BST 解析 (一)
这篇博文主要初步介绍Binary Search Tree(BST)的一些基本功能以及应用场景,由于BST的相关知识比较多,下一节会接着补充BST的一些功能。这一节主要分为以下六个要素:
- BST 的定义
- BST的应用场景
- BST searching 分析
- BST insertion 分析
- 最大值/最小值的查找
- Next Larger Key的分析
一:BST的定义
invariant:
BST是对于任意的node x,如果node y是node x的左边的节点, 那么Key(y) <= Key(x); 对于任意的node x, 如果node y 是node x的右边的节点, 那么key(y)>=key(x).
下图是一个BST结构的example:

注意上面的树状结构和Heap很相似,但其实他们是有非常大的本质区别的;heap的结构本质是array,每一个node本身是没有一个指向children和parent的pointer的。然而BST的每一个node都是包含有指向它的children和parent的pointer。 BST中的node的C++的实现如下:
class Node{
private:
int key;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *parent;
public:
//constructor
Node();
//key set & get
void setKey(int innerKey);
int getKey();
//left child pointer's get & set
void setLeft(Node *innerLeft);
Node * getLeft();
//right child pointer's get & set
void setRight(Node *innerRight);
Node *getRight();
//parent pointer's get & set
void setParent(Node *innerParent);
Node *getParent();
}
二:BST的应用场景
例如比赛场馆的预订这个案例中,要求预订的时间前后一个小时这个场馆并没有被其他人预订;在这个案例中,我的预订时间前面之前的被别人预订过的时间肯定小于我的预订时间, 而后面的预订时间肯定大于我的预订时间, 如果想成功预订还得继续比较他们的中间时间差是否大于1小时。为了更好的描述这个案例, 我用下面的图示来帮助说明:
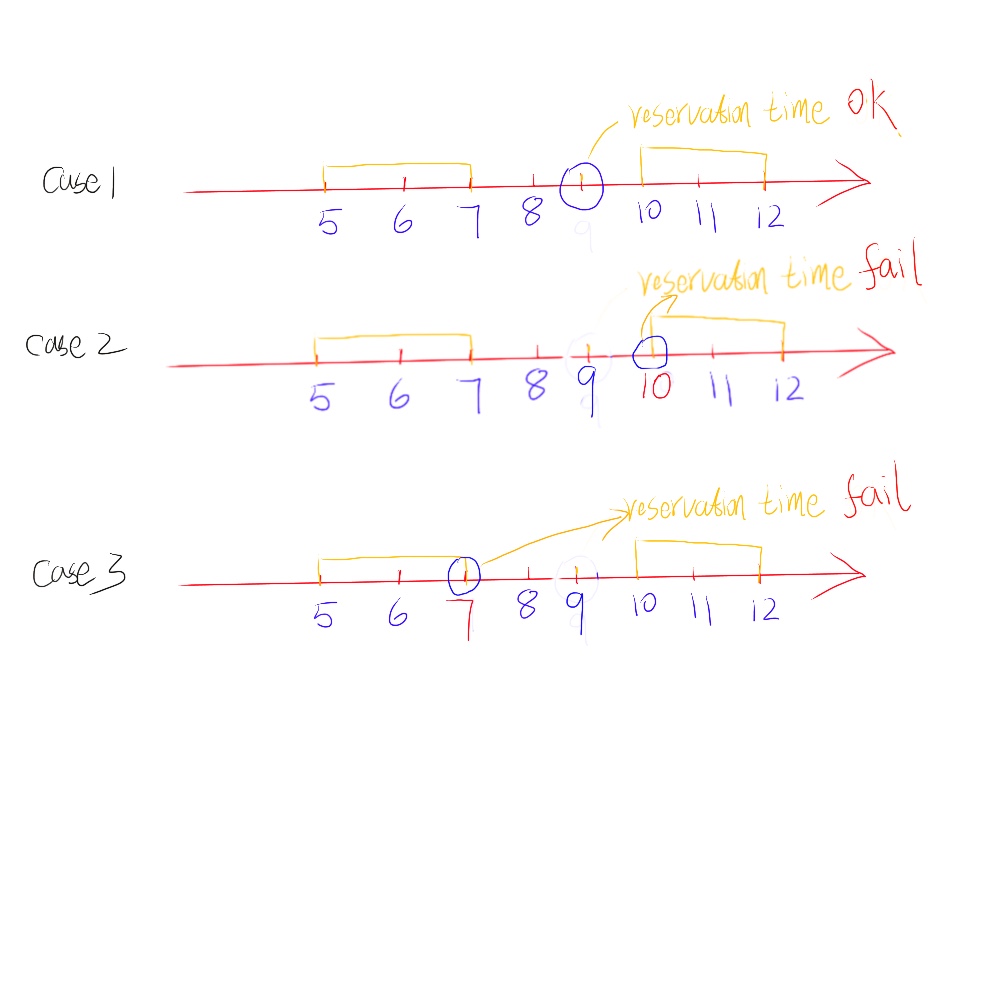
上面这就是一个典型的BST的案例,虽然我是用一个一维的coordinate表示,但其本质就是一个BST。
三:BST searching 分析
如果有-个BST的数据结构,让我们找一个key,那么这个过程是怎样的呢?首先第一步从root开始比较,如果小于root的key则跟left child比较,否则跟right child接着比较;如此递归下去直到找到我们的key或者一直到了BST的leaf。如果找到key,则返回这个key;如果一直到了leaf都没有找到,则说明这个key根本就不在这个BST,返回NULL。这个过程是一直比较的过程,所有步骤中的basic operation都是比较的话,称之为Comparison Model. 下面两符图分别展示了返回key和返回NULL 的2中情况:

下面代码的过程是用C++实现BST 的searching的过程。
/*
*Description: search(int key) is publically invoked, in order to search the key in the BST
*
*parameters:
1. key //the value which we want to find within the BST
*
*return void
*
*/
Node *BST::search(int key){ if (this->root == NULL) {//the BST has not initialzed yet return NULL; }else{ return search(key, this->root);
