Python入门 来点栗子
查天气(1)
http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?citykey=101280804
http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/WeatherApi?citykey=101280804
http://bbs.crossincode.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=8&extra=page%3D4
http://bbs.crossincode.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=9&extra=page%3D4
查天气(2)
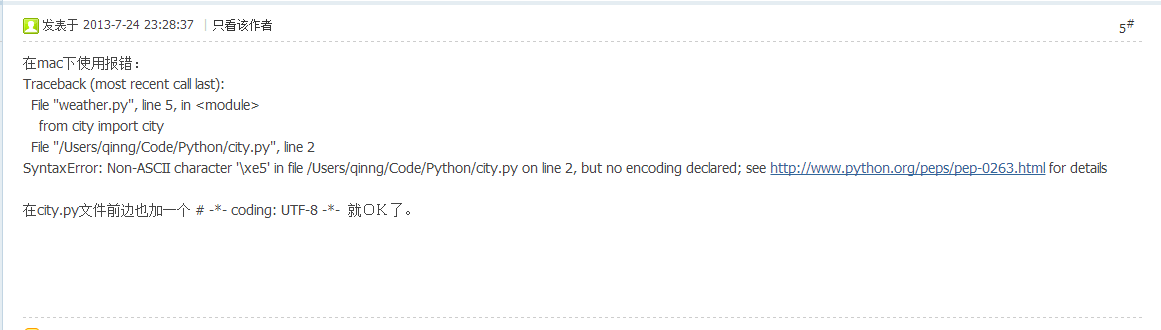
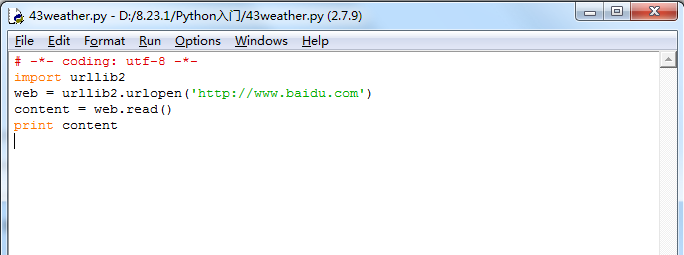
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import urllib2
web = urllib2.urlopen('http://www.baidu.com')
content = web.read()
print content
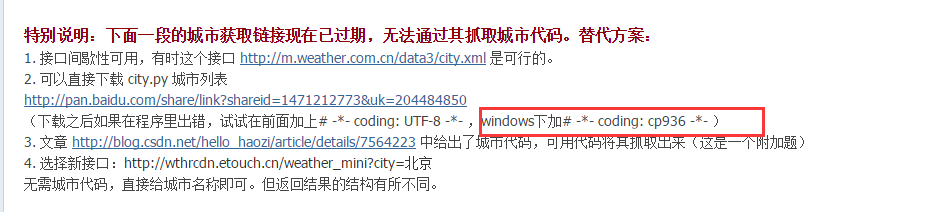
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import urllib2
import json
from city import city
cityname = raw_input('你想查哪个城市的天气?\n')
citycode = city.get(cityname)
if citycode:
url = ('http://www.weather.com.cn/data/cityinfo/%s.html' % citycode)
