04-树6. Huffman Codes--优先队列(堆)在哈夫曼树与哈夫曼编码上的应用
题目来源:http://www.patest.cn/contests/mooc-ds/04-%E6%A0%916
In 1953, David A. Huffman published his paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes", and hence printed his name in the history of computer science. As a professor who gives the final exam problem on Huffman codes, I am encountering a big problem: the Huffman codes are NOT unique. For example, given a string "aaaxuaxz", we can observe that the frequencies of the characters 'a', 'x', 'u' and 'z' are 4, 2, 1 and 1, respectively. We may either encode the symbols as {'a'=0, 'x'=10, 'u'=110, 'z'=111}, or in another way as {'a'=1, 'x'=01, 'u'=001, 'z'=000}, both compress the string into 14 bits. Another set of code can be given as {'a'=0, 'x'=11, 'u'=100, 'z'=101}, but {'a'=0, 'x'=01, 'u'=011, 'z'=001} is NOT correct since "aaaxuaxz" and "aazuaxax" can both be decoded from the code 00001011001001. The students are submitting all kinds of codes, and I need a computer program to help me determine which ones are correct and which ones are not.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives an integer N (2 <= N <= 63), then followed by a line that contains all the N distinct characters and their frequencies in the following format:
c[1] f[1] c[2] f[2] ... c[N] f[N]
where c[i] is a character chosen from {'0' - '9', 'a' - 'z', 'A' - 'Z', '_'}, and f[i] is the frequency of c[i] and is an integer no more than 1000. The next line gives a positive integer M (<=1000), then followed by M student submissions. Each student submission consists of N lines, each in the format:
c[i] code[i]
where c[i] is the i-th character and code[i] is a string of '0's and '1's.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in each line either “Yes” if the student’s submission is correct, or “No” if not.
Sample Input:
7
A 1 B 1 C 1 D 3 E 3 F 6 G 6
4
A 00000
B 00001
C 0001
D 001
E 01
F 10
G 11
A 01010
B 01011
C 0100
D 011
E 10
F 11
G 00
A 000
B 001
C 010
D 011
E 100
F 101
G 110
A 00000
B 00001
C 0001
D 001
E 00
F 10
G 11
Sample Output:
Yes
Yes
No
No
题目大意:通过给定的字符及其访问次数,判断给定的编码是否为哈夫曼编码