}
} /*
*Description: recuresivly to search the key, the work starts from root and level by level down to leaf, if fails to find out, return NULL.
*
*
*parameters:
* 1: key//value which should be searched
* 2: node//this is the node the the key compares with
*
*return Node *
**/
Node* BST::search(int key, Node *node){ if (node==NULL) {//we have found all the nodes, but no one matches, which means it is not within the BST return NULL; }else if (key == node->getKey()) {//we spot on the key, return the node return node; }else if (key < node->getKey()){//the key is smaller than the node, so it is must be in the left subtree. return search(key, node->getLeft()); }else{// the key is bigger than the node, so it is must be in the right subtree. return search(key, node->getRight()); } }
根据以上的步骤的分析,BST search的worst case efficiency = height of BST, 即efficiency = O(h), h 是指BST的高度,注意这里的h不像Heap那样是logN哦,这里的h是一个介于logN和N之间的一个值;当然了我们可以通过BST的balancing过程将BST的高度都转换成logN,但这一块比较复杂需要在后面讲解。现在我们只需要知道是BST的height就行。
四:BST 的insertion分析
如果希望向BST插入一个node (称为A),并且继续保持BST的结构,则需要通过以下几个步骤:
- 从root开始比较,如果A的key小于node,则跟node的left child接着比较,如果大于等于node的key,则跟node的right child的key接着比较;一直比较到leaf为止
- 如果A的key值小于leaf的值,则将node A 插入到当前leaf的左边,否则插入node的右边;
其具体的图示过程如下所示:

insertion的c++实现过程如下代码所示:
/*
*insert(int key) is publically invoked, and the key could be inserted at proper position
*
*parameters:
1. key //the value of an node *
*return void
*
*/
void BST::insert(int key){ if (this->root != NULL) {//The BST has already intialized, so we need to compare the keys level by level according to the BST critirals. //we gonna start from the root node to compare values until we find a leaf
insert(key, this->root); }else{ Node *rootNode = new Node();
this->root = rootNode;
