《python可以这样学》第一章
一、Python基础
查看Python版本
Python 3.7.3 (v3.7.3:ef4ec6ed12, Mar 25 2019, 22:22:05) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license()" for more information.
>>> import platform #导入Python模块platform
>>> platform.python_version() #调用模块中的函数
'3.7.3'
>>> import sys #导入Python模块sys
>>> sys.version
'3.7.3 (v3.7.3:ef4ec6ed12, Mar 25 2019, 22:22:05) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)]'
>>> sys.winver
'3.7'
>>> sys.version_info
sys.version_info(major=3, minor=7, micro=3, releaselevel='final', serial=0)
>>> sys.executable #查看Python主程序文件
'D:\\python3-7\\pythonw.exe'
platform模块提供查看操作系统信息的函数
>>> platform.win32_ver()
('', '6.1.7601', 'SP1', 'Multiprocessor Free')
>>> platform.machine()
'AMD64'
>>> platform.python_compiler()
'MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)'
>>> platform.version()
'6.1.7601'
在IDLE界面中使用菜单“File”==>“New File”创建一个程序文件,输入代码并保存为.py或.pyw文件。
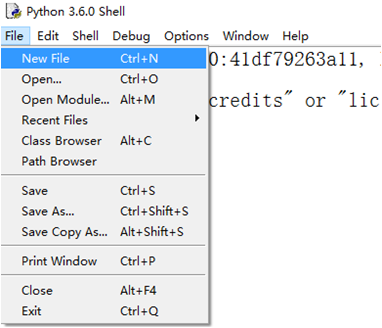
使用菜单“Run”==>“Check Module”来检查程序中是否存在语法错误,或者使用菜单“Run”==>“Run Module”运行程序,程序运行结果将直接显示在IDLE交互界面上。
打印hello world
def main ():
print ('hello world')
main ()
运行结果如下
>>>
============== RESTART: C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/test.py ==============
Hello world
>>>
变量、运算符与表达式
Python变量与内置数据类型
Python变量
>>> x = 3
创建了整型变量x,并赋值为3
>>> x = 'Hello world.'
创建了字符串变量x,并赋值为'Hello world.'
Python变量类型的变化
>>> x = 3
>>> print(type(x))
<class 'int'>
>>> x = 'Hello world.'
>>> print(type(x)) #查看变量类型
<class 'str'>
>>> x = [1,2,3]
>>> print(type(x))
<class 'list'>
>>> isinstance(3, int) #测试对象是否是某个类型的实例
True
>>> isinstance('Hello world', str)
True
如果变量出现在赋值运算符或复合赋值运算符(例如+=、*=等等)的左边则表示创建变量或修改变量的值,否则表示引用该变量的值,这一点同样适用于使用下标来访问列表、字典等可变序列以及其他自定义对象中元素的情况。
>>> x = 3 #创建整型变量
>>> print(x**2)
9
>>> x += 6 #修改变量值
>>> print(x) #读取变量值并输出显示
9
>>> x = [1,2,3] #创建列表对象
>>> x[1] = 5 #修改列表元素值
>>> print(x) #输出显示整个列表
[1, 5, 3]
>>> print(x[2]) #输出显示列表指定元素
3
幂运算符
>>> 3 ** 4
81
实数相加、相减
>>> 0.3 + 0.3
0.6
>>>
>>> 0.4 - 0.1
0.30000000000000004
>>>
>>> 0.4 - 0.1 == 0.3
False
>>>
>>> 0.9 - 0.5
0.4
>>>
复数运算
>>> x = 3 + 4j
>>> y = 5 + 6j
>>> x + y
(8+10j)
>>> x - y
(-2-2j)
>>> x * y
(-9+38j)
>>> x / y
(0.6393442622950819+0.03278688524590165j)
>>> abs(x) #复数的模
5.0
>>> x.imag #虚部
4.0
>>> x.real #实部
3.0
>>> x.conjugate() #共轭复数
(3-4j)
分数运算
>>> from fractions import Fraction #从标准库fractions中导入Fraction对象
>>> x = Fraction(3, 5) #创建分数
>>> y = Fraction(3, 7)
>>> x
Fraction(3, 5)
>>> x.numerator #分子
3
>>> x.denominator #分母
5
>>> x + y
Fraction(36, 35)
>>> x * y
Fraction(9, 35)
>>> x / y
Fraction(7, 5)
>>> x - y
Fraction(6, 35)
>>> x * 2
Fraction(6, 5)
字符串和元组属于不可变序列,不能通过下标的方式来修改其中的元素值
>>> x = (1, 2, 3) #创建一个元组
>>> print(x)
(1, 2, 3)
>>> x[1] = 5 #通过下标的方式来修改其中的元素值
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#99>", line 1, in <module>
x[1] = 5
