Programming Assignment 5: Burrows–Wheeler Data Compression
编程作业五
作业链接:Burrows-Wheeler Data Compression & Checklist
我的代码:MoveToFront.java & CircularSuffixArray.java & BurrowsWheeler.java
问题简介
Burrows-Wheeler 数据压缩算法包括三个部分:Burrows-Wheeler transform,Move-to-front encoding 和 Huffman compression,前面两个部分把文本转换成易于用哈夫曼压缩的形式,或者说更适合,然后展开时再逆着变回原来的文本。哈夫曼压缩部分可以直接调用课程写好的,作业要求我们实现前面两个部分。
Move-to-front
这是一种对字符串编码方式,输入字符串,输出编码。做法不难说明:先初始个有序字母表序列,然后开始读入字符,输出其在字母表序列中的位置,并将字母表中的该字符移动到首位,再继续读下一个字符。例子:
move-to-front in out
------------- --- ---
A B C D E F C 2
C A B D E F A 1
A C B D E F A 0
A C B D E F A 0
A C B D E F B 2
B A C D E F C 2
C B A D E F C 0
C B A D E F C 0
C B A D E F A 2
A C B D E F C 1
C A B D E F C 0
C A B D E F F 5
F C A B D E
输入字符串为 CAAABCCCACCF,则初始有序字母表序列为 ABCDEF。读入字符 C,输出位置索引 2,字母表序列更新为 CABDEF;读入 A,输出位置索引 1,序列更新为 ACBDEF ... 解码的时候类似,辅助序列初始为 ABCDEF,编码 2 输出 C,更新序列为 CABDEF;编码 1 输出 A,更新序列为 ACBDEF;编码 0 输出 A ...
不难发现,要是输入的字符串中存在很多相邻相同字符,那输出的编码就会有很多小整数,像 0,1 和 2。因为每次都会把读入的字符移到首位,这个字符老是出现,那它的位置也就总是很靠前。编码中小整数出现频率很高,这样的编码就很适合再用哈夫曼算法来压缩。而 Burrows-Wheeler 就是为 Move-to-front 准备这种字符串的,它可以把文本进行一定的转换,让一些相同的字符彼此相邻。
Burrows–Wheeler transform
Burrows-Wheeler 变换只改变字符串中字符的顺序而并不改变其字符,如果原字符串有几个出现多次的子串,那么转换过的字符串上就会有一些连续重复的字符。
摘自维基百科:链接。
这个关键的转换需要用到一个基础的数据结构:循环后缀数组(circular suffix array),姑且这么写吧。例子:
i Original Suffixes Sorted Suffixes t index[i]
-- ----------------------- ----------------------- --------
0 A B R A C A D A B R A ! ! A B R A C A D A B R A 11
1 B R A C A D A B R A ! A A ! A B R A C A D A B R 10
2 R A C A D A B R A ! A B A B R A ! A B R A C A D 7
*3 A C A D A B R A ! A B R A B R A C A D A B R A ! *0
4 C A D A B R A ! A B R A A C A D A B R A ! A B R 3
5 A D A B R A ! A B R A C A D A B R A ! A B R A C 5
6 D A B R A ! A B R A C A B R A ! A B R A C A D A 8
7 A B R A ! A B R A C A D B R A C A D A B R A ! A 1
8 B R A ! A B R A C A D A C A D A B R A ! A B R A 4
9 R A ! A B R A C A D A B D A B R A ! A B R A C A 6
10 A ! A B R A C A D A B R R A ! A B R A C A D A B 9
11 ! A B R A C A D A B R A R A C A D A B R A ! A B 2
原始字符串是 ABRACADABRA!,循环后缀数组就是每次循环左移得到的 12 个字符串,然后我们再对这 12 个字符串排序,最终输出的变换字符串即排序后的最后一列 t[]。此外,为了后续的还原,输出变换字符串前还要输出原始字符串在排序后的行号 3。
Burrows-Wheeler 变换的目的是把字符串中一些相同字符放在一起,这是一种比较适于压缩的形式,那选排序后的第一列不是更合适吗我想。后来觉得可能是因为考虑到还原的问题,你对 t[] 排下序也就得到了第一列,只有第一列大概不好还原。那不要最后一列,其它列也行吗,排序后多少也会比原字符串的重复字符多些。实际上,变换选最后一列是因为:
It relies on the following intuition: if you see the letters hen in English text, then most of the time the letter preceding it is t or w. If you could somehow group all such preceding letters together (mostly t’s and some w’s), then you would have an easy opportunity for data compression.
