升大家对存储栈的理解. https://www.thomas-kren ...
- Linux Kernel Stack
整理一些杂乱的内容.以下x86架构. Linux 内核栈大小 内核栈大小是固定的,默认为8k,曾经有选项可以设置为4k栈.由于大小固定,申请过大的栈内存,或者函数调用层次过深,都可能导致栈溢出. 关注 ...
- 《Monitoring and Tuning the Linux Networking Stack: Receiving Data》翻译
Overview 从宏观的角度来看,一个packet从网卡到socket接收缓冲区的路径如下所示: 驱动加载并初始化 packet到达网卡 packet通过DMA被拷贝到内核中的一个ring buff ...
- The Linux Storage Stack Diagram
相关文章: 如何提高Linux下块设备IO的整体性能?
- linux io stack
- The Linux Storage Stack Diagram 内核 4.0 版的 I/O 栈
- Linux Storage Stack Diagram 4.0
https://www.thomas-krenn.com/en/wiki/Linux_Storage_Stack_Diagram
随机推荐
- 大整数四则运算(vector与数组两种版本实现)
每逢大整数四则运算,都会怯懦,虽是算法竞赛必会的东西,也零散的学过,简单的总结过,但不成体系的东西心里一直没底. 所以今天消耗了大量的卡路里,啃了几套模板之后终于总结成了一套自己的模板 再也不用担心大 ...
- Hiho1422 Harmonic Matrix Counter (高斯消元)
16年北京站A题 真的难啊.. 题意: 定义和谐矩阵 就是每个元素和上下左右的xor值=0 输出一个超大数 然后最多800个询问 求字典序第k小的和谐矩阵 x y位置上的数 题解: 首先这个超大数的范 ...
- Windows10与虚拟机中CentOS-7.2进行ftp通信
首先Linux的IP地址可以通过以下命令获取: ifconfig Windows10上面IP地址通过下面命令获取 ipconfig 你首先要保证你的主机和Linux虚拟机是可以ping通的(ping都 ...
- 【noi 2.7_2987】小兔子捡金币(算法效率)
题意:问蛇形回文的访问次序. 解法:很基础的一道题,先算出询问的点处在第几环,再用4个while一个个走一遍这一圈.P.S.我一直想办法想用不用while(),可是真的一直WA!所以用while()既 ...
- HDU 3537 Daizhenyang's Coin 翻硬币博弈
题意: 给你n个硬币,你可以从中拿出来1.2.3个硬币,它们不一定要连续,你只需要保证拿出来的硬币中那个下标最大的硬币一定要是正面朝上,最后谁不能操作,谁就输了 题解: 翻硬币游戏 结论: 局面的SG ...
- 2019 Multi-University Training Contest 5——permutation 2
传送门 题意: t组输入,之后每组例子有三个数n.x.y代表在一个以x为开头y为结尾的长为n的数组里面,开头和结尾数据已经固定,让你从1--n中找其他数据填入数组中 (每个数据不能重复使用),使它满足 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 69 (Rated for Div. 2) C. Array Splitting (思维)
题意:给你一个长度为\(n\)的升序序列,将这个序列分成\(k\)段,每一段的值为最大值和最小值的差,求\(k\)段值的最小和. 题解:其实每一段的最大值和最小值的差,其实就是这段元素的差分和,因为是 ...
- Warm up HDU - 4612 树的直径
题意:给出n个点和m条边的无向图,存在重边,问加一条边以后,剩下的桥的数量最少为多少. 题解: 你把这个无向图缩点后会得到一个只由桥来连接的图(可以说这个图中的所有边都是桥,相当于一棵树),然后我们只 ...
- MIT 6.S081 聊聊xv6的文件系统(中)日志层与事务
前言 我本想把上篇中没讲完的剩余层全部在本篇中讲完,但没想到越写越多.日志层的代码不多,其思想和解决问题的手段也不算难以理解,但其背后涉及的原理和思想还是非常值得回味的,因此我打算用一整篇完整的blo ...
- MySql 执行 DELETE/UPDATE时,报 Error Code: 1175错误
MySql 执行 DELETE FROM Table 时,报 Error Code: 1175. You are using safe update mode and you tried to upd ...
