Depth-first search and Breadth-first search 深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索
Depth-first search
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures.
The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking 回溯.
For the following graph:
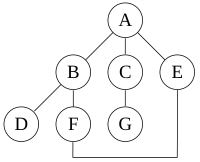
a depth-first search starting at A,
assuming that the left edges in the shown graph are chosen before right edges,
and assuming the search remembers previously visited nodes and will not repeat them (since this is a small graph),
will visit the nodes in the following order: A, B, D, F, E, C, G.
The edges traversed in this search form a Trémaux tree, a structure with important applications in graph theory.
Performing the same search without remembering previously visited nodes results in visiting nodes in the order A, B, D, F, E, A, B, D, F, E, etc. forever, caught in the A, B, D, F, E cycle and never reaching C or G.
Iterative deepening is one technique to avoid this infinite loop and would reach all nodes.
深度优先的算法实现
Input: A graph G and a vertex v of G
Output: All vertices reachable from v labeled as discovered
A recursive implementation of DFS:[5]
1 procedure DFS(G,v):
2 label v as discovered
3 for all edges from v to w in G.adjacentEdges(v) do
4 if vertex w is not labeled as discovered then
5 recursively call DFS(G,w)
The order in which the vertices are discovered by this algorithm is called the lexicographic order.
A non-recursive implementation of DFS with worst-case space complexity O(|E|):[6] (使用栈,先进后出)
1 procedure DFS-iterative(G,v):
2 let S be a stack
3 S.push(v)
4 while S is not empty
5 v = S.pop()
6 if v is not labeled as discovered:
7 label v as discovered
8 for all edges from v to w in G.adjacentEdges(v) do
9 S.push(w)
These two variations of DFS visit the neighbors of each vertex in the opposite order from each other: the first neighbor of v visited by the recursive variation is the first one in the list of adjacent edges, while in the iterative variation the first visited neighbor is the last one in the list of adjacent edges. The recursive implementation will visit the nodes from the example graph in the following order: A, B, D, F, E, C, G. The non-recursive implementation will visit the nodes as: A, E, F, B, D, C, G.
The non-recursive implementation is similar to breadth-first search but differs from it in two ways:
- it uses a stack instead of a queue, and
- it delays checking whether a vertex has been discovered until the vertex is popped from the stack rather than making this check before adding the vertex.
Breadth-first search
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures.
It starts at the tree root (or some arbitrary node of a graph, sometimes referred to as a 'search key'[1]), and explores all of the neighbor nodes at the present depth prior to moving on to the nodes at the next depth level.
It uses the opposite strategy as depth-first search, which instead explores the highest-depth nodes first before being forced to backtrack回溯 and expand shallower nodes.
shallower是shallow的比较级,较浅的
广度优先的实现 (使用队列,先进先出)
Input: A graph Graph and a starting vertex顶点 root of Graph
Output: Goal state. The parent links trace the shortest path back to root
1 procedure BFS(G,start_v):
2 let S be a queue
3 S.enqueue(start_v)
4 while S is not empty
5 v = S.dequeue()
6 if v is the goal:
7 return v
8 for all edges from v to w in G.adjacentEdges(v) do
9 if w is not labeled as discovered:
10 label w as discovered
11 w.parent = v
12 S.enqueue(w)
More details
This non-recursive implementation is similar to the non-recursive implementation of depth-first search, but differs from it in two ways:
- it uses a queue (First In First Out) instead of a stack and
- it checks whether a vertex顶点 has been discovered before enqueueing the vertex rather than delaying this check until the vertex is dequeued from the queue.
The Q queue contains the frontier along which the algorithm is currently searching.
Nodes can be labelled as discovered by storing them in a set, or by an attribute on each node, depending on the implementation.
Note that the word node is usually interchangeable with the word vertex.
The parent attribute of each vertex is useful for accessing the nodes in a shortest path, for example by backtracking from the destination node up to the starting node, once the BFS has been run, and the predecessors nodes have been set.
Breadth-first search produces a so-called breadth first tree. You can see how a breadth first tree looks in the following example.
Depth-first search and Breadth-first search 深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索的更多相关文章
- DFS_BFS(深度优先搜索 和 广度优先搜索)
package com.rao.graph; import java.util.LinkedList; /** * @author Srao * @className BFS_DFS * @date ...
- 【Python排序搜索基本算法】之深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索、拓扑排序、强联通&Kosaraju算法
Graph Search and Connectivity Generic Graph Search Goals 1. find everything findable 2. don't explor ...
