Adaptive gradient descent without descent
概
本文提出了一种自适应步长的梯度下降方法(以及多个变种方法), 并给了收敛性分析.
主要内容
主要问题:
\min_x \: f(x).
\]
局部光滑的定义:
若可微函数\(f(x)\)在任意有界区域内光滑,即
\]
其中\(\mathcal{C}\)有界.
本文的一个基本假设是函数\(f(x)\)凸且局部光滑.
算法1 AdGD

定理1 ADGD-L
定理1. 假设\(f: \mathbb{R}^d \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) 为凸函数且局部光滑. 则由算法1生成的序列\((x^k)\)收敛到(1)的最优解, 且
\]
其中\(\hat{x}^k := \frac{\sum_{i=1}^k \lambda_i x^i + \lambda_1 \theta_1 x^1}{S_k}\), \(S_k:= \sum_{i=1}^k \lambda_i + \lambda_1 \theta\).
算法2

在\(L\)已知的情况下, 我们可以对算法1进行改进.
定理2
定理2 假设\(f\)凸且\(L\)光滑, 则由算法(2)生成的序列\((x^k)\)同样使得
\]
成立.
算法3 ADGD-accel
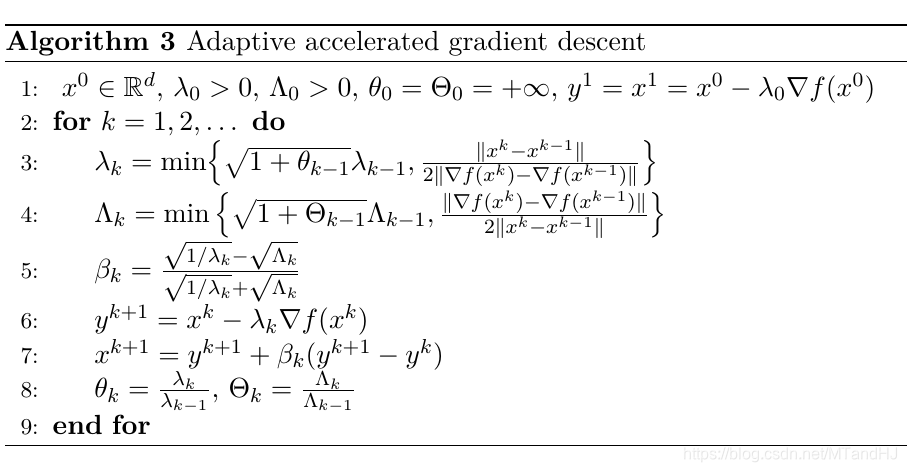
这部分没有理论证明, 是作者基于Nesterov中的算法进行的改进.
算法4 Adaptive SGD
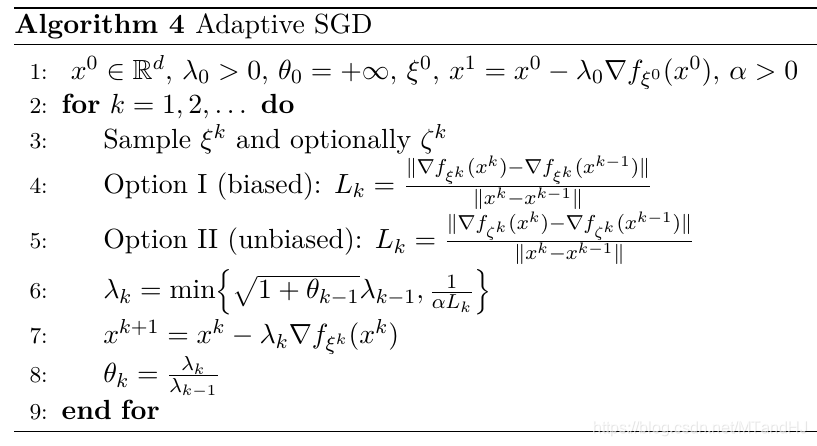
这个算法是对SGD的一个改进.
