给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(2)-LinkedList源码解析
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
可以看出LinkedList 继承AbstractSequentialList 抽象类,实现了List,Deque,Cloneable,Serializable 几个接口,AbstractSequentialList 继承 AbstractList,是对其中方法的再抽象,其主要作用是最大限度地减少了实现受“连续访问”数据存储(如链接列表)支持的此接口所需的工作,简单说就是,如果需要快速的添加删除数据等,用AbstractSequentialList抽象类,若是需要快速随机的访问数据等用AbstractList抽象类(详细说明会在iterator 分析中进行解释)。
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> {
void addFirst(E e);
boolean offerFirst(E e);
boolean offerLast(E e);
E removeFirst();
E removeLast();
E pollFirst();
E pollLast();
E getFirst();
E getLast();
E peekFirst();
E peekLast();
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);
// *** Queue methods ***
boolean add(E e);
boolean offer(E e);
E remove();
E poll();
E element();
E peek();
// *** Stack methods ***
void push(E e);
E pop();
// *** Collection methods ***
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean contains(Object o);
public int size();
Iterator<E> iterator();
Iterator<E> descendingIterator();
}
3.底层存储
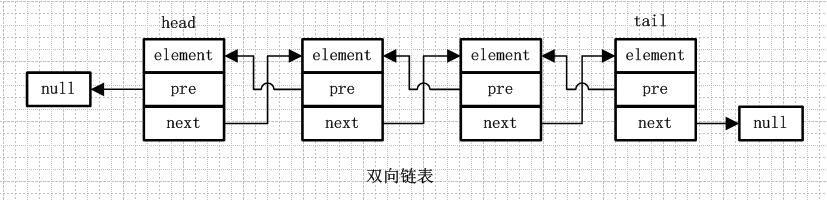
private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
private transient int size = 0;
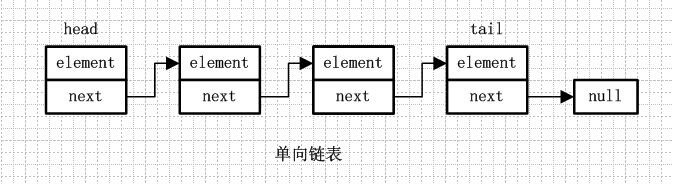
LinkedList中提供了上面两个属性,其中size和ArrayList中一样用来计数,表示list的元素数量,而header则是链表的头结点,Entry则是链表的节点对象。
private static class Entry<E> {
E element; // 当前存储元素
Entry<E> next; // 下一个元素节点
Entry<E> previous; // 上一个元素节点
Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) {
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
}
/**
* 构造一个空的LinkedList .
*/
public LinkedList() {
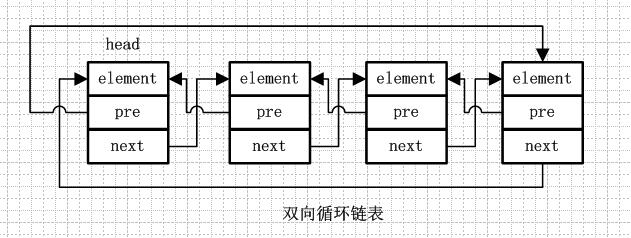
//将header节点的前一节点和后一节点都设置为自身
header.next = header. previous = header ;
} /**
* 构造一个包含指定 collection 中的元素的列表,这些元素按其 collection 的迭代器返回的顺序排列
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
public LinkedList() {
header.next = null;
header. previous = null;
}
/**
* 将一个元素添加至list尾部
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
// 在header前添加元素e,header前就是最后一个结点啦,就是在最后一个结点的后面添加元素e
addBefore(e, header);
return true;
}
/**
* 在指定位置添加元素
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
// 如果index等于list元素个数,则在队尾添加元素(header之前),否则在index节点前添加元素
addBefore(element, (index== size ? header : entry(index)));
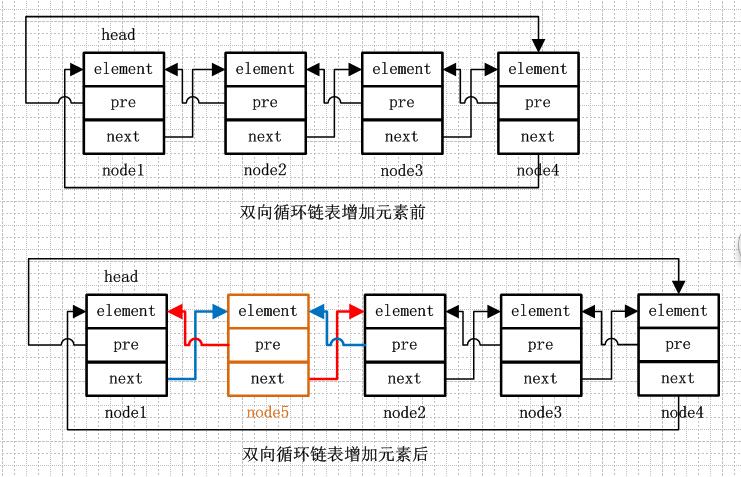
} private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) {
// 用entry创建一个要添加的新节点,next为entry,previous为entry.previous,意思就是新节点插入entry前面,确定自身的前后引用,
Entry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous);
// 下面修改newEntry的前后节点的引用,确保其链表的引用关系是正确的
// 将上一个节点的next指向自己
newEntry. previous.next = newEntry;
// 将下一个节点的previous指向自己
newEntry. next.previous = newEntry;
// 计数+1
size++;
modCount++;
return newEntry;
}
/**
* 添加一个集合元素到list中
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 将集合元素添加到list最后的尾部
return addAll(size , c);
} /**
* 在指定位置添加一个集合元素到list中
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 越界检查
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size );
Object[] a = c.toArray();
// 要插入元素的个数
int numNew = a.length ;
if (numNew==0)
return false;
modCount++; // 找出要插入元素的前后节点
// 获取要插入index位置的下一个节点,如果index正好是lsit尾部的位置那么下一个节点就是header,否则需要查找index位置的节点
Entry<E> successor = (index== size ? header : entry(index));
// 获取要插入index位置的上一个节点,因为是插入,所以上一个点击就是未插入前下一个节点的上一个
Entry<E> predecessor = successor. previous;
// 循环插入
for (int i=0; i<numNew; i++) {
// 构造一个节点,确认自身的前后引用
Entry<E> e = new Entry<E>((E)a[i], successor, predecessor);
// 将插入位置上一个节点的下一个元素引用指向当前元素(这里不修改下一个节点的上一个元素引用,是因为下一个节点随着循环一直在变)
predecessor. next = e;
// 最后修改插入位置的上一个节点为自身,这里主要是为了下次遍历后续元素插入在当前节点的后面,确保这些元素本身的顺序
predecessor = e;
}
// 遍历完所有元素,最后修改下一个节点的上一个元素引用为遍历的最后一个元素
successor. previous = predecessor; // 修改计数器
size += numNew;
return true;
}
/**
* 删除第一个匹配的指定元素
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
// 遍历链表找到要被删除的节点
if (o==null) {
for (Entry<E> e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) {