也就是维基百科中说的有相同子串,变换后才会有重复字符。排序后 hen 开头的都排在一起,前缀也就是最后一列啦,很大几率是重复的 t 或 w。
现在来说还原的问题,怎么从原字符串排序后的行号和变换字符串得到原字符串。
i Sorted Suffixes t next[i]
-- ----------------------- -------
0 ! ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 3
1 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? R 0
2 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? D 6
*3 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ! 7
4 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? R 8
5 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? C 9
6 B ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 10
7 B ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 11
8 C ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 5
9 D ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 2
10 R ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? B 1
11 R ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? B 4
我们对 t[] 进行排序,也就得到了第一列数据,加上原字符串排序后的行号 3,马上知道原字符串第一个字符是 A。然后查看 next[3] 是 7,说明第二个字符是第七行的 B,就这样一个字符一个字符的还原。于是乎,关键就是这个 next 数组要怎么生成啦。
next[i] 表示循环后缀数组第 i 个字符串的下一个字符串在排序后的行号,对于在原字符串中只出现一次的字符来说,next 值很好算:
i Sorted Suffixes t next[i]
-- ----------------------- -------
0 ! ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 3
1 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? R
2 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? D
*3 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? !
4 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? R
5 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? C
6 B ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A
7 B ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A
8 C ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 5
9 D ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 2
10 R ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? B
11 R ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? B
考虑字符 C,它只出现了一次。根据循环后缀数组定义,在以 C 开头的字符串下面是以 C 结尾的字符串,也就是排序后第五行字符串,所以 next[8] = 5。类似的,next[0] = 3,next[9] = 2。
不止出现一次的字符,没法一下一次对应,但实际上也不难区分。像上面字符 R,出现了两次,以 R 结尾的字符串有两个,要怎么和 next[10],next[11] 对应起来呢。正确的答案是:next[10] = 1,next[11] = 4。因为第 10 和第 11 行都以 R 开头,而这个又是排好序的,那这两字符串的后 11 位肯定是前者小于后者,用这两 11 位开头的字符串自然也是前者排在前面。
任务摘要
MoveToFront.java
Name your program MoveToFront.java and organize it using the following API:
public class MoveToFront {
// apply move-to-front encoding, reading from standard input and writing to standard output
public static void encode() // apply move-to-front decoding, reading from standard input and writing to standard output
public static void decode() // if args[0] is '-', apply move-to-front encoding
// if args[0] is '+', apply move-to-front decoding
public static void main(String[] args)
}
CircularSuffixArray.java
Your job is to implement the following circular suffix array API, which provides the client access to the index[] values:
public class CircularSuffixArray {
public CircularSuffixArray(String s) // circular suffix array of s
public int length() // length of s
public int index(int i) // returns index of ith sorted suffix
public static void main(String[] args) // unit testing (required)
}
BurrowsWheeler.java
Name your program BurrowsWheeler.java and organize it using the following API:
public class BurrowsWheeler {
// apply Burrows-Wheeler transform, reading from standard input and writing to standard output
public static void transform() // apply Burrows-Wheeler inverse transform, reading from standard input and writing to standard output
public static void inverseTransform() // if args[0] is '-', apply Burrows-Wheeler transform
// if args[0] is '+', apply Burrows-Wheeler inverse transform
public static void main(String[] args)
}
问题分析
依旧是照着 Checklist 里建议的编程步骤进行。
第一步建议我们实现 CircularSuffixArray 类,特别指出不要显示存储 N 个字符串,那会花费平方级的时间和空间:
Warning: beginning with Java 7, Update 6, the substring() method takes time and space proportional to the length of the substring—in other words, you cannot form the n circular suffixes explicitly because that would take both quadratic time and space.
同时也提示我们只要保留每个循环后缀的索引,对索引数组进行排序即可:
Instead for each suffix, you only need to keep an index that indicates which character is the beginning of the suffix. This way you can build the N suffixes in linear time and space. Then sort this array of indices. It's just like sorting an array of references.