this->root->setKey(key);
this->root->setLeft(NULL);
this->root->setRight(NULL);
this->root->setParent(NULL); }
} /*
*Description: recuresivly to find where the key should be inserted, the work starts from root and level by level down to leaf
*
*CAUTION: WE DO NOT DISCUSS DUPLICATE KEYS HERE
*
*parameters:
* 1: key//value which should be inserted
* 2: node//this is the node the the key compares with
*
*return void
**/ void BST::insert(int key, Node *node){ if (key<node->getKey()) {//indicates that the key should be in the left side of node; if (node->getLeft()!=NULL) {//node's left child is not null, so we need to down to search insert(key, node->getLeft()); }else{//node is a leaf, we have hit the spot Node *newNode = new Node();
newNode->setKey(key);
newNode->setLeft(NULL);
newNode->setRight(NULL);
newNode->setParent(node);
node->setLeft(newNode); } }else if (key > node->getKey()){//indicates that the key should be in the right side of node; if (node->getRight()!=NULL) {//node's right child is not null, so we need to search down insert(key, node->getRight()); }else{//node is a leaf, spot on Node *newNode = new Node();
newNode->setKey(key);
newNode->setLeft(NULL);
newNode->setRight(NULL);
newNode->setParent(node);
node->setRight(newNode); } } }
上面的过程和BST的search很类似,也是通过不断的比较,只是在最后在leaf后面插入一个元素,找到leaf后插入的动作可以看做是常量O(1)。那么insertion 的时间复杂度是:efficiency = O(h)+O(1)=O(h); 所以它同样是BST的高度height。
五:最值的查找
由于BST自身特点和结构,我们其实非常容易就可以找到最大值和最小值的。由于BST中比当前node小的node始终在左边,而比当前node大的node始终在自己的右边。所以我们就可以从root开始一直开始遍历node的left child,知道leftchild等于nil为止,那么就说明这个node就是最小值;相反如果找最大值,就一直找node的right child,直到right child为nil为止。其具体的图例和实现过程如:
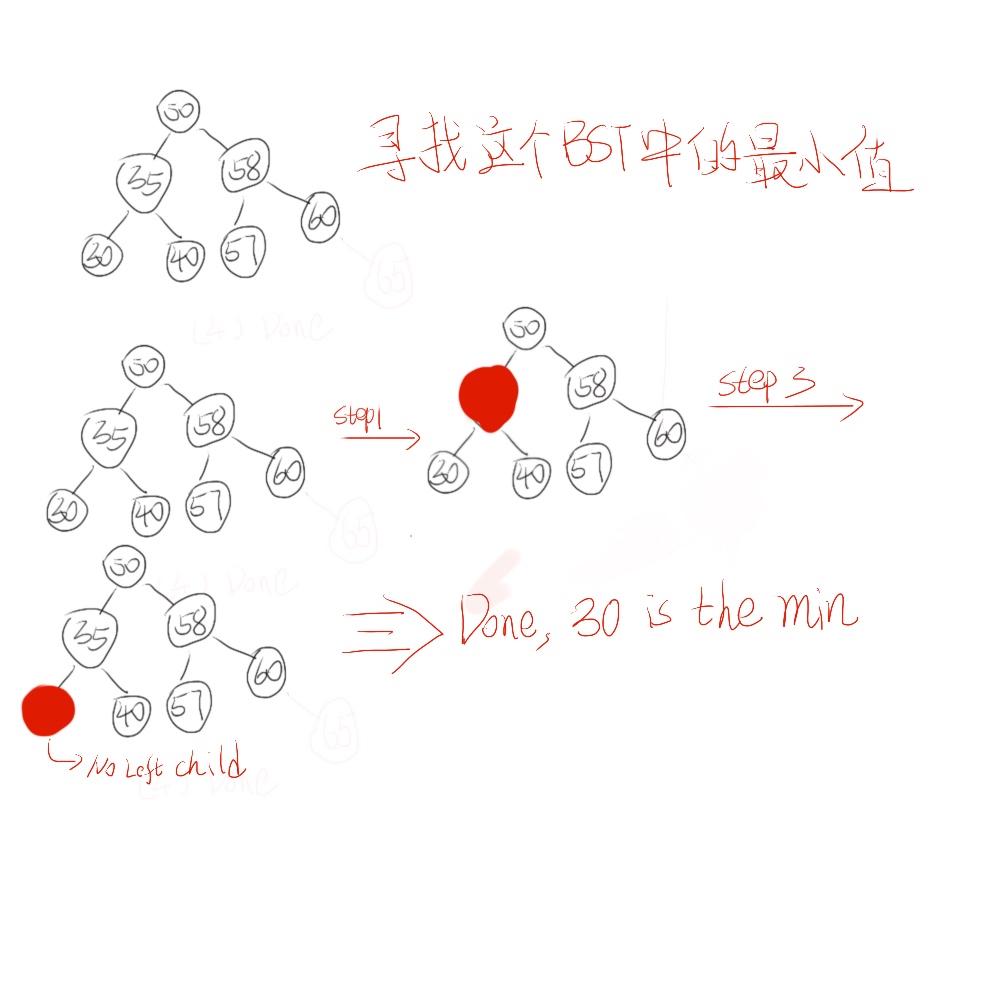
/*
*Description: The function is to find out the minimum key node within the subtree rooted at self
*
*
*parameters: void