- 【js数据结构】图的深度优先搜索与广度优先搜索
图类的构建 function Graph(v) {this.vertices = v;this.edges = 0;this.adj = []; for (var i = 0; i < this ...
- DFS或BFS(深度优先搜索或广度优先搜索遍历无向图)-04-无向图-岛屿数量
给定一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,计算岛屿的数量.一个岛被水包围,并且它是通过水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成的.你可以假设网格的四个边均被水包围. 示例 1: 输入: ...
- 深度优先搜索DFS和广度优先搜索BFS简单解析(新手向)
深度优先搜索DFS和广度优先搜索BFS简单解析 与树的遍历类似,图的遍历要求从某一点出发,每个点仅被访问一次,这个过程就是图的遍历.图的遍历常用的有深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索,这两者对于有向图和无向图 ...
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)
深度优先搜索(DFS) 广度优先搜索(BFS) 1.介绍 广度优先搜索(BFS)是图的另一种遍历方式,与DFS相对,是以广度优先进行搜索.简言之就是先访问图的顶点,然后广度优先访问其邻接点,然后再依次 ...
- 深度优先搜索DFS和广度优先搜索BFS简单解析
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/FZfangzheng/p/8529132.html 深度优先搜索DFS和广度优先搜索BFS简单解析 与树的遍历类似,图的遍历要求从某一点出发,每 ...
- Unity中通过深度优先算法和广度优先算法打印游戏物体名
前言:又是一个月没写博客了,每次下班都懒得写,觉得浪费时间.... 深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索的定义,网络上已经说的很清楚了,我也是看了网上的才懂的,所以就不在这里赘述了.今天讲解的实例,主要是通过自 ...
- 广度优先搜索(Breadth First Search, BFS)
广度优先搜索(Breadth First Search, BFS) BFS算法实现的一般思路为: // BFS void BFS(int s){ queue<int> q; // 定义一个 ...
随机推荐
- 5.无监督学习-DBSCAN聚类算法及应用
DBSCAN方法及应用 1.DBSCAN密度聚类简介 DBSCAN 算法是一种基于密度的聚类算法: 1.聚类的时候不需要预先指定簇的个数 2.最终的簇的个数不确定DBSCAN算法将数据点分为三类: 1 ...
- BIOS 搭配 MBR/GPT 的开机流程
鸟哥私房菜书上内容: BIOS 搭配 MBR/GPT 的开机流程 在计算机概论里面我们有谈到那个可爱的BIOS与CMOS两个东西, CMOS是记录各项硬件参数且嵌入在主板上面的储存器,BIOS则是一个 ...
- linux常用命令:cd 命令
Linux cd 命令可以说是Linux中最基本的命令语句,其他的命令语句要进行操作,都是建立在使用 cd 命令上的.所以,学习Linux 常用命令,首先就要学好 cd 命令的使用方法技巧. 1. 命 ...
- flask模板结构组织(局部模板、宏、模板继承)
模板结构组织 除了使用函数.过滤器等工具控制模板的输出外,jinja2还提供了一些工具来在宏观上组织模板内容. 局部模板 在Web程序中,我们通常会为每一类页面编写一个独立的模板.比如主页模板.用户资 ...
- Windows Services(NT)
本文主要记录什么是Windows Service,及其主要组成?并通过一个列子来创建一个Windows Services,同时,记录几个在查资料碰到的问题. Windows Services全文简称N ...
- Android Auto开发初探
一.Android Auto 概述 二.Android Auto 使用方法 四.Android Auto应用开发 五.Android Auto开发总结 一.Android Auto 概述 最近物联网是 ...
- 文件缓冲区在fork后复制
场景:父进程trace进程A,当A进程fork子进程B时,让父进程也fork子进程去trace子进程B,用于trace的进程将被trace的进程发生的系统调用号通过fprintf存入各自文件中 问题: ...
- router.go,router.push,router.replace的区别
除了使用 <router-link> 创建 a 标签来定义导航链接,我们还可以借助 router 的实例方法,通过编写代码来实现.当你点击 <router-link> 时,这个 ...
- dubbo原理
1,观察DubboBeanDefinitionParser 的构造方法,给它打一个断点,发现其前一步在DubboNamespaceHandler 应用启动会连续调此方法 DubboBeanDefini ...
- Docker MySQL5.5镜像
定制MySQL的镜像有个很大的难题:mysqld启动之前要初始化数据目录,5.5自带有空账号密码需要初始化. Dockerfile FROM centos # 拷贝需要的安装和MySQL初始脚本 CO ...
