手动实现自己的spring事务注解
spring事务是基于同一个数据连接来实现的,认识到这一点是spring事务的关键,spring事务的关键点便在于在事务中不管执行几次db操作,始终使用的是同一个数据库连接。通过查看源码,我们可以看到spring事务实现思路如下
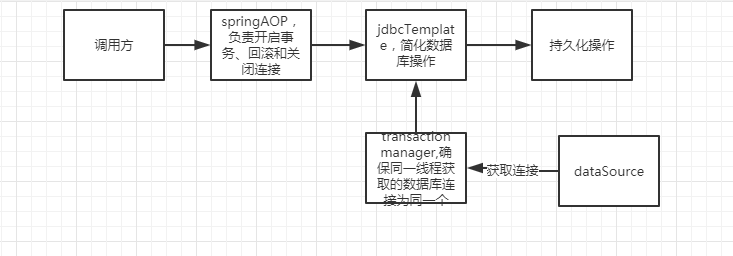
这其中的关键点就在于如何保证在事务内获取的数据库连接为同一个以及通过aop来代理数据库连接的提交、回滚。代码如下
构建自己的事务管理器,使用threadlocal来保证一个线程内获取到的数据库连接为同一个
package com.jlwj.custom; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException; /**
* Created by Administrator on 2019/8/31.
*/
@Component
public class MyTransactionManager { private ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); @Autowired
@Qualifier("dataSource")
private DataSource dataSource; public Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection = null;
if(threadLocal.get()!=null){
connection = threadLocal.get();
}else{
try {
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
threadLocal.set(connection);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} }
return connection;
} }
自定义注解
package com.jlwj.custom; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; /**
* Created by Administrator on 2019/8/31.
*/ @Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyTransactionAnnotation {
}
自定义jdbcTemplate简化db操作
package com.jlwj.custom; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException; /**
* Created by Administrator on 2019/8/31.
*/
@Component
public class MyJdbcTemplate {
@Autowired
private MyTransactionManager transactionManager; public void execute(String sql,@Nullable Object... args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = transactionManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
if(args[i] instanceof Integer){
preparedStatement.setInt(i+1, (Integer) args[i]);
}else if(args[i] instanceof String){
preparedStatement.setString(i+1, (String) args[i]);
}
}
preparedStatement.execute(); }
}
aop切面,对添加了我们自定义注解的方法进行增强,开启事务
package com.jlwj.custom; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException; /**
* Created by Administrator on 2019/8/31.
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class Aop { @Autowired
private MyTransactionManager myTransactionManager; @Around("@annotation(com.jlwj.custom.MyTransactionAnnotation)")
public Object doTransaction(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
Object o = null;
Connection connection = myTransactionManager.getConnection();
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
o = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
connection.commit(); } catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
connection.rollback();
}finally {
connection.close();
}
return o;
}
}
测试service及测试类
package com.jlwj.service; import com.jlwj.custom.MyJdbcTemplate;
import com.jlwj.custom.MyTransactionAnnotation;
import com.jlwj.custom.MyTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement; /**
* Created by Administrator on 2019/8/31.
*/
@Service
public class TransactionTestService2 { @Autowired
private MyJdbcTemplate myJdbcTemplate; @Autowired
private MyTransactionManager transactionManager; @MyTransactionAnnotation
public void addUser(String userName,Integer userId){
String sql1 = "insert into t_user(user_id,user_name,password,phone) values(?,?,?,?)";
String sql2 = "insert into t_log(content)values (?)";
try {
myJdbcTemplate.execute(sql1,userId,userName,"1231456","123213213123");
myJdbcTemplate.execute(sql2,userName);
// int a = 1/0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} } public void addUser2(String userName,Integer userId){
String sql1 = "insert into t_user(user_id,user_name,password,phone) values(?,?,?,?)";
String sql2 = "insert into t_log(content)values (?)";
try {
myJdbcTemplate.execute(sql1,userId,userName,"1231456","123213213123");
myJdbcTemplate.execute(sql2,userName);
int a = 1/0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} } }
package com.jlwj; import com.jlwj.service.TransactionTestService;
import com.jlwj.service.TransactionTestService2;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class CustomTransactionApplicationTests { @Autowired
private TransactionTestService transactionTestService; @Autowired
private TransactionTestService2 transactionTestService2; @Test
public void contextLoads() {
transactionTestService.addUser("wangwu",3);
} @Test
public void contextLoad2() {
transactionTestService2.addUser("qwe",7);
} @Test
public void contextLoad3() {
transactionTestService2.addUser2("123",8);
} }
为了方便,构建了一个spingboot项目,依赖和配置如下
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test02?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
initial-size: 1
max-active: 20
max-wait: 6000
pool-prepared-statements: true
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20
connection-properties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=2000
min-idle: 1
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
validation-query: select 1
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
手动实现自己的spring事务注解的更多相关文章
- 关于spring事务注解实战
1.概述 spring的事务注解@Transaction 相信很多人都用过,而@Transaction 默认配置适合80%的配置. 本篇文章不是对spring注解事务做详细介绍,而是解决一些实际场景下 ...
