201709021工作日记--Volley源码详解(五)
学习完了CacheDispatcher这个类,下面我们看下NetworkDispatcher这个类的具体细节,先上代码:
/**
* 提供一个线程执行网络调度的请求分发
* Provides a thread for performing network dispatch from a queue of requests.
*
* 请求被添加到了指定的队列中
* 返回的数据通过ResponseDelivery接口返回
* Requests added to the specified queue are processed from the network via a
* specified {@link Network} interface. Responses are committed to cache, if
* eligible, using a specified {@link Cache} interface. Valid responses and
* errors are posted back to the caller via a {@link ResponseDelivery}.
*/
public class NetworkDispatcher extends Thread {
/** The queue of requests to service. */
private final BlockingQueue<Request<?>> mQueue;
/** The network interface for processing requests. */
private final Network mNetwork;
/** The cache to write to. */
private final Cache mCache;
/** For posting responses and errors. */
private final ResponseDelivery mDelivery;
/** Used for telling us to die. */
private volatile boolean mQuit = false; /**
* 创建一个新的网络调度线程,必须调用start()方法开启处理线程
* Creates a new network dispatcher thread. You must call {@link #start()}
* in order to begin processing.
*
* @param queue Queue of incoming requests for triage
* @param network Network interface to use for performing requests 执行请求
* @param cache Cache interface to use for writing responses to cache
* @param delivery Delivery interface to use for posting responses 结果返回
*/
public NetworkDispatcher(BlockingQueue<Request<?>> queue,
Network network, Cache cache,
ResponseDelivery delivery) {
mQueue = queue;
mNetwork = network;
mCache = cache;
mDelivery = delivery;
} /**
* 防止超时还一直占用资源
* Forces this dispatcher to quit immediately. If any requests are still in
* the queue, they are not guaranteed to be processed.
*/
public void quit() {
mQuit = true;
interrupt();
} @TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH)
private void addTrafficStatsTag(Request<?> request) {
// Tag the request (if API >= 14)
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
TrafficStats.setThreadStatsTag(request.getTrafficStatsTag());
}
} @Override
public void run() {
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
while (true) {
long startTimeMs = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
Request<?> request;
try {
// Take a request from the queue.
// 获取一个请求消息
request = mQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.
if (mQuit) {
return;
}
continue;
} try {
request.addMarker("network-queue-take"); // If the request was cancelled already, do not perform the
// network request.查看请求是否被取消掉了
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("network-discard-cancelled");
continue;
} addTrafficStatsTag(request); // Perform the network request.
// 开始执行用户请求,并接受一个请求后的响应
NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);
request.addMarker("network-http-complete"); // If the server returned 304 AND we delivered a response already,
// we're done -- don't deliver a second identical response.
if (networkResponse.notModified && request.hasHadResponseDelivered()) {
request.finish("not-modified");
continue;
} // Parse the response here on the worker thread.
// 对返回的响应进行处理
Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse(networkResponse);
request.addMarker("network-parse-complete"); // Write to cache if applicable.
// 将返回的响应消息写入Cache缓存
// TODO: Only update cache metadata instead of entire record for 304s.
if (request.shouldCache() && response.cacheEntry != null) {
mCache.put(request.getCacheKey(), response.cacheEntry);
request.addMarker("network-cache-written");
} // Post the response back.
