Johnson 全源最短路径算法
解决单源最短路径问题(Single Source Shortest Paths Problem)的算法包括:
- Dijkstra 单源最短路径算法:时间复杂度为 O(E + VlogV),要求权值非负;
- Bellman-Ford 单源最短路径算法:时间复杂度为 O(VE),适用于带负权值情况;
对于全源最短路径问题(All-Pairs Shortest Paths Problem),可以认为是单源最短路径问题的推广,即分别以每个顶点作为源顶点并求其至其它顶点的最短距离。例如,对每个顶点应用 Bellman-Ford 算法,则可得到所有顶点间的最短路径的运行时间为 O(V2E),由于图中顶点都是连通的,而边的数量可能会比顶点更多,这个时间没有比 Floyd-Warshall 全源最短路径算法 O(V3) 更优。那么,再试下对每个顶点应用 Dijkstra 算法,则可得到所有顶点间的最短路径的运行时间为 O(VE + V2logV),看起来优于 Floyd-Warshall 算法的 O(V3),所以看起来使用基于 Dijkstra 算法的改进方案好像更好,但问题是 Dijkstra 算法要求图中所有边的权值非负,不适合通用的情况。
在 1977 年,Donald B. Johnson 提出了对所有边的权值进行 "re-weight" 的算法,使得边的权值非负,进而可以使用 Dijkstra 算法进行最短路径的计算。
我们先自己思考下如何进行 "re-weight" 操作,比如,简单地对每条边的权值加上一个较大的正数,使其非负,是否可行?
1 1 1
s-----a-----b-----c
\ /
\ /
\______/
4
比如上面的图中,共 4 条边,权值分别为 1,1,1,4。当前 s --> c 的最短路径是 {s-a, a-b, b-c} 即 1+1+1=3。而如果将所有边的权值加 1,则最短路径就会变成 {s-c} 的 5,因为 2+2+2=6,实际上导致了最短路径的变化,显然是错误的。
那么,Johnson 算法是如何对边的权值进行 "re-weight" 的呢?以下面的图 G 为例,有 4 个顶点和 5 条边。

首先,新增一个源顶点 4,并使其与所有顶点连通,新边赋权值为 0,如下图所示。
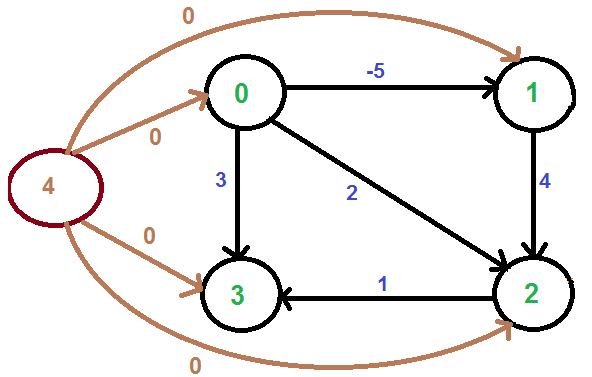
使用 Bellman-Ford 算法 计算新的顶点到所有其它顶点的最短路径,则从 4 至 {0, 1, 2, 3} 的最短路径分别是 {0, -5, -1, 0}。即有 h[] = {0, -5, -1, 0}。当得到这个 h[] 信息后,将新增的顶点 4 移除,然后使用如下公式对所有边的权值进行 "re-weight":
w(u, v) = w(u, v) + (h[u] - h[v]).