content = urllib2.urlopen(url).read()
print content
http://www.weather.com.cn/data/cityinfo/101280800.html

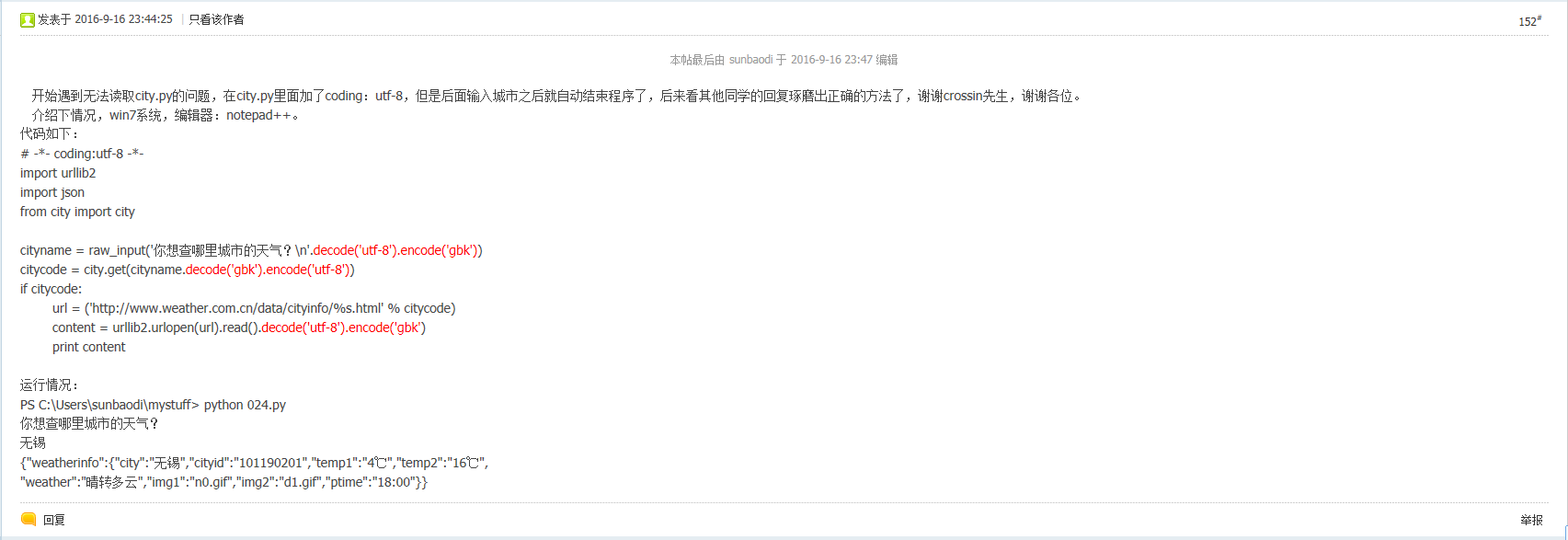
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import urllib2
import json
from city import city cityname = raw_input('你想查哪个城市的天气?\n'.decode('utf-8').encode('gbk'))
citycode = city.get(cityname.decode('gbk').encode('utf-8'))
if citycode:
url = ('http://www.weather.com.cn/data/cityinfo/%s.html'%citycode)
print url
content = urllib2.urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8').encode('gbk')
print content
查天气(3)
看一下我们已经拿到的json格式的天气数据:
{"weatherinfo":{"city":"佛山","cityid":"101280800","temp1":"14℃","temp2":"24℃","weather":"晴","img1":"n0.gif","img2":"d0.gif","ptime":"18:00"}}
{
"weatherinfo":{
"city":"佛山",
"cityid":"101280800",
"temp1":"14℃",
"temp2":"24℃",
"weather":"晴",