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment #抛出异常
允许多个变量指向同一个值,修改其中的一个变量,不影响另一个变量
>>> x = 3
>>> id(x)
8791496024784
>>> y = x
>>> id(y)
8791496024784
>>>
>>> x += 6
>>> id(x)
8791496024976
>>> y
3
>>> id(y)
8791496024784
定义变量注意一下问题:
isidentifier()函数
作用:
判断指定字符串是否可以作为变量名、函数名、类名等标识符
>>> 'abc'.isidentifier()
True
>>>
>>> '3abc'.isidentifier() #变量名不能以数字开始
False
>>>
>>> '_3abc'.isidentifier()
True
>>>
>>> '__3abc'.isidentifier()
True
>>>
>>> ',__3abc'.isidentifier() #变量名不能以标点符号开头
False
>>>
>>> '__3abc('.isidentifier() #变量名中也不能含有标点符号
False
>>>
>>> '__3a,bc'.isidentifier()
False
常用内置函数
定义:不需要导入任何模块即可直接使用
列出所有内置函数和内置对象
>>> dir(__builtins__)
['ArithmeticError', 'AssertionError', 'AttributeError', 'BaseException', 'BlockingIOError', 'BrokenPipeError', 'BufferError', 'BytesWarning', 'ChildProcessError', 'ConnectionAbortedError', 'ConnectionError', 'ConnectionRefusedError', 'ConnectionResetError', 'DeprecationWarning', 'EOFError', 'Ellipsis', 'EnvironmentError', 'Exception', 'False', 'FileExistsError', 'FileNotFoundError', 'FloatingPointError', 'FutureWarning', 'GeneratorExit', 'IOError', 'ImportError', 'ImportWarning', 'IndentationError', 'IndexError', 'InterruptedError', 'IsADirectoryError', 'KeyError', 'KeyboardInterrupt', 'LookupError', 'MemoryError', 'ModuleNotFoundError', 'NameError', 'None', 'NotADirectoryError', 'NotImplemented', 'NotImplementedError', 'OSError', 'OverflowError', 'PendingDeprecationWarning', 'PermissionError', 'ProcessLookupError', 'RecursionError', 'ReferenceError', 'ResourceWarning', 'RuntimeError', 'RuntimeWarning', 'StopAsyncIteration', 'StopIteration', 'SyntaxError', 'SyntaxWarning', 'SystemError', 'SystemExit', 'TabError', 'TimeoutError', 'True', 'TypeError', 'UnboundLocalError', 'UnicodeDecodeError', 'UnicodeEncodeError', 'UnicodeError', 'UnicodeTranslateError', 'UnicodeWarning', 'UserWarning', 'ValueError', 'Warning', 'WindowsError', 'ZeroDivisionError', '_', '__build_class__', '__debug__', '__doc__', '__import__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'abs', 'all', 'any', 'ascii', 'bin', 'bool', 'breakpoint', 'bytearray', 'bytes', 'callable', 'chr', 'classmethod', 'compile', 'complex', 'copyright', 'credits', 'delattr', 'dict', 'dir', 'divmod', 'enumerate', 'eval', 'exec', 'exit', 'filter', 'float', 'format', 'frozenset', 'getattr', 'globals', 'hasattr', 'hash', 'help', 'hex', 'id', 'input', 'int', 'isinstance', 'issubclass', 'iter', 'len', 'license', 'list', 'locals', 'map', 'max', 'memoryview', 'min', 'next', 'object', 'oct', 'open', 'ord', 'pow', 'print', 'property', 'quit', 'range', 'repr', 'reversed', 'round', 'set', 'setattr', 'slice', 'sorted', 'staticmethod', 'str', 'sum', 'super', 'tuple', 'type', 'vars', 'zip']
可以使用help(函数名)查看某个函数的用法


内置函数bin()、oct()、int()、hex()用来将数字转换为二进制、八进制、十进制、十六进制
把数字转换二进制
bin()
