Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 2) A~C
A. Laptops
time limit per test:1 second
memory limit per test:256 megabytes
input:standard input
output:standard output
One day Dima and Alex had an argument about the price and quality of laptops. Dima thinks that the more expensive a laptop is, the better it is. Alex disagrees. Alex thinks that there are two laptops, such that the price of the first laptop is less (strictly smaller) than the price of the second laptop but the quality of the first laptop is higher (strictly greater) than the quality of the second laptop.
Please, check the guess of Alex. You are given descriptions of n laptops. Determine whether two described above laptops exist.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of laptops.
Next n lines contain two integers each, ai and bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n), where ai is the price of the i-th laptop, and bi is the number that represents the quality of the i-th laptop (the larger the number is, the higher is the quality).
All ai are distinct. All bi are distinct.
If Alex is correct, print "Happy Alex", otherwise print "Poor Alex" (without the quotes).
2
1 2
2 1
Happy Alex
题意 : 给你n台笔记本的价格和质量,如果能找出一台电脑的价格比另一台的高可是质量却比他低就输出Happy Alex,否则输出Poor Alex。
思路 :将价格排序,然后找相邻的是否质量后边的大于前边那台的。这样做的道理是,价格排完序之后,如果存在不相邻的后者质量小于前者质量,那么中间必定有相邻的质量不符合前小于后。例如,价格3 4 5的电脑,如果5的质量比3的差,那么4的质量高于3时,说明4的质量高于5,4 5相邻。如果4的质量低于5的话,那么4的质量低于3,3 4 相邻。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std ; struct node
{
int price ;
int qua ;
}a[]; int cmp(node x,node y)
{
return x.price < y.price ;
}
int main()
{
int n ;
scanf("%d",&n) ;
for(int i = ; i < n ; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&a[i].price,&a[i].qua) ; }
sort(a,a+n,cmp) ;
int flag = ;
for(int i = ; i < n- ; i++)
{
if(a[i].qua > a[i+].qua)
{
flag = ;
break ;
}
}
if(flag)
puts("Happy Alex") ;
else puts("Poor Alex") ;
return ;
}
B. Fedya and Maths
time limit per test:1 second
memory limit per test:256 megabytes
input:standard input
output:standard output
Fedya studies in a gymnasium. Fedya's maths hometask is to calculate the following expression:
(1n + 2n + 3n + 4n) mod 5
for given value of n. Fedya managed to complete the task. Can you? Note that given number n can be extremely large (e.g. it can exceed any integer type of your programming language).
The single line contains a single integer n (0 ≤ n ≤ 10105). The number doesn't contain any leading zeroes.
Print the value of the expression without leading zeros.
4
4
124356983594583453458888889
0
Operation x mod y means taking remainder after division x by y.
Note to the first sample:
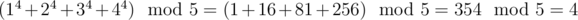
题意 : 给你一个N,让你求(1n+2n+3n+4n)%5的值。
思路 : 1到9这9的数字的n次方都是有规律的,1无论几次方个位数一定是1,而2的几次方个位数则是6,2,4,8分别代表是n模4为0,则2n个位数是6,n模4为1,则个位数是2……,
3的与2一样的规律,分别是1 3 9 7,而4的规律则是6 4,只有两个,我们写成以下形式:
n%4 = 0 1 + 6 + 1 + 6 = 14
n%4 = 1 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10
n%4 = 2 1 + 4 + 9 + 6 = 20
n%4 = 3 1 + 8 + 7 + 4 = 20
由此可见,只有在n%4为0时,取余为4,其余都为0.。。。
import java.math.*;
import java.util.*; public class Main
{ public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in) ;
BigInteger n;
n = cin.nextBigInteger();
BigInteger t = n.mod(BigInteger.valueOf(4));
if(t.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO) == 0)
System.out.println(4) ;
else System.out.println(0) ;
cin.close();
}
}
C. Boredom
memory limit per test:256 megabytes
input:standard input
output:standard output
Alex doesn't like boredom. That's why whenever he gets bored, he comes up with games. One long winter evening he came up with a game and decided to play it.
Given a sequence a consisting of n integers. The player can make several steps. In a single step he can choose an element of the sequence (let's denote it ak) and delete it, at that all elements equal to ak + 1 and ak - 1 also must be deleted from the sequence. That step brings ak points to the player.
Alex is a perfectionist, so he decided to get as many points as possible. Help him.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) that shows how many numbers are in Alex's sequence.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 105).
Print a single integer — the maximum number of points that Alex can earn.
2
1 2
2
3
1 2 3
4
9
1 2 1 3 2 2 2 2 3
10
Consider the third test example. At first step we need to choose any element equal to 2. After that step our sequence looks like this [2, 2, 2, 2]. Then we do 4 steps, on each step we choose any element equals to 2. In total we earn 10 points.