判断条件:满足条件的编码形成的哈夫曼树可能不同,但其带权路径长度WPL一定相同且最小;且满足前缀码(前缀码是任何字符的编码都不是另一字符编码的前缀,前缀码可以避免二义性)
解题思路:
1.根据输入的节点(字符)以及权重(访问次数),模拟建立哈夫曼树,并求出其WPL
a.把权重建成一个最小堆(数组实现),然后每次弹出最小堆的最小元素即根节点
b.构造一个新的节点:从堆中依次弹出两个最小的元素的和作为新节点的权重,再将新节点插入堆中
c.WPL的值就是所有新节点的权重的和
2.根据输入的编码计算WPL用来判断是否与哈夫曼树的WPL相同
WPL等于每个字符编码访问次数与编码长度的乘积之和
3.根据输入的编码判断是否为前缀码
双重循环遍历,判断两个字符中某一个字符编码是否是另一个字符编码的前缀
图解建立哈夫曼树的过程中最小堆与哈夫曼树的变化如下:
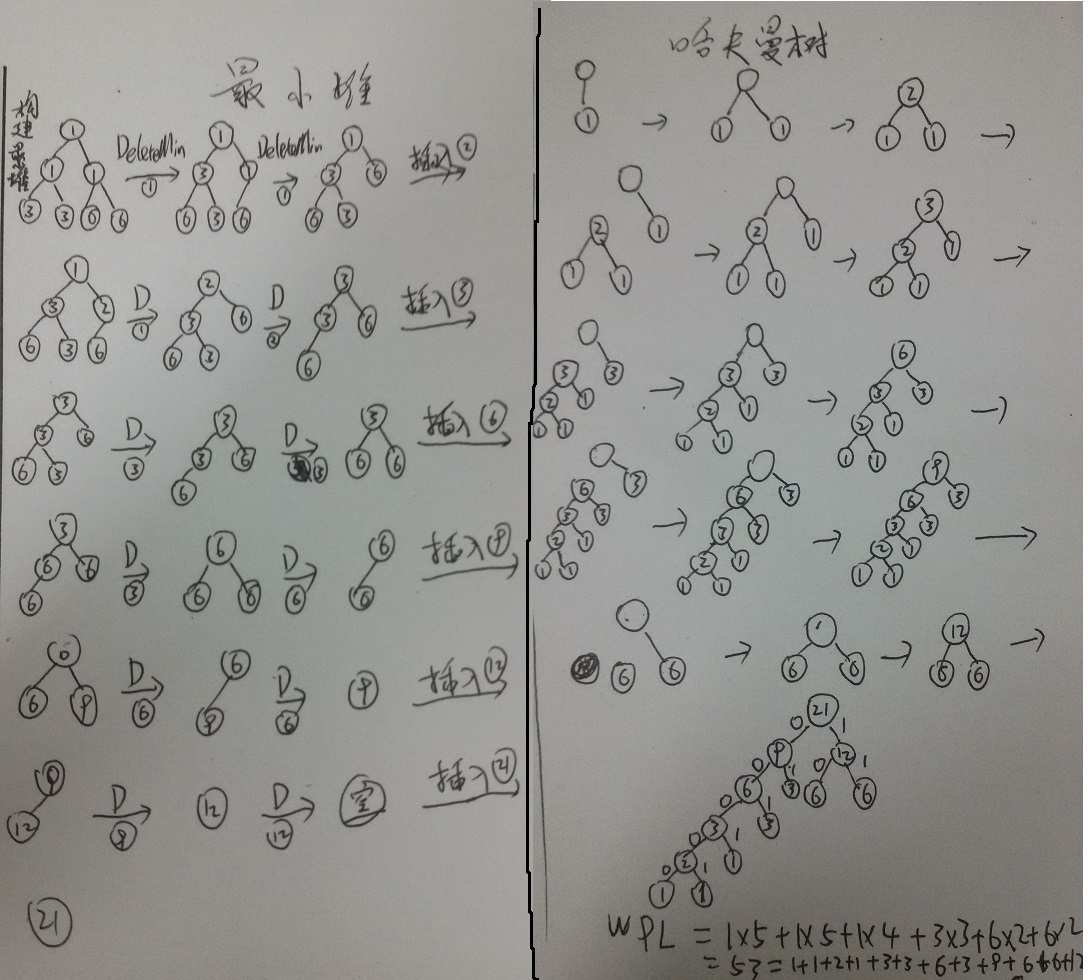
代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstring> #define N 64 //最大字符数
#define M 200 //最大编码长度 int HuffmanWPL(int heap[]); /*模拟建立哈夫曼树,返回WPL*/
void PercolateDown(int heap[], int *Size, int parent); /*从节点parent开始下滤*/
void BuildMinHeap(int heap[], int *Size); /*通过传入的完全二叉树(数组)建立最小堆*/
int DeleteMin(int heap[], int *Size); /*删除堆中最小元素 */
void Insert(int minHeap[], int * Size, int weight); /*向最小堆中插入权重为weight的节点*/
int CountWPL(int f[], char code[][M]); /*计算一种编码的WPL*/
bool IsPrefixcode(char code[][M]); /*判断某种编码是否为前缀码*/
bool IsPrefix(char *s1, char *s2); /*判断两个字符中某一个字符编码是否是另一个字符编码的前缀*/ int n; //全局变量,字符的个数 int main()
{
char ch, code[N][M];
int f[N];
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
while(ch = getchar()) {
if (isalpha(ch) || isdigit(ch) || ch == '_') { //如果是字符
scanf("%d", &f[i]); //输出对应的访问次数
break;
}
}
}
int minWPL = HuffmanWPL(f); //通过模拟哈夫曼树得到最小WPL int stusNum; //学生个数(编码种类)
scanf("%d", &stusNum);
for (int i = ; i < stusNum; i++) {
for (int j = ; j <= n; j++) {
while(ch = getchar()) {
if (isalpha(ch) || isdigit(ch) || ch == '_') { //若为字符
scanf("%s", code[j]); //输入对应字符的编码
break;
}
}
}
int thisWPL = CountWPL(f, code);
if (thisWPL == minWPL && IsPrefixcode(code)) //若WPL为最小且为前缀码
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
return ;
} bool IsPrefixcode(char code[][M])
{
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = i+; j <= n; j++)
if (IsPrefix(code[i], code[j]))
return false;
return true;
} bool IsPrefix(char *s1, char *s2)
{
while (s1 && s2 && *s1 == *s2) { //从编码首位向后遍历,当遍历到末端或两者不相等时退出循环
s1++;
s2++;
}
if (*s1 == '\0' || *s2 == '\0') //若遍历到某个字符编码的末端
return true; //则该字符是另一字符的前缀
else
return false;
