安卓app开发-05-Android xml布局详细介绍
安卓app开发-05-Android xml布局详细介绍
- 虽然说有 墨刀,墨客 这些图形化开发工具来做 Android 的界面设计,但是我们还是离不开要去学习做安卓原生app,学习 xml 布局还是必要的
(1)准备
- 首先我们要了解 android 到底有那些布局,和每个布局类型的区别
- 学习时最好打开 Android Studio 打开 xml 文件对应看一下
- 配置参数的详细含义不用着急全部理解,放在文章后面,可收藏做查阅【可通过目录跳转】
(2)学习目标
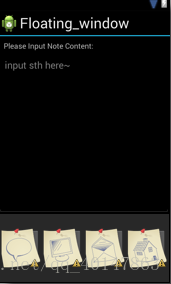
- 学习下xml的布局文件具体写法。这一节我们要绘制如下图所示的界面
(3)线性布局 LinearLayout
- 线性布局分两种。一种是水平布局,一种是垂直布局。下面我们根据上图举例子
- 上图代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/note_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:padding="10dp"></TextView>
<LinearLayout android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1">
<EditText android:id="@+id/EditText02" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:gravity="left"
android:hint="@string/edithint"></EditText>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="2"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ImageButton android:id="@+id/ImageButton01" android:layout_width="72dp" android:layout_height="72dp" android:src="@drawable/sketchy_paper_003" android:layout_margin="3dp"></ImageButton> <ImageButton android:id="@+id/ImageButton02" android:layout_width="72dp" android:layout_height="72dp" android:src="@drawable/sketchy_paper_004" android:layout_margin="3dp"></ImageButton> <ImageButton android:id="@+id/ImageButton03" android:layout_width="72dp" android:layout_height="72dp" android:src="@drawable/sketchy_paper_007" android:layout_margin="3dp"></ImageButton> <ImageButton android:id="@+id/ImageButton04" android:layout_width="72dp" android:layout_height="72dp" android:src="@drawable/sketchy_paper_011" android:layout_margin="3dp"></ImageButton> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
- 可以看到,上图是由三部分组成。在大的LinearLayout从上而下垂直分布着三个内容:TextView,LinearLayout,LinearLayout。所以总体的 LinearLayout 是垂直布局
- 下面我们来看水平布局
- 其实就是上图中的最下面那个 LinearLayout。四个图标平行排列。
android:orientation="horizontal"
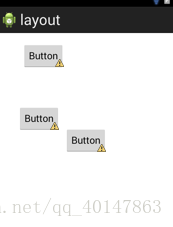
(4)相对布局 RelativeLayout
- 这个布局相对简单一点。一般来讲利用ADT自己拖放按钮就可以。基本上可以随意布局。如下图所示
- 上图代码:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/button1"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/button1"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_marginRight="14dp"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/button1"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="97dp"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button1"
android:layout_below="@+id/button3"
android:layout_marginTop="89dp"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignTop="@+id/button4"
android:text="Button" />
</RelativeLayout>
- layout_marginBottom是指控件边以外空下的距离,比如Button1和Button2垂直显示,将Button1中layout_marginBottom = 10dp,那么Button1与Button2之间将有10dp距离
- 下面这两句是居左显示和居右显示
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true" - 【提示】:相对视图应该是最有用的,具体的操作比较复杂,更多的是通过图形界面拖拉,再用代码微调
(5)帧布局 FrameLayout
- 这个布局很简单,而且感觉有点二二的,哈哈!就是控件一个挨一个在左上角罗列
- 上图代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="126dp"
android:layout_height="135dp"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="194dp"
android:layout_height="232dp"
android:text="Button" />
</FrameLayout>
(6)绝对布局 AbsoluteLayout
- 绝对布局比较容易使用,就是以左上方为原点建立坐标系。每个控件用layout_x和layout_y表示位置。但是据说这种布局比较刚性,不容易适配各种终端,所以要慎用!