- Spring事务注解分析
1.使用spring事务注解 2.手写事务注解 1).sql执行器 2).事务注解定义 3).AOP实现事务具体实现(同一个线程中使用同一个连接) 4).应用使用注解前 5).应用使用注解后
- Spring事务注解@Transactional失效的问题
在项目中发现事务失效,使用@Transactional注解标注的Service业务层实现类方法全部不能回滚事务了,最终发现使用因为Spring与shiro进行整合之后导致的问题,将所有的Service ...
- Spring事务管理者与Spring事务注解--声明式事务
1.在Spring的applicationContext.xml中配置事务管理者 PS:具体的说明请看代码中的注释 Xml代码: <!-- 声明式事务管理的配置 --> <!-- 添 ...
- spring事务注解
@Transactional只能被应用到public方法上, 对于其它非public的方法,如果标记了@Transactional也不会报错,但方法没有事务功能. Spring使用声明式事务处理,默认 ...
- 这一次搞懂Spring事务注解的解析
前言 事务我们都知道是什么,而Spring事务就是在数据库之上利用AOP提供声明式事务和编程式事务帮助我们简化开发,解耦业务逻辑和系统逻辑.但是Spring事务原理是怎样?事务在方法间是如何传播的?为 ...
- Spring 事务注解 错误问题
碰到个问题,在一个springmvc项目中,设置好事务,然后在service上添加@Transactional注解,只要一添加这个注解,该service就无法被spring创建成功, error cr ...
- Spring事务注解@Transactional回滚问题
Spring配置文件,声明事务时,如果rollback-for属性没有指定异常或者默认不写:经测试事务只回滚运行时异常(RuntimeException)和错误(Error). <!-- 配置事 ...
- spring 事务注解
在spring中使用事务需要遵守一些规范和了解一些坑点,别想当然.列举一下一些注意点. 在需要事务管理的地方加@Transactional 注解.@Transactional 注解可以被应用于接口定义 ...
随机推荐
- Alternatives to Activiti for all platforms with any license
Activiti Activiti is a light-weight workflow and Business Process Management (BPM) Platform targeted ...
- Windows下压缩包安装Mysql
1. 下载mysql压缩包 2. 解压到指定目录,例如D:\Program Files\mysql-5.7.25-winx64 3. 在目录下创建配置文件my.ini [mysqld] port = ...
- [转]3D渲染管线
转自:http://tgerm.org/SRP/ 在3D中有两种渲染管线,分别是图形渲染管线和GPU渲染管线. 图形渲染管线 <Render-Time Rendering Third Editi ...
- Linux记录-批量安装ssh(转载)
首先,需要检查expect是否安装:rpm -qa|grep expect 然后,在操作机上创建公钥:ssh-keygen 一路回车即可 创建好之后到/root/.ssh/下就可以看到id开头的2个文 ...
- ABAP DEMO 年月的搜索帮助
效果图: *&---------------------------------------------------------------------* *& Report YCX_ ...
- ready与load的区别
JQuery里有ready和load事件 $(document).ready(function() { // ...代码... }) //document ready 简写 $(function() ...
- vue 的反向代理
情景描述: 原本的vue打包文件是放在.net core 项目的www文件夹下去发布的.这样运行没问题,但是公司领导让服务器单独部署vue,前后端要完全分离.然后这样就出问题了,有一个上传接口的地址一 ...
- 安装 KVM
安装 KVM 需要的包 sudo apt-get install -y qemu-kvm qemu-system libvirt-bin virt-manager bridge-utils vlan ...
- Configuring and Running Django + Celery in Docker Containers
Configuring and Running Django + Celery in Docker Containers Justyna Ilczuk Oct 25, 2016 0 Commen ...
- pt-osc 变更时遇到 “MySQL error 1300” 报错问题解决
目的 线上一张表的字段长度变更 `sGuid` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'sGuid' => `sGuid` varchar(512) DEFAULT ...