// 将响应信息返回
request.markDelivered();
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} catch (VolleyError volleyError) {
volleyError.setNetworkTimeMs(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTimeMs);
parseAndDeliverNetworkError(request, volleyError);
} catch (Exception e) {
VolleyLog.e(e, "Unhandled exception %s", e.toString());
VolleyError volleyError = new VolleyError(e);
volleyError.setNetworkTimeMs(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTimeMs);
mDelivery.postError(request, volleyError);
}
}
} private void parseAndDeliverNetworkError(Request<?> request, VolleyError error) {
error = request.parseNetworkError(error);
mDelivery.postError(request, error);
}
}
网络调度线程也是从队列中取出请求并且判断是否被取消了,如果没取消就去请求网络得到响应并回调给主线程。请求网络时调用this.mNetwork.performRequest(request),这个mNetwork是一个接口,实现它的类是BasicNetwork,我们下一个就需要看看BasicNetwork的performRequest()方法。
下面这张图是网络调度线程的执行控制流图:
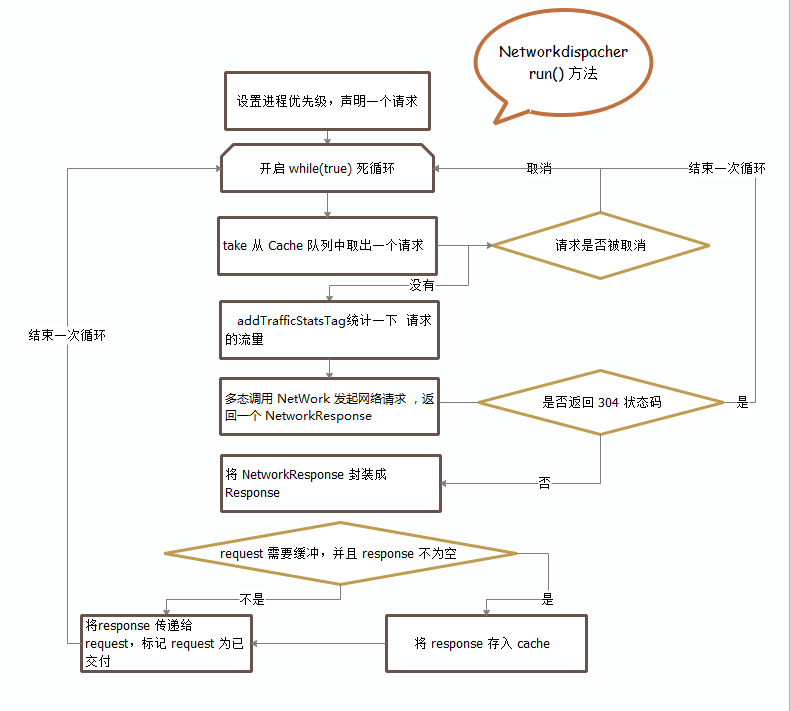
现在跟着代码流程走到了BasicNetwork这个类中,这个类通过HttpStack这个接口去处理请求队列中的请求消息。这个类中只有一个核心方法performRequest(),这个方法的目的就是构造一个返回响应消息。
/**
* 这个方法主要就是构造new NetWorkResponse()的构造函数,
* 1.HTTP状态码
* 2.响应消息体
* 3.响应返回的消息头
* 4.返回304或者缓存命中则为TRUE
* 5.返回响应的时间
* @param request Request to process
* @return
* @throws VolleyError
*/
@Override
public NetworkResponse performRequest(Request<?> request) throws VolleyError {
long requestStart = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
while (true) {
HttpResponse httpResponse = null;
byte[] responseContents = null;
Map<String, String> responseHeaders = Collections.emptyMap();
try {
// Gather headers.
// 收集请求消息头信息
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<String, String>();
addCacheHeaders(headers, request.getCacheEntry()); //调用HttpStack进行网络访问,获取返回响应值
httpResponse = mHttpStack.performRequest(request, headers);
//获取返回响应状态以及响应返回码
StatusLine statusLine = httpResponse.getStatusLine();
int statusCode = statusLine.getStatusCode();
//返回消息头信息
responseHeaders = convertHeaders(httpResponse.getAllHeaders());
//SC_NOT_MODIFIED就是304请求响应
//对304响应请求的处理流程
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED) {
Entry entry = request.getCacheEntry();
if (entry == null) {
//如果是304请求,且没有改动,则返回304状态码,响应消息头,以及从请求到响应的时间
return new NetworkResponse(HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED, null,
responseHeaders, true,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
} // A HTTP 304 response does not have all header fields. We
// have to use the header fields from the cache entry plus
// the new ones from the response.
// http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec10.html#sec10.3.5
// 304的返回消息头信息如果不为空,我们需要从缓存消息中获取完整的消息去填充完整响应消息头
// 最后返回完整的响应消息头
entry.responseHeaders.putAll(responseHeaders);
return new NetworkResponse(HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED, entry.data,
entry.responseHeaders, true,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
} // Some responses such as 204s do not have content. We must check.
// 对204返回码的验证
if (httpResponse.getEntity() != null) {
responseContents = entityToBytes(httpResponse.getEntity()); //将HTTP中返回的内容转换成字节数组
} else {
// Add 0 byte response as a way of honestly representing a
// no-content request.
responseContents = new byte[0];
} // if the request is slow, log it.