"img1":"n0.gif",
"img2":"d0.gif",
"ptime":"18:00"}
}
直接在命令行中看到的应该是没有换行和空格的一长串字符,这里我把格式整理了一下。可以看出,它像是一个字典的结构,但是有两层。最外层只有一个key--“weatherinfo”,它的value是另一个字典,里面包含了好几项天气信息,现在我们最关心的就是其中的temp1,temp2和weather。
虽然看上去像字典,但它对于程序来说,仍然是一个字符串,只不过是一个满足json格式的字符串。我们用python中提供的另一个模块json提供的loads方法,把它转成一个真正的字典。
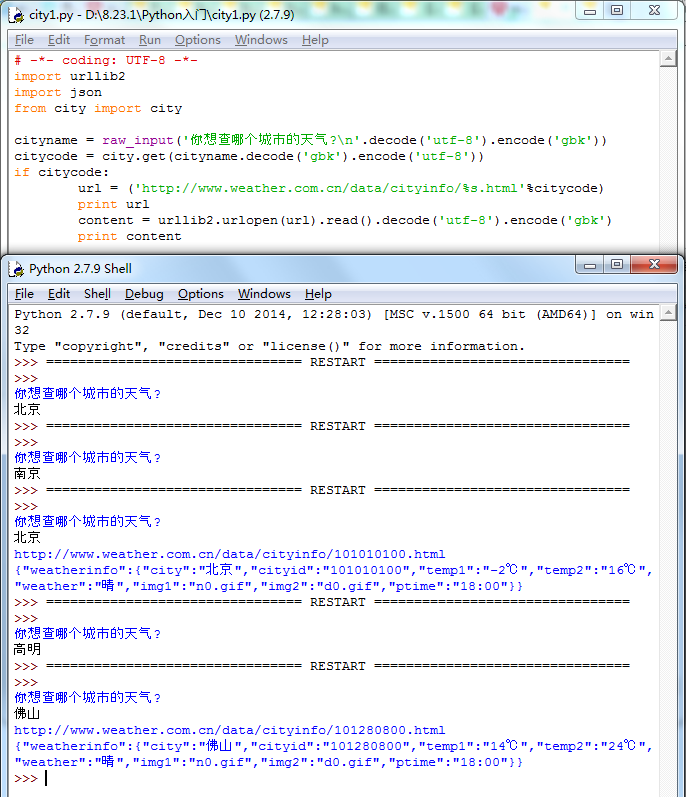
import json
data = json.loads(content)
这时候的data已经是一个字典,尽管在控制台中输出它,看上去和content没什么区别,只是编码上有些不同:
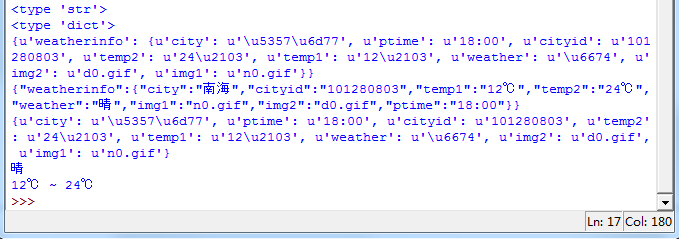
{u'weatherinfo': {u'city': u'\u4f5b\u5c71', u'ptime': u'18:00', u'cityid': u'101280800', u'temp2': u'24\u2103', u'temp1': u'14\u2103', u'weather': u'\u6674', u'img2': u'd0.gif', u'img1': u'n0.gif'}}
但如果你用type方法看一下它们的类型:
print type(content)
print type(data)
就知道区别在哪里了。
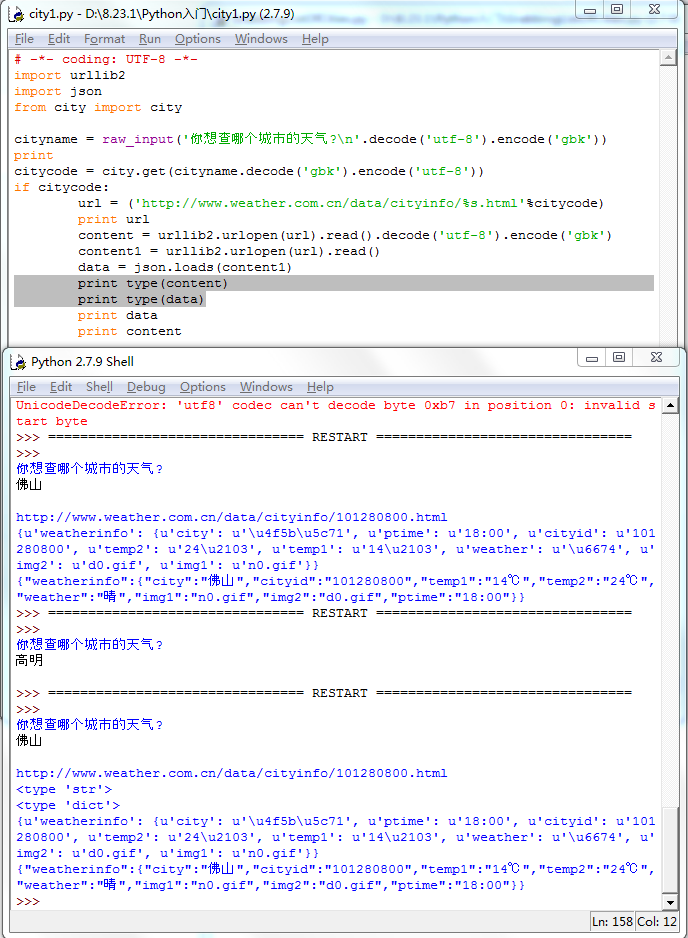
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import urllib2
import json
