orocos_kdl学习(一):坐标系变换
KDL中提供了点(point)、坐标系(frame)、刚体速度(twist),以及6维力/力矩(wrench)等基本几何元素,具体可以参考 Geometric primitives 文档。
Creating a Frame, Vector and Rotation
PyKDL中创建一个坐标系时有下面4种构造函数:
__init__() # Construct an identity frame __init__(rot, pos) # Construct a frame from a rotation and a vector
# Parameters:
# pos (Vector) – the position of the frame origin
# rot (Rotation) – the rotation of the frame __init__(pos) # Construct a frame from a vector, with identity rotation
# Parameters:
# pos (Vector) – the position of the frame origin __init__(rot) # Construct a frame from a rotation, with origin at 0, 0, 0
# Parameters:
# rot (Rotation) – the rotation of the frame
下面是一个例子:
#! /usr/bin/env python import PyKDL # create a vector which describes both a 3D vector and a 3D point in space
v = PyKDL.Vector(1,3,5) # create a rotation from Roll Pitch, Yaw angles
r1 = PyKDL.Rotation.RPY(1.2, 3.4, 0) # create a rotation from ZYX Euler angles
r2 = PyKDL.Rotation.EulerZYX(0, 1, 0) # create a rotation from a rotation matrix
r3 = PyKDL.Rotation(1,0,0, 0,1,0, 0,0,1) # create a frame from a vector and a rotation
f = PyKDL.Frame(r2, v) print f
结果将如下所示,前9个元素为代表坐标系姿态的旋转矩阵,后三个元素为坐标系f的原点在参考坐标系中的坐标。
[[ 0.540302, 0, 0.841471;
0, 1, 0;
-0.841471, 0, 0.540302]
[ 1, 3, 5]]
根据机器人学导论(Introduction to Robotics Mechanics and Control)附录中的12种欧拉角表示方法,ZYX欧拉角代表的旋转矩阵为:
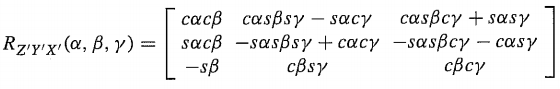
代入数据验证,KDL的计算与理论一致。
Extracting information from a Frame, Vector and Rotation
PyKDL中坐标系类Frame的成员M为其旋转矩阵,p为其原点坐标。
#! /usr/bin/env python import PyKDL # frame
f = PyKDL.Frame(PyKDL.Rotation.RPY(0,1,0),
PyKDL.Vector(3,2,4)) # get the origin (a Vector) of the frame
origin = f.p # get the x component of the origin
x = origin.x()
x = origin[0]
print x # get the rotation of the frame
rot = f.M
print rot # get ZYX Euler angles from the rotation
[Rz, Ry, Rx] = rot.GetEulerZYX()
print Rz,Ry,Rx # get the RPY (fixed axis) from the rotation
[R, P, Y] = rot.GetRPY()
print R,P,Y
将上述获取到的数据打印出来,结果如下:
3.0
[ 0.540302, 0, 0.841471;
0, 1, 0;
-0.841471, 0, 0.540302]
0.0 1.0 0.0
0.0 1.0 0.0
注意GetEulerZYX和GetRPY的结果是一样的,这其实不是巧合。因为坐标系的旋转有24种方式(本质上只有12种结果):绕自身坐标系旋转有12种方式(欧拉角),绕固定参考坐标系旋转也有12种方式(RPY就是其中一种)。EulerZYX按照Z→Y→X的顺序绕自身坐标轴分别旋转$\alpha$、$\beta$、$\gamma$角;RPY按照X→Y→Z的顺序绕固定坐标系旋转$\gamma$、$\beta$、$\alpha$角,这两种方式最后得到的旋转矩阵是一样的。