// 如果请求时间过长则产生日志进行记录
long requestLifetime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart;
logSlowRequests(requestLifetime, request, responseContents, statusLine); // 其他请求返回码的处理,抛出IO异常
if (statusCode < 200 || statusCode > 299) {
throw new IOException();
}
//返回响应消息头
return new NetworkResponse(statusCode, responseContents, responseHeaders, false,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
} catch (SocketTimeoutException e) {
attemptRetryOnException("socket", request, new TimeoutError());
} catch (ConnectTimeoutException e) {
attemptRetryOnException("connection", request, new TimeoutError());
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Bad URL " + request.getUrl(), e);
} catch (IOException e) {
int statusCode;
if (httpResponse != null) {
statusCode = httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
} else {
throw new NoConnectionError(e);
}
VolleyLog.e("Unexpected response code %d for %s", statusCode, request.getUrl());
//对网络返回的数据进行验证,对错误的响应进行处理
NetworkResponse networkResponse;
if (responseContents != null) {
networkResponse = new NetworkResponse(statusCode, responseContents,
responseHeaders, false, SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_UNAUTHORIZED || //401以及403响应消息
statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_FORBIDDEN) {
attemptRetryOnException("auth",
request, new AuthFailureError(networkResponse));
} else if (statusCode >= 400 && statusCode <= 499) {
// Don't retry other client errors.
//编号为400—499范围的状态码表用户的请求未完成并需要用户提供更多的信息来实现对所需资源的访问
throw new ClientError(networkResponse);
} else if (statusCode >= 500 && statusCode <= 599) {
//由于内部服务器错误造成的
if (request.shouldRetryServerErrors()) {
attemptRetryOnException("server",
request, new ServerError(networkResponse));
} else {
throw new ServerError(networkResponse);
}
} else {
// 3xx? No reason to retry.
throw new ServerError(networkResponse);
}
} else {
attemptRetryOnException("network", request, new NetworkError());
}
}
}
}
下面是这个方法的流程图:
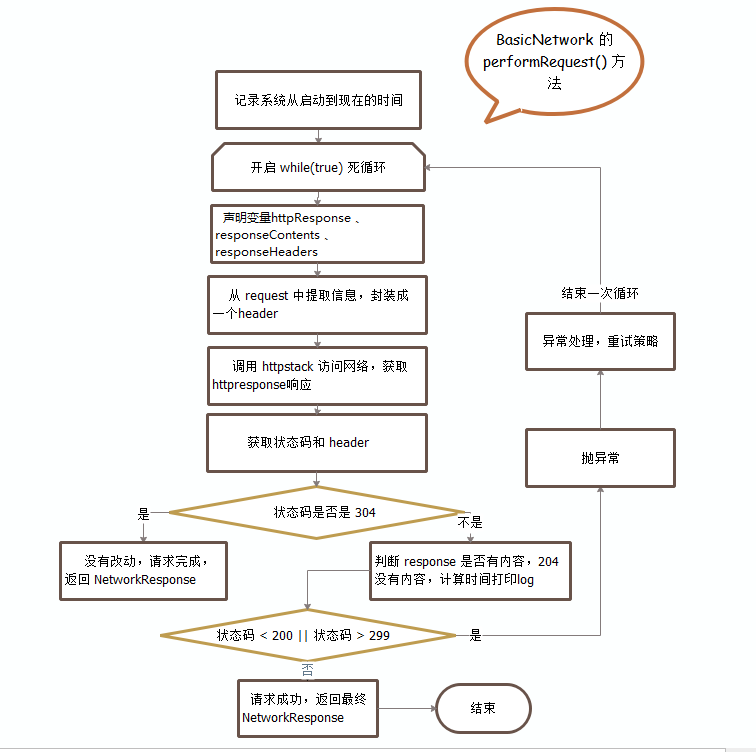
下面再来看下他的成员变量
//最长请求时间
private static final int SLOW_REQUEST_THRESHOLD_MS = 3000; //线程池的内存容量大小
private static final int DEFAULT_POOL_SIZE = 4096; //真正执行网络请求的类
protected final HttpStack mHttpStack; protected final ByteArrayPool mPool;
- 两个常量,分别表示最长请求时间和线程池大小
- 一个HttpStack 接口,真正执行网络请求的类
- 二进制数组池,一个工具类
从构造函数中可以看出网络请求最终是由HTTPStack完成的。
扫码顺序:

参考相关网站:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/e475f4479fb2
http://www.jianshu.com/p/33be82da8f25 手撕1
http://www.jianshu.com/p/358b766c8d27 手撕2
http://www.jianshu.com/p/63c0cd0fd99c 手撕3
201709021工作日记--Volley源码详解(五)的更多相关文章
- 201709011工作日记--Volley源码详解(二)
1.Cache接口和DiskBasedCache实现类 首先,DiskBasedCache类是Cache接口的实现类,因此我们需要先把Cache接口中的方法搞明白. 首先分析下Cache接口中的东西, ...