则可得到下图中的结果:

此时,所有边的权值已经被 "re-weight" 为非负。此时,就可以利用 Dijkstra 算法对每个顶点分别进行最短路径的计算了。
Johnson 算法描述如下:
- 给定图 G = (V, E),增加一个新的顶点 s,使 s 指向图 G 中的所有顶点都建立连接,设新的图为 G’;
- 对图 G’ 中顶点 s 使用 Bellman-Ford 算法计算单源最短路径,得到结果 h[] = {h[0], h[1], .. h[V-1]};
- 对原图 G 中的所有边进行 "re-weight",即对于每个边 (u, v),其新的权值为 w(u, v) + (h[u] - h[v]);
- 移除新增的顶点 s,对每个顶点运行 Dijkstra 算法求得最短路径;
Johnson 算法的运行时间为 O(V2logV + VE)。
Johnson 算法伪码实现如下:

Johnson 算法 C# 代码实现如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq; namespace GraphAlgorithmTesting
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// build a directed and negative weighted graph
Graph directedGraph1 = new Graph();
directedGraph1.AddEdge(, , -);
directedGraph1.AddEdge(, , );
directedGraph1.AddEdge(, , );
directedGraph1.AddEdge(, , );
directedGraph1.AddEdge(, , );
directedGraph1.AddEdge(, , );
directedGraph1.AddEdge(, , );
directedGraph1.AddEdge(, , -); Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Graph Vertex Count : {0}", directedGraph1.VertexCount);
Console.WriteLine("Graph Edge Count : {0}", directedGraph1.EdgeCount);
Console.WriteLine(); int[,] distSet1 = directedGraph1.Johnsons();
PrintSolution(directedGraph1, distSet1); // build a directed and positive weighted graph
Graph directedGraph2 = new Graph();
directedGraph2.AddEdge(, , );
directedGraph2.AddEdge(, , );
directedGraph2.AddEdge(, , );
directedGraph2.AddEdge(, , ); Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Graph Vertex Count : {0}", directedGraph2.VertexCount);
Console.WriteLine("Graph Edge Count : {0}", directedGraph2.EdgeCount);
Console.WriteLine(); int[,] distSet2 = directedGraph2.Johnsons();
PrintSolution(directedGraph2, distSet2); Console.ReadKey();
} private static void PrintSolution(Graph g, int[,] distSet)
{
Console.Write("\t");
for (int i = ; i < g.VertexCount; i++)
{
Console.Write(i + "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("\t");
for (int i = ; i < g.VertexCount; i++)
{
Console.Write("-" + "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine();
for (int i = ; i < g.VertexCount; i++)
{
Console.Write(i + "|\t");
for (int j = ; j < g.VertexCount; j++)
{
if (distSet[i, j] == int.MaxValue)
{
Console.Write("INF" + "\t");
}
else
{
Console.Write(distSet[i, j] + "\t");
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
} class Edge
{
public Edge(int begin, int end, int weight)
{
this.Begin = begin;
this.End = end;
this.Weight = weight;
} public int Begin { get; private set; }
public int End { get; private set; }
public int Weight { get; private set; } public void Reweight(int newWeight)
{
this.Weight = newWeight;
} public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format(
"Begin[{0}], End[{1}], Weight[{2}]",
Begin, End, Weight);
}
} class Graph
{
private Dictionary<int, List<Edge>> _adjacentEdges
= new Dictionary<int, List<Edge>>(); public Graph(int vertexCount)
{
this.VertexCount = vertexCount;
} public int VertexCount { get; private set; } public int EdgeCount
{
get
{
return _adjacentEdges.Values.SelectMany(e => e).Count();
}
} public void AddEdge(int begin, int end, int weight)
{
if (!_adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(begin))
{
var edges = new List<Edge>();
_adjacentEdges.Add(begin, edges);
} _adjacentEdges[begin].Add(new Edge(begin, end, weight));
} public void AddEdge(Edge edge)
{
AddEdge(edge.Begin, edge.End, edge.Weight);
} public void AddEdges(IEnumerable<Edge> edges)
{
foreach (var edge in edges)
{
AddEdge(edge);
}
} public IEnumerable<Edge> GetAllEdges()
{
return _adjacentEdges.Values.SelectMany(e => e);
} public int[,] Johnsons()
{
// distSet[,] will be the output matrix that will finally have the shortest
// distances between every pair of vertices
int[,] distSet = new int[VertexCount, VertexCount]; for (int i = ; i < VertexCount; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < VertexCount; j++)
{
distSet[i, j] = int.MaxValue;
}
}
for (int i = ; i < VertexCount; i++)
{
distSet[i, i] = ;
} // step 1: add new vertex s and connect to all vertices
Graph g = new Graph(this.VertexCount + );
g.AddEdges(this.GetAllEdges()); int s = this.VertexCount;
for (int i = ; i < this.VertexCount; i++)
{
g.AddEdge(s, i, );