} int CountWPL(int f[], char code[][M])
{
int WPL = ;
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++)
WPL += f[i] * strlen(code[i]); //权重*编码长
return WPL;
} void PercolateDown(int heap[], int *Size, int parent)
{
int temp = heap[parent];
int i, child; for (i = parent; i* <= (*Size); i = child){
child = * i;
if (child != (*Size) && heap[child+] < heap[child]) //找到值更小的儿子
child++;
if (temp > heap[child]) //如果值比下一层的大
heap[i] = heap[child]; //下滤
else
break;
}
heap[i] = temp;
} void BuildMinHeap(int heap[], int *Size)
{
for (int i = (*Size) / ; i > ; i--) //从最后一个有儿子的节点开始
PercolateDown(heap, Size, i); //向前构造最小堆
} int DeleteMin(int heap[], int *Size)
{
int minElem = heap[]; //最小堆根节点为最小值
heap[] = heap[*Size]; //将最小堆最后一个节点放到根节点处
(*Size)--; //节点数减一
PercolateDown(heap, Size, ); //从根节点开始下滤
return minElem;
} void Insert(int heap[], int * Size, int weight)
{
int i;
for (i = ++(*Size); i > && heap[i/] > weight; i /= ) //先将要插入的节点放最后
heap[i] = heap[i/]; //再上滤
heap[i] = weight;
} int HuffmanWPL(int heap[])
{
int minHeap[N];
int Size = ; for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
minHeap[Size++] = heap[i]; //将构造最小堆的数组初始化
minHeap[Size] = heap[n];
BuildMinHeap(minHeap, &Size); int WPL = ;
for (int i = ; i < n; i++) {
int leftWeight = DeleteMin(minHeap, &Size);
int rightWeight = DeleteMin(minHeap, &Size);
int rootWeight = leftWeight + rightWeight;
WPL += rootWeight;
Insert(minHeap, &Size, rootWeight);
}
return WPL;
}
04-树6. Huffman Codes--优先队列(堆)在哈夫曼树与哈夫曼编码上的应用的更多相关文章
- P3378 【模板】堆 (内含左偏树实现)
P3378 [模板]堆 题解 其实就是一个小根堆啦,STL就可以解决,但是拥有闲情雅致的我学习了Jelly_Goat的左偏树,增加了代码长度,妙啊 Solution 1 STL STL 里面prior ...
- 05-树9 Huffman Codes
哈夫曼树 Yes 需满足两个条件:1.HuffmanTree 结构不同,但WPL一定.子串WPL需一致 2.判断是否为前缀码 开始判断用的strstr函数,但其传值应为char *,不能用在strin ...
- 05-树9 Huffman Codes及基本操作
哈夫曼树与哈弗曼编码 哈夫曼树 带权路径长度(WPL):设二叉树有n个叶子结点,每个叶子结点带有权值 Wk,从根结点到每个叶子结点的长度为 Lk,则每个叶子结点的带权路径长度之和就是: WPL = 最 ...
- 哈夫曼树(C++优先队列的使用)
给定n个权值作为n个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若带权路径长度达到最小,称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree).哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近. 构造 假设有n个权 ...
