PTA Deque (C语言)
A "deque" is a data structure consisting of a list of items, on which the following operations are possible:
- Push(X,D): Insert item X on the front end of deque D.
- Pop(D): Remove the front item from deque D and return it.
- Inject(X,D): Insert item X on the rear end of deque D.
- Eject(D): Remove the rear item from deque D and return it. Write routines to support the deque that take O(1) time per operation.
Format of functions:
Deque CreateDeque();
int Push( ElementType X, Deque D );
ElementType Pop( Deque D );
int Inject( ElementType X, Deque D );
ElementType Eject( Deque D );
where Deque is defined as the following:
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node {
ElementType Element;
PtrToNode Next, Last;
};
typedef struct DequeRecord *Deque;
struct DequeRecord {
PtrToNode Front, Rear;
};
Here the deque is implemented by a doubly linked list with a header. Front and Rear point to the two ends of the deque respectively. Front always points to the header. The deque is empty when Front and Rear both point to the same dummy header. Note: Push and Inject are supposed to return 1 if the operations can be done successfully, or 0 if fail. If the deque is empty, Pop and Eject must return ERROR which is defined by the judge program.
Sample program of judge:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #define ElementType int
#define ERROR 1e5
typedef enum { push, pop, inject, eject, end } Operation; typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node {
ElementType Element;
PtrToNode Next, Last;
};
typedef struct DequeRecord *Deque;
struct DequeRecord {
PtrToNode Front, Rear;
};
Deque CreateDeque();
int Push( ElementType X, Deque D );
ElementType Pop( Deque D );
int Inject( ElementType X, Deque D );
ElementType Eject( Deque D ); Operation GetOp(); /* details omitted */
void PrintDeque( Deque D ); /* details omitted */ int main()
{
ElementType X;
Deque D;
int done = ; D = CreateDeque();
while (!done) {
switch(GetOp()) {
case push:
scanf("%d", &X);
if (!Push(X, D)) printf("Memory is Full!\n");
break;
case pop:
X = Pop(D);
if ( X==ERROR ) printf("Deque is Empty!\n");
break;
case inject:
scanf("%d", &X);
if (!Inject(X, D)) printf("Memory is Full!\n");
break;
case eject:
X = Eject(D);
if ( X==ERROR ) printf("Deque is Empty!\n");
break;
case end:
PrintDeque(D);
done = ;
break;
}
}
return ;
} /* Your function will be put here */
Sample Input:
Pop
Inject
Pop
Eject
Push
Push
Eject
Inject
End
Sample Output:
Deque is Empty!
Deque is Empty!
Inside Deque:
题意:这道题要求设计一个链式双端队列 deque,并且要求有头指针。
初始时,链表为空,头指针 Front 和尾指针 Rear 指向同一片空的空间,

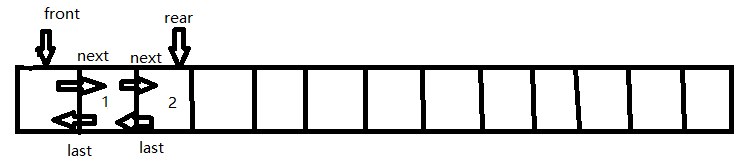
Push :将项 X 插入双端队列 D 的前端。下图为 Push(2) Push(1) 操作结果
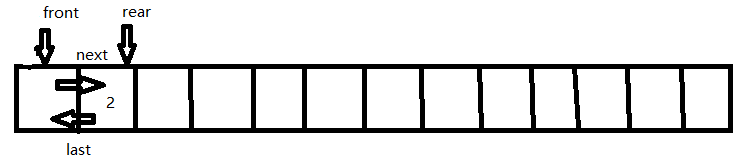
Pop:从双端队列 D 中删除前端一项并返回。下图为 Pop() 操作结果
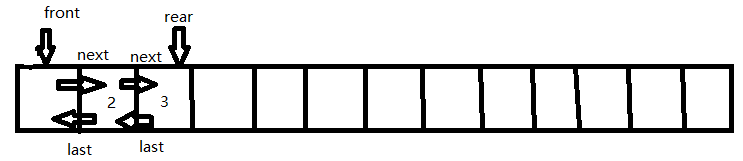
Inject:将项目 X 插入双端队列 D 的后端。下图为 Inject(3) 操作结果
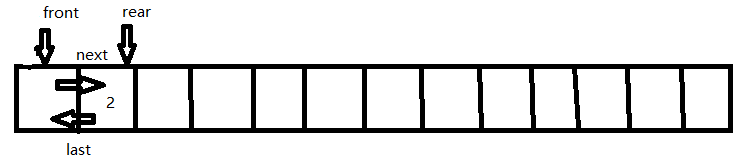
Eject:从双端队列 D 中删除后端一项并返回。下图为Eject() 操作结果
若 Push 和 Inject操作成功,返回1,否则返回0;若双端队列为空,Pop 和 Eject 返回 ERROR,否则返回弹出结点的 Element。
代码:
Deque CreateDeque() {
PtrToNode temnode = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temnode->Next = temnode->Last = NULL;
Deque D = (Deque)malloc(sizeof(struct DequeRecord));
D->Front = D->Rear = temnode;
return D;
}
int Push(ElementType X, Deque D) {
PtrToNode temnode= (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temnode->Element = X;
temnode->Next = temnode->Last = NULL;
if (D->Front == D->Rear)
D->Rear = temnode;
else {
temnode->Next = D->Front->Next;
D->Front->Next->Last = temnode;
}
D->Front->Next = temnode;
temnode->Last = D->Front;
return ;
}
ElementType Pop(Deque D) {
if (D->Front == D->Rear)
return ERROR;
PtrToNode delnode = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
delnode = D->Front->Next;
if (delnode->Next == NULL)
D->Rear = D->Front;
else{
delnode->Next->Last = D->Front;
D->Front->Next = delnode->Next;
}
return delnode->Element;
free(delnode);
}
int Inject(ElementType X, Deque D) {
PtrToNode temnode = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temnode->Element = X;
temnode->Next = temnode->Last = NULL;
if (D->Front == D->Rear) {
D->Front->Next = temnode;
temnode->Last = D->Front;
}
else {
D->Rear->Next = temnode;
temnode->Last = D->Rear;
}
D->Rear = temnode;
return ;
}
ElementType Eject(Deque D) {
if (D->Front == D->Rear)
return ERROR;
PtrToNode delnode = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
delnode = D->Rear;
if (delnode->Last == D->Front)
D->Rear = D->Front;
else
D->Rear = delnode->Last;
return delnode->Element;
free(delnode);
}
PTA Deque (C语言)的更多相关文章
- 小白专场-FileTransfer-c语言实现
目录 一.集合的简化表示 二.题意理解 三.程序框架搭建 3.1 Input_connection 3.2 Check_connection 3.3 Check_network 四.pta测试 五.按 ...