} // step 2: use Bellman-Ford to evaluate shortest paths from s
int[] h = g.BellmanFord(s); // step 3: re-weighting edges of the original graph
// w(u, v) = w(u, v) + (h[u] - h[v])
foreach (var edge in this.GetAllEdges())
{
edge.Reweight(edge.Weight + (h[edge.Begin] - h[edge.End]));
} // step 4: use Dijkstra for each edges
for (int begin = ; begin < this.VertexCount; begin++)
{
int[] dist = this.Dijkstra(begin);
for (int end = ; end < dist.Length; end++)
{
if (dist[end] != int.MaxValue)
{
distSet[begin, end] = dist[end] - (h[begin] - h[end]);
}
}
} return distSet;
} public int[,] FloydWarshell()
{
/* distSet[,] will be the output matrix that will finally have the shortest
distances between every pair of vertices */
int[,] distSet = new int[VertexCount, VertexCount]; for (int i = ; i < VertexCount; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < VertexCount; j++)
{
distSet[i, j] = int.MaxValue;
}
}
for (int i = ; i < VertexCount; i++)
{
distSet[i, i] = ;
} /* Initialize the solution matrix same as input graph matrix. Or
we can say the initial values of shortest distances are based
on shortest paths considering no intermediate vertex. */
foreach (var edge in _adjacentEdges.Values.SelectMany(e => e))
{
distSet[edge.Begin, edge.End] = edge.Weight;
} /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of a iteration, we have shortest distances between all
pairs of vertices such that the shortest distances consider only the
vertices in set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as intermediate vertices.
---> After the end of a iteration, vertex no. k is added to the set of
intermediate vertices and the set becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} */
for (int k = ; k < VertexCount; k++)
{
// Pick all vertices as source one by one
for (int i = ; i < VertexCount; i++)
{
// Pick all vertices as destination for the above picked source
for (int j = ; j < VertexCount; j++)
{
// If vertex k is on the shortest path from
// i to j, then update the value of distSet[i,j]
if (distSet[i, k] != int.MaxValue
&& distSet[k, j] != int.MaxValue
&& distSet[i, k] + distSet[k, j] < distSet[i, j])
{
distSet[i, j] = distSet[i, k] + distSet[k, j];
}
}
}
} return distSet;
} public int[] BellmanFord(int source)
{
// distSet[i] will hold the shortest distance from source to i
int[] distSet = new int[VertexCount]; // Step 1: Initialize distances from source to all other vertices as INFINITE
for (int i = ; i < VertexCount; i++)
{
distSet[i] = int.MaxValue;
}
distSet[source] = ; // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. A simple shortest path from source
// to any other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 edges
for (int i = ; i <= VertexCount - ; i++)
{
foreach (var edge in _adjacentEdges.Values.SelectMany(e => e))
{
int u = edge.Begin;
int v = edge.End;
int weight = edge.Weight; if (distSet[u] != int.MaxValue
&& distSet[u] + weight < distSet[v])
{
distSet[v] = distSet[u] + weight;
}
}
} // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. The above step guarantees
// shortest distances if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle.
// If we get a shorter path, then there is a cycle.
foreach (var edge in _adjacentEdges.Values.SelectMany(e => e))
{
int u = edge.Begin;
int v = edge.End;
int weight = edge.Weight; if (distSet[u] != int.MaxValue
&& distSet[u] + weight < distSet[v])
{
Console.WriteLine("Graph contains negative weight cycle.");
}
} return distSet;
} public int[] Dijkstra(int source)
{
// dist[i] will hold the shortest distance from source to i
int[] distSet = new int[VertexCount]; // sptSet[i] will true if vertex i is included in shortest
// path tree or shortest distance from source to i is finalized
bool[] sptSet = new bool[VertexCount]; // initialize all distances as INFINITE and stpSet[] as false
for (int i = ; i < VertexCount; i++)
{
distSet[i] = int.MaxValue;
sptSet[i] = false;
} // distance of source vertex from itself is always 0
distSet[source] = ; // find shortest path for all vertices
for (int i = ; i < VertexCount - ; i++)
{
// pick the minimum distance vertex from the set of vertices not
// yet processed. u is always equal to source in first iteration.