if (e.element ==null) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Entry<E> e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) {
if (o.equals(e.element )) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} private E remove(Entry<E> e) {
if (e == header )
throw new NoSuchElementException(); // 被删除的元素,供返回
E result = e. element;
// 下面修正前后对该节点的引用
// 将该节点的上一个节点的next指向该节点的下一个节点
e. previous.next = e.next;
// 将该节点的下一个节点的previous指向该节点的上一个节点
e. next.previous = e.previous;
// 修正该节点自身的前后引用
e. next = e.previous = null;
// 将自身置空,让gc可以尽快回收
e. element = null;
// 计数器减一
size--;
modCount++;
return result;
}
上面对于链表增加元素总结了,一句话就是“改变前后的互相指向关系”,删除也是同样的道理,由于节点被删除,该节点的上一个节点和下一个节点互相拉一下小手就可以了,注意的是“互相”,不能一厢情愿。
/**
* 修改指定位置索引位置的元素
*/
public E set( int index, E element) {
// 查找index位置的节点
Entry<E> e = entry(index);
// 取出该节点的元素,供返回使用
E oldVal = e. element;
// 用新元素替换旧元素
e. element = element;
// 返回旧元素
return oldVal;
}
/**
* 查找指定索引位置的元素
*/
public E get( int index) {
return entry(index).element ;
} /**
* 返回指定索引位置的节点
*/
private Entry<E> entry( int index) {
// 越界检查
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size );
// 取出头结点
Entry<E> e = header;
// size>>1右移一位代表除以2,这里使用简单的二分方法,判断index与list的中间位置的距离
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
// 如果index距离list中间位置较近,则从头部向后遍历(next)
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++)
e = e. next;
} else {
// 如果index距离list中间位置较远,则从头部向前遍历(previous)
for (int i = size; i > index; i--)
e = e. previous;
}
return e;
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this list contains
* at least one element <tt>e</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return <tt> true</tt> if this list contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
} /**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o==null) {
for (Entry e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) {
if (e.element ==null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Entry e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) {
if (o.equals(e.element ))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
} /**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size ;
if (o==null) {
for (Entry e = header .previous; e != header; e = e.previous ) {
index--;
if (e.element ==null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Entry e = header .previous; e != header; e = e.previous ) {
index--;
if (o.equals(e.element ))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this list.
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
public int size() {
return size ;
} /**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* <p>This implementation returns <tt>size() == 0 </tt>.
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return <tt> true</tt> (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @since 1.5
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
} /**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list
* @return the head of this list, or <tt>null </tt> if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E poll() {
if (size ==0)
return null;
return removeFirst();
} /**
* Removes and returns the first element from this list.
*
* @return the first element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeFirst() {
return remove(header .next);
} /**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
* @return the head of this list, or <tt>null </tt> if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E peek() {
if (size ==0)
return null;
return getFirst();
} /**
* Returns the first element in this list.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getFirst() {
if (size ==0)
throw new NoSuchElementException(); return header .next. element;
} /**
* Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, inserts the element at the front of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}.