>>> bin(192)
'0b11000000'
>>>
>>> bin(255)
'0b11111111'
转换为八进制
oct()
>>> oct(10)
'0o12'
>>>
>>> oct(16)
'0o20'
>>>
>>> oct(64)
'0o100'
>>>
>>> oct(57)
'0o71'
转换为十六进制
hex()
>>> hex(64)
'0x40'
>>>
>>> hex(128)
'0x80'
>>>
>>> hex(255)
'0xff'
>>>
>>> hex(78)
'0x4e'
int()
把十六进制数转换为十进制数
>>> hex(555)
'0x22b'
>>>
>>> int(_, 16)
555
ord()返回单个字符的Unicode码
chr()返回Unicode码对应的字符
支持中文
>>> ord('a')
97
>>> chr(97)
'a'
>>>
>>> ord('A')
65
>>> chr(65)
'A'
str()直接将任意类型参数转换为字符串
>>> str(12345)
''
>>> str([1, 2, 3])
'[1, 2, 3]'
>>> str((1, 2, 3))
'(1, 2, 3)'
>>> str({1, 2, 3})
'{1, 2, 3}'
计算列表、元组或其他可迭代对象中的最大值、最小值、和
>>> from random import randint
>>> a = [randint(1, 100) for i in range(10)] #包含10个[1, 100]之间随机数的列表
>>> print(a)
[38, 78, 77, 93, 9, 36, 43, 35, 14, 37]
>>> print(max(a), min(a), sum(a)) #最大值、最小值、所有元素之和
93 9 460
>>> sum(a) / len(a) #计算平均值
46.0
查看模块中可用对象
>>> import math
>>> dir(math)
['__doc__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'acos', 'acosh', 'asin', 'asinh', 'atan', 'atan2', 'atanh', 'ceil', 'copysign', 'cos', 'cosh', 'degrees', 'e', 'erf', 'erfc', 'exp', 'expm1', 'fabs', 'factorial', 'floor', 'fmod', 'frexp', 'fsum', 'gamma', 'gcd', 'hypot', 'inf', 'isclose', 'isfinite', 'isinf', 'isnan', 'ldexp', 'lgamma', 'log', 'log10', 'log1p', 'log2', 'modf', 'nan', 'pi', 'pow', 'radians', 'remainder', 'sin', 'sinh', 'sqrt', 'tan', 'tanh', 'tau', 'trunc']
查看指定方法的使用帮助
>>> help(math.sqrt)
Help on built-in function sqrt in module math: sqrt(x, /)
Return the square root of x. >>>
>>> help(math.sin)
Help on built-in function sin in module math: sin(x, /)
Return the sine of x (measured in radians). >>>
查看复数类型成员
>>> dir(3 + 4j)
['__abs__', '__add__', '__bool__', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__divmod__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__float__', '__floordiv__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__int__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__neg__', '__new__', '__pos__', '__pow__', '__radd__', '__rdivmod__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rfloordiv__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__rpow__', '__rsub__', '__rtruediv__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__sub__', '__subclasshook__', '__truediv__', 'conjugate', 'imag', 'real']
查看字符串类型成员
>>> dir('')
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
判断数据类型
>>> type(3) #查看3的类型
<class 'int'>
>>> type([3]) #查看[3]的类型
<class 'list'>
>>> type({3}) in (list, tuple, dict) #判断{3}是否为list、tuple或dict
False
>>> type({3}) in (list, tuple, dict, set) #判断{3}是否为list、tuple、dict或set
True
>>> isinstance(3, int)
True
>>> isinstance(3j, int)
False
>>> isinstance(3j, (int, float, complex)) #判断3是否为int、folat或complex类型的实例
True
Python之禅
>>> import this
The Zen of Python, by Tim Peters Beautiful is better than ugly.