int u = CalculateMinDistance(distSet, sptSet); // mark the picked vertex as processed
sptSet[u] = true; // update dist value of the adjacent vertices of the picked vertex.
for (int v = ; v < VertexCount; v++)
{
// update dist[v] only if is not in sptSet, there is an edge from
// u to v, and total weight of path from source to v through u is
// smaller than current value of dist[v]
if (!sptSet[v]
&& distSet[u] != int.MaxValue
&& _adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(u)
&& _adjacentEdges[u].Exists(e => e.End == v))
{
int d = _adjacentEdges[u].Single(e => e.End == v).Weight;
if (distSet[u] + d < distSet[v])
{
distSet[v] = distSet[u] + d;
}
}
}
} return distSet;
} private int CalculateMinDistance(int[] distSet, bool[] sptSet)
{
int minDistance = int.MaxValue;
int minDistanceIndex = -; for (int v = ; v < VertexCount; v++)
{
if (!sptSet[v] && distSet[v] <= minDistance)
{
minDistance = distSet[v];
minDistanceIndex = v;
}
} return minDistanceIndex;
}
}
}
}
运行结果如下:

参考资料
- 广度优先搜索
- 深度优先搜索
- Breadth First Traversal for a Graph
- Depth First Traversal for a Graph
- Dijkstra 单源最短路径算法
- Bellman-Ford 单源最短路径算法
- Bellman–Ford algorithm
- Introduction To Algorithm
- Floyd-Warshall's algorithm
- Bellman-Ford algorithm for single-source shortest paths
- Dynamic Programming | Set 23 (Bellman–Ford Algorithm)
- Dynamic Programming | Set 16 (Floyd Warshall Algorithm)
- Johnson’s algorithm for All-pairs shortest paths
- Floyd-Warshall's algorithm
- 最短路径算法--Dijkstra算法,Bellmanford算法,Floyd算法,Johnson算法
- QuickGraph, Graph Data Structures And Algorithms for .NET
- CHAPTER 26: ALL-PAIRS SHORTEST PATHS
本篇文章《Johnson 全源最短路径算法》由 Dennis Gao 发表自博客园,未经作者本人同意禁止任何形式的转载,任何自动或人为的爬虫转载行为均为耍流氓。
Johnson 全源最短路径算法的更多相关文章
- Johnson 全源最短路径算法学习笔记
Johnson 全源最短路径算法学习笔记 如果你希望得到带互动的极简文字体验,请点这里 我们来学习johnson Johnson 算法是一种在边加权有向图中找到所有顶点对之间最短路径的方法.它允许一些 ...
- Floyd-Warshall 全源最短路径算法
Floyd-Warshall 算法采用动态规划方案来解决在一个有向图 G = (V, E) 上每对顶点间的最短路径问题,即全源最短路径问题(All-Pairs Shortest Paths Probl ...
- 【学习笔记】 Johnson 全源最短路
前置扯淡 一年多前学的最短路,当时就会了几个名词的拼写,啥也没想过 几个月之前,听说了"全源最短路"这个东西,当时也没说学一下,现在补一下(感觉实在是没啥用) 介绍 由于\(spf ...
- Johnson全源最短路
例题:P5905 [模板]Johnson 全源最短路 首先考虑求全源最短路的几种方法: Floyd:时间复杂度\(O(n^3)\),可以处理负权边,但不能处理负环,而且速度很慢. Bellman-Fo ...
- Johnson 全源最短路
学这个是为了支持在带负权值的图上跑 Dijkstra. 为了这个我们要考虑把负的权值搞正. 那么先把我们先人已经得到的结论摆出来.我们考虑先用 SPFA 对着一个满足三角形不等式的图跑一次最短路,具体 ...
