[ Python ] 基本数据类型及属性(下篇)
1. 基本数据类型
(1) list 列表
(2) tuple 元组
(3) dict 字典
(4) set 集合
2. list 列表方法
Python 内置的一种数据类型,list是一种有序的集合,可以随时添加删除其中的元素。
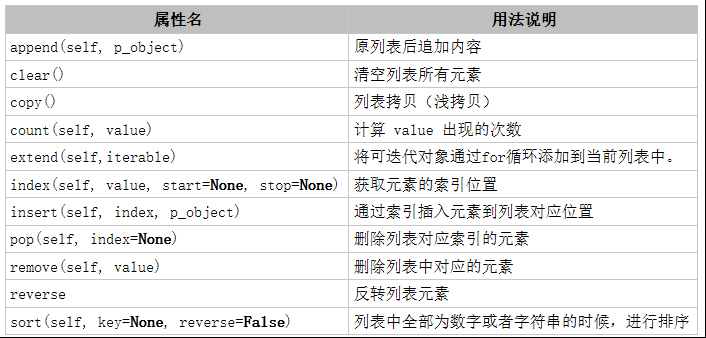
( 1 ) append(self, p_object)
原列表后追加内容
list1 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
list1.append('good')
print(list1) # 执行结果:
# ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3, 'good']
(2)clear()
清空列表所有元素
list1 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
list1.clear()
print(list1) # 执行结果:
# []
(3)copy()
列表拷贝(浅拷贝)
list1 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
list2 = list1.copy()
print(list2) # 执行结果:
# ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
(4)count(self, value)
计算 value 出现的次数
list1 = ['hkey', 'b', 'c', 'hkey', 1, 2, 3]
print(list1.count('hkey')) # 执行结果:
# 2
(5)extend(self,iterable)
将可迭代对象通过for循环添加到当前列表中。
iterable:可迭代对象,能用于 for 循环的数据都是可迭代对象
list1 = ['hkey', 'b', 'c', 'hkey', 1, 2, 3]
list2 = ['hello', 'world'] list1.extend(list2)
print(list1) # 执行结果:
# ['hkey', 'b', 'c', 'hkey', 1, 2, 3, 'hello', 'world']
extend 和 append 进行比较:
extend是通过 for 循环把可迭代对象,一个一个append添加到当前列表的
append是将元素一次性的全部追加到元素末尾
(6)index(self, value, start=None, stop=None)
获取元素的索引位置
list1 = ['hkey', 'b', 'c', 'hkey', 1, 2, 3]
print(list1.index('hkey'))
# 从左到右查找元素,第一个出现的位置
# 执行结果:
# 0
(7)insert(self, index, p_object)
通过索引插入元素到列表对应位置
list1 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3] list1.insert(1, 'hello')
print(list1) # 执行结果:
# ['a', 'hello', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
(8)pop(self, index=None)
删除列表对应索引的元素
list1 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
list1.pop(2)
print(list1) # 执行结果:
# ['a', 'b', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
(9)remove(self, value)
删除列表中对应的元素
list1 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
list1.remove('c')
print(list1) # 执行结果:
# ['a', 'b', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
(10)reverse
反转列表元素
list1 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3]
list1.reverse()
print(list1) # 执行结果:
# [3, 2, 1, 'd', 'c', 'b', 'a']
(11)sort(self, key=None, reverse=False)
列表中全部为数字或者字符串的时候,进行排序
list1 = [1, 3, 2]
list2 = ['d', 'z', 'a']
list1.sort()
list2.sort()
print('list1:', list1)
print('list2:', list2) # 执行结果:
# list1: [1, 2, 3]
# list2: ['a', 'd', 'z']
3. tuple(元组)
元组也是有序序列,但是tuple一旦初始化就不能修改。
元组示例:(1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c'),元组只有 2 个方法
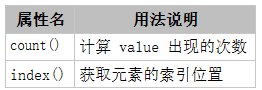
(1)count
计算 value 出现的次数
list1 = ('a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3, 'd')