Explicit is better than implicit.
Simple is better than complex.
Complex is better than complicated.
Flat is better than nested.
Sparse is better than dense.
Readability counts.
Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.
Although practicality beats purity.
Errors should never pass silently.
Unless explicitly silenced.
In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.
There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it.
Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.
Now is better than never.
Although never is often better than *right* now.
If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.
Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!
运算符与表达式
列表、元组、和字符串的合并或连接,生成新对象
>>> + ( + 4j) #整数和复数相加
(+4j)
>>> [, , ] + [, , ] #连接两个列表
[, , , , , ]
>>> (, , ) + (, ) #连接两个元组
(, , , )
>>> 'abcd' + '' #连接两个字符串
'abcd1234'
集合运算符的用法
差集
>>> {, , , , } - {}
{, , , }
并集
>>> {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} | {6}
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
交集
>>> {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} & {3}
{3}
对称差集
>>> {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} ^ {5, 6, 7, 8}
{1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8}
序列与整数的乘法
>>> [1, 2, 3] * 3
[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
>>> (1, 2, 3) * 3
(1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3)
>>> 'abc' * 3
'abcabcabc'
Python列表中存储的是地址而不是元素值
>>> x = [[1]] * 3
>>> x
[[1], [1], [1]]
>>> id(x[0]) == id(x[1]) == id(x[2])
True
>>> x[0].append(3)
>>> x
[[1, 3], [1, 3], [1, 3]]
>>> id(x[0]) == id(x[1]) == id(x[2])
True
运算符/和//在Python中分别表示算术除法和算术求整商
>>> 3 / 2
1.5
>>> 15 // 4
3
整数或实数的求余数
>>> 123.45 % 3.2
1.849999999999996
>>> 789 % 23
7
字符串格式化
>>> '%c, %d' % (65, 65)
'A, 65'
数字之间比较大小
>>> 1 < 3 < 5
True
>>> 3 < 5 > 2
True
>>> 1> 6 < 8
False
字符串不能比较大小
>>> 'hello' > 'world'
False
列表比较大小
>>> [1, 2, 3] < [1, 3, 4]
True
字符串和数字不能比较大小
>>> 'hello' > 3
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#31>", line 1, in <module>
'hello' > 3
TypeError: '>' not supported between instances of 'str' and 'int'
成员测试,即测试一个对象是否是另一个对象的成员
测试3是否为列表成员
>>> 3 in [1, 2, 3]
True
>>> 'abc' in 'abcdefg'
True
range()是用来生成指定范围数字的内置函数
>>> 5 in range(1, 10, 1)
True
循环遍历成员
>>> for i in (3, 5, 7):
print(i, end = '\t') 3 5 7
位运算符只能用于整数,内部执行过程是:
首先将整数转换为二进制数,然后右对齐,必要的时候左侧补0,按位进行运算,最后再把计算转换为十进制数字返回
左移
>>> 3 << 2
12