- C语言Ⅰ博客作业07
这个作业属于那个课程 C语言程序设计II 这个作业要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/CST2019-3/homework/9933 我在这个课程的目 ...
- C语言Ⅰ博客作业05
这个作业属于那个课程 C语言程序设计II 这个作业要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/CST2019-3/homework/9827 我在这个课程的目 ...
- 第二周c语言PTA作业留
6-1 计算两数的和与差(10 分) 本题要求实现一个计算输入的两数的和与差的简单函数. 函数接口定义: void sum_diff( float op1, float op2, float psum ...
- C语言第一次实验报告————PTA实验1.2.3内容
一.PTA实验作业 题目1.温度转换 本题要求编写程序,计算华氏温度100°F对应的摄氏温度.计算公式:C=5×(F−32)/9,式中:C表示摄氏温度,F表示华氏温度,输出数据要求为整型. 1.实验代 ...
- c语言课本及pta作业中运用到的程序思维
c语言课本运用到的程序思维 我个人觉得在写程序的时候,有很多题目会用到我们学过的解决一个程序或者一个问题的方法,把这些方法运用起来,将会使自己更加灵活地解决诸多问题,为今后打下良好地基础. (因为还没 ...
- PTA 汉诺塔的非递归实现(C 语言)
借助堆栈以非递归(循环)方式求解汉诺塔的问题(n, a, b, c), 即将N个盘子从起始柱(标记为“a”)通过借助柱(标记为“b”)移动到目标柱(标记为“c”), 并保证每个移动符合汉诺塔问题的要求 ...
- PTA 学生成绩链表处理(C语言)
本题要求实现两个函数,一个将输入的学生成绩组织成单向链表:另一个将成绩低于某分数线的学生结点从链表中删除. 函数接口定义: struct stud_node *createlist(); struct ...
- PTA 简单计算器(C语言)
模拟简单运算器的工作.假设计算器只能进行加减乘除运算,运算数和结果都是整数,四种运算符的优先级相同,按从左到右的顺序计算. 输入格式:输入在一行中给出一个四则运算算式,没有空格,且至少有一个操作数.遇 ...
随机推荐
- OpenCV3入门(四)图像的基础操作
1.访问图像像素 1)灰度图像 2)彩色图像 OpenCV中的颜色顺序是BGR而不是RGB. 访问图像的像素在OpenCV中就是访问Mat矩阵,常用的有三种方法. at定位符访问 Mat数据结构,操作 ...
- myeclipse 项目引入 com.sun.image.codec.jpeg 的api报错解决方法
今天在做压缩图片的功能的时候发现JDK自带的jar找不到的问题,网上找到一个方法,实测可行,这边记录下: 在Eclipse中处理图片,需要引入两个包: import com.sun.image.c ...
- 如何查看dll或者exe是X86还是X64架构
使用VS里面的dumpbin.exe 用法:dumpbin /headers *.exe(需要运行vcvarsall.bat) C32 or Winhex PE L为x86.PE d†为x64 P ...
- Java入门基础(变量、操作符与表达式)
Java入门基础 1. 第一个程序 2.变量(命名.运算.整数/小数/字符串.布尔类型) 3.操作符与表达式(算术/逻辑/关系/赋值/自增/类型转换操作符) HelloWorld! public cl ...
- 机器学习总结-bias–variance tradeoff
bias–variance tradeoff 通过机器学习,我们可以从历史数据学到一个\(f\),使得对新的数据\(x\),可以利用学到的\(f\)得到输出值\(f(x)\).设我们不知道的真实的\( ...
- Codeforces_739_B
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/739/B dfs,记录距离前缀和,每次找到离最近的不符合的点. #include<iostream> # ...
- 《N诺机试指南》(二)C++自带实用函数
1.排序sort函数: 2.查找: 实例: 3. 队列:
- java5循环结构一
public class jh_01_循环学习需要用到的知识点 { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 1;// 把数值1赋值给int类型 ...
- Go语言实现:【剑指offer】表示数值的字符串
该题目来源于牛客网<剑指offer>专题. 请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数).例如,字符串"+100","5e2",&qu ...
- Linux系统基础认知
什么是操作系统? 操作系统作为接口的示意图: 没有安装操作系统的计算机,通常被称为裸机 如果想在 裸机 上运行自己所编写的程序,就必须用机器语言书写程序 如果计算机上安装了操作系统,就可以在操作系统上 ...