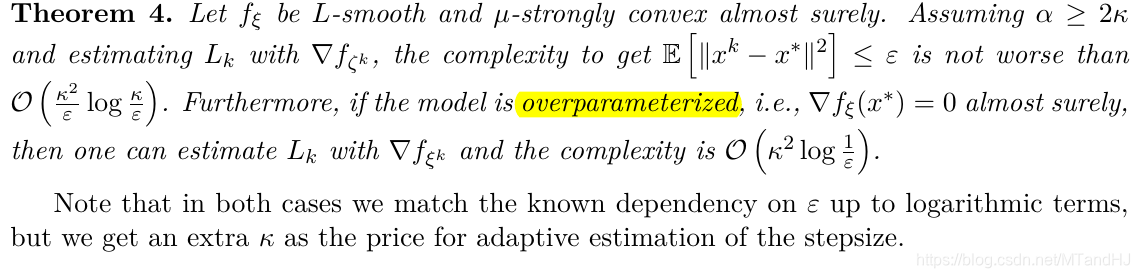
定理4
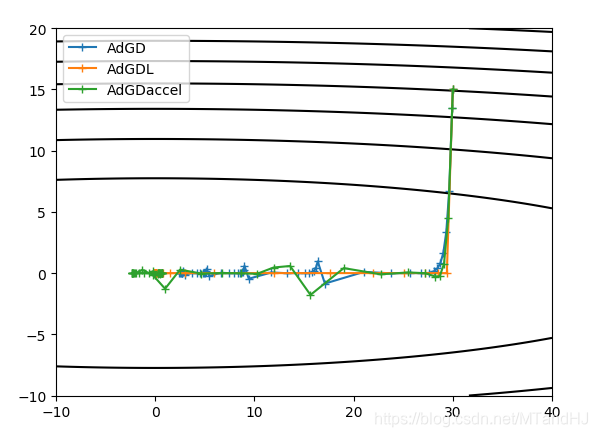
代码
\(f(x, y) = x^2+50y^2\), 起点为\((30, 15)\).
"""
adgd.py
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
State = "Test"
class FuncMissingError(Exception): pass
class StateNotMatchError(Exception): pass
class AdGD:
def __init__(self, x0, stepsize0, grad, func=None):
self.func_grad = grad
self.func = func
self.points = [x0]
self.points.append(self.calc_one(x0, self.calc_grad(x0),
stepsize0))
self.prestepsize = stepsize0
self.theta = None
def calc_grad(self, x):
self.pregrad = self.func_grad(x)
return self.pregrad
def calc_one(self, x, grad, stepsize):
return x - stepsize * grad
def calc_stepsize(self, grad, pregrad):
part2 = (
np.linalg.norm(self.points[-1]
- self.points[-2]) /
(np.linalg.norm(grad - pregrad) * 2)
)
if not self.theta:
return part2
else:
part1 = np.sqrt(self.theta + 1) * self.prestepsize
return min(part1, part2)
def update_theta(self, stepsize):
self.theta = stepsize / self.prestepsize
self.prestepsize = stepsize
def step(self):
pregrad = self.pregrad
prex = self.points[-1]
grad = self.calc_grad(prex)
stepsize = self.calc_stepsize(grad, pregrad)
nextx = self.calc_one(prex, grad, stepsize)
self.points.append(nextx)
self.update_theta(stepsize)
def multi_steps(self, times):
for k in range(times):
self.step()
def plot(self):
if self.func is None:
raise FloatingPointError("func is not defined...")