- Dijkstra 单源最短路径算法
Dijkstra 算法是一种用于计算带权有向图中单源最短路径(SSSP:Single-Source Shortest Path)的算法,由计算机科学家 Edsger Dijkstra 于 1956 年 ...
- Bellman-Ford 单源最短路径算法
Bellman-Ford 算法是一种用于计算带权有向图中单源最短路径(SSSP:Single-Source Shortest Path)的算法.该算法由 Richard Bellman 和 Leste ...
- 经典贪心算法(哈夫曼算法,Dijstra单源最短路径算法,最小费用最大流)
哈夫曼编码与哈夫曼算法 哈弗曼编码的目的是,如何用更短的bit来编码数据. 通过变长编码压缩编码长度.我们知道普通的编码都是定长的,比如常用的ASCII编码,每个字符都是8个bit.但在很多情况下,数 ...
- 单源最短路径算法:迪杰斯特拉 (Dijkstra) 算法(二)
一.基于邻接表的Dijkstra算法 如前一篇文章所述,在 Dijkstra 的算法中,维护了两组,一组包含已经包含在最短路径树中的顶点列表,另一组包含尚未包含的顶点.使用邻接表表示,可以使用 BFS ...
随机推荐
- [高并发]Java高并发编程系列开山篇--线程实现
Java是最早开始有并发的语言之一,再过去传统多任务的模式下,人们发现很难解决一些更为复杂的问题,这个时候我们就有了并发. 引用 多线程比多任务更加有挑战.多线程是在同一个程序内部并行执行,因此会对相 ...
- 前端CSS预处理器Sass
前面的话 "CSS预处理器"(css preprocessor)的基本思想是,用一种专门的编程语言,进行网页样式设计,然后再编译成正常的CSS文件.SASS是一种CSS的开发工 ...
- ASP.NET Core 之 Identity 入门(二)
前言 在 上篇文章 中讲了关于 Identity 需要了解的单词以及相对应的几个知识点,并且知道了Identity处在整个登入流程中的位置,本篇主要是在 .NET 整个认证系统中比较重要的一个环节,就 ...
- 01.LoT.UI 前后台通用框架分解系列之——小图片背景全屏显示(可自动切换背景)
LOT.UI分解系列汇总:http://www.cnblogs.com/dunitian/p/4822808.html#lotui LoT.UI开源地址如下:https://github.com/du ...
- JAVA问题集锦Ⅰ
1.Java的日期添加: import java.util.Date ; date=new date();//取时间 Calendar calendar = new GregorianCalendar ...
- Kooboo CMS技术文档之二:Kooboo CMS的安装步骤
在IIS上安装Kooboo CMS Kooboo CMS安装之后 安装的常见问题 1. 在IIS上安装Kooboo CMS Kooboo CMS部署到正式环境相当简单,安装过程是一个普通MVC站点在I ...
- ES6的一些常用特性
由于公司的前端业务全部基于ES6开发,于是给自己开个小灶补补ES6的一些常用特性.原来打算花两天学习ES6的,结果花了3天才勉强过了一遍阮老师的ES6标准入门(水好深,ES6没学好ES7又来了...) ...
- 一个诡异的COOKIE问题
今天下午,发现本地的测试环境突然跑不动了,thinkphp直接跑到异常页面,按照正常的排错思路,直接看thinkphp的log 有一条 [ error ] [2]setcookie() expects ...
- PHP代码优化
1 代码优化 1 尽量静态化 如果一个方法能被静态,那就声明它为静态的,速度可提高1/4,甚至我测试的时候,这个提高了近三倍. 当然了,这个测试方法需要在十万级以上次执行,效果才明显. 其实静态方法和 ...
- 通过AngularJS实现前端与后台的数据对接(一)——预备工作篇
最近,笔者在做一个项目:使用AngularJS,从而实现前端与后台的数据对接.笔者这是第一次做前端与后台的数据对接的工作,因此遇到了许多问题.笔者在这些问题中,总结了一些如何实现前端与后台的数据对接的 ...
