GPU Tips
<1> Basic
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
#define NUM 15
__global__ void square(float *dout,float *din)
{
int idx = threadIdx.x;
float f = din[idx];
dout[idx] = f*f;
} int main(int argc,char **argv)
{ const int bytes = sizeof(float) * NUM;
float host_in[NUM];
// save some value
for(int i=;i<NUM;i++)
{
host_in[i] = float(i);
} float host_out[NUM]; cudaError_t cudaStatus;
// GPU SETTINGS
// Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system.
cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?");
return;
} // define gpu memory, GPU memory allocation
float *device_in = ;
float *device_out = ;
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&device_in, bytes);
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&device_out,bytes); cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(device_in,host_in,bytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // GPU kernel
// 1 block,Num threads
square<<<,NUM>>>(device_out,device_in); cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus);
} cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(host_out, device_out, bytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
} // Free GPU memory
cudaFree(device_in);
cudaFree(device_out); for(int i=;i<NUM;i++)
{
fprintf(stdout,"%f \n",host_out[i]);
} getchar(); return ; }
<2> N blocks and block's threads one dim
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ARRAYSize 50000000
#define THREADS_PER_BLOCK 1024 #define fnvalue(a,size)\
{\
for(int i=;i<size;i++) \
{\
a[i] = float(i);\
}\
}\ #define CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(STATUS)\
{\
if (STATUS != cudaSuccess)\
{\
fprintf(stdout,"Error in line %d\n ",__LINE__);\
}\
}\ __global__ void add(float *d_out,float *d_x, float *d_y)
{ int index = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (index<ARRAYSize)
{
d_out[index] = d_x[index] + d_y[index];
} } int main(int argc,char **argv)
{ const int bytes = sizeof(float)*ARRAYSize; // host memory
float *h_x = (float*)malloc(bytes);
float *h_y = (float*)malloc(bytes);
float *h_out = (float*)malloc(bytes); // give host value
fnvalue(h_x,ARRAYSize);
fnvalue(h_y,ARRAYSize); // device memory
float *d_x,*d_y,*d_out;
// cuda setttings
cudaError_t dstat;
dstat = cudaSetDevice();
CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat);
dstat = cudaMalloc((void**)&d_x, bytes);
CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat);
dstat = cudaMalloc((void**)&d_y, bytes);
CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat);
dstat = cudaMalloc((void**)&d_out, bytes);
CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat); fprintf(stdout,"Copy data go GPU\n");
cudaMemcpy(d_x,h_x,bytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_y,h_y,bytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); add<<<ARRAYSize/THREADS_PER_BLOCK,THREADS_PER_BLOCK>>>(d_out,d_x,d_y); fprintf(stdout,"Copy GPU data to cpu\n");
dstat = cudaMemcpy(h_out,d_out,bytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // DEBUG SOME VALUE for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
if ((i+)%==)
{
fprintf(stdout,"%f\n", h_out[i]);
}
else
{
fprintf(stdout,"%f ", h_out[i]);
}
} getchar(); // FREE CPU MEMORY
free(h_x);
free(h_y);
free(h_out); // FREE GPU MEMORY
dstat = cudaFree(d_x);
CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat);
dstat = cudaFree(d_y);
CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat);
dstat = cudaFree(d_out);
CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat); return ; }
<3> Unified memory:
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
// Kernel function to add the elements of two arrays
__global__
void add(int n, float *x, float *y)
{
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
y[i] = x[i] + y[i];
} int main(void)
{
int N = <<;
float *x, *y; // Allocate Unified Memory – accessible from CPU or GPU
cudaMallocManaged(&x, N*sizeof(float));
cudaMallocManaged(&y, N*sizeof(float)); // initialize x and y arrays on the host
for (int i = ; i < N; i++) {
x[i] = 1.0f;
y[i] = 2.0f;
} // Run kernel on 1M elements on the GPU
add<<<, >>>(N, x, y); // Wait for GPU to finish before accessing on host
cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // Check for errors (all values should be 3.0f)
float maxError = 0.0f;
for (int i = ; i < N; i++)
maxError = fmax(maxError, fabs(y[i]-3.0f));
std::cout << "Max error: " << maxError << std::endl; // Free memory
cudaFree(x);
cudaFree(y); return ;
}
<4>Some tips
(1)
下图表示一维的block是由grid生成的。
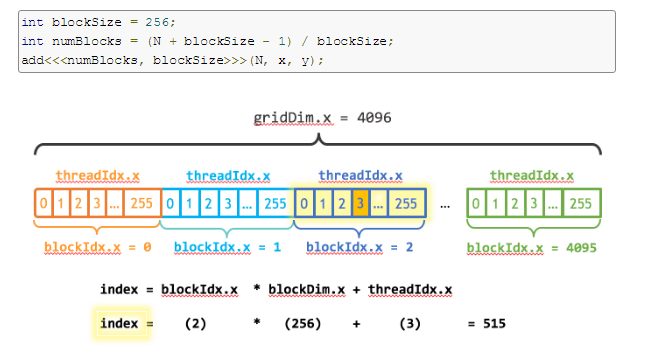