if State != "Test":
raise StateNotMatchError()
xs = np.array(self.points)
x = np.linspace(-40, 40, 1000)
y = np.linspace(-20, 20, 500)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
ax.contour(X, Y, self.func([X, Y]), colors='black')
ax.plot(xs[:, 0], xs[:, 1], "+-")
plt.show()
class AdGDL(AdGD):
def __init__(self, x0, L, grad, func=None):
super(AdGDL, self).__init__(x0, 1 / L, grad, func)
self.lipschitz = L
def calc_stepsize(self, grad, pregrad):
lk = (
np.linalg.norm(grad - pregrad) /
np.linalg.norm(self.points[-1]
- self.points[-2])
)
part2 = 1 / (self.prestepsize * self.lipschitz ** 2) \
+ 1 / (2 * lk)
if not self.theta:
return part2
else:
part1 = np.sqrt(self.theta + 1) * self.prestepsize
return min(part1, part2)
class AdGDaccel(AdGD):
def __init__(self, x0, stepsize0, convex0, grad, func=None):
super(AdGDaccel, self).__init__(x0, stepsize0, grad, func)
self.preconvex = convex0
self.Theta = None
self.prey = self.points[-1]
def calc_convex(self, grad, pregrad):
part2 = (
(np.linalg.norm(grad - pregrad) * 2) /
np.linalg.norm(self.points[-1]
- self.points[-2])
) / 2
if not self.Theta:
return part2
else:
part1 = np.sqrt(self.Theta + 1) * self.preconvex
return min(part1, part2)
def calc_beta(self, stepsize, convex):
part1 = 1 / stepsize
part2 = convex
return (part1 - part2) / (part1 + part2)
def calc_more(self, y, beta):
nextx = y + beta * (y - self.prey)
self.prey = y
return nextx
def update_Theta(self, convex):
self.Theta = convex / self.preconvex
self.preconvex = convex
def step(self):
pregrad = self.pregrad
prex = self.points[-1]
grad = self.calc_grad(prex)
stepsize = self.calc_stepsize(grad, pregrad)
convex = self.calc_convex(grad, pregrad)
beta = self.calc_beta(stepsize, convex)
y = self.calc_one(prex, grad, stepsize)
nextx = self.calc_more(y, beta)
self.points.append(nextx)
self.update_theta(stepsize)
self.update_Theta(convex)
config.json:
{
"AdGD": {
"stepsize0": 0.001
},
"AdGDL": {
"L": 100
},
"AdGDaccel": {
"stepsize0": 0.001,
"convex0": 2.0
}
}
"""
测试代码
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import json
from adgd import AdGD, AdGDL, AdGDaccel
with open("config.json", encoding="utf-8") as f:
configs = json.load(f)
partial_x = lambda x: 2 * x
partial_y = lambda y: 100 * y
grad = lambda x: np.array([partial_x(x[0]),
partial_y(x[1])])
func = lambda x: x[0] ** 2 + 50 * x[1] ** 2
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(-10, 40, 500)
y = np.linspace(-10, 20, 500)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
ax.contour(X, Y, func([X, Y]), colors='black')
def process(methods, times=50):
for method in methods:
method.multi_steps(times)
def initial(methods, **kwargs):
instances = []
for method in methods:
config = configs[method.__name__]
config.update(kwargs)
instances.append(method(**config))
return instances
def plot(methods):
for method in methods:
xs = np.array(method.points)
ax.plot(xs[:, 0], xs[:, 1], "+-", label=method.__class__.__name__)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
x0 = np.array([30., 15.])
methods = [AdGD, AdGDL, AdGDaccel]
instances = initial(methods, x0=x0, grad=grad, func=func)
process(instances)
plot(instances)
Adaptive gradient descent without descent的更多相关文章
- 【转】Caffe初试(九)solver及其设置
solver算是caffe的核心的核心,它协调着整个模型的运作.caffe程序运行必带的一个参数就是solver配置文件.运行代码一般为 #caffe train --solver=*_solver. ...
- 【深度学习】之Caffe的solver文件配置(转载自csdn)
原文: http://blog.csdn.net/czp0322/article/details/52161759 今天在做FCN实验的时候,发现solver.prototxt文件一直用的都是mode ...
- Caffe学习系列(7):solver及其配置
solver算是caffe的核心的核心,它协调着整个模型的运作.caffe程序运行必带的一个参数就是solver配置文件.运行代码一般为 # caffe train --solver=*_slover ...
- tensorflow 学习(一)
改系列只为记录我学习 udacity 中深度学习课程!! 1. 整个课程分为四个部分,如上图所示. 第一部分将研究逻辑分类器,随机优化以及实际数据训练. 第二部分我们将学习一个深度网络,和使用正则化技 ...