- 上图代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="44dp"
android:layout_y="18dp"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="122dp"
android:layout_y="173dp"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="36dp"
android:layout_y="133dp"
android:text="Button" />
</AbsoluteLayout>
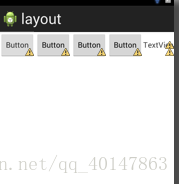
(7)表格布局 TableLayout
- TableLayout有点像一个表格或是矩阵。在布局中加入TableRow,它的属性是horizontal所以每个TableRow只能横放。它里面的每个控件的高都是一样的。下图所示,是加入了一个TableRow和里面的控件
- 上图代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
xml 配置参数大全
第一类:属性值为true或false
android:layout_centerHrizontal 水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical 垂直居中
android:layout_centerInparent 相对于父元素完全居中
android:layout_alignParentBottom 贴紧父元素的下边缘
android:layout_alignParentLeft 贴紧父元素的左边缘
android:layout_alignParentRight 贴紧父元素的右边缘
android:layout_alignParentTop 贴紧父元素的上边缘
android:layout_alignWithParentIfMissing 如果对应的兄弟元素找不到的话就以父元素做参照物第二类:属性值必须为id的引用名
android:layout_below 在某元素的下方
android:layout_above 在某元素的的上方
android:layout_toLeftOf 在某元素的左边
android:layout_toRightOf 在某元素的右边
android:layout_alignTop 本元素的上边缘和某元素的的上边缘对齐
android:layout_alignLeft 本元素的左边缘和某元素的的左边缘对齐
android:layout_alignBottom 本元素的下边缘和某元素的的下边缘对齐
android:layout_alignRight 本元素的右边缘和某元素的的右边缘对齐第三类:属性值为具体的像素值,如30dip,40px
android:layout_marginBottom 离某元素底边缘的距离
android:layout_marginLeft 离某元素左边缘的距离
android:layout_marginRight 离某元素右边缘的距离
android:layout_marginTop 离某元素上边缘的距离
EditText的android:hint 设置EditText为空时输入框内的提示信息。
android:gravity
android:gravity属性是对该view 内容的限定.比如一个button 上面的text. 你可以设置该text 在view的靠左,靠右等位置.以button为例,android:gravity="right"则button上面的文字靠右
android:layout_gravity
android:layout_gravity是用来设置该view相对与起父view 的位置.比如一个button 在linearlayout里,你想把该button放在靠左、靠右等位置就可以通过该属性设置.以button为例,android:layout_gravity="right"则button靠右
android:scaleType:
android:scaleType是控制图片如何resized/moved来匹对ImageView的size。ImageView.ScaleType / android:scaleType值的意义区别:
CENTER /center 按图片的原来size居中显示,当图片长/宽超过View的长/宽,则截取图片的居中部分显示
CENTER_CROP / centerCrop 按比例扩大图片的size居中显示,使得图片长(宽)等于或大于View的长(宽)
CENTER_INSIDE / centerInside 将图片的内容完整居中显示,通过按比例缩小或原来的size使得图片长/宽等于或小于View的长/宽
FIT_CENTER / fitCenter 把图片按比例扩大/缩小到View的宽度,居中显示
FIT_END / fitEnd 把图片按比例扩大/缩小到View的宽度,显示在View的下部分位置
FIT_START / fitStart 把图片按比例扩大/缩小到View的宽度,显示在View的上部分位置
FIT_XY / fitXY 把图片不按比例扩大/缩小到View的大小显示
MATRIX / matrix 用矩阵来绘制,动态缩小放大图片来显示。
** 要注意一点,Drawable文件夹里面的图片命名是不能大写的。
android:id 为控件指定相应的ID
android:text 指定控件当中显示的文字,需要注意的是,这里尽量使用strings.xml文件当中的字符串
android:gravity 指定View组件的对齐方式,比如说居中,居右等位置 这里指的是控件中的文本位置并不是控件本身
android:layout_gravity 指定Container组件的对齐方式.比如一个button 在linearlayout里,你想把该button放在靠左、靠右等位置就可以通过该属性设置.以button为 例,android:layout_gravity="right"则button靠右