位于运算
>>> 3 & 7
3
位或运算
>>> 3 | 8
11
>>> 4 | 6
6
位异或运算
>>> 3 ^ 5
6
人机对话基本接口
输入和输出input()和print()
对于input()而言,不论用户输入什么内容,一律作为字符串对待
>>> x = input('please input:')
please input:345
>>> x
''
>>> type(x)
<class 'str'>
把字符串转化为十进制
int()
>>> int(x)
345
对字符串求值
>>> eval(x)
345
例:
>>> x = input('please input:')
please input:[1, 2, 3]
>>> x
'[1, 2, 3]'
>>> type(x)
<class 'str'>
>>> eval(x)
[1, 2, 3]
>>> x = input('please input:')
please input:'hello world'
>>> x
"'hello world'"
>>> eval(x)
'hello world'
内置函数print()用于输入特定信息
语法格式:
print(value, …, sep = '', end = '\n', file = sys.stdout, flush = false)
修改默认分隔符
>>> print(1, 3, 5, 7, sep = '\t')
1 3 5 7
修改默认行尾结束符,不换行
>>> for i in range(10):
print(i, end = '') 0123456789
重定向,将内容输出到文件中
>>> fp = open('D:\\test.txt', 'a+')
>>> print('hello world!', file=fp)
>>> fp.close()
标准库sys提供read()和readline()方法用来从键盘接收指定数量的字符
读取5个字符,如果输入不足5个,等待继续输入
>>> x = sys.stdin.read(5)
asd
s
>>> x
'asd\ns'
读取5个字符,如果超出5个,截断
>>> import sys
>>> x = sys.stdin.read(5)
abcdefghijkmln
>>> x
'abcde'
从缓冲区内继续读取5个字符
>>> x = sys.stdin.read(5)
>>> x
'fghij'
>>> x = sys.stdin.read(5)
>>> x
'kmln\n'
如果缓冲区内容比需要的少,就遇到换行符结束
>>> x = sys.stdin.readline(13)
abcdefg
>>> x
'abcdefg\n'
如果缓冲区内容比需要的多,就截断
>>> x = sys.stdin.readline(13)
abcdefghijklmnopqrst
>>> x
'abcdefghijklm'
从缓冲区继续读取
>>> x = sys.stdin.readline(13)
>>> x
'nopqrst\n'
更加友好的输入函数:pprint()
自动添加换行和缩进来更好地展示内容的结构
>>> import pprint
>>> t = [[[['black', 'cyan'], 'white', ['green', 'red']], [['magenta', 'yellow'], 'blue']]]
>>> pprint.pprint(t, width=50)
[[[['black', 'cyan'], 'white', ['green', 'red']],
[['magenta', 'yellow'], 'blue']]]
>>>
>>> pprint.pprint(t) #默认width=80
[[[['black', 'cyan'], 'white', ['green', 'red']],
[['magenta', 'yellow'], 'blue']]]
>>>
>>>
>>> pprint.pprint(t, width=30)
[[[['black', 'cyan'],
'white',
['green', 'red']],
[['magenta', 'yellow'],
'blue']]]
end
《python可以这样学》第一章的更多相关文章
- 流畅的python学习笔记:第一章
这一章中作者简要的介绍了python数据模型,主要是python的一些特殊方法.比如__len__, __getitem__. 并用一个纸牌的程序来讲解了这些方法 首先介绍下Tuple和nametup ...
- Python之旅_第一章Python入门
一.编程语言分类 1.机器语言:即计算机能听懂的二进制语言,0000 0001,直接操控硬件: 2.汇编语言:简写的英文标识符代替二进制语言,本质同样是直接操控硬件: 3.高级语言:用更贴近人类的语言 ...
- 【Python自然语言处理】第一章学习笔记——搜索文本、计数统计和字符串链表
这本书主要是基于Python和一个自然语言工具包(Natural Language Toolkit, NLTK)的开源库进行讲解 NLTK 介绍:NLTK是一个构建Python程序以处理人类语言数据的 ...
- python 机器学习基础教程——第一章,引言
https://www.cnblogs.com/HolyShine/p/10819831.html # from sklearn.datasets import load_iris import nu ...