- caffe中各层的作用:
关于caffe中的solver: cafffe中的sover的方法都有: Stochastic Gradient Descent (type: "SGD"), AdaDelta ( ...
- Caffe学习系列(8):solver优化方法
上文提到,到目前为止,caffe总共提供了六种优化方法: Stochastic Gradient Descent (type: "SGD"), AdaDelta (type: &q ...
- Caffe学习系列(二)Caffe代码结构梳理,及相关知识点归纳
前言: 通过检索论文.书籍.博客,继续学习Caffe,千里之行始于足下,继续努力.将自己学到的一些东西记录下来,方便日后的整理. 正文: 1.代码结构梳理 在终端下运行如下命令,可以查看caffe代码 ...
- 深度学习——优化器算法Optimizer详解(BGD、SGD、MBGD、Momentum、NAG、Adagrad、Adadelta、RMSprop、Adam)
在机器学习.深度学习中使用的优化算法除了常见的梯度下降,还有 Adadelta,Adagrad,RMSProp 等几种优化器,都是什么呢,又该怎么选择呢? 在 Sebastian Ruder 的这篇论 ...
- 【深度学习】深入理解优化器Optimizer算法(BGD、SGD、MBGD、Momentum、NAG、Adagrad、Adadelta、RMSprop、Adam)
在机器学习.深度学习中使用的优化算法除了常见的梯度下降,还有 Adadelta,Adagrad,RMSProp 等几种优化器,都是什么呢,又该怎么选择呢? 在 Sebastian Ruder 的这篇论 ...
随机推荐
- 微信小程序的wx.login用async和data解决code不一致的问题
由于wx.login是异步函数,导致在我们获取微信小程序返回的code去请求我们的登录接口时code的值会异常.现在用promise封装一下,将他success的结果返回,在登陆函数中await就可以 ...
- day17 阶段测验
题目 1.找出/proc/meminfo文件中以s开头的行,至少用三种方式忽略大小写 有以下几种方法: [root@localhost ~]# grep -iE "^s" /pro ...
- LeetCode33题——搜索旋转排序数组
1.题目描述 假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转. ( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] ). 搜索一个给定的目标值,如果数组中存 ...
- virtualBox 系统移植
把virtualbox已经存在的系统移植到其他机器. 1.把系统如下文件考到一个安装了virtualbox的机器. 2.点击控制-->注册 然后浏览到复制的文件路径. 3.修改uuid 不管是l ...
- MyBatis(1):实现MyBatis程序
一,MyBatis介绍 MyBatis是一个支持普通SQL查询,存储过程和高级映射的优秀持久层框架.MyBatis消除了几乎所有的JDBC代码和参数的手工设置以及对结果集的检索封装.MyBatis可以 ...
- 【spring AOP】AspectJProxyFactory
AspectJProxyFactory,可能大家对这个比较陌生,但是@Aspect这个注解大家应该很熟悉吧,通过这个注解在spring环境中实现aop特别的方便. 而AspectJProxyFacto ...
- 观察者模式之spring事件机制
ddsspring中的事件机制使用到设计模式中的观察者模式 ,观察者模式有两个概念,1.观察者.被观察者.2.被观察者做出相应得动作,观察者能接收到.不分析设计模式,学习下spring中的事件机制实际 ...
- 使用OPC与PLC通讯 一
总结自己在opc与自控开发的经验.首先介绍OPC DA模式下的OPC各种操作. 在使用opc时需要引用到 OPCDAAuto.dll 这个类库. 在项目引用后需要注册这个类库,否则程序跑起来会报错,& ...
- 启动Springboot 报错 Whitelabel Error Page This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback. Sat Jan 12 15:50:25 CST 2019 There was an unexpected error (type=Not
解决方案:http://www.cnblogs.com/michaelShao/p/6675186.html
- 关于og4j漏洞修复解决方案及源码编译
最近log4j爆出重大漏洞,程序员要赶紧修复了!文末提供已经编译好的jar包. 建议最好修复到log4j-2.15.0-rc2版本,临时解决方案还是存在jndi漏洞. 打开log4j官网https:/ ...