from city import city cityname = raw_input('你想查哪个城市的天气?\n'.decode('utf-8').encode('gbk'))
citycode = city.get(cityname.decode('gbk').encode('utf-8'))
if citycode:
url = ('http://www.weather.com.cn/data/cityinfo/%s.html'%citycode)
print url
content = urllib2.urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8').encode('gbk')
content1 = urllib2.urlopen(url).read()
data = json.loads(content1)
print type(content)
print type(data)
print data
print content
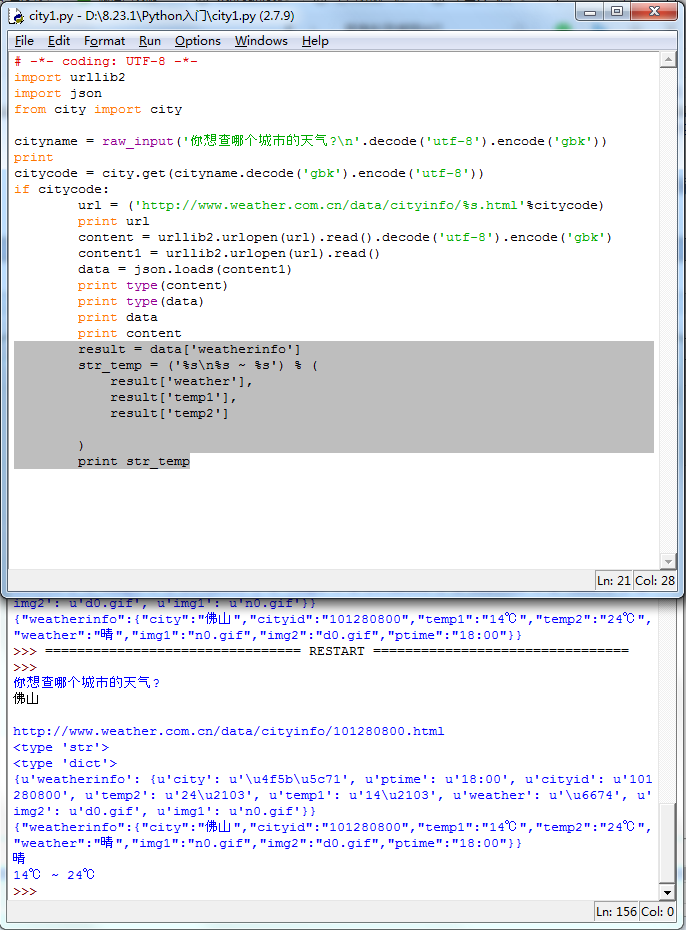
之后的事情就比较容易了。
result = data['weatherinfo']
str_temp = ('%s\n%s ~ %s') % (
result['weather'],
result['temp1'],
result['temp2'] )
print str_temp
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import urllib2
import json
from city import city cityname = raw_input('你想查哪个城市的天气?\n'.decode('utf-8').encode('gbk'))
citycode = city.get(cityname.decode('gbk').encode('utf-8'))