list2 = list1.count('d')
print(list2)
# 执行结果:
# 2
(2)index
获取元素的索引位置
list1 = ('a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 1, 2, 3, 'd')
print(list1.index('c'))
# 执行结果:
# 2
4. dict 字典
Python 内置字典类型,使用 键 - 值(key-value)存储,具有极快的查找速度。
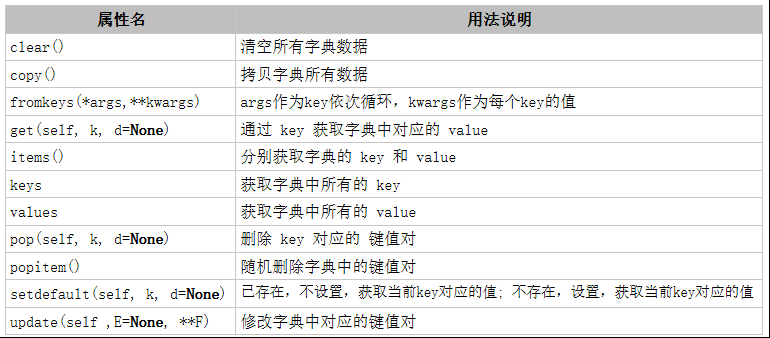
(1)clear()
清空所有字典数据
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
dict1.clear()
print(dict1)
# 执行结果:
# {}
(2)copy()
拷贝字典所有数据
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
dict2 = dict1.copy()
print(dict2)
# 执行结果:
# {'age': 20, 'gender': '男', 'name': 'hkey'}
(3)fromkeys(*args,**kwargs)
args作为key依次循环,kwargs作为每个key的值
fromkeys 是 dict 类的静态方法,调用:dict.fromkeys
dict2 = dict.fromkeys(['a', 'b', 'c'], ['hello', 'world'])
print(dict2) # 执行结果:
# {'a': ['hello', 'world'], 'c': ['hello', 'world'], 'b': ['hello', 'world']}
(4)get(self, k, d=None)
通过 key 获取字典中对应的 value
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
print(dict1.get('age'))
# 如果 get 没有找到对应的 key 则返回 None
# 执行结果:
# 20
(5)items
分别获取字典的 key 和 value
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
for k, v in dict1.items():
print(k, v)
# 执行结果:
# age 20
# gender 男
# name hkey
(6)keys
获取字典中所有的 key
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
for k in dict1.keys():
print(k)
# 执行结果:
# gender
# age
# name
(7)values
获取字典中所有的 value
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
for v in dict1.values():
print(v)
# 执行结果:
# 20
# 男
# hkey
(8)pop(self, k, d=None)
删除 key 对应的 键值对
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
dict1.pop('name')
print(dict1)
# 执行结果:
# {'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
(9)popitem
随机删除字典中的键值对
通过变量可以获取被删除的键值对
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
dict2 = dict1.popitem()
print('随机删除后的dict1', dict1)
print('获取随机删除的键值对:', dict2)
# 执行结果:
# 随机删除后的dict1 {'gender': '男', 'name': 'hkey'}
# 获取随机删除的键值对:('age',20)
(10)setdefault(self, k, d=None)
已存在,不设置,获取当前key对应的值
不存在,设置,获取当前key对应的值
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
d1 = dict1.setdefault('name1', 'xiaofei')
print(d1)
# 执行结果:
# xiaofei
(11)update(self ,E=None, **F)
修改字典中对应的键值对
dict1 = {'name': 'hkey', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'}
dict1.update({'name': 'xiaofei'})
dict1.update(age=19)
print(dict1)
# 执行结果:
# {'gender': '男', 'age': 19, 'name': 'xiaofei'}
总结:
字典有以下几个特点:
(1)字典的 value 可以是任何值
(2)布尔值(1, 0)、列表、字典不能作为字典的key
(3)字典是无序的
(4)字典支持 del 删除
[ Python ] 基本数据类型及属性(下篇)的更多相关文章
- [ Python ] 基本数据类型及属性(上篇)
1. 基本数据类型 (1) 数字 - int (2) 字符串 - str (3) 布尔值 - bool 2. int 类型中重要的方法 (1) int 将字符串转 ...