- 《Python基础教程》第一章:基础知识
如果希望只执行普通的除法,可以在程序前加上以下语句:from __future__ import division.还有另外一个方法,如果通过命令行运行Python, 可以使用命令开关-Qnew.此时 ...
- Python核心编程2第一章课后练习
1-1 在windows下的安装方法在网上下载python2.7直接安装到C盘1)在系统变量中找到path. 2)编辑path值,添加你安装的python路径,C:\Python27. 3)检验pyt ...
- python cookbook学习笔记 第一章 文本(1)
1.1每次处理一个字符(即每次处理一个字符的方式处理字符串) print list('theString') #方法一,转列表 结果:['t', 'h', 'e', 'S', 't', 'r', 'i ...
- Python基础教程笔记 第一章
/ 表示整除,当导入_future_模块中的version时,/ 表示正常的的除法, 此时可用//表示整除,不论数字是整型还是浮点型,都可以用//表示整除. ** 表示幂次方 例如 2**3 ...
- python cookbook学习笔记 第一章 文本(2)
1.6合并字符串 ka=list('kaluoc') #字符串转成字符串列表 print ''.join(ka) #大量的字符串相连,join是最高效的 print '%s%s something % ...
- 《Python自然语言处理》第一章-练习17
问题描述: 使用text9.index()查找词sunset的索引值.你需要将这个词作为一个参数插入到圆括号之间.通过尝试和出错的过程中,找到完整的句子中包含这个词的切片. 解题思路: 用两个集合,一 ...
随机推荐
- Flutter全面屏适配
笔者在这篇文章ReactNative全面屏(Android)适配问题提及了现在的全面屏问题,不仅是Android平台,IOS平台也是,给我的感觉就是手机越来越长了. 现在的手机长宽比早就不是之前的16 ...
- macOS 10.11.* 安装scrapy
1.安装brew,然后修改brew源为某高校 2.更新python brew install python 3.安装pip 4.安装scrapy,这里肯定会有一个坑,之前在网上看到10.11开启了什么 ...
- Flash 上下文管理
1.Local() 作用:为每个协程或线程创建一个独立的内存空间 储存格式: { 唯一标识: {'stack': []} } 代码 try: from greenlet import getcurre ...
- 【新书推荐】《ASP.NET Core微服务实战:在云环境中开发、测试和部署跨平台服务》 带你走近微服务开发
<ASP.NET Core 微服务实战>译者序:https://blog.jijiechen.com/post/aspnetcore-microservices-preface-by-tr ...
- C++模板编程与宏编程经验谈
C++模板编程与宏编程经验谈 有人说C 与C++的不同主要是因为C++支持模板,不要说区别是面向对象化编程,因为C同样能很好的实现对象化编程,面向对象化其实只是思想,在很多语言中都能实现,区别在于实现 ...
- C++ vector对象是如何增长的
为了支持快速随机访问,vector将元素连续存储---每个元素紧挨着前一个元素存储. 如果没有空间容纳新元素: 容器必须分配新的内存空间来保存已有元素和新元素,将已有元素从旧位置移动到新空间中,然后添 ...
- Idea破解至2089年
我是用的版本是2018.3.6,别的朋友使用的是2019的某个版本,不过关都不影响破解 下载jar包:链接:https://pan.***baidu.***com/s/1aRR0***2YNI9jew ...
- 源码详解系列(七) ------ 全面讲解logback的使用和源码
什么是logback logback 用于日志记录,可以将日志输出到控制台.文件.数据库和邮件等,相比其它所有的日志系统,logback 更快并且更小,包含了许多独特并且有用的特性. logback ...
- c/python 的区别
c python ...
- Linux(Centos)安装tomcat并且部署Java Web项目
步骤一.下载安装包 a. 下载tomcat linux安装包,地址:http://tomcat.apache.org/download-80.cgi , 我们下载的版本是8.0,下载方式如图: b ...
