Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(三)logistic regression(逻辑回归)
# 逻辑回归
## 逻辑回归处理二元分类
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#显示中文
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\msyh.ttc", size=10)
import numpy as np
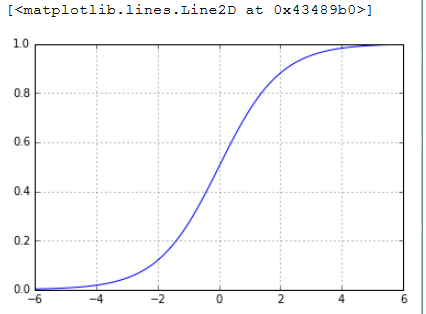
plt.figure()
plt.axis([-6,6,0,1])
plt.grid(True)
X=np.arange(-6,6,0.1)
y=1/(1+np.e**(-X))
plt.plot(X,y,'b-')
## 垃圾邮件分类
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv('SMSSpamCollection',delimiter='\t',header=None)
df.head()

from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
#用pandas加载数据.csv文件,然后用train_test_split分成训练集(75%)和测试集(25%):
X_train_raw, X_test_raw, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df[1],df[0])
#我们建一个TfidfVectorizer实例来计算TF-IDF权重:
vectorizer=TfidfVectorizer()
X_train=vectorizer.fit_transform(X_train_raw)
X_test=vectorizer.transform(X_test_raw)
#LogisticRegression同样实现了fit()和predict()方法
classifier=LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
predictions=classifier.predict(X_test) for i ,prediction in enumerate(predictions[-5:]):
print '预测类型:%s.信息:%s' %(prediction,X_test_raw.iloc[i])
输出结果:
预测类型:ham.信息:Waiting in e car 4 my mum lor. U leh? Reach home already?
预测类型:ham.信息:Dear got train and seat mine lower seat
预测类型:spam.信息:I just really need shit before tomorrow and I know you won't be awake before like 6
预测类型:ham.信息:What should i eat fo lunch senor
预测类型:ham.信息:645
## 二元分类效果评估方法
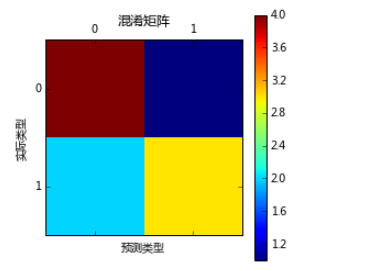
#混淆矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
y_test = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
y_pred = [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]
confusion_matrix=confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred)
print confusion_matrix
plt.matshow(confusion_matrix)
plt.title(u'混淆矩阵')
plt.colorbar()
plt.ylabel(u'实际类型')
plt.xlabel(u'预测类型')
plt.show()
## 准确率
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split,cross_val_score df=pd.read_csv('SMSSpamCollection',delimiter='\t',names=["label","message"])
X_train_raw, X_test_raw, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df['message'], df['label'])
vectorizer=TfidfVectorizer()
X_train=vectorizer.fit_transform(X_train_raw)
X_test=vectorizer.transform(X_test_raw)
classifier=LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
scores=cross_val_score(classifier,X_train,y_train,cv=5)
print '准确率',np.mean(scores),scores
输出结果:
准确率 0.954292731612 [ 0.96057348 0.96052632 0.94617225 0.95808383 0.94610778]
## 精确率和召回率
scikit-learn结合真实类型数据,提供了一个函数来计算一组预测值的精确率和召回率。
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split, cross_val_score df['label']=pd.factorize(df['label'])[0]
X_train_raw, X_test_raw, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df['message'],df['label'])
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()
X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(X_train_raw)
X_test = vectorizer.transform(X_test_raw)
classifier = LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
precisions = cross_val_score(classifier, X_train, y_train, cv=5, scoring=
'precision')
print u'精确率:', np.mean(precisions), precisions
recalls = cross_val_score(classifier, X_train, y_train, cv=5, scoring='recall')
print u'召回率:', np.mean(recalls), recalls
plt.scatter(recalls, precisions)
输出结果:
精确率: 0.990243902439 [ 1. 0.95121951 1. 1. 1. ]
召回率: 0.691498103666 [ 0.65486726 0.69026549 0.69911504 0.71681416 0.69642857]
## 计算综合评价指标
fls=cross_val_score(classifier,X_train,y_train,cv=5,scoring='f1')
print '综合指标评价',np.mean(fls),fls
输出结果:
综合指标评价 0.791683999687 [ 0.76243094 0.79781421 0.8 0.77094972 0.82722513] ## ROC AUC
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split,cross_val_score
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve,auc df['label']=pd.factorize(df['label'])[0]
X_train_raw, X_test_raw, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df['message'],df['label'])
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()
X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(X_train_raw)
X_test = vectorizer.transform(X_test_raw)