__global__
void add(int n, float *x, float *y)
{
int index = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int stride = blockDim.x * gridDim.x;
for (int i = index; i < n; i += stride)
y[i] = x[i] + y[i];
}
(2) 关于SharedMemory ,其实是在一个block上的共享memory
code:
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
#include <device_functions.h> #define RADIUS 3
#define BLOCKSIZE 10 __global__ void process(int *d_out,int *d_in,int *shared_mem)
{
__shared__ int temp[BLOCKSIZE + * RADIUS ];
int gindex = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
int lindex = threadIdx.x + RADIUS;
//printf("%d ",lindex);
// Read input elements into shared memory
temp[lindex] = d_in[gindex]; if (threadIdx.x < RADIUS)
{
temp[lindex - RADIUS] = d_in[gindex - RADIUS];
temp[lindex + BLOCKSIZE] = d_in[gindex + BLOCKSIZE]; } shared_mem[lindex] = lindex;
// this code for debug __syncthreads(); // Apply the stencil
int result = ;
for (int offset = -RADIUS ; offset <= RADIUS ; offset++)
{
result += temp[lindex + offset]; } // Store the result
d_out[gindex] = result; } int main(int argc,char**argv)
{
// allocation of memory int host_rawSize = ; int host_bytes = sizeof(int) * host_rawSize;
int shared_bytes = (host_rawSize+*RADIUS) * sizeof(int); int *host_data = (int*)malloc(host_bytes);
int *host_outData = (int*)malloc(host_bytes);
int *host_sharedMemData = (int*)malloc(shared_bytes);
for(int i=;i<host_rawSize;i++)
{
host_data[i] = int(i)+;
}
for(int i=;i<host_rawSize;i++)
{
fprintf(stdout,"%d ",host_data[i]);
}
fprintf(stdout,"\n"); int *dev_in;
cudaMallocManaged((void**)&dev_in , host_bytes);
//cudaMallocManaged(&dev_in , host_bytes);
//cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_rawdata,bytes);
cudaMemcpy(dev_in,host_data,host_bytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); int dev_out_bytes = host_rawSize *sizeof(int); // 4*sizeof(float)
int *dev_out;
int *dev_shared;
cudaMallocManaged(&dev_out , dev_out_bytes);
cudaMallocManaged(&dev_shared , shared_bytes); process<<<,host_rawSize>>>(dev_out,dev_in,dev_shared); cudaMemcpy(host_outData, dev_out, dev_out_bytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
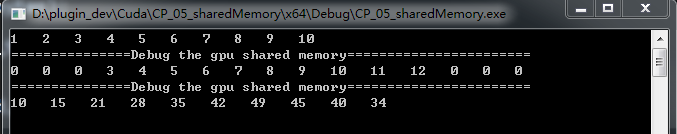
cudaMemcpy(host_sharedMemData,dev_shared,shared_bytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); printf("===============Debug the gpu shared memory=======================\n");
for(int i=;i<host_rawSize + *RADIUS;i++)
{
fprintf(stdout,"%d ",host_sharedMemData[i]);
}
printf("\n===============Debug the gpu shared memory=======================\n"); for(int i=;i<host_rawSize;i++)
{
fprintf(stdout,"%d ",host_outData[i]);
}
fprintf(stdout,"\n"); getchar(); return ;
}
<1>simple caculation:
I = (R+G+B)/3
I = R*0.299f + G*0.587f + 0.114f*B
CPU:
// Serial implementation for running on CPU using a single thread.
void rgbaToGreyscaleCpu(const uchar4* const rgbaImage, unsigned char *const greyImage,
const size_t numRows, const size_t numCols)
{
for (size_t r = ; r < numRows; ++r) {
for (size_t c = ; c < numCols; ++c) {
const uchar4 rgba = rgbaImage[r * numCols + c];
const float channelSum = .299f * rgba.x + .587f * rgba.y + .114f * rgba.z;
greyImage[r * numCols + c] = channelSum;
}
}
}
GPU:
// CUDA kernel which is run in parallel by many GPU threads.
__global__
void rgbaToGreyscaleCudaKernel(const uchar4* const rgbaImage,
unsigned char* const greyImage,
const int numRows, const int numCols)
{
//First create a mapping from the 2D block and grid locations
//to an absolute 2D location in the image, then use that to
//calculate a 1D offset
const long pointIndex = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x*blockIdx.x; if(pointIndex<numRows*numCols) { // this is necessary only if too many threads are started
uchar4 const imagePoint = rgbaImage[pointIndex];
greyImage[pointIndex] = .299f*imagePoint.x + .587f*imagePoint.y + .114f*imagePoint.z;
}
} // Parallel implementation for running on GPU using multiple threads.
void rgbaToGreyscaleCuda(const uchar4 * const h_rgbaImage, uchar4 * const d_rgbaImage,
unsigned char* const d_greyImage, const size_t numRows, const size_t numCols)
{
const int blockThreadSize = ;
const int numberOfBlocks = + ((numRows*numCols - ) / blockThreadSize); // a/b rounded up
const dim3 blockSize(blockThreadSize, , );
const dim3 gridSize(numberOfBlocks , , );
rgbaToGreyscaleCudaKernel<<<gridSize, blockSize>>>(d_rgbaImage, d_greyImage, numRows, numCols);
}
GPU Tips的更多相关文章
- Optimizing graphics performance
看U3D文档,心得:对于3D场景,使用分层次的距离裁剪,小物件分到一个层,稍远时就被裁掉,大物体分到一个层,距离很远时才裁掉,甚至不载.中物体介于二者之间. 文档如下: Good performanc ...