索引数组用对应的循环后缀字符串作为键进行排序,而且这些字符串没有被显示地存储,所以课程里实现过的对字符串的排序算法不能直接调用(像 Quick3string.java,3-way string quicksort)。作业大概是想让我们自己写排序吧,但前期搜索过程中发现了更简单的做法(博客链接):重写比较器里的 compare() 方法,用 Arrays.sort() 排。
Arrays.sort(index, new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer idx1, Integer idx2) {
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c1 = value[(i + idx1) % length];
char c2 = value[(i + idx2) % length];
if (c1 > c2) return 1;
if (c1 < c2) return -1;
}
return 0;
}
});
最终提交上去,时间测试勉强通过。后来又看到 github 上有个小哥 gzc 就是自己写课程里的快速三向字符串排序来做这编程作业,后面较短的字符串还用插入排序改进性能,厉害了。下面是测试结果的比较。
Tests 14-26: time to create circular suffix array for n random ASCII characters
and call index(i) for each i
[ max allowed time = 10 seconds and <= 20x reference ]
n student reference ratio gzc ratio
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
=> passed 1000 0.00 0.00 4.92 0.00 1.94
=> passed 2000 0.00 0.00 3.95 0.00 0.80
=> passed 4000 0.00 0.00 3.95 0.00 0.72
=> passed 8000 0.00 0.00 6.48 0.00 1.95
=> passed 16000 0.01 0.00 4.96 0.00 2.91
=> passed 32000 0.02 0.00 7.22 0.00 3.56
=> passed 64000 0.03 0.00 8.30 0.01 4.10
=> passed 128000 0.07 0.01 8.40 0.02 3.37
=> passed 256000 0.15 0.03 4.30 0.04 2.32
=> passed 512000 0.35 0.08 4.43 0.08 1.48
=> passed 1024000 0.70 0.06 11.53 0.18 1.62
=> passed 2048000 1.74 0.15 11.60 0.42 1.96
=> passed 4096000 3.91 0.33 11.74 0.94 2.88
Estimated running time (using last 6 measurements)
= 6.79e-08 * n^1.17 (R^2 = 1.00)
针对字符串的排序效果自然更好,但简单的可以满足性能要求,也就不再学小哥去自己打啦。
接着建议我们实现 Burrows-Wheeler 类,说其中的 inverseTransform() 方法是作业最具技巧性的部分:
The Burrows-Wheeler decoding is the trickiest part, but it is very little code once you understand how it works. (Not including declarations and input, our solution is about 10 lines of code.) You may find the key-indexed counting algorithm from the string sorting lecture to be useful.
提示我们要用到基数排序(键索引计数算法),但我是没想出来。。。还是看 gzc 小哥的才知道怎么做。
int len = lastCol.length();
int[] next = new int[len];
int[] count = new int[R + 1];
char[] firstCol = new char[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
count[lastCol.charAt(i) + 1]++;
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
count[i + 1] += count[i];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int posi = count[lastCol.charAt(i)]++;
firstCol[posi] = lastCol.charAt(i);
next[posi] = i;
}
关键在于怎么构建 next 数组。解码的时候我们知道循环后缀数组的最后一列字符,于是对其进行基数排序来得到第一列。但在基数排序的时候,最后加一行代码就能很容易地同时算出 next 数组。用图会很好理解:
i Sorted Suffixes t next[i]
-- ----------------------- -------
0 ! ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 3
1 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? R 0
2 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? D 6
*3 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ! 7
4 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? R 8
5 A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? C 9
6 B ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 10
7 B ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 11
8 C ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 5
9 D ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? A 2
10 R ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? B 1
11 R ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? B 4
前面计算 count 数组后,最后一个循环遍历数组 t,能直接把 t[i] 放在排序后的对应位置。像 t[] 的第 0 个字符 A,排序后的位置是 count[A](上图代码计算后得到的是 1),所以第 0 行末尾的 A 和第 1 行开头的 A 是同一个。那么,在还没有排序之前,第 0 行的字符串即是第 1 行字符串的下一行(第 1 行循环左移一位得到第 0 行)。所以,按照 next 数组的定义:排序前第 i 条字符串的下一行字符串在排序后的行号,next[i] 就等于 i。
最后的 MoveToFront 类比较简单,不提。
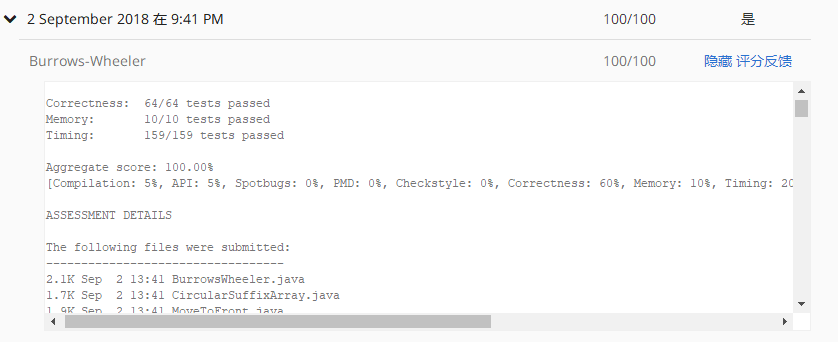
测试结果
Programming Assignment 5: Burrows–Wheeler Data Compression的更多相关文章
- 课程一(Neural Networks and Deep Learning),第三周(Shallow neural networks)—— 3.Programming Assignment : Planar data classification with a hidden layer
Planar data classification with a hidden layer Welcome to the second programming exercise of the dee ...
