HDU-3839-Ancient Messages(DFS)
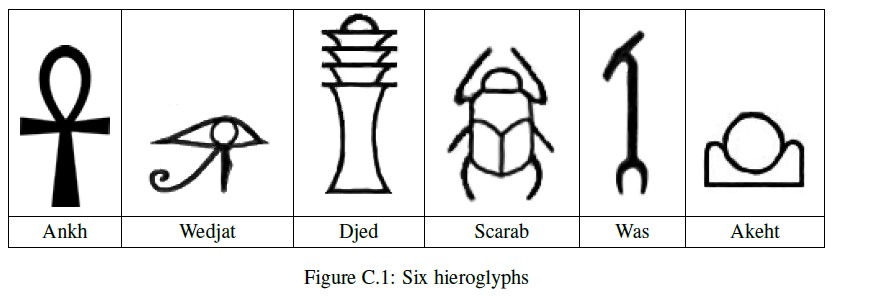
hieroglyphs and their names. In this problem, you will write a program to recognize these six characters.
of black pixels (represented by 1) and white pixels (represented by 0). In the input data, each scan line is encoded in hexadecimal notation. For example, the sequence of eight pixels 10011100 (one black pixel, followed by two white pixels, and so on) would
be represented in hexadecimal notation as 9c. Only digits and lowercase letters a through f are used in the hexadecimal encoding. The first line of each test case contains two integers, H and W: H (0 < H <= 200) is the number of scan lines in the image. W
(0 < W <= 50) is the number of hexadecimal characters in each line. The next H lines contain the hexadecimal characters of the image, working from top to bottom. Input images conform to the following rules:
- The image contains only hieroglyphs shown in Figure C.1.
- Each image contains at least one valid hieroglyph.
- Each black pixel in the image is part of a valid hieroglyph.
- Each hieroglyph consists of a connected set of black pixels and each black pixel has at least one other black pixel on its top, bottom, left, or right side.
- The hieroglyphs do not touch and no hieroglyph is inside another hieroglyph.
- Two black pixels that touch diagonally will always have a common touching black pixel.
- The hieroglyphs may be distorted but each has a shape that is topologically equivalent to one of the symbols in Figure C.11.
The last test case is followed by a line containing two zeros.
1Two figures are topologically equivalent if each can be transformed into the other by stretching without tearing.
Ankh: A
Wedjat: J
Djed: D
Scarab: S
Was: W
Akhet: K
In each output string, print the codes in alphabetic order. Follow the format of the sample output.
The sample input contains descriptions of test cases shown in Figures C.2 and C.3. Due to space constraints not all of the sample input can be shown on this page.

100 25
0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
...(50 lines omitted)...
00001fe0000000000007c0000
00003fe0000000000007c0000
...(44 lines omitted)...
0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
150 38
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
...(75 lines omitted)...
0000000003fffffffffffffffff00000000000
0000000003fffffffffffffffff00000000000
...(69 lines omitted)...
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
0 0
Case 1: AKW
Case 2: AAAAA
思路:依据圈的数量来识别。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; char ts[201],mes[6]={'W','A','K','J','S','D'},ans[10];
bool vis[205][205];
int n,m,mp[205][205],nxt[4][2]={{1,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1}},num; void dfs(int x,int y)
{
int i; for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
x+=nxt[i][0];
y+=nxt[i][1]; if(x>=0 && x<n && y>=0 && y<m && !vis[x][y] && !mp[x][y])
{
vis[x][y]=1;
dfs(x,y);
} x-=nxt[i][0];
y-=nxt[i][1];
}
} void dfs3(int x,int y)
{
int i; for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
x+=nxt[i][0];
y+=nxt[i][1]; if(x>=0 && x<n && y>=0 && y<m && !vis[x][y] && !mp[x][y])
{
vis[x][y]=1;
dfs3(x,y);
} x-=nxt[i][0];
y-=nxt[i][1];
}
} void dfs2(int x,int y)
{
int i; for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
x+=nxt[i][0];
y+=nxt[i][1]; if(x>=0 && x<n && y>=0 && y<m && !vis[x][y])
{
if(mp[x][y])
{
vis[x][y]=1;
dfs2(x,y);
}
else
{
vis[x][y]=1;
num++;
dfs3(x,y);
} } x-=nxt[i][0];
y-=nxt[i][1];
}
} int main()
{
int i,j,t,casenum=1,cnt; while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) && n)
{
n++;
m*=4;
m++; for(i=0;i<=n;i++) for(j=0;j<=m;j++) vis[i][j]=0; for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
gets(ts); if(!ts[0])
{
i--;
continue;
} for(j=0;ts[j];j++)
{
if(ts[j]>='a' && ts[j]<='f')
{
t=ts[j]-'a'+10; mp[i][j*4+1]=t/8;
mp[i][j*4+2]=t%8/4;
mp[i][j*4+3]=t%4/2;
mp[i][j*4+4]=t%2/1;
}
else
{
t=ts[j]-'0'; mp[i][j*4+1]=t/8;
mp[i][j*4+2]=t%8/4;
mp[i][j*4+3]=t%4/2;
mp[i][j*4+4]=t%2/1;
}
}
} for(i=0;i<=m;i++) mp[n][i]=0;
for(i=0;i<=n;i++) mp[i][m]=0; n++;
m++; vis[0][0]=1;
dfs(0,0); cnt=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<m;j++)
{
if(mp[i][j] && !vis[i][j])
{
num=0; vis[i][j]=1; dfs2(i,j); ans[cnt++]=mes[num];
}
}
} sort(ans,ans+cnt); ans[cnt]=0; printf("Case %d: ",casenum++); puts(ans);
}
}
版权声明:本文博客原创文章,博客,未经同意,不得转载。
HDU-3839-Ancient Messages(DFS)的更多相关文章
- HDU 3839 Ancient Messages(DFS)
In order to understand early civilizations, archaeologists often study texts written in ancient lang ...