- 20170908工作日记--Volley源码详解
Volley没有jar包,需要从官网上下载源码自己编译出来,或者做成相关moudle引入项目中.我们先从最简单的使用方法入手进行分析: //创建一个网络请求队列 RequestQueue reques ...
- 201709011工作日记--Volley源码详解(三)
1. RequestQueue类 我们使用 Volley 的时候创建一个 request 然后把它丢到 RequestQueue 中就可以了.那么来看 RequestQueue 的构造方法,含有四个参 ...
- 201709021工作日记--Volley源码解读(四)
接着volley源码(三)继续,本来是准备写在(三)后面的,但是博客园太垃圾了,写了半天居然没保存上,要不是公司这个博客还没被限制登陆,鬼才用这个...真是垃圾 继续解读RequestQueue的源码 ...
- OkHttp3源码详解(五) okhttp连接池复用机制
1.概述 提高网络性能优化,很重要的一点就是降低延迟和提升响应速度. 通常我们在浏览器中发起请求的时候header部分往往是这样的 keep-alive 就是浏览器和服务端之间保持长连接,这个连接是可 ...
- 20170906工作日记--volley源码的相关方法细节学习
1. 在StringRequest类中的75行--new String();使用方法 /** * 工作线程将会调用这个方法 * @param response Response from the ne ...
- Activiti架构分析及源码详解
目录 Activiti架构分析及源码详解 引言 一.Activiti设计解析-架构&领域模型 1.1 架构 1.2 领域模型 二.Activiti设计解析-PVM执行树 2.1 核心理念 2. ...
- 源码详解系列(六) ------ 全面讲解druid的使用和源码
简介 druid是用于创建和管理连接,利用"池"的方式复用连接减少资源开销,和其他数据源一样,也具有连接数控制.连接可靠性测试.连接泄露控制.缓存语句等功能,另外,druid还扩展 ...
- [转]【视觉 SLAM-2】 视觉SLAM- ORB 源码详解 2
转载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/kyjl888/article/details/72942209 1 ORB-SLAM2源码详解 by 吴博 2 https://github.c ...
随机推荐
- tair介绍以及配置
简介 tair 是淘宝自己开发的一个分布式 key/value 存储引擎. tair 分为持久化和非持久化两种使用方式. 非持久化的 tair 可以看成是一个分布式缓存. 持久化的 tair 将数据存 ...
- avalon的常见问题
随着avalon的普及,越来越多人加入avalon的大家庭.随之而来的是各种问题.本文在这里统一解答一下. 使用avalon基本上有几个方针要坚持 数据必须先定义后使用,只能VM中定义,不能V中定义. ...
- request传递参数
当客户请求时,Servlet容器创建SrevletRequest对象(用于封装客户的请求信息),这个对象将被容器作为service()方法的参数之一传递给Srevlet,Servlet可以利用Serv ...
- 通过Roslyn构建自己的C#脚本(更新版)(转)
http://www.cnblogs.com/TianFang/p/6939723.html 之前写过文章介绍过如何通过Roslyn构建自己的C#脚本,但那篇文章是参考自Roslyn CTP版 ...
- Genetics in geographically structured populations: defining, estimating and interpreting FST
摘要:Wright’s F‑statistics, and especially FST, provide important insights into the evolutionary proce ...
- 运行Maven项目时出现invalid LOC header (bad signature)
为Maven小白,今天这问题困扰了我好久,经过多次在网上查询,终于找到了原因.明明一个小问题却耗费很多时间,着实不应该,所以必须记录一下. 报错信息如下: 对话框: 控制台: <span s ...
- Css定位元素
Css定位selenium极力推荐使用Css定位,而不是xpath定位元素,原因是css定位比xpath定位块,速度快,语法更加简洁 css常用的定位方法:1.find_element_by_css_ ...
- BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext的区别
今天在网上查资料无意中看到这一行代码 BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext ...
- 求含有n个因子的最小正整数(n<=1000000)
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/331/G 思路: 根据唯一分解定理,如果一个数n可以表示成 n=p1a1*p2a2*...*pkak (pi是第i个 ...
- C++ 静态数据成员和静态成员函数
一 静态数据成员: 1.静态数据成员的定义. 静态数据成员实际上是类域中的全局变量.所以,静态数据成员的定义(初始化)不应该被放在头文件中,因为这样做会引起重复定义这样的错误.即使加上#ifndef ...