题意 : 删掉某个数x,之后你可以得到x分,但同时数列中所有x-1与x+1都要删除,问怎么样删除能得到最大的分数,输出这个分数。
思路 :先哈希一下再dp,dp[i]=max(dp[i-1],dp[i-2]+i*hashh[i]),这个方程代表的是当删除 i 的时候能得到分数,要么是你不删除i,而删除i-1,则得到的是删除i-1时得到的最大的分数,此时i与i-2都会被删掉。
如果你要删除 i ,因此i-1需要被删除,此时得到的分数就是你删除i-2时得到的最大值再加上删除 i 得到的分数。
例如6 7 8
你要是删除7,那你到8这个位置的时候能得到的最大值就是删除7得到的最大值。可是如果你删除6的话,那你到8这个位置时就是删除6得到的最大值再加上删除自己能够得到的分数。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#define LL long long using namespace std ; int a[] ;
LL hashh[],dp[] ; int main()
{
int n ;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
memset(hashh,,sizeof(hashh)) ;
memset(dp,,sizeof(dp)) ;
int maxx = ;
for(int i = ; i < n ; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]) ;
hashh[a[i]] ++ ;
maxx = max(a[i],maxx) ;
}
dp[] = hashh[] ;
for(int i = ; i <= maxx ; i++)
dp[i] = max(dp[i-],dp[i-]+i*hashh[i]) ;
printf("%I64d\n",dp[maxx]) ;
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 2) A~C的更多相关文章
- DP Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) A. Boredom
题目传送门 /* 题意:选择a[k]然后a[k]-1和a[k]+1的全部删除,得到点数a[k],问最大点数 DP:状态转移方程:dp[i] = max (dp[i-1], dp[i-2] + (ll) ...
- 递推DP Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) A. Boredom
题目传送门 /* DP:从1到最大值,dp[i][1/0] 选或不选,递推更新最大值 */ #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #in ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 2)AB
http://codeforces.com/contest/456/problem/A A. Laptops time limit per test 1 second memory limit per ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) D. Serega and Fun 分块
D. Serega and Fun Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/455/pro ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) C. Civilization 并查集,直径
C. Civilization Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/455/probl ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) A - Boredom DP
A. Boredom Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/455/problem/A ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) A. Boredom (简单dp)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/455/A 给你n个数,要是其中取一个大小为x的数,那x+1和x-1都不能取了,问你最后取完最大的和是多少. ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) 455 A. Boredom (DP)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/455/A A. Boredom time limit per test 1 second memory l ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 2)
A. Laptops 题目意思: 给定n台电脑,第i台电脑的价格是ai ,质量是bi ,问是否存在一台电脑价格比某台电脑价格底,但质量确比某台电脑的质量高,即是否存在ai < aj 且 bi & ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 2) C
Description Alex doesn't like boredom. That's why whenever he gets bored, he comes up with games. On ...
随机推荐
- ORACLE 分区表简介
参考链接:http://blog.csdn.net/ziwen00/article/details/9158725ORACLE-分区表 此文从以下几个方面来整理关于分区表的概念及操作: 1.表空间及分 ...
- 学长们的求职血泪史(C/C++/JAVA)
以下分三个方向讲解,每个方向都是一个学长独自撰稿. (一) C语言篇 C语言求职血泪史 华为(实习):机试.一面.性格测试被鄙视.优招被鄙视.普招被鄙视 锐捷:笔试.面试莫名其妙被鄙视 创新工场:笔 ...
- Android:ViewPager实现屏幕轮转和使用PagerTabStrip
① ViewPager类直接继承了ViewGroup类,所有它是一个容器类,可以在其中添加其他的view类. ② ViewPager类需要一个PagerAdapter适配器类给它提供数据. ③ Vie ...
- Golang与MySQL
1. 在golib下载go-sql-driver/mysql go get github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql 2. 代码引入 import ( "database ...
- iOS学习之基础控件
一.UILabel 1.UILabel(标签):是显示文本的空间.在App中UILabel是出现频率最高的控件. 2.UILabel是UIView的子类,作为子类一般是为了扩充父类 ...
- 通过store为toolbar添加按钮
目的是实现导航条toolbar可以动态加载按钮. ExtJS的版本是4.0. 实现方案有两个.方案一:添加render事件监听,在监听事件处理函数中使用Ext.Ajax获取按钮信息,实现动态添加按钮. ...
- Photoshop/PS中如何写维吾尔语等语言 乱码
在新疆的朋友都了解很多标语上面都会有汉语.维语等两种语言.有很多维吾尔语.哈萨克语.柯尔克孜语等语言 要在PS 里进行设计处理,这时在Photoshop中进行设计时文字粘贴进来后出现不正常是乱码形式. ...
- PLSQL读取XML的数据
最近公司做的几个项目,都是通过EBS与外部系统的Web Service进行数据的交互,而调用Web Service的时候,我们所传送的数据,都是按照约定的XML格式来传递,所以EBS接收到数据之后,需 ...
- ios-仿新浪微博app-第1天UI搭建
1:不用storyboard 点击工程删除main ui加载全部手码 >> 在application的代理方法didFinishLaunchingWithOptions中添加代码显示w ...
- 【转】PLSQL developer 连接不上64位Oracle 的解决方法
PLSQL developer 连接不上64位Oracle 的解决方法 快乐无极 , 2012/06/13 10:10 , 开发文档 , 评论(6) , 阅读(140430) , Via 本站原创 大 ...