- hdu 3839 Ancient Messages (dfs )
题目大意:给出一幅画,找出里面的象形文字. 要你翻译这幅画,把象形文字按字典序输出. 思路:象形文字有一些特点,分别有0个圈.1个圈.2个圈...5个圈.然后dfs或者bfs,就像油井问题一样,找出在 ...
- K - Ancient Messages(dfs求联通块)
K - Ancient Messages Time Limit:3000MS Memory Limit:0KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Subm ...
- HDOJ(HDU).2660 Accepted Necklace (DFS)
HDOJ(HDU).2660 Accepted Necklace (DFS) 点我挑战题目 题意分析 给出一些石头,这些石头都有自身的价值和重量.现在要求从这些石头中选K个石头,求出重量不超过W的这些 ...
- HDOJ(HDU).1045 Fire Net (DFS)
HDOJ(HDU).1045 Fire Net [从零开始DFS(7)] 点我挑战题目 从零开始DFS HDOJ.1342 Lotto [从零开始DFS(0)] - DFS思想与框架/双重DFS HD ...
- HDOJ(HDU).1241 Oil Deposits(DFS)
HDOJ(HDU).1241 Oil Deposits(DFS) [从零开始DFS(5)] 点我挑战题目 从零开始DFS HDOJ.1342 Lotto [从零开始DFS(0)] - DFS思想与框架 ...
- HDOJ(HDU).1035 Robot Motion (DFS)
HDOJ(HDU).1035 Robot Motion [从零开始DFS(4)] 点我挑战题目 从零开始DFS HDOJ.1342 Lotto [从零开始DFS(0)] - DFS思想与框架/双重DF ...
- HDU 1501 Zipper 【DFS+剪枝】
HDU 1501 Zipper [DFS+剪枝] Problem Description Given three strings, you are to determine whether the t ...
- HDU 1401 Solitaire 双向DFS
HDU 1401 Solitaire 双向DFS 题意 给定一个\(8*8\)的棋盘,棋盘上有4个棋子.每一步操作可以把任意一个棋子移动到它周围四个方向上的空格子上,或者可以跳过它四个方向上的棋子(就 ...
- ACM: HDU 2563 统计问题-DFS+打表
HDU 2563 统计问题 Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u HDU 2 ...
随机推荐
- ASP.NET 的 ViewState Cookie Session 等的比較
类型 值保存在哪 值的有效范围 备注 View State client 不能跨页面传递.仅仅能在当前页面保存数据. 在HTML中能够看到ViewState值,只是是加密. 不是明文. ViewSta ...
- css 翻牌 翻转 3d翻转 特效
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- [Linux] Use find to search for filename patterns
Learn how to use find to identify filenames matching specified patterns. We'll use find to identify ...
- ios开发多选照片实现
#import "ViewController.h" #import <Photos/Photos.h> @interface ViewController () &l ...
- HDU2473 Junk-Mail Filter - 并查集删除操作(虚父节点)
传送门 题意: 每次合并两份邮件,或者将某一份邮件独立出来,问最后有多少个邮件集合. 分析: 考虑初始化每个节点的祖先为一个虚父节点(i + n),虚父节点指向它自己.这样可以进行正常的合并操作. 而 ...
- CSDN站点CODE配置记录
为了出门写代码方便.决定还是开个项目.因此才有了这次经历. 原来有在windows下用过git,只是使用方法跟svn一样.尽管曾经也在souceforge或者git上看一些代码,可是对操作一直没有了解 ...
- scala读写文件 comparing values of types Unit and Int using `!=' will always yield true
由于scala没有对写入文件的支持,所以写文件时通常借助java进行IO操作 //方式一(小文件) /* val s1 = Source.fromFile("D:\\inputword\\h ...
- 小强的HTML5移动开发之路(21)—— PhoneGap
一.PhoneGap是什么 PhoneGap 是一个用基于 HTML,CSS 和 JavaScript 的,创建移动跨平台移动应用程序的快速开发框架.它使开发者能够利用 iPhone,Android, ...
- 学习鸟哥的Linux私房菜笔记(2)——基础指令
ls :列出文件和目录 ls -l :列出文件和目录的详细信息 ls -a:列出所有的文件和目录(包括隐藏目录) cp:拷贝文件 cp 源文件目录 目标目录 cp -r :拷贝目录 mv :移动或重 ...
- nth-child与nth-of-type
nth-of-type这个CSS3伪类还从来没有用过,今天好好研究一番,发现还是有用的.现在下面的Demo <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> ...