if citycode:
url = ('http://www.weather.com.cn/data/cityinfo/%s.html'%citycode)
print url
content = urllib2.urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8').encode('gbk')
content1 = urllib2.urlopen(url).read()
data = json.loads(content1)
print type(content)
print type(data)
print data
print content
result = data['weatherinfo']
str_temp = ('%s\n%s ~ %s') % (
result['weather'],
result['temp1'],
result['temp2'] )
print str_temp
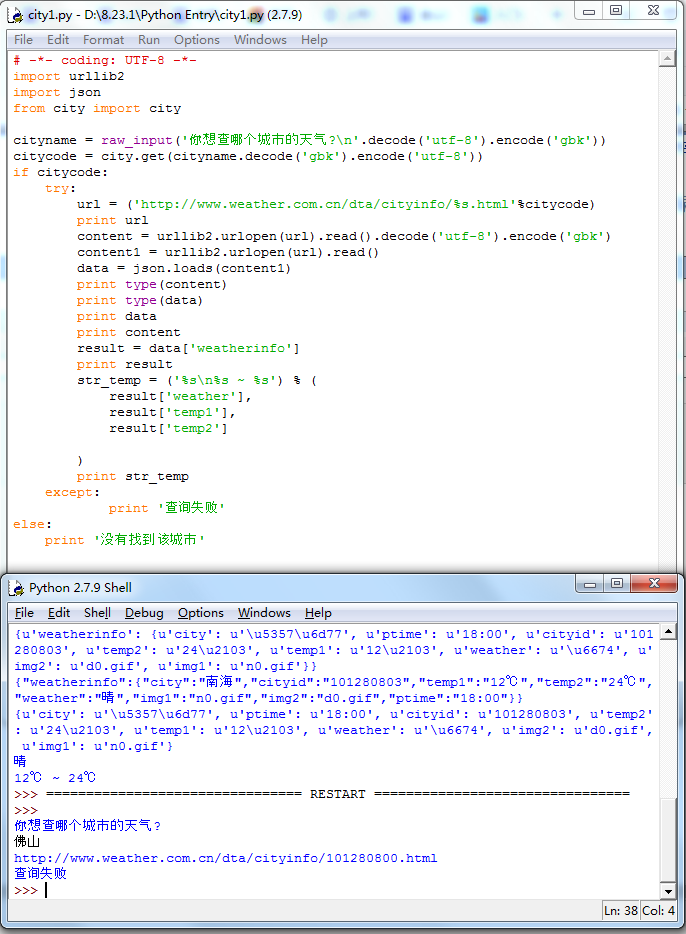
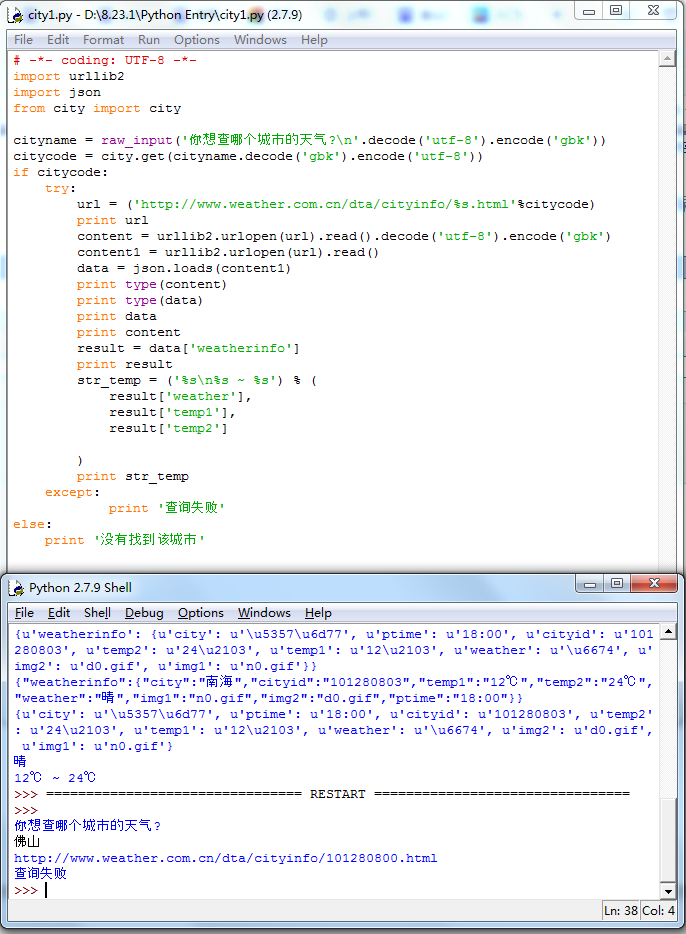
为了防止在请求过程中出错,我加上了一个异常处理。
try:
###
###
except:
print '查询失败'
以及没有找到城市时的处理:
if citycode:
###
###
else:
print '没有找到该城市'
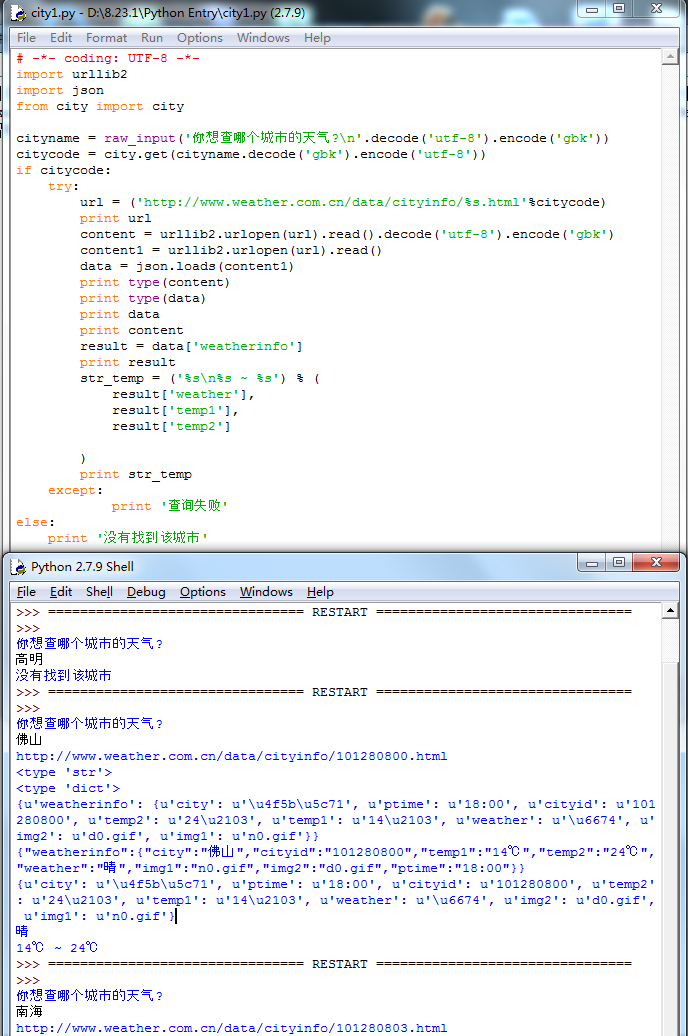
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import urllib2
import json
from city import city cityname = raw_input('你想查哪个城市的天气?\n'.decode('utf-8').encode('gbk'))