classifier = LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions=classifier.predict_proba(X_test)#每一类的概率
false_positive_rate, recall, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, predictions[:
, 1])
roc_auc=auc(false_positive_rate,recall)
plt.title('Receiver Operating Characteristic')
plt.plot(false_positive_rate, recall, 'b', label='AUC = %0.2f' % roc_auc)
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.plot([0,1],[0,1],'r--')
plt.xlim([0.0,1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0,1.0])
plt.ylabel('Recall')
plt.xlabel('Fall-out')
plt.show()

## 网格搜索
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score, recall_score, accuracy_score pipeline = Pipeline([
('vect', TfidfVectorizer(stop_words='english')),
('clf', LogisticRegression())
]) parameters = {
'vect__max_df': (0.25, 0.5, 0.75),
'vect__stop_words': ('english', None),
'vect__max_features': (2500, 5000, 10000, None),
'vect__ngram_range': ((1, 1), (1, 2)),
'vect__use_idf': (True, False),
'vect__norm': ('l1', 'l2'),
'clf__penalty': ('l1', 'l2'),
'clf__C': (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10),
} grid_search = GridSearchCV(pipeline, parameters, n_jobs=-1, verbose=1, scoring='accuracy', cv=3)
df=pd.read_csv('SMSSpamCollection',delimiter='\t',names=["label","message"])
df['label']=pd.factorize(df['label'])[0] X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df['message'],df['label'])
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
print('最佳效果:%0.3f' % grid_search.best_score_)
输出结果;
最佳效果:0.986
print '最优参数组合'
best_parameters=grid_search.best_estimator_.get_params()
for param_name in sorted(parameters.keys()):
print '\t%s:%r' %(param_name,best_parameters[param_name]) predictions=grid_search.predict(X_test)
print '准确率:',accuracy_score(y_test,predictions)
print '精确率:',precision_score(y_test,predictions)
print '召回率:',recall_score(y_test,predictions)
输出结果:
clf__C:10
clf__penalty:'l2'
vect__max_df:0.25
vect__max_features:2500
vect__ngram_range:(1, 2)
vect__norm:'l2'
vect__stop_words:None
vect__use_idf:True
准确率: 0.979899497487
精确率: 0.974683544304
召回率: 0.865168539326
# logistics 多分类
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv("logistic_data/train.tsv",header=0,delimiter='\t')
print df.count()
print df.head()
df.Phrase.head(10)
df.Sentiment.describe()
df.Sentiment.value_counts()
df.Sentiment.value_counts()/df.Sentiment.count()
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report,accuracy_score,confusion_matrix
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV pipeline=Pipeline([
('vect',TfidfVectorizer(stop_words='english')),
('clf',LogisticRegression())])
parameters={
'vect__max_df':(0.25,0.5),
'vect__ngram_range':((1,1),(1,2)),
'vect__use_idf':(True,False),
'clf__C':(0.1,1,10),
}
df=pd.read_csv("logistic_data/train.tsv",header=0,delimiter='\t')
X,y=df.Phrase,df.Sentiment.as_matrix()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,train_size=0.5)
grid_search=GridSearchCV(pipeline,parameters,n_jobs=-1,verbose=1,scoring="accuracy")
grid_search.fit(X_train,y_train)
print u'最佳效果:%0.3f'%grid_search.best_score_
print u'最优参数组合:'
best_parameters=grid_search.best_estimator_.get_params()
for param_name in sorted(parameters.keys()):
print '\t%s:%r'%(param_name,best_parameters[param_name])
数据结果:
Fitting 3 folds for each of 24 candidates, totalling 72 fits
## 多类分类效果评估
predictions=grid_search.predict(X_test)
print u'准确率',accuracy_score(y_test,predictions)
print u'混淆矩阵',confusion_matrix(y_test,predictions)
print u'分类报告',classification_report(y_test,predictions)
数据结果:
准确率 0.636614122773
混淆矩阵 [[ 1133 1712 595 67 1]
[ 919 6136 6006 553 35]
[ 213 3212 32637 3634 138]
[ 22 420 6548 8155 1274]
[ 4 45 546 2411 1614]]
分类报告 precision recall f1-score support
0 0.49 0.32 0.39 3508
1 0.53 0.45 0.49 13649
2 0.70 0.82 0.76 39834
3 0.55 0.50 0.52 16419
4 0.53 0.35 0.42 4620
avg / total 0.62 0.64 0.62 78030
Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(三)logistic regression(逻辑回归)的更多相关文章
- Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(七)the perceptron(感知器)
一.感知器 感知器是Frank Rosenblatt在1957年就职于Cornell航空实验室时发明的,其灵感来自于对人脑的仿真,大脑是处理信息的神经元(neurons)细胞和链接神经元细胞进行信息传 ...
- Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(一)_一元回归
一.引入相关库 %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.font_manager import FontP ...
- Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(一)_Feature Extraction and Preprocessing(特征提取与预处理)
# Extracting features from categorical variables #Extracting features from categorical variables 独热编 ...
- Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(五)k-means(聚类)
# K的选择:肘部法则 如果问题中没有指定 的值,可以通过肘部法则这一技术来估计聚类数量.肘部法则会把不同 值的成本函数值画出来.随着 值的增大,平均畸变程度会减小:每个类包含的样本数会减少,于是样本 ...
- Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(六) dimensionality-reduction-with-pca
# 用PCA降维 #计算协方差矩阵 import numpy as np X=[[2,0,-1.4], [2.2,0.2,-1.5], [2.4,0.1,-1], [1.9,0,-1.2]] np.c ...
- Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(四)decision_tree(决策树)
# 决策树 import pandas as pd from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.cross_validat ...
- muduo网络库学习笔记(三)TimerQueue定时器队列
目录 muduo网络库学习笔记(三)TimerQueue定时器队列 Linux中的时间函数 timerfd简单使用介绍 timerfd示例 muduo中对timerfd的封装 TimerQueue的结 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 6_Logistic Regression 逻辑回归
Lecture6 Logistic Regression 逻辑回归 6.1 分类问题 Classification6.2 假设表示 Hypothesis Representation6.3 决策边界 ...
- Coursera DeepLearning.ai Logistic Regression逻辑回归总结
既<Machine Learning>课程后,Andrew Ng又推出了新一系列的课程<DeepLearning.ai>,注册了一下可以试听7天.之后每个月要$49,想想还是有 ...
随机推荐
- uva 10375
/* 选择与除法_________________________________________________________________________________ #include & ...
- cvMat结构体详解
/* *CvMat矩阵头 */ typedef struct CvMat { int type; //数据类型,比如CV_32FC1含义是32位浮点型单通道,再比如CV_8UC3含义是8位无符号整型三 ...
- MySql变量,
http://blog.csdn.net/rdarda/article/details/7878836 1.变量的定义 在Mysql里面可以像我们写代码中一样定义变量来保持中间结果,看下面的格式: [ ...
- Bootstap datetimepicker报错TypeError: intermediate value(转)
原文转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20332519-id-5733546.html Bootstrap datetimepicker有多个版本,官方的链接中,只是d ...
- lumen 错误&日志
1.简介 开始一个新的Lumen项目的时候,错误和异常处理已经默认为你配置好了.此外,Lumen还集成了提供各种功能强大日志处理器的Monolog日志库. 2.配置 2.1 错误详情 配置文件.env ...
- < 独立项目 - 文本挖掘 > - 2016/11/13 第二更 - <Python环境准备>
< 独立项目 - 文本挖掘 > 项目立项的相关背景介绍,TODO方向. 一.Ubuntu环境配置 主机系统:Windows 7 SP1 64位操作系统 | i5-4210 CPU | ...
- 自动 点击切换 按钮切换 轮播无缝选项卡 ----原生js
<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name ...
- ThinkPad E440 加内存后导致开不了机
上周五新买的ThinkPad E440,原装内存是4G DDR3 1600Hz,明显不够用,于是在京东上买了一根南亚易胜的4G DDR3 1600Hz.安装之后正常开机,明显感觉速度快了很多.可是用了 ...
- 2.HTML5 标准改变,准备工作
1.HTML5 标准改变: Html5 不是SGML,XML语言,没有有效性检查,是规范,有松散的写法 不许写结束标签:area,base,br,col,hr,img,input,link,sourc ...
- 关于http协议详解
Author :Jeffrey 引言 HTTP是一个属于应用层的面向对象的协议,由于其简捷.快速的方式,适用于分布式超媒体信息系统.它于1990年提出,经过几年的使用与发展,得到不断地完善和扩展.目前 ...