- SQL SERVER ->> Data Compression
最近做了一个关于数据压缩的项目,要把整个SQL SERVER服务器下所有的表对象要改成页压缩.于是趁此机会了解了一下SQL SERVER下压缩技术. 这篇文章几乎就是完全指导手册了 https://t ...
- Algorithms: Design and Analysis, Part 1 - Programming Assignment #1
自我总结: 1.编程的思维不够,虽然分析有哪些需要的函数,但是不能比较好的汇总整合 2.写代码能力,容易挫败感,经常有bug,很烦心,耐心不够好 题目: In this programming ass ...
- Algorithms : Programming Assignment 3: Pattern Recognition
Programming Assignment 3: Pattern Recognition 1.题目重述 原题目:Programming Assignment 3: Pattern Recogniti ...
- Data Compression Category
Data Compression is an approach to compress the origin dataset and save spaces. According to the Eco ...
- dimensionality reduction动机---data compression(使算法提速)
data compression可以使数据占用更少的空间,并且能使算法提速 什么是dimensionality reduction(维数约简) 例1:比如说我们有一些数据,它有很多很多的feat ...
- 课程一(Neural Networks and Deep Learning),第二周(Basics of Neural Network programming)—— 2、编程作业常见问题与答案(Programming Assignment FAQ)
Please note that when you are working on the programming exercise you will find comments that say &q ...
- Programming Assignment 2: Randomized Queues and Deques
实现一个泛型的双端队列和随机化队列,用数组和链表的方式实现基本数据结构,主要介绍了泛型和迭代器. Dequeue. 实现一个双端队列,它是栈和队列的升级版,支持首尾两端的插入和删除.Deque的API ...
- Programming Assignment 2: Deques and Randomized Queues
编程作业二 作业链接:Deques and Randomized Queues & Checklist 我的代码:Deque.java & RandomizedQueue.java & ...
随机推荐
- sqlserver中调用服务器中的webservice接口
declare @ServiceUrl as varchar(1000) declare @UrlAddress varchar(500)--WebService地址:以http开头,结尾带斜杠,例如 ...
- 【解决】 无法打开包括文件:“windows.h”: No such file or directory
vs编译时错误: 无法打开包括文件:“windows.h”: No such file or directory 出现这种错误什么都不用配置(环境变量),最好办法是将VS安装在C盘,让开发工具自动包含 ...
- Kafka、RabbitMQ、RocketMQ消息中间件的对比
引言 分布式系统中,我们广泛运用消息中间件进行系统间的数据交换,便于异步解耦.现在开源的消息中间件有很多,目前对Kafka.RabbitMQ.RocketMQ这三个消息中间件做下对比分析. - - k ...
- KATANA Owin 资料收集
https://www.cnblogs.com/xishuai/p/asp-net-5-owin-katana.html http://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/thi ...
- 开包即食的教程带你浅尝最新开源的C# Web引擎Blazor
在今年年初,恰逢新春佳节临近的时候.微软给全球的C#开发者们,着实的送上了一分惊喜.微软正式开源Blazor,将.NET带回到浏览器. 这个小惊喜,迅速的在dotnet开发者中间传开了.201 ...
- python可变对象与不可变对象
可变/不可变对象定义 不可变对象 该对象所指向的内存中的值不能被改变.当改变某个变量时候,由于其所指的值不能被改变,相当于把原来的值复制一份后再改变,这会开辟一个新的地址,变量再指向这个新的地址. 可 ...
- Cocoa pod导入第三方框架遇到的那点事儿
废话不多说,直接上干货. 以下所有操作均是在Cocoapod导入第三方库,并且是.xcworkspace的工程里面操作的, 1.导入头文件找不到,也就是所谓的,not find ''AFNetwork ...
- android chrome iframe设置src属性无法启动app
0x01 Android Intents with Chrome Android有一个很少人知道的特性可以通过web页面发送intent来启动apps.以前通过网页启动app是通过设置iframe的s ...
- html active属性
源代码 <div class="col-md-3"> <div class="list-group"> <a href=" ...
- 【小程序】返回顶部wx.pageScrollTo和scroll-view的对比
一.wx.pageScrollTo(https://mp.weixin.qq.com/debug/wxadoc/dev/api/scroll.html) 1. 小程序中双击顶部的textbar.会默认 ...