Transforming a point
frame既可以用来描述一个坐标系的位置和姿态,也可以用于变换。下面创建了一个frame,然后用其对一个空间向量或点进行坐标变换:
#! /usr/bin/env python import PyKDL # define a frame
f = PyKDL.Frame(PyKDL.Rotation.RPY(0,1,0),
PyKDL.Vector(3,2,4)) # define a point
p = PyKDL.Vector(1, 0, 0)
print p # transform this point with f
p = f * p
print p
Creating from ROS types
tf_conversions这个package包含了一系列转换函数,用于将tf类型的数据(point, vector, pose, etc) 转换为与其它库同类型的数据,比如KDL和Eigen。用下面的命令在catkin_ws/src中创建一个测试包:
catkin_create_pkg test rospy tf geometry_msgs
test.py程序如下(注意修改权限chmod +x test.py):
#! /usr/bin/env python
import rospy
import PyKDL
from tf_conversions import posemath
from geometry_msgs.msg import Pose # you have a Pose message
pose = Pose() pose.position.x = 1
pose.position.y = 1
pose.position.z = 1
pose.orientation.x = pose.orientation.y = pose.orientation.z = 0
pose.orientation.w = 1 # convert the pose into a kdl frame
f1 = posemath.fromMsg(pose) # create another kdl frame
f2 = PyKDL.Frame(PyKDL.Rotation.RPY(0,1,0),
PyKDL.Vector(3,2,4)) # Combine the two frames
f = f1 * f2
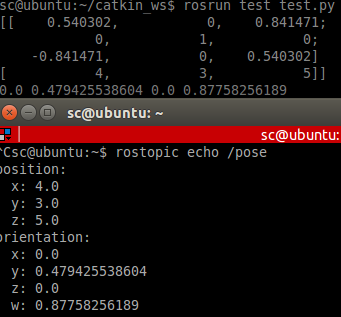
print f [x, y, z, w] = f.M.GetQuaternion()
print x,y,z,w # and convert the result back to a pose message
pose = posemath.toMsg(f) pub = rospy.Publisher('pose', Pose, queue_size=1)
rospy.init_node('test', anonymous=True)
rate = rospy.Rate(1) # 1hz while not rospy.is_shutdown():
pub.publish(pose)
rate.sleep()
通过posemath.toMsg可以将KDL中的frame转换为geometry_msgs/Pose类型的消息。最后为了验证,创建了一个Publisher将这个消息发布到pose话题上。使用catkin_make编译后运行结果如下:
参考:
Orocos Kinematics and Dynamics
kdl / Tutorials / Frame transformations (Python)
orocos_kdl学习(一):坐标系变换的更多相关文章
- 5. svg学习笔记-坐标系变换
之前我们编写图形元素的时候,编写好了位置大小就是固定的,通过坐标系变换,可以移动缩放,旋转图形,但必须声明的是,进行变换时是图形相对于坐标系的变化,就是图形是不发生变化的,而是坐标系发生了变化,比如缩 ...
- ROS Learning-014 learning_tf(编程) 坐标系变换(tf)广播员 (Python版)
ROS Indigo learning_tf-01 坐标系变换(tf)广播员 (Python版) 我使用的虚拟机软件:VMware Workstation 11 使用的Ubuntu系统:Ubuntu ...
- 【转】QPainter中坐标系变换问题
转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_67cf08270100ww0p.html 一.坐标系简介. Qt中每一个窗口都有一个坐标系,默认的,窗口左上角为坐标原点,然后水平 ...
- BZOJ3210: 花神的浇花集会(坐标系变换)
题面 传送门 题解 坐标系变换把切比雪夫距离转化为曼哈顿距离 那么对于所有的\(x\)坐标中,肯定是中位数最优了,\(y\)坐标同理 然而有可能这个新的点不合法,也就是说不存在\((x+y,x-y)\ ...
- OSG数学基础:坐标系变换
三维实体对象需要经过一系列的坐标变换才能正确.真实地显示在屏幕上.在一个场景中,当读者对场景中的物体进行各种变换及相关操作时,坐标系变换是非常频繁的. 坐标系变换通常包括:世界坐标系-物体坐标系变换. ...