- 玩转渗透神器Kali:Kali Linux作为主系统使用的正确姿势TIPS
Kali Linux 前身是著名渗透测试系统BackTrack ,是一个基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版,包含很多安全和取证方面的相关工具. 本文假设你在新装好的kali linux环境下… ...
- shader程序员需要注意的优化Tips
在写shader的时候,其实一些写法对于其执行影响非常大,而且由于gpu和cpu在架构上的不同,代码的优化思想也不一样,最近一直在写几个shader,为了性能问题,查阅了很多资料,把一些tips总结下 ...
- Ubuntu16 编译源码安装MXNet 可变卷积Deformable-ConvNets GPU版
[引言]最近接手了公司的关于虫子识别的项目,使用MXNet框架开发,但是实际用的是Deformable-ConvNets. Deformable-ConvNets为微软研究研究院提出的可变卷积网络,可 ...
- 动画性能优化-requestAnimationFrame、GPU等
最近在做一个场景动画,有一个欢迎界面和一个主动画界面,两个界面之间的连接通过一个进度条来完成,当进度条完成,提供通往主动画的按钮. 画面会从一个个的场景移动过去,用户可通过点击抽奖.查看气泡商铺等进行 ...
- ubuntu16.04 Detectron目标检测库配置(包含GPU驱动,Cuda,Caffee2等配置梳理)
Detectron概述 Detectron是Facebook FAIR开源了的一个目标检测(Object Detection)平台. 用一幅图简单说明下Object Detection.如Mask R ...
- Tensorflow、Pytorch、Keras的多GPU使用
Tensorflow.Pytorch.Keras的多GPU的并行操作 方法一 :使用深度学习工具提供的 API指定 1.1 Tesorflow tensroflow指定GPU的多卡并行的时候,也是可以 ...
- Adreno GPU Profiler工具使用总结
Adreno Profiler介绍 Adreno Profiler 是高通公司开发的一款针对运行在高通骁龙处理器上用于图形和GPGPU技术应用的性能分析和帧调试工具.工具本质上是一个OpenGL ES ...
- Generating Complex Procedural Terrains Using GPU
前言:感慨于居然不用tesselation也可以产生这么复杂的地形,当然致命的那个关于不能有洞的缺陷还是没有办法,但是这个赶脚生成的已经足够好了,再加上其它模型估 计效果还是比较震撼的.总之好文共分享 ...
随机推荐
- spring 整合 redis,以及spring的RedisTemplate如何使用
需要的jar包 spring-data-redis-1.6.2.RELEASE.jar jedis-2.7.2.jar(依赖 commons-pool2-2.3.jar) commons-pool2- ...
- Hbase 1.3.0 Rsgroup
HBase RSGroup Git环境window环境下,警用crlf自动转换git config --global core.autocrlf false protobuf环境yum install ...
- angular,vue,react的基本语法—样式处理
基本语法 样式处理: vue: 动态属性: v-bind:class 简写 :class react: 变量:class={selecter} angular: 指令:[ngClass]=" ...
- eclipse将javaSE项目导出成可执行jar包
将第三方包和项目打包到一块 step1:选中要导出的项目,右键选择Export step2:选择java/Runable JAR file step3:选择main主程序,选择第三方包打包的形式,推荐 ...
- 【1】BIO,NIO,AIO与Reactor,Proactor
讲解IO思路: BIO(一个连接一个线程) -->大并发问题-->NIO(操作系统层面:IO多路复用) -->NIO两个问题:1.谁去监听就绪(Boss),2.谁来处理已就绪(Wor ...
- Nginx 之六: Nginx服务器的正向及反向代理功能
一:Nginx作为正向代理服务器: 1.正向代理:代理(proxy)服务也可以称为是正向代理,指的是将服务器部署在公司的网关,代理公司内部员工上外网的请求,可以起到一定的安全作用和管理限制作用,正向代 ...
- 使用JAVA数组实现顺序栈
1,首先总结一下线性表(分为顺序表和链接表,[即顺序存储结构和链式存储结构的区别])和栈(顺序栈和链接栈)还有队列(顺序队列和链接队列)的JAVA类库中的实现: java.util.ArrayList ...
- gai_strerror函数
一.函数原型 #include <netdb.h> const char *gai_strerror(int error); 返回:指向错误描述消息字符串的指针 二.由getaddrinf ...
- 通过GUI制作一个简单的消息对话框互发消息
public class LTS extends JFrame { private JPanel contentPane; private JTextField textField; private ...
- ROI Pooling层详解
目标检测typical architecture 通常可以分为两个阶段: (1)region proposal:给定一张输入image找出objects可能存在的所有位置.这一阶段的输出应该是一系列o ...