- Python基础数据类型-列表(list)和元组(tuple)和集合(set)
Python基础数据类型-列表(list)和元组(tuple)和集合(set) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 本篇博客使用的是Python3.6版本,以及以后分享的 ...
- Python基本数据类型之字符串、数字、布尔
一.数据类型种类 Python中基本数据类型主要有以下几类: Number(数字) String(字符串) Bool (布尔) List(列表) Tuple(元组) Sets(集合) Diction ...
- Python之路番外:PYTHON基本数据类型和小知识点
Python之路番外:PYTHON基本数据类型和小知识点 一.基础小知识点 1.如果一行代码过长,可以用续行符 \换行书写 例子 if (signal == "red") and ...
- [python学习手册-笔记]002.python核心数据类型
python核心数据类型 ❝ 本系列文章是我个人学习<python学习手册(第五版)>的学习笔记,其中大部分内容为该书的总结和个人理解,小部分内容为相关知识点的扩展. 非商业用途转载请注明 ...
- 跟我学Python图像处理丨获取图像属性、兴趣ROI区域及通道处理
摘要:本篇文章主要讲解Python调用OpenCV获取图像属性,截取感兴趣ROI区域,处理图像通道. 本文分享自华为云社区<[Python图像处理] 三.获取图像属性.兴趣ROI区域及通道处理 ...
- python 基本数据类型分析
在python中,一切都是对象!对象由类创建而来,对象所拥有的功能都来自于类.在本节中,我们了解一下python基本数据类型对象具有哪些功能,我们平常是怎么使用的. 对于python,一切事物都是对象 ...
- python常用数据类型内置方法介绍
熟练掌握python常用数据类型内置方法是每个初学者必须具备的内功. 下面介绍了python常用的集中数据类型及其方法,点开源代码,其中对主要方法都进行了中文注释. 一.整型 a = 100 a.xx ...
- 闲聊之Python的数据类型 - 零基础入门学习Python005
闲聊之Python的数据类型 让编程改变世界 Change the world by program Python的数据类型 闲聊之Python的数据类型所谓闲聊,goosip,就是屁大点事可以咱聊上 ...
随机推荐
- 122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II (Array)
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i. Design an al ...
- springMVC+spring+mybatis搭建最近
一:概述SSM框架在项目开发中经常使用到,相比于SSH框架,它在仅几年的开发中运用的更加广泛. Spring作为一个轻量级的框架,有很多的拓展功能,最主要的我们一般项目使用的就是IOC和AOP. Sp ...
- BZOJ4872:[SHOI2017]分手是祝愿——题解
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=4872 https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P3750 Zei ...
- BZOJ2038:[2009国家集训队]小Z的袜子——题解
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2038 Description 作为一个生活散漫的人,小Z每天早上都要耗费很久从一堆五颜六色的袜子中找 ...
- CF939E:Maximize! ——题解
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/939/E https://vjudge.net/problem/CodeForces-939E 给一个集合,每次两个 ...
- 洛谷 P2024 [NOI2001]食物链 解题报告
P2024 [NOI2001]食物链 题目描述 动物王国中有三类动物 A,B,C,这三类动物的食物链构成了有趣的环形.A 吃 B,B 吃 C,C 吃 A. 现有 N 个动物,以 1 - N 编号.每个 ...
- SRM16 B-2(DP)
老鼠和洞按坐标排序 f[i][j]表示前i个洞进j只老鼠的最短距离 比赛的时候强行分三类去推式子,推是推出来了,也看出来是可以用三个单调队列去优化的,但是太繁琐了,要我敲我真没办法T^T 赛后经 on ...
- HDU 3081 最大流+二分
Marriage Match II Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others ...
- Java中String的hash函数分析
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/hengyunabc/article/details/7198533 JDK6的源码: [java] view plaincopy /** * Ret ...
- vijos 1081 野生动物园 函数式线段树
描述 cjBBteam拥有一个很大的野生动物园.这个动物园坐落在一个狭长的山谷内,这个区域从南到北被划分成N个区域,每个区域都饲养着一头狮子.这些狮子从北到南编号为1,2,3,…,N.每头狮子都有一个 ...