- CSS学习笔记2-2d变换和过渡属性
前言:今天又是一个周末,心情不错,趁着闲暇之余,把剩下来的CSS3学习的内容全部整理出来,练习用的源码也稍微整理了一下. 2D转换 transform:translate||rotate||scale ...
- svg坐标系变换
svg的坐标变换有三个属性来决定:viewport, viewBox, 和 preserveAspectRatio,我发现三篇比较详细的博客,转载如下: 理解SVG坐标系和变换:视窗,viewBox和 ...
- orocos_kdl学习(二):KDL Tree与机器人运动学
KDL(Kinematics and Dynamics Library)中定义了一个树来代表机器人的运动学和动力学参数,ROS中的kdl_parser提供了工具能将机器人描述文件URDF转换为KDL ...
- 洛谷P3964 [TJOI2013]松鼠聚会(坐标系变换)
题面 传送门 题解 对于两个点\((x_i,y_i)\)和\(x_j,y_j\),我们定义它们之间的曼哈顿距离为 \[|x_i-x_j|+|y_i-y_j|\] 定义它们的切比雪夫距离为 \[\max ...
随机推荐
- .NetCore源码阅读笔记系列之Security (三) Authentication & AddOpenIdConnect
通过第二篇文章我们已经知道了授权的内部实现通过自定义的授权Handler来的,同样的道理 OpenIdConnect 同样是通过 OpenIdConnectHandler来请求授权的 那么它内部又是怎 ...
- 里氏代换原则(Liskov Substitution Principle,LSP)
第一种定义: 如果对每一个类型为S的对象o1,都有类型为T的对象o2,使得以T定义的所有程序P在所有的对象o1都代换为o2,程序P的行为没有发生变化,那么类型S是类型T的子类型. 第二种定义: 所有引 ...
- hdu 1240 3维迷宫 求起点到终点的步数 (BFS)
题意,给出一个N,这是这个三空间的大小,然后给出所有面的状况O为空地,X为墙,再给出起始点的三维坐标和终点的坐标,输出到达的步数 比较坑 z是x,x是y,y是z,Sample InputSTART 1 ...
- springbank 开发日志 一次因为多线程问题导致的applicationContext.getBean()阻塞
几天前遇到的这个问题.由于交易是配置的,不同的交易是同一个类的不同实例,所以不可能提前将其以@autowired类似的方式注入到需要的类中 <op:transaction id="Re ...
- [转] 理解Web路由
1. 什么是路由 在Web开发过程中,经常会遇到『路由』的概念.那么,到底什么是路由?简单来说,路由就是URL到函数的映射. 2. router和route的区别 route就是一条路由,它将一个UR ...
- 解析Linux下\r\n的问题(回车和换行)
http://www.jb51.net/article/37389.htm 深入解析Linux下\r\n的问题 http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2006/04/post_ ...
- BZOJ1826 [JSOI2010]缓存交换 堆 贪心
欢迎访问~原文出处——博客园-zhouzhendong 去博客园看该题解 题目传送门 - BZOJ1826 题意概括 Cache中有m个储存单元,接下来有n个访问地址,每个地址用一个数字表示.访问每一 ...
- mysql5.7一键安装脚本
0. 概述 最近鼓捣出了一个mysql安装脚本,将该脚本,mysql的my.cnf文件,mysql的安装包这三个文件放在同一个目录下面,执行sh mysql-auto-install.sh就可以完成m ...
- 大数据量时 Mysql LIMIT如何正确对其进行优化(转载)
以下的文章主要是对Mysql LIMIT简单介绍,我们大家都知道LIMIT子句一般是用来限制SELECT语句返回的实际行数.LIMIT取1个或是2个数字参数,如果给定的是2个参数,第一个指定要返回的第 ...
- osds have slow requests
ceph health detailHEALTH_WARN 14 requests are blocked > 32 sec; 11 osds have slow requests7 ops a ...