*
*
*return: node;//the minimum node
*
*
*****/
Node * Node::findMin(){ Node *currentNode = this; while (currentNode->getLeft() != NULL) { currentNode = currentNode->getLeft();
} return currentNode;
}
最值的寻找的时间复杂度同样是这个BST的高度height,即O(h);
六:next larger/smaller 分析
next larger 是指比某个node A 大的值,但是比所有其他大于node A的nodes 都要小;比较绕口,其实本质就是在所有比node A 大的集合中,key值最接近node A 的哪一个node。同理可知next smaller的含义。那么在BST中如何寻找一个node的next larger或者next smaller呢?看下图展示寻找next larger的过程

根据以上寻找next larger的图示,可以总结出以下2条规律:
1. 如果node有right subtree,那么这个node的next larger就是它的right subtree的最小值
2.如果node没有subtree, 那么这个node的next larger就需要一直的往parent node traversal, 直到node 是 它的left children tree的一个节点为止。
那么它的worst case的时间复杂度同样是0(h)。
next larger的实现代码如下:
/*
*
*Description: this function's aim is to find the next next of this node
*
*
*parameters: void
*
*
*return: Node// the next larger node
*
*
*/
Node* Node::findNextLarger(){ if (this->getRight() == NULL) {//this node does not have any right subtree Node *tempNode = this; while (tempNode->getParent()->getLeft() != tempNode) { tempNode = tempNode->getParent(); if (tempNode == NULL) {//no next larger value exsits return NULL;
} } return tempNode->getParent(); }else{//this node does have a right subtree return this->getRight()->findMin();//return the right subtree's minimun key } }
那么这章的BST(一)的内容就结束了,那么这里还有几个小问题哈,从头到尾我们没有分析BST的height具体是多少,也没有介绍delete node的过程,下一节我会分析这2块。
如果有什么问题,欢迎大家指教。
BST 解析 (一)的更多相关文章
- BST 解析 (二)height and deletion
前面一章介绍了BST的结构和一些简单的基本功能,例如:insert,findMin,nextLarger等等.这一节主要讲解一些BST的delete node操作还有BST的height的分析以及一些 ...
- Word2Vec源码解析
Reference:http://blog.csdn.net/itplus/article/details/37969519 (Word2Vec解析(部分有错)) 源码:http://pan.bai ...
- c#如何解析时区字符串
常见时区缩写可参考: http://time.123cha.com/knowledge/6.html 常见时区缩写如下: IDLE +12:00 国际日期变更线,东边 NZDT +13:00 新西兰 ...