citycode = city.get(cityname.decode('gbk').encode('utf-8'))
if citycode:
try:
url = ('http://www.weather.com.cn/data/cityinfo/%s.html'%citycode)
print url
content = urllib2.urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8').encode('gbk')
content1 = urllib2.urlopen(url).read()
data = json.loads(content1)
print type(content)
print type(data)
print data
print content
result = data['weatherinfo']
print result
str_temp = ('%s\n%s ~ %s') % (
result['weather'],
result['temp1'],
result['temp2'] )
print str_temp
except:
print '查询失败'
else:
print '没有找到该城市'
查天气(4)
这一课算是“查天气”程序的附加内容。没有这一课,你也查到天气了。但了解一下城市代码的抓取过程,会对网页抓取有更深的理解。
天气网的城市代码信息结构比较复杂,所有代码按层级放在了很多xml为后缀的文件中。而这些所谓的“xml”文件又不符合xml的格式规范,导致在浏览器中无法显示,给我们的抓取又多加了一点难度。
首先,抓取省份的列表:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import urllib2 url1 = 'http://m.weather.com.cn/data3/city.xml' content1 = urllib2.urlopen(url1).read() provinces = content1.split(',') print content1
输出content1可以查看全部省份代码:
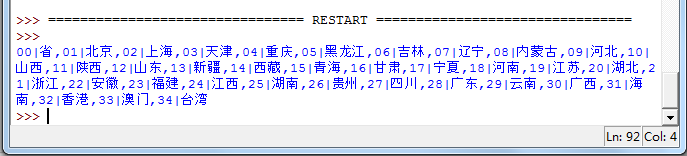
对于每个省,抓取城市列表:
url = 'http://m.weather.com.cn/data3/city%s.xml'
for p in provinces:
p_code = p.split('|')[0]
url2 = url % p_code
content2 = urllib2.urlopen(url2).read()
cities = content2.split(',')
print content2.decode('utf-8')
输出content2可以查看此省份下所有城市代码:
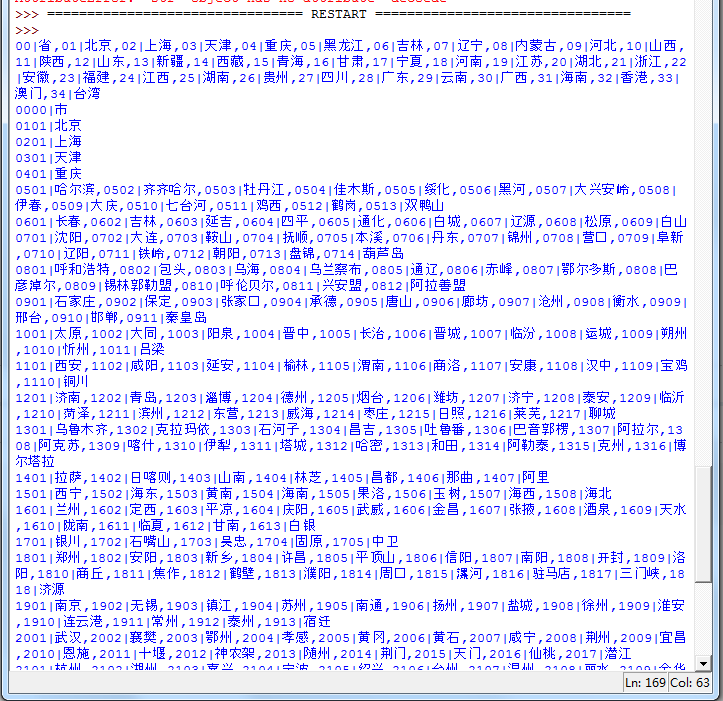
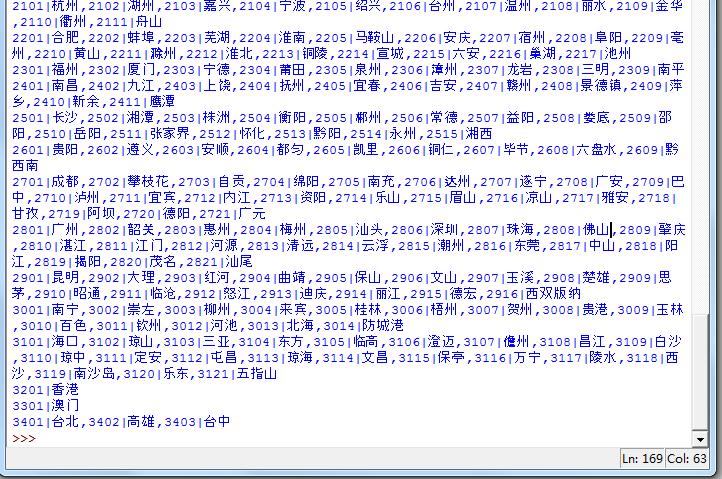
再对于每个城市,抓取地区列表:
for c in cities[:3]:
c_code = c.split('|')[0]
url3 = url % c_code
content3 = urllib2.urlopen(url3).read()
districts = content3.split(',')
print content3.decode('utf-8')
content3是此城市下所有地区代码:
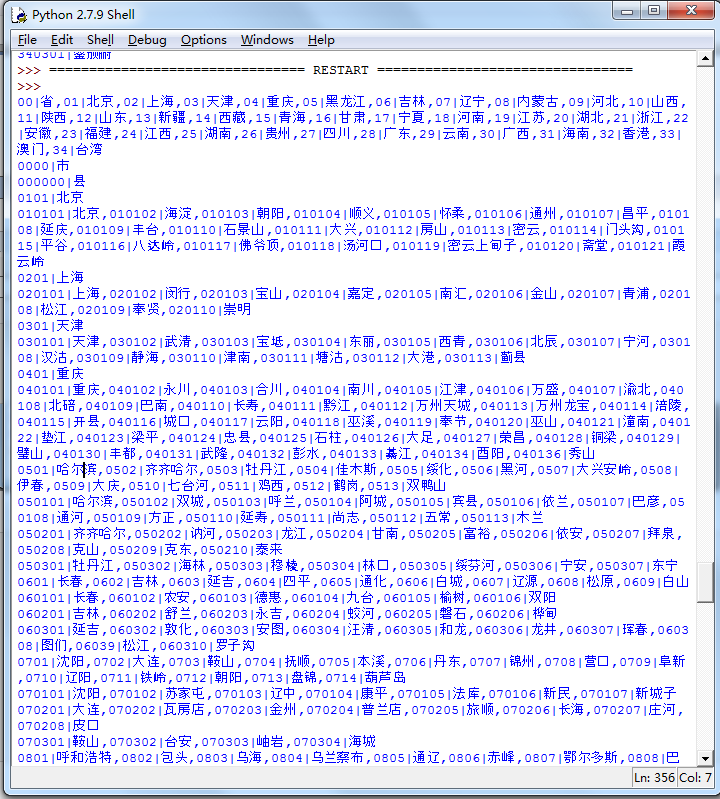

最后,对于每个地区,我们把它的名字记录下来,然后再发送一次请求,得到它的最终代码:
Python入门 来点栗子的更多相关文章
- python入门之小栗子
1 点球小游戏: from random import choice score=[0,0]direction=['left','center','right'] def kick(): print ...