android:textSize 指定控件当中字体的大小
android:background 指定该控件所使用的背景色,RGB命名法
android:width 指定控件的宽度
android:height 指定控件的高度
android:layout_width 指定Container组件的宽度
android:layout_height 指定Container组件的高度
android:layout_weight View中很重要的属性,按比例划分空间
android:padding* 指定控件的内边距,也就是说控件当中的内容
android:sigleLine 如果设置为真的话,则控件的内容在同一行中进行显示
android:scaleType 是控制图片如何resized/moved来匹对ImageView的siz
android:layout_centerHrizontal 水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical 垂直居中
android:layout_centerInparent 相对于父元素完全居中
android:layout_alignParentBottom 贴紧父元素的下边缘
android:layout_alignParentLeft 贴紧父元素的左边缘
android:layout_alignParentRight 贴紧父元素的右边缘
android:layout_alignParentTop 贴紧父元素的上边缘
android:layout_alignWithParentIfMissing 如果对应的兄弟元素找不到的话就以父元素做参照物
android:layout_below 在某元素的下方
android:layout_above 在某元素的的上方
android:layout_toLeftOf 在某元素的左边
android:layout_toRightOf 在某元素的右边
android:layout_alignTop 本元素的上边缘和某元素的的上边缘对齐
android:layout_alignLeft 本元素的左边缘和某元素的的左边缘对齐
android:layout_alignBottom 本元素的下边缘和某元素的的下边缘对齐
android:layout_alignRight 本元素的右边缘和某元素的的右边缘对齐
android:layout_marginBottom 离某元素底边缘的距离
android:layout_marginLeft 离某元素左边缘的距离
android:layout_marginRight 离某元素右边缘的距离
android:layout_marginTop 离某元素上边缘的距离
android:paddingLeft 本元素内容离本元素右边缘的距离
android:paddingRight 本元素内容离本元素上边缘的距离
android:hint 设置EditText为空时输入框内的提示信息
android:LinearLayout 它确定了LinearLayout的方向,其值可以为vertical,表示垂直布局horizontal, 表示水平布局
android:interpolator
可能有很多人不理解它的用法,文档里说的也不太清楚,其实很简单,看下面:interpolator定义一个动画的变化率(the rate of change)。这使得基本的动画效果(alpha, scale, translate, rotate)得以加速,减速,重复等。用通俗的一点的话理解就是:动画的进度使用 Interpolator 控制。interpolator 定义了动画的变化速度,可以实现匀速、正加速、负加速、无规则变加速等。Interpolator 是基类,封装了所有 Interpolator 的共同方法,它只有一个方法,即 getInterpolation (float input),该方法 maps a point on the timeline to a multiplier to be applied to the transformations of an animation。Android 提供了几个 Interpolator 子类,实现了不同的速度曲线,如下:
AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator 在动画开始与介绍的地方速率改变比较慢,在中间的时侯加速
AccelerateInterpolator 在动画开始的地方速率改变比较慢,然后开始加速
CycleInterpolator 动画循环播放特定的次数,速率改变沿着正弦曲线
DecelerateInterpolator 在动画开始的地方速率改变比较慢,然后开始减速
LinearInterpolator 在动画的以均匀的速率改变
对于 LinearInterpolator ,变化率是个常数,即 f (x) = x.
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
return input;
}
Interpolator其他的几个子类,也都是按照特定的算法,实现了对变化率。还可以定义自己的 Interpolator 子类,实现抛物线、自由落体等物理效果
更多文章链接:安卓app开发
- 本笔记不允许任何个人和组织转载
安卓app开发-05-Android xml布局详细介绍的更多相关文章
- 安卓app开发-03-项目的基本开发步骤
android项目的基本开发步骤 这里分享一下开发 安卓 app 的流程,当然有些感觉不必要,其实不然,前期工作也是极为重要的额,就像开发的时候如果目标不对的话,到后期后很迷的,所以一定要提前做好规划 ...
- 安卓app开发-01-开发工具及环境配置
安卓app开发-01-开发工具及环境配置 请大家根据推荐指数和自己的意愿选择 使用 Android Studio 1.可以使用 Android Studio 下载地址:http://www.andro ...