- Java8获取当前时间、新的时间日期类如Java8的LocalDate与Date相互转换、ZonedDateTime等常用操作包含多个使用示例、Java8时区ZoneId的使用方法、Java8时间字符串解析成类
下面将依次介绍 Date转Java8时间类操作 ,Java8时间类LocalDate常用操作(如获得当前日期,两个日期相差多少天,下个星期的日期,下个月第一天等) 解析不同时间字符串成对应的Java ...
- 图解算法——恢复一棵二叉搜索树(BST)
题目来源 基础:给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,该树中的两个节点被错误地交换.请在不改变其结构的情况下,恢复这棵树. 进阶:使用 O(n) 空间复杂度的解法很容易实现.你能想出一个只使用常数空间的 ...
- 【原】Android热更新开源项目Tinker源码解析系列之三:so热更新
本系列将从以下三个方面对Tinker进行源码解析: Android热更新开源项目Tinker源码解析系列之一:Dex热更新 Android热更新开源项目Tinker源码解析系列之二:资源文件热更新 A ...
- .NET Core中的认证管理解析
.NET Core中的认证管理解析 0x00 问题来源 在新建.NET Core的Web项目时选择“使用个人用户账户”就可以创建一个带有用户和权限管理的项目,已经准备好了用户注册.登录等很多页面,也可 ...
- Html Agility Pack 解析Html
Hello 好久不见 哈哈,今天给大家分享一个解析Html的类库 Html Agility Pack.这个适用于想获取某网页里面的部分内容.今天就拿我的Csdn的博客列表来举例. 打开页面 用Fir ...
- 【原】Android热更新开源项目Tinker源码解析系列之一:Dex热更新
[原]Android热更新开源项目Tinker源码解析系列之一:Dex热更新 Tinker是微信的第一个开源项目,主要用于安卓应用bug的热修复和功能的迭代. Tinker github地址:http ...
随机推荐
- 简述Apache的ab测试主要有那些关键指标
一.ab的原理 ab是apachebench命令的缩写. ab的原理:ab命令会创建多个并发访问线程,模拟多个访问者同时对某一URL地址进行访问.它的测试目标是基于URL的,因此,它既可以用来测试ap ...
- django(注册→登录→主页)增强版
首先准备一张空白的数据表: urls展示: views主要的几个函数以及数据库链接代码:↓ 后端编写结束↑ ↓前端 前端界面:↓ 幸好成功了,接下来看看数据库有没有插入数据.... 这么 ...
- Kotlin——最详细的控制语句使用
在前面 的章节中讲解了Kotlin语言中的数据类型.变量与常量的定义.不了解请参见前面的内容: Kotlin从无到有系列之数据类型介绍. Kotlin从无到有系列之变量.常量.注释的使用. 下面详细为 ...
- Servlet 笔记-Cookie 处理
Cookie 是存储在客户端计算机上的文本文件,并保留了各种跟踪信息. 识别返回用户包括三个步骤: 服务器脚本向浏览器发送一组 Cookie.例如:姓名.年龄或识别号码等. 浏览器将这些信息存储在本地 ...
- JPA之helloWorld
在 Eclipse 下创建 JPA 工程 1.在eclipse上安装JPA插件(网上自行百度) 2.new 一个Jpa工程 3:点击下一步,下一步,第一次运行jpa插件会让我们装相关类库如下图,等到再 ...
- LeetCode 229. Majority Element II (众数之二)
Given an integer array of size n, find all elements that appear more than ⌊ n/3 ⌋ times. The algorit ...
- Redis主从环境配置
1.Redis主从同步原理 redis主服务器会周期性的把更新的数据写入磁盘或者把修改操作写入追加的记录文件,然后将数据文件同步给从服务器,从服务器加载记录文件,在内存库中更新新数据. 2.VMWar ...
- swift 之设计模式 适配器
大学的时候,有一个<近世代数>的教授,他上课从来不看课本,并且也不按课本来讲解课程,但是他讲的东西比书本深刻形象(幽默,口才杠杠的),有层次感,除了授业,他还经常给我讲一些为人处世,做学问 ...
- C语言(记录)——内存相关_2:内存的编址与管理
本文是基于嵌入式的C语言 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- Leetcode题解(32)
107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II 题目 直接代码: /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct ...