- PYTHON 学习笔记1 PYTHON 入门 搭建环境与基本类型
简介 Python,当然大家听到这个名词不再是有关于像JAVA 一样的关于后台,我们学习Python 的目的在于对于以后数据分析和机器学习AI 奠定基础,Python 在数据分析这一块,可谓是有较好的 ...
- python入门简介
Python前世今生 python的创始人为吉多·范罗苏姆(Guido van Rossum).1989年的圣诞节期间,吉多·范罗苏姆为了在阿姆斯特丹打发时间,决心开发一个新的脚本解释程序,作为ABC ...
- python入门学习课程推荐
最近在学习自动化,学习过程中,越来越发现coding能力的重要性,不会coding,基本不能开展自动化测试(自动化工具只是辅助). 故:痛定思痛,先花2个星期将python基础知识学习后,再进入自动化 ...
- Python运算符,python入门到精通[五]
运算符用于执行程序代码运算,会针对一个以上操作数项目来进行运算.例如:2+3,其操作数是2和3,而运算符则是“+”.在计算器语言中运算符大致可以分为5种类型:算术运算符.连接运算符.关系运算符.赋值运 ...
- Python基本语法[二],python入门到精通[四]
在上一篇博客Python基本语法,python入门到精通[二]已经为大家简单介绍了一下python的基本语法,上一篇博客的基本语法只是一个预览版的,目的是让大家对python的基本语法有个大概的了解. ...
- Python基本语法,python入门到精通[二]
在上一篇博客Windows搭建python开发环境,python入门到精通[一]我们已经在自己的windows电脑上搭建好了python的开发环境,这篇博客呢我就开始学习一下Python的基本语法.现 ...
- visual studio 2015 搭建python开发环境,python入门到精通[三]
在上一篇博客Windows搭建python开发环境,python入门到精通[一]很多园友提到希望使用visual studio 2013/visual studio 2015 python做demo, ...
- python入门教程链接
python安装 选择 2.7及以上版本 linux: 一般都自带 windows: https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/ mac os: https:/ ...
随机推荐
- UIResponder详解
UIResponder Class Reference Managing the Responder Chain 1.- (UIResponder *)nextResponder 返回接收者的下一个相 ...
- Win10电脑如何更改开机启动项
https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/5970355284f0458fc1074049.html
- Weex框架源码分析(Android)(一)
一.weexSDK初始化流程 WXSDKEngine.initialize(Application application,InitConfig config); //WXSDKEngine的init ...
- Error from server at http://127.0.0.1:8983/solr/xxx: undefined field type
undefined field type就是说没有定义type类型,这样情况下,可以新建一个带type的索引,比如:{type:1, id:1, name:"张三"}
- iview Table表格单选框互斥
表格中添加单选框,并且互斥 首先带data中定义 currentid : 0 :表示默认不选中 { title: "名称", key: "name", re ...
- 18清明校内测试T1
消失的数字(number) Time Limit:1000ms Memory Limit:128MB 题目描述 rsy拥有n个数,这n个数分别是a1,a2,…,an. 后来出现了一个熊孩子zhw, ...
- Excel 绘制正态概率图-正态性检验
- python爬虫17 | 听说你又被封 ip 了,你要学会伪装好自己,这次说说伪装你的头部
这两天 有小伙伴问小帅b 为什么我爬取 xx 网站的时候 不返回给我数据 而且还甩一句话给我 “系统检测到您频繁访问,请稍后再来” 小帅b看了一下他的代码 ): requests.get(url) 瞬 ...
- 第一节:web爬虫之requests
Requests库是用Python编写的,并且Requests是一个优雅而简单的Python HTTP库,在使用Requests库时更加方便,可以节约我们大量的工作,完全满足HTTP测试需求.
- vue 根据网站路由判断页面主题色
需求: 不同品牌对应不同版本配色 做法: 根据域名带的参数判断进入哪个品牌,对应哪个版本 在main.js中 import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' ...