- 安卓app开发-02-安卓app快速开发
安卓app开发-02-安卓app快速开发 上一篇介绍了安卓 app 开发的工具和环境配置,本篇不涉及编程技术,适合小团队快速高效开发 APP制作流程 当有一个APP创意,该如何实现呢?是花数十万找AP ...
- 学习笔记:APP切图那点事儿–详细介绍android和ios平台
学习笔记:APP切图那点事儿–详细介绍android和ios平台 转载自:http://www.woofeng.cn/articles/168.html 版权归原作者所有 作者:亚茹有李 原文地址 ...
- android xml布局文件属性说明
android xml布局文件属性说明 [摘]android xml布局文件属性说明 LinearLayout和RelativeLayout 共有属性:java代码中通过btn1关联次控件androi ...
- Android SQLite 数据库详细介绍
Android SQLite 数据库详细介绍 我们在编写数据库应用软件时,需要考虑这样的问题:因为我们开发的软件可能会安装在很多用户的手机上,如果应用使用到了SQLite数据库,我们必须在用户初次使用 ...
- 【软件配置】JDK+AndroidStudio4.1开发安卓APP环境安装和配置教程详细
目录 一.专业名词 二.搭建前资源准备 2.1 JDK资源下载 2.2 AndroidStudio下载 三.安装 3.1 JDK安装配置 3.2 AndroidStudio安装 四.创建安卓APP工程 ...
- 安卓APP开发的初步了解
今天成功安装了Android Studio 并且对APP的开发框架结构进行了初步了解 如上图:app基本结构情况 下面来仔细解释一下各个方面目录的作用 首先 manifests目录:包含Android ...
- 当前主流的安卓APP开发IDE
什么是主流的开发安卓APP的方式? 我是去年4月份接触的Android开发,因此特别有感触,可以明显的感受到安卓APP主流开发方式的改变. 去年,2015年年初,各大安卓开发群大部分大牛在用Eclip ...
随机推荐
- Compile android source and kernel for emulator in Debian
1.download the android source code Reference from http://source.android.com/source/downloading.html ...
- JavaScript设计模式-1.函数
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title> ...
- django显示SQL语句
django显示SQL语句 有时候我们使用模型查询数据,但是并不知道具体执行的SQL语句到底对不对.那么可以通过下面的方法打印出具体执行的SQL语句.这样有助于调试: queryset = MyMod ...
- Java PrepareStatement
1.PreparedStatement是预编译的,对于批量处理可以大大提高效率. 也叫JDBC存储过程2.使用 Statement 对象.在对数据库只执行一次性存取的时侯,用 Statement 对象 ...
- Comet:基于 HTTP 长连接的“服务器推”技术(转载)
“服务器推”技术的应用 传统模式的 Web 系统以客户端发出请求.服务器端响应的方式工作.这种方式并不能满足很多现实应用的需求,譬如: 监控系统:后台硬件热插拔.LED.温度.电压发生变化: 即时通信 ...
- PTA (Advanced Level) 1010 Radix
Radix Given a pair of positive integers, for example, 6 and 110, can this equation 6 = 110 be true? ...
- vue.js 开发环境搭建
1.安装node.js(http://www.runoob.com/nodejs/nodejs-install-setup.html) 2.基于node.js,利用淘宝npm镜像安装相关依赖 在cmd ...
- 【TCP协议】MTU和MSS详解
需要注意的是,区别两种帧封装格式:802标准帧和以太网帧 1,在802标准定义的帧格式中,长度字段是指它后续数据的字节长度,但不包括C R C检验码.RFC 1042(IEEE 802) 2,RFC ...
- WCF-netTcpBinding端口共享
在同一台机器上一个端口在某时刻只能被一个应用程序占用.对于WCF服务来说,如果服务器上有多个服务并且这些服务寄宿在不同的应用程序中,我们需要某种途径来共享它们的端口.下面是一个示例来演示使用TcpBi ...
- guava快速入门(二)
Guava工程包含了若干被Google的 Java项目广泛依赖 的核心库,例如:集合 [collections] .缓存 [caching] .原生类型支持 [primitives support] ...