- PTA 05-树9 Huffman Codes (30分)
题目地址 https://pta.patest.cn/pta/test/16/exam/4/question/671 5-9 Huffman Codes (30分) In 1953, David ...
- 数据结构慕课PTA 05-树9 Huffman Codes
题目内容 In 1953, David A. Huffman published his paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Re ...
- 【algo&ds】【吐血整理】4.树和二叉树、完全二叉树、满二叉树、二叉查找树、平衡二叉树、堆、哈夫曼树、B树、字典树、红黑树、跳表、散列表
本博客内容耗时4天整理,如果需要转载,请注明出处,谢谢. 1.树 1.1树的定义 在计算机科学中,树(英语:tree)是一种抽象数据类型(ADT)或是实作这种抽象数据类型的数据结构,用来模拟具有树状结 ...
- PAT 05-树8 Huffman Codes
以现在的生产力,是做不到一天一篇博客了.这题给我难得不行了,花了两天时间在PAT上还有测试点1没过,先写上吧.记录几个做题中的难点:1.本来比较WPL那块我是想用一个函数实现的,无奈我对传字符串数组无 ...
- 树-哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)
概述 哈夫曼树:树的带权路径长度达到最小. 构造规则 1. 将w1.w2.-,wn看成是有n 棵树的森林(每棵树仅有一个结点): 2. 在森林中选出根结点的权值最小的两棵树进行合并,作为一棵新树的左. ...
随机推荐
- Spring学习(2):面向接口编程思想
一. 引言 Spring核心的IOC的实体用了面向接口编程思想,所以有必要了解下.简单来说的话,Spring就是一个轻量级的控制反转(IOC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架. 接口的定义的概念:泛指实 ...
- 该用哪个:Redis与Memcached之间如何选择呢?
华为云分布式缓存Redis5.0和Memcached都是华为云DCS的核心产品. 那么在不同的使用场景之下,如何选择Redis5.0和Memcached呢? 就由小编为大家进行详细的数据对比分析吧 R ...
- PHP autoload与spl_autoload自动加载机制的深入理解
PHP autoload与spl_autoload自动加载机制的深入理解 作者: 字体:[增加 减小] 类型:转载 时间:2013-06-05我要评论 本篇文章是对PHP中的autoload与spl_ ...
- 关于cnblog.com的用户体验
首先我自己目前是一个学生党,每天在博客园上就上发布一些自己做的东西以及老师布置的作业,还能在上面学习很多别人的一些好的列子,我就希望博客园能够很好地为我们这些学生服务,当我们用它时能够很好地达到我们的 ...
- 第二周:PSP&进度条
PSP: 一.词频统计改进 1.表格: C类型 C内容 S开始时间 E结束时间 I时间间隔 T净时间(mins) 预计花费时间(hrs) 学习 <构建之法>.Java 8:46 1 ...
- java基础知识学习笔记
本文知识点以js为参照.对比分析得出笔记.JavaScript之所以叫JavaScript是打算借助java推广自己.虽然都是开发语言,但JavaScript一开始主要运行在 客户端,而java主要运 ...
- PHP伪类型和伪变量
一.伪类型 PHP伪类型有三种,分别是:1,mixed混合类型.2,number数字类型.3,callback回调类型. 1,mixed混合类型: mixed说明一个参数可以接受多种不同的类型,但并不 ...
- SQL 抛出异常的例子 RAISERROR 的使用
先创建一个procedure 当输入的值不在0-100之间时会报出异常 create proc proc_x @a int as begin ) ,) else select @a end go 测试 ...
- npm 安装 不快的解决办法
npm config list 查看配置 npm config set prefix “c:\dev\nvm\npm”(配置用npm下载包时全局安装的包路径) npm install npm -g ...
- ZOJ2290_Game
题目意思是这样的,给定一个数N,第一个可以减去任意一个数(不能为N本身),然后接下来轮流减去一个数字,下一个人减去的数字必须大于0,且不大于2倍上一次被减去的数字. 把N减为0的人获胜. 看完题目后不 ...