*
* @param e the element to push
* @since 1.6
*/
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
} /**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
addBefore(e, header.next );
}
给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(2)-LinkedList源码解析的更多相关文章
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(5)-LinkedHashMap源码解析
前面分析了HashMap的实现,我们知道其底层数据存储是一个hash表(数组+单向链表).接下来我们看一下另一个LinkedHashMap,它是HashMap的一个子类,他在HashMap的基础上维持 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(4)-HashMap源码解析
前面了解了jdk容器中的两种List,回忆一下怎么从list中取值(也就是做查询),是通过index索引位置对不对,由于存入list的元素时安装插入顺序存储的,所以index索引也就是插入的次序. M ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(7)-TreeMap源码解析
TreeMap是基于红黑树结构实现的一种Map,要分析TreeMap的实现首先就要对红黑树有所了解. 要了解什么是红黑树,就要了解它的存在主要是为了解决什么问题,对比其他数据结构比如数组,链 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(6)-HashSet源码解析&Map迭代器
今天的主角是HashSet,Set是什么东东,当然也是一种java容器了. 现在再看到Hash心底里有没有会心一笑呢,这里不再赘述hash的概念原理等一大堆东西了(不懂得需要先回去看下Has ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(12)-PriorityQueue源码解析
PriorityQueue是一种什么样的容器呢?看过前面的几个jdk容器分析的话,看到Queue这个单词你一定会,哦~这是一种队列.是的,PriorityQueue是一种队列,但是它又是一种什么样的队 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(1)-ArrayList源码解析
工作中经常听到别人讲“容器”,各种各样的容器,话说到底什么是容器,通俗的讲“容器就是用来装东西的器皿,比如:水桶就是用来盛水的,水桶就是一个容器.” ok,在我们写程序的时候常常要对大量的对象进行管理 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(13)-总结篇之Java集合与数据结构
是的,这篇blogs是一个总结篇,最开始的时候我提到过,对于java容器或集合的学习也可以看做是对数据结构的学习与应用.在前面我们分析了很多的java容器,也接触了好多种常用的数据结构,今天 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(11)-Queue之ArrayDeque源码解析
前面讲了Stack是一种先进后出的数据结构:栈,那么对应的Queue是一种先进先出(First In First Out)的数据结构:队列. 对比一下Stack,Queue是一种先进先出的容 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(10)-Stack&Vector源码解析
前面我们已经接触过几种数据结构了,有数组.链表.Hash表.红黑树(二叉查询树),今天再来看另外一种数据结构:栈. 什么是栈呢,我就不找它具体的定义了,直接举个例子,栈就相当于一个很窄的木桶 ...
随机推荐
- 第二百八十八天 how can I坚持
明天,就要回济南了.早上八点的票,去火车站还得一个半小时,六点就得起床啊,好早,忍了. 这两天又没法更新日志了.周一才能回来. 今天好忙,事情好杂. 其实不想请假. 算了,睡觉了,没什么可写的了.是没 ...
- Web Service学习之五:WSDL详解
WSDL是Web Service定义文档,不同平台 不同语言实现Web Service遵循的共同协议 ,在解析XML时按照各自语言的特点解析成相应的具体类.方法.参数和数据类型. WSDL是一个XML ...
- HTML+CSS+JS学习总结
HTML: 什么是 HTML? HTML 是用来描述网页的一种语言. HTML 指的是超文本标记语言 (Hyper Text Markup Language) HTML 不是一种编程语言,而是一种标记 ...
- [iOS微博项目 - 2.0] - OAuth授权3步
A.概念 OAUTH协议为用户资源的授权提供了一个安全的.开放而又简易的标准.与以往的授权方式不同之处是OAUTH的授权不会使第三方触及到用户的帐号信息(如用户名与密码),即第三方无需使用用 ...
- 【转】C#传委托给C的函数指针调用问题
C#传委托给C的函数指针调用问题C代码如下: #include "stdio.h" __declspec(dllexport) int Call(int (*qq)(int num ...
- Oracle 的 INSERT ALL和INSERT FIRST
描述性的东西就不来了,搞技术的,最喜欢实在的实例.通过下面的例子,大家很快就能明白insert all 与 insert first 的功能,比文字描述更通俗易懂. 一.INSERT ALL 不带条件 ...
- checked 选中
<input type="radio" name="singleAnswer" value="0" <s:property va ...
- ArrayList常用方法
ArrayList常用方法 import java.util.*; public class JIHe04 { // ArrayList add 添加方法 public static void fun ...
- UVa712 S-Trees
// UVa712 S-Trees // Rujia Liu // 题意:给一棵满二叉树,每一层代表一个01变量,取0时往左走,取1时往右走.给出所有叶子的值,以及一些查询(即每个变量的值),求最后到 ...
- java中hashcode和equals的区别和联系
HashSet和HashMap一直都是JDK中最常用的两个类,HashSet要求不能存储相同的对象,HashMap要求不能存储相同的键. 那么Java运行时环境是如何判断HashSet中相同对象.Ha ...